Abstract
Despite its relatively streamlined genome, there are many important examples of regulated RNA splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Here, we report a role for the chromatin remodeler SWI/SNF in respiration, partially via the regulation of splicing. We find that a nutrient-dependent decrease in Snf2 leads to an increase in splicing of the PTC7 transcript. The spliced PTC7 transcript encodes a mitochondrial phosphatase regulator of biosynthesis of coenzyme Q6 (ubiquinone or CoQ6) and a mitochondrial redox-active lipid essential for electron and proton transport in respiration. Increased splicing of PTC7 increases CoQ6 levels. The increase in PTC7 splicing occurs at least in part due to down-regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression, leading to the redistribution of spliceosomes from this abundant class of intron-containing RNAs to otherwise poorly spliced transcripts. In contrast, a protein encoded by the nonspliced isoform of PTC7 represses CoQ6 biosynthesis. Taken together, these findings uncover a link between Snf2 expression and the splicing of PTC7 and establish a previously unknown role for the SWI/SNF complex in the transition of yeast cells from fermentative to respiratory modes of metabolism.
Keywords: alternative splicing, chromatin remodeling, gene expression, lipid metabolism, metabolic regulation, mitochondrial metabolism, phosphorylation, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, coenzyme Q
Introduction
Similar to other eukaryotic genomes, genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae may be interrupted by non-coding sequences, called introns. Introns are removed from the pre-mRNA through the action of the spliceosome, a macromolecular machine composed of five small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. The spliceosome recognizes consensus sequence signals on the pre-mRNA, termed splice sites, by which it subsequently binds to the intron and catalyzes its removal via two transesterification reactions (1). Pre-mRNA splicing is critical for accurate gene expression in all eukaryotes, and there is significant evidence that alterations in microenvironments, such as changes in the chromatin state or chromatin-modifying factors, can affect splicing outcomes (1). However, the mechanisms for how chromatin and chromatin factors influence splicing are not completely understood.
Although the genome of S. cerevisiae contains a smaller number of introns than metazoan genomes, there are, nonetheless, numerous examples of intron-dependent gene regulation (2). The largest functional class of intron-containing genes (ICGs)4 in budding yeast is ribosomal protein genes (RPGs) that encode the protein components of the ribosome. Therefore, the energy-intensive process of translation is under the heavy regulatory control of the spliceosome, such that splicing of RPGs can be finely tuned to the cells' environmental conditions and to nutrient availability (3).
Interestingly, this enrichment of introns within RPGs impacts the splicing of, as well as provides an opportunity for the regulation of, other ICGs within the yeast genome. About a third of yeast introns occur in RPGs, and the high transcription levels of these genes means that about 90% of the intron load encountered by the spliceosome is from this one functional class of genes (4). Indeed, the prevalence of RPG introns functions to titrate spliceosomes away from other introns, especially those containing suboptimal splice sites. Conversely, down-regulating RPG expression promotes the splicing of transcripts harboring suboptimal splice sites. This effect is perhaps best described during the process of yeast meiosis. Under conditions of vegetative growth, a number of meiosis-specific ICGs are expressed, but they possess suboptimal splice sites and are therefore poorly recognized by the spliceosome and suboptimally spliced. However, upon the down-regulation of RPGs during meiosis, increased availability of the previously limiting pool of spliceosomes leads to improved splicing efficiency of introns in meiosis-specific transcripts (5, 6).
There are other important examples of intron-based regulation in S. cerevisiae, especially among ICGs with non-consensus splice sites (7, 8). One such gene is PTC7, which encodes a Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent, type 2C serine/threonine protein phosphatase (9). The intron within PTC7 is particularly intriguing because it contains a non-consensus branch-point sequence, rendering its splicing relatively inefficient under logarithmic growth conditions. The PTC7 intron lacks a premature termination codon and is translated in-frame. The longer, non-spliced (ns) form of the PTC7 RNA encodes a longer protein (Ptc7ns) that contains a single trans-membrane helix located near the N terminus but is otherwise identical to the protein isoform derived from the spliced PTC7 RNA (Ptc7s). The read-through nature of the PTC7 intron is conserved across yeast species, indicating potential functionality for both Ptc7s and Ptc7ns protein isoforms (10). Ptc7ns has been localized to the nuclear membrane, whereas Ptc7s is located within mitochondria (10). Ptc7s has been implicated in regulation of coenzyme Q (also termed ubiquinone or CoQ) biosynthesis via its phosphatase activity (11, 12). However, mechanisms of regulation of Ptc7 itself and the role of the evolutionarily conserved Ptc7ns isoform remain outstanding questions.
