Sir,
Acute peritoneal dialysis (PD) is the oldest form of renal replacement therapy (RRT), whereas sustained low-efficiency dialysis (SLED) is a newer hybrid therapy between continuous RRT and intermittent hemodialysis. There are very few studies comparing these two modalities of RRT,[1] so we undertook a prospective study to evaluate outcomes of patients receiving intermittent PD (IPD) using rigid peritoneal catheter with SLED. The decision for instituting IPD or SLED was of the treating unit.
Critically ill patients with dialysis-requiring acute kidney injury (AKI) more than 18 years of age admitted to our hospital from July 2013 to December 2014 were enrolled. Patients who died within 12 h of initiating RRT, those having preexisting chronic kidney disease/or end-stage renal disease, pregnant patients and subjects with obstructive uropathy were excluded from this study. Acute physiology and chronic health II and daily Sequential organ failure assessment scores were calculated. Kt/V urea was calculated per session of RRT. The primary outcome of the study was patient and renal survival at 28 and 90 days. Secondary outcomes were an improvement in metabolic and clinical parameters (hyperkalemia, acidosis, encephalopathy, and fluid overload) and length of hospital stay. Complications of IPD and SLED were also noted.
Thirty-three patients were eligible for enrollment out of which 17 underwent IPD and 16 underwent SLED. Patients in both groups had similar baseline characteristics. A total of 54 sessions of IPD were carried out with average dialysate volume of 16.65 L/session and mean ultrafiltration achieved was 2.4 L/session. A total of fifty sessions of SLED were carried out. Weekly mean Kt/V achieved in the SLED and IPD group was 4.7 and 2.02, respectively (P < 0.001). Ultrafiltration achieved with IPD was significantly higher during first two sessions (2.35 L and 2.7 L) as compared to the ultrafiltration achieved with SLED (1.2 L and 1.3 L) (P = 0.03 and P = 0.018). At the end of the study, patient survival at day 28 and 90 was 11.6 and 6.2% in IPD group vis-a-vis 5.8 and 6.2% in SLED group. Hyperkalemia was resolved in 100% of patients in IPD group after the first session. Secondary outcomes are mentioned in Table 1.
Table 1.
Comparsion of various clinical parameters of patients' treated with IPD and SLED
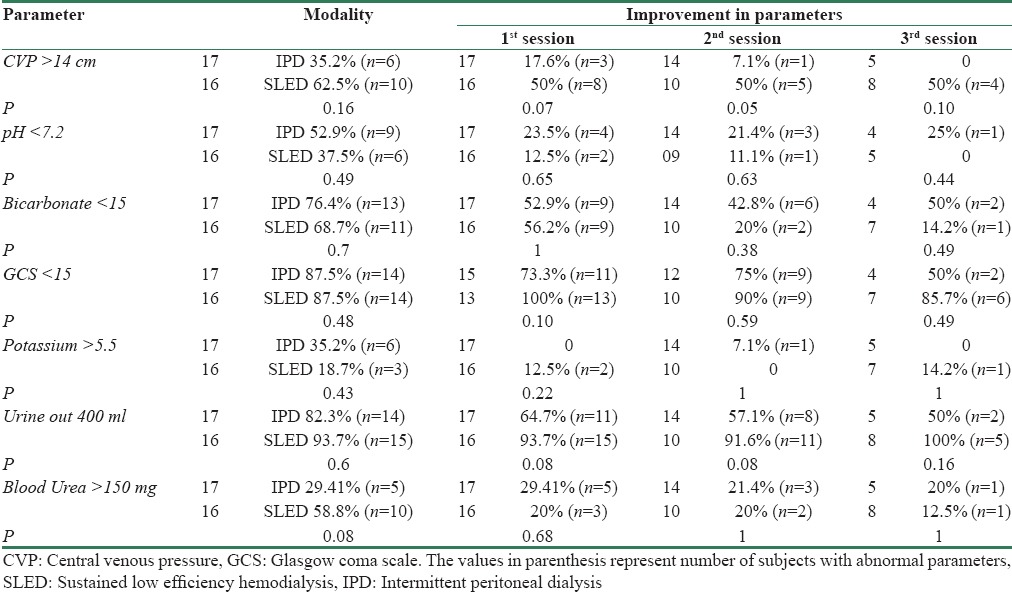
The only study comparing PD and extended hemodialysis was carried by Ponce et al.[2] The authors randomized 143 cases of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients requiring dialysis to high volume peritoneal dialsysis or extended hemodialysis and found no significant difference in the mortality rate, renal recovery, need of chronic dialysis, and median ICU. The results of the present study are similar to that reported by Ponce et al. To conclude, in the management of dialysis-requiring AKI in critically ill patients, IPD is comparable to SLED in terms of correction of metabolic and clinical derangements.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Gabriel DP, Caramori JT, Martin LC, Barretti P, Balbi AL. Continuous peritoneal dialysis compared with daily hemodialysis in patients with acute kidney injury. Perit Dial Int. 2009;29(Suppl 2):S62–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ponce D, Berbel MN, Abrão JM, Goes CR, Balbi AL. A randomized clinical trial of high volume peritoneal dialysis versus extended daily hemodialysis for acute kidney injury patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 2013;45:869–78. doi: 10.1007/s11255-012-0301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