CoQ is a redox-active lipid composed of a fully substituted benzoquinone ring and a polyisoprenoid tail and is required for mitochondrial electron transport. The length of the polyisoprenoid group is species-specific; humans produce CoQ10, and S. cerevisiae produce CoQ6, with 10 and 6 isoprene units, respectively. The primary role of CoQ in the inner mitochondrial membrane is to accept the electrons from complex I and complex II and pass those electrons to complex III. Several other metabolic pathways, such as pyrimidine synthesis, sulfide oxidation, and fatty acid β-oxidation, rely on CoQ as an electron carrier (13). CoQ is present in all intracellular membranes, where it may function as a lipid-soluble antioxidant. Several human syndromes, including encephalomyopathy, ataxia, cerebellar atrophy, myopathy, and steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome, are linked to primary deficiencies in CoQ biosynthesis (14–17).
Mitochondrial proteins are responsible for facilitating the biosynthesis of CoQ6 in S. cerevisiae and include Coq1–Coq11 (18). Many of the Coq proteins necessary for the biosynthesis of CoQ6 associate in a high-molecular weight complex (termed the “CoQ-synthome”), a multisubunit complex that is peripherally associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane on the matrix side (18). Ptc7s has been shown to localize to the mitochondria, where it is thought to regulate the phosphorylation state of Coq7 (11) and/or influence mitochondrial respiratory metabolism (12). In the former case, Ptc7s is believed to control, at least in part, the phosphorylation state of the Coq7 polypeptide, which modulates its hydroxylase activity. Coq7 catalyzes the hydroxylation of 5-demethoxy-Q6 (DMQ6), the penultimate step in the biosynthesis of CoQ6 in yeast (19, 20).
The conserved SWI/SNF complex utilizes ATP hydrolysis by Snf2, the catalytic subunit, to disrupt specific histone–DNA contacts, resulting in the sliding or eviction of nucleosomes from the locus. As a result, Snf2 activity contributes to transcriptional regulation (21, 22). The genome-wide distribution of SWI/SNF is responsive to conditions of stress, and the complex is required for transcription of a number of stress response genes (23, 24). We have previously reported that levels of Snf2 change in response to nutrient conditions. We have also reported that the change in Snf2 leads to changes in levels of RPG transcripts, thereby regulating splicing outcomes (6). Here, we show that changes in levels of Snf2 modulate the CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway in S. cerevisiae. First, we show that deletion of Snf2 alters the relative levels of Ptc7s and Ptc7ns isoforms in yeast and increases both the rate of synthesis and steady-state levels of CoQ6. This is due to down-regulation of RPG transcripts and an increase in the available pool of spliceosomes. Moreover, we find that the Snf2 protein is down-regulated over time under batch growth conditions and nutrient depletion, and together with a concomitant increase in the splicing of PTC7, this leads to higher CoQ6 levels in preparation for the transition from a fermentative mode of metabolism to a respiratory mode. Furthermore, we show that the two Ptc7 isoforms have opposing effects on the CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway, which may explain contradictory reports in the literature about the effects of Ptc7 on CoQ6 levels (11, 12). Importantly, although Snf2 is down-regulated in response to nutrient-depleted conditions, it is nonetheless required for growth on nonfermentable carbon sources, suggesting that dynamic control of Snf2 levels is crucial for the transition from fermentation to respiration.
Results
Deletion of Snf2 leads to enhanced splicing of PTC7 and a shift in the ratios of Ptc7 protein isoforms
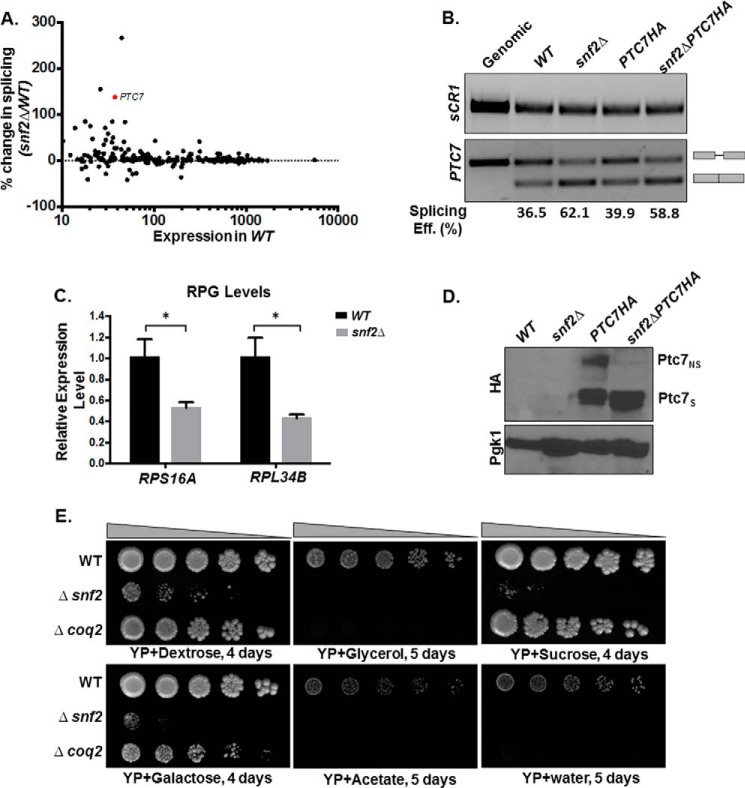
Previously published RNA sequencing data for yeast lacking Snf2, the core ATPase component of the SWI/SNF complex (GEO accession number GSE94404), revealed an increase in splicing of a number of introns (6). Satisfyingly, the greatest improvement in splicing upon deletion of Snf2 is experienced by RPL22B, via a previously described mechanism consistent with down-regulation of RPG expression (25). The next two largest improvements in splicing efficiency are experienced by YBR062C (an ORF of unknown function) and PTC7, a previously described type 2C serine-threonine mitochondrial phosphatase that contains all 11 canonical motifs of the PPM family (type 2C) protein phosphatases, previously reported to play a role in CoQ6 biosynthesis in yeast (11) (Fig. 1A). This increase in splicing of PTC7 RNA was verified by RT-PCR (Fig. 1B). In addition, the results from the RNA-seq and RT-PCR were also independently verified by qPCR (data not shown). It has previously been demonstrated that increased splicing of poorly recognized introns can be achieved by decreased expression of competing, highly expressed RPGs (5). Furthermore, we have shown that deletion of Snf2 causes en masse down-regulation of RPGs and consequent improvement in splicing of a large number of introns (6). RPG down-regulation in the absence of Snf2 was validated by RT-PCR analysis. For example, expression of RPS16A and RPL34B, two intron-containing RPGs, is down-regulated in snf2Δ yeast compared with WT (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1.
Deletion of SNF2 enhances splicing of PTC7 and the steady-state levels of the short Ptc7 protein isoform. A, deletion of SNF2 enhances splicing of a subset of yeast RNAs, including PTC7. The scatter plot shows changes in splicing of individual introns in snf2Δ yeast over WT plotted against expression in WT. Percentage change in splicing is calculated as 100 × (S.E. in snf2Δ − S.E. in WT)/(S.E. in WT). PTC7 is represented by the red dot. B, expression and splicing of PTC7 in WT and snf2Δ yeast with HA-tagged and untagged Ptc7. Semiquantitative analysis of splicing efficiency of PTC7 mRNA is indicated below each lane. sCR1 served as an internal control. Gray bars, exons of the RNA; thin gray line, intron. C, RT-qPCR measurement of selected intron-containing RPG transcripts between WT and snf2Δ yeast strains. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test; *, p < 0.05). Error bars, S.D. D, deletion of SNF2 affects steady-state levels of HA-tagged Ptc7 proteins. Proteins derived from the nonspliced and spliced forms of the PTC7-HA RNA are denoted as Ptc7nsHA and Ptc7sHA, respectively. Pgk1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1) served as a loading control. E, serial dilutions (5-fold) of WT BY4741, snf2Δ, and coq2Δ (negative respiratory-deficient control; W303 background, because the deletion is unstable in the BY background) on YP agar plates with the indicated carbon sources.
The PTC7 transcript makes two distinct protein isoforms, one from the nonspliced and one from the spliced RNA. The spliced isoform (Ptc7s) localizes to the mitochondria, whereas the nonspliced isoform (Ptc7ns) has been reported to localize to the nuclear envelope (10). The PTC7 gene was endogenously HA-tagged, and Western blot analysis demonstrated that deletion of Snf2 leads to an increase in the levels of Ptc7s compared with Ptc7ns (Fig. 1D). It is noteworthy that the increase in the ratio of Ptc7s/Ptc7ns polypeptides in the WT and snf2Δ cells appears to be greater than the increased ratio of spliced/unspliced RNA.
It has previously been demonstrated that yeast strains lacking Snf2 fail to grow on non-fermentable carbon sources, such as glycerol or acetate (26). However, snf2Δ mutants frequently incur secondary mutations, and the growth of such strains can resemble WT. Therefore, growth on fermentable and non-fermentable carbon sources was used as a quality control for the assessment of the bona fide phenotype (24) of snf2Δ prior to each experiment (Fig. 1E).
Deletion of Snf2 leads to increased CoQ6 synthesis in yeast and improves the flux from DMQ6 to CoQ6
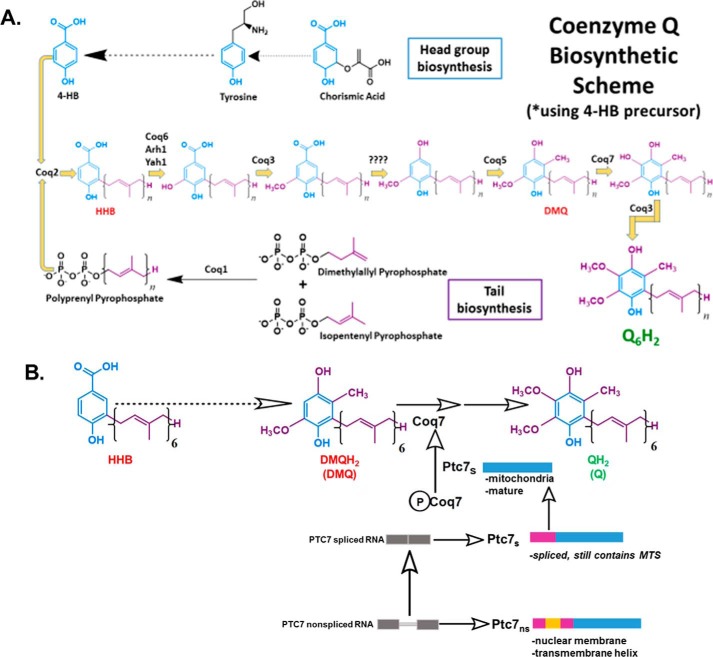
Ptc7s has previously been described as playing a role in regulating CoQ6 synthesis in S. cerevisiae (11). A schematic of the entire CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway with 4-hydroxybenzoic acid as the ring precursor and the role of Ptc7 is detailed in Fig. 2A. Ptc7s is thought to enhance CoQ6 biosynthesis via its activation of Coq7 and subsequent catalysis of the hydroxylation of DMQ6, the penultimate step of CoQ6 biosynthesis (Fig. 2B) (11, 27).
Figure 2.
CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway in S. cerevisiae and role of Ptc7s isoform on Coq7 phosphorylation and function. A, schematic of CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway in yeast using 4HB as a ring precursor, ultimately forming the reduced CoQ6H2 product in vivo. The question marks above the decarboxylation and second hydroxylation steps denote that the enzyme(s) responsible is still unknown. B, schematic of the CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway in yeast. The proposed function of Ptc7s as a mitochondrial phosphatase modulating Coq7 activity is indicated. Ptc7ns has been localized to nuclear membrane. The gray bars represent the exon regions of the RNA, and the thin gray line represents the intron region of the RNA. The pink-colored regions represent the predicted 38-amino acid mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) of the protein, the yellow region represents the 31-amino acid intron of the protein (which interrupts the MTS after amino acid 19, hence spanning from amino acid 20 to 50), and the blue region depicts the mature and spliced polypeptide, which spans from amino acid 51 to 374 (47).
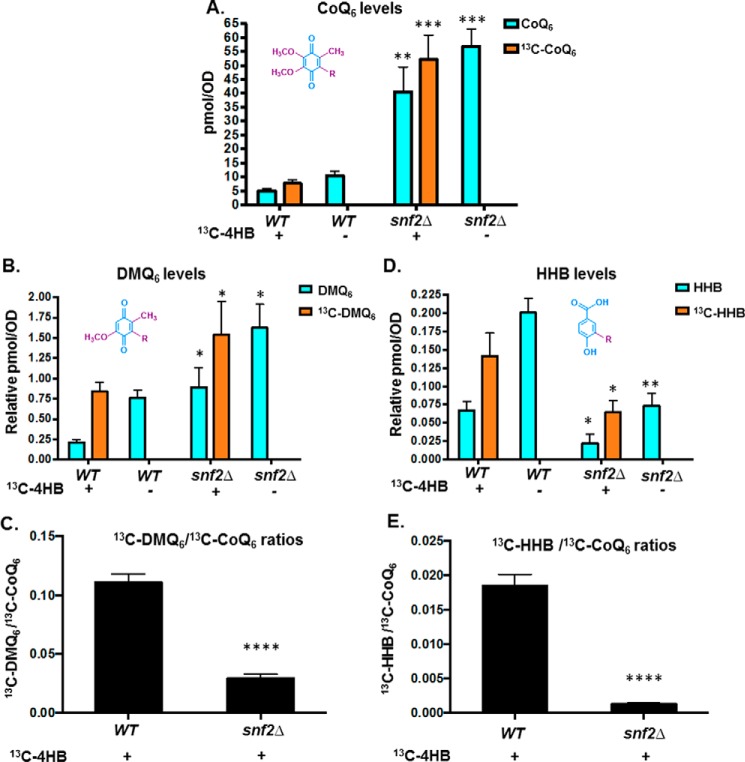
13C6-Labeled 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (13C6-4HB), a ring precursor for Q biosynthesis, was used to determine the levels of 13C6-CoQ6 biosynthesis in WT versus snf2Δ yeast grown to similar culture densities. The absence of Snf2 causes increased steady-state levels of CoQ6 and increased de novo biogenesis of 13C6-CoQ6 (Fig. 3A). Additionally, there are significant changes in the levels of de novo synthesized DMQ6, as well as 3-hexaprenyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid (HHB), an early CoQ6 biosynthetic intermediate (Fig. 3, B and D). Consistent with the increased synthesis of CoQ6 being a consequence of Ptc7 action, the snf2Δ yeast show significantly lower ratios of 13C6-DMQ6 level to 13C6-CoQ6 content, indicating a significant increase in the efficiency of conversion of DMQ6 to CoQ6, namely the step catalyzed by Coq7, a target of Ptc7s (Fig. 3C) (11). Strikingly, we also observe that the levels of both steady-state and de novo synthesized HHB are significantly lower in snf2Δ than in the WT yeast (Fig. 3D). This suggests that the deletion of Snf2 not only causes higher CoQ6 production by regulating catalysis from DMQ6 but that it also funnels the early precursors more efficiently than WT, thus allowing a more streamlined conversion of intermediates of the pathway to the overall product of CoQ6. This is reinforced by the observation that snf2Δ yeast show significantly lower ratios of 13C6-HHB to 13C6-CoQ6 content (Fig. 3E).
Figure 3.
Deletion of SNF2 leads to increased steady state levels and de novo CoQ6 biosynthesis in yeast and improves the flux from DMQ6 to CoQ6. A, levels of steady-state CoQ6 (12C-CoQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized CoQ6 (13C6-CoQ6, orange bars) were determined in WT and snf2Δ yeast. 13C6-4HB was added during midlog phase (A600 = 0.5), and labeling was allowed to proceed until a cell density of A600 ∼1.75 was reached by both strains. 12C-CoQ6 and 13C6-CoQ6 present in yeast cell pellets were quantified by HPLC-MS/MS, as described under “Experimental procedures.” Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005). B, levels of steady-state (12C-DMQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized DMQ6 (13C6-DMQ6, orange bars) were determined in WT and snf2Δ yeast. DMQ6 was determined from the same cultures as in A. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT; *, p < 0.05). C, ratios of 13C6-DMQ6/13C6-CoQ6 in WT and snf2Δ yeast, depicting flux of conversion of 13C6-DMQ6 to 13C6-CoQ6. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT; ****, p < 0.00005). D, levels of steady-state HHB (12C-HHB, blue bars) and de novo synthesized HHB (13C6-HHB, orange bars) were determined in WT and snf2Δ yeast. HHB was determined from the same cultures as in A. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005). E, ratios of 13C-HHB/13C-CoQ6 in WT and snf2Δ yeast, depicting flux of conversion of 13C6-HHBto 13C6-CoQ6. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT; ****, p < 0.00005).
Depletion of Snf2 during batch growth is associated with increased PTC7 splicing and increased CoQ6 production
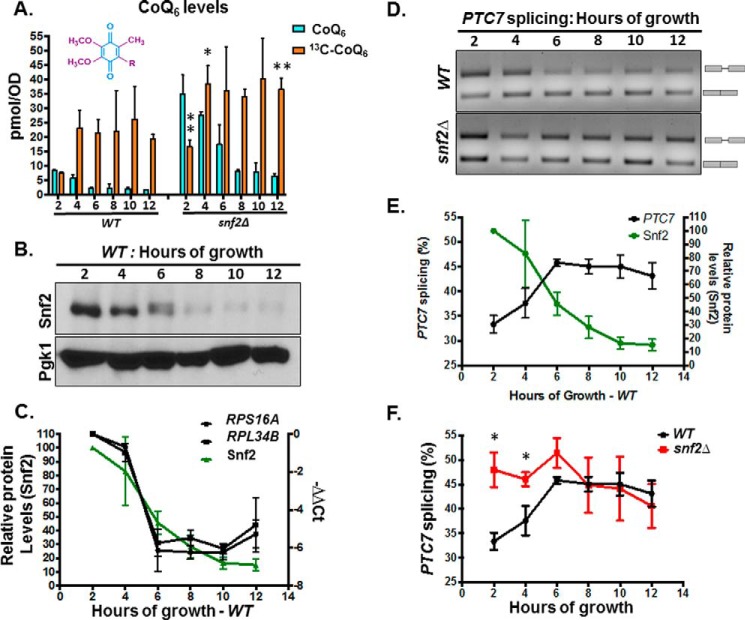
Because snf2Δ yeast have a significantly slower growth rate than WT, we considered the possibility that the increased CoQ6 synthesis was a consequence of the increased time in culture required to achieve equal cell density. To address this, rates of CoQ6 biosynthesis in WT and snf2Δ yeast were determined at timed intervals of culture. First, measurements of steady-state and de novo synthesis rates of CoQ6 between 2 and 12 h of batch growth in YPD revealed that whereas there is indeed an increased rate of synthesis in the snf2Δ yeast strain, the steady-state levels of CoQ6 plateau within 4–6 h of labeling (Fig. 4A). We also observe decreasing levels of Snf2 as the time course progresses and nutrients are depleted (Fig. 4B). Consistent with the role of Snf2 in RPG transcription, RPG levels decrease with time in batch cultures of yeast, in a manner that tracks well with decreasing levels of Snf2 (Fig. 4C). This decrease also coincides with a concomitant increase in the splicing of PTC7 (Fig. 4, D and E). Notably, splicing of the PTC7 transcript in snf2Δ yeast starts off higher than in WT yeast, but as Snf2 is depleted from the WT strain, splicing of the PTC7 transcript approaches the levels of splicing in the snf2Δ strain (Fig. 4F).
Figure 4.
Snf2 levels decrease during batch growth, coinciding with increased PTC7 splicing and increased CoQ6 synthesis. A, levels of steady-state CoQ6 (12C-CoQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized CoQ6 (13C6-CoQ6, orange bars) in WT and snf2Δ yeast were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005). B, steady-state levels of Snf2 protein in WT cells corresponding to samples from A were determined by immunoblot. Pgk1 served as a loading control. C, RT-qPCR measurement of selected intron-containing RPG transcripts (black lines) and Snf2 protein levels (green line) in WT yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB as indicated in A. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars, S.D. D, expression and splicing of PTC7 in WT and snf2Δ yeast cells corresponding to samples from A. PCR products representing the spliced and nonspliced forms are indicated. E, quantification of splicing of PTC7 transcript (black line) and Snf2 protein levels (green line) in WT yeast cells corresponding to samples from D. Snf2 protein levels were previously depicted in C and are shown here again for purposes of comparison. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars, S.D. F, quantification of splicing of PTC7 transcripts in WT and snf2Δ yeast cells corresponding to samples from D. The splicing of WT PTC7 shown in D is depicted again here for purposes of comparison. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars, S.D. (unpaired Student's t test; *, p < 0.05.
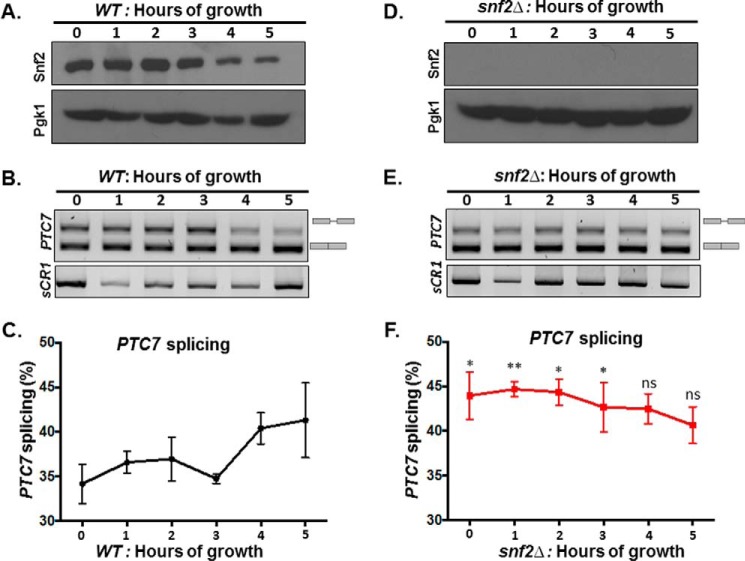
To better understand the kinetics of CoQ6 synthesis, a shorter time course was performed to capture points preceding the plateau, between 0 and 5 h of labeling. Within 4 h after labeling with 13C-4HB precursor, significant down-regulation in the levels of Snf2 protein is evident (Fig. 5A). The decrease in the level of Snf2 protein is mirrored in the increase in splicing efficiency of PTC7 transcript in the WT strain (Fig. 5, B–E). It is interesting to note that the PTC7 transcript is initially better spliced in the snf2Δ strain than in WT, but as the levels of Snf2 in the WT yeast decrease, splicing improves to a degree comparable with the snf2Δ strain (Fig. 5, D and compare C and F).
Figure 5.
The decrease in Snf2 levels over time in batch cultures of WT yeast correlates with enhanced splicing of PTC7 RNA. A, steady-state levels of Snf2 protein in WT cells corresponding to samples from indicated time points were determined by immunoblot. Pgk1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1) served as a loading control. B, expression and splicing of PTC7 in WT yeast cells corresponding to samples from A; PCR products represent the spliced and nonspliced forms, as indicated. C, quantification of splicing of PTC7 transcript (black line) in WT yeast cells corresponding to samples from B. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars, S.D. D, the Snf2 protein is absent in snf2Δ cells corresponding to samples from the indicated time points as determined by immunoblot. Pgk1 served as a loading control. E, expression and splicing of PTC7 in snf2Δ yeast cells corresponding to samples from D; PCR products representing the spliced and nonspliced forms are indicated. F, quantification of splicing of PTC7 transcript (red line) in snf2Δ yeast cells corresponding to samples from E. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars, S.D. (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT in C; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005).
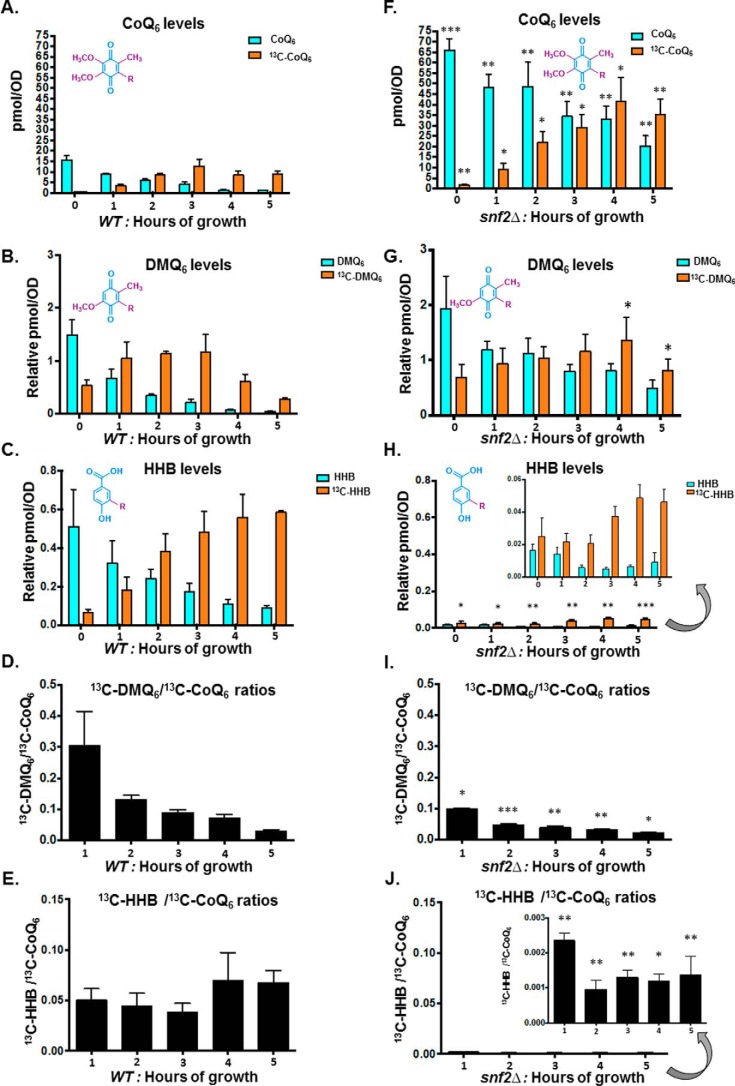
Additionally, there is a striking increase in the overall CoQ6 product and its de novo biosynthesis in the snf2Δ yeast within 0–5 h of labeling, as compared with CoQ6 levels of the WT during the same time course (Fig. 6, compare A and F). Furthermore, the gradual increase in CoQ6 biosynthesis observed in the WT strain plateaus at 3–4 h after labeling (Fig. 6A), by which point the significant down-regulation in the levels of Snf2 protein is also evident (Fig. 5A). The steady-state and de novo synthesized levels of DMQ6 and HHB were also measured in the 5-h time course of WT and snf2Δ yeast (Fig. 6, B, C, G, and H). Strikingly, the conversion of de novo DMQ6 to CoQ6 increases (as shown by the decreased ratio of 13C6-DMQ6 to 13C6-CoQ6) in a manner concurrent with the decrease in Snf2 levels and increase in PTC7 splicing in WT (compare Fig. 6D with Fig. 5 (A and B)). In fact, as the levels of Snf2 in WT yeast decrease, the conversion efficiency of DMQ6 to CoQ6 approaches the low ratio of DMQ6 to CoQ6 in snf2Δ yeast (Fig. 6, compare D and I). The role of Ptc7s in the increased synthesis of CoQ6 in the absence of Snf2 can be inferred from the observation that whereas the conversion efficiency from DMQ6 to CoQ6 is higher in the absence of Snf2, the level of DMQ6 itself does not change appreciably between WT and snf2Δ yeast over the 5-h time course (Fig. 6, compare B and G). However, the snf2Δ cells also show significantly lower rates of HHB synthesis (Fig. 6, compare C and H), as well as lower ratios of 13C6-HHB to 13C6-CoQ6 content (Fig. 6, compare E and J), consistent with the observation that deletion of Snf2 markedly accelerates the synthesis of CoQ6, presumably by expediting the conversion of these intermediates to the final product.
Figure 6.
Overall conversion efficiency of the CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway increases upon depletion of Snf2, with increased conversions of both DMQ6 to Q6 and HHB to Q6. A, levels of steady-state CoQ6 (12C-CoQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized CoQ6 (13C6-CoQ6, orange bars) in WT yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. B, levels of steady-state DMQ6 (12C-DMQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized DMQ6 (13C6-DMQ6, orange bars) in WT yeast were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. C, levels of steady-state HHB (12C-HHB, blue bars) and de novo synthesized (13C6-HHB, orange bars) in WT and snf2Δ yeast were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. D, the ratio of 13C6-DMQ6/13C6-CoQ6 in WT yeast was determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. The 0-h time point is excluded, because the ratio is not indicative of pathway conversion. E, the ratio of 13C6-HHB/13C6-CoQ6 in WT yeast was determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. The 0-h time point is excluded, because the ratio is not indicative of pathway conversion. F, levels of steady-state CoQ6 (12C-CoQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized (13C6-CoQ6, orange bars) in snf2Δ yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT in A; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005). G, levels of steady-state DMQ6 (12C-DMQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized DMQ6 (13C6-DMQ6, orange bars) in snf2Δ yeast were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT in B; *, p < 0.05). H, levels of steady-state HHB (12C-HHB, blue bars) and de novo synthesized HHB (13C6-HHB, orange bars) in snf2Δ yeast were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT in C; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005). I, the ratio of 13C6-DMQ6/13C6-CoQ6 in snf2Δ yeast cells was determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT in D; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005). The 0-h time point is excluded, because the ratio is not indicative of pathway conversion. J, the ratio of 13C6-HHB/13C6-CoQ6 in snf2Δ yeast cells was determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for snf2Δ and WT in E; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005). The 0-h time point is excluded, because the ratio is not indicative of pathway conversion.
RPG down-regulation in general leads to increased PTC7 splicing
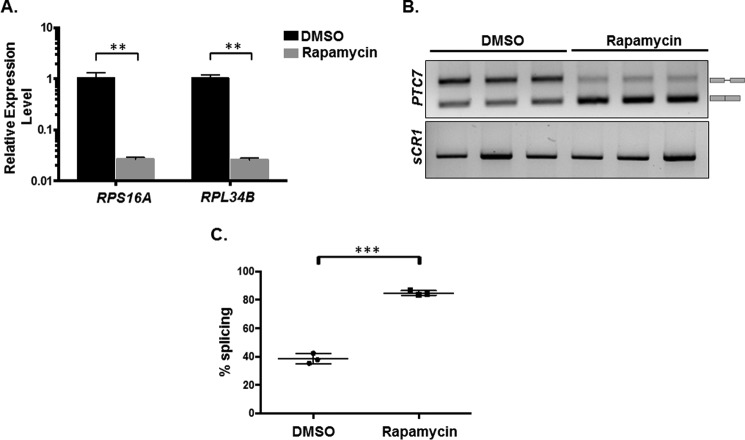
Our previous work showed that Snf2-dependent down-regulation of ribosomal protein genes enhances splicing, particularly of genes with nonconsensus splice sites. To determine whether the observed increase in PTC7 splicing is a consequence of RPG down-regulation per se, rapamycin was used to inhibit target of rapamycin (TOR)-dependent RPG transcription in a Snf2-independent manner (28) (Fig. 7A). It has also been previously published that rapamycin mitigates certain mitochondrial disorders in Drosophila and improves lifespan in response to TOR inhibition, purportedly by modulating carbon metabolism (29). In our work, rapamycin treatment led to a significant increase in the splicing of the PTC7 transcript (Fig. 7, B and C). As previously observed, the change in the ratio of Ptc7s/Ptc7ns protein (Fig. 1D) is greater than the change in the ratio of spliced to nonspliced transcript upon the deletion of Snf2 (Fig. 1B). This suggests that whereas Snf2-dependent RPG down-regulation changes the splicing of the PTC7 transcript, there are probably additional layers of gene regulation that control the relative levels of the Ptc7s and Ptc7ns protein isoforms. Experiments probing these mechanisms are currently ongoing. Nonetheless, these results are consistent with a model whereby down-regulation of RPG expression redirects spliceosomes from these abundant transcripts to otherwise poorly spliced transcripts, such as PTC7 (5, 6). In light of the role of Snf2 in RPG expression, changes in Snf2 levels allow fine-tuning of splicing in response to the cell's metabolic needs.
Figure 7.
RPG down-regulation and redistribution of spliceosomes result in increased PTC7 splicing. A, RT-qPCR measurement of selected intron-containing RPG transcripts between WT yeast treated with rapamycin and a vehicle control. Mean of three biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test, **p < 0.005). Error bars, S.D. B, expression and splicing of PTC7 in WT yeast treated with rapamycin and a vehicle control (DMSO). PCR products representing the spliced and nonspliced forms are indicated. C, quantification of three independent biological replicates of B (unpaired Student's t test; ***, p < 0.0005). Error bars, S.D.
Ptc7 isoforms have differing and opposing effects on CoQ6 synthesis
The predicted structures of the two isoforms of Ptc7, Ptc7s and Ptc7ns, have been modeled (Fig. 8, A and B). In fact, the Ptc7ns contains a transmembrane helix, encoded for by the PTC7 intron, which is capable of spanning the nuclear membrane. Overall, the presence of this transmembrane helix is not predicted to influence the folding of the rest of the protein, thus potentially retaining its phosphatase activity (Fig. 8).
Figure 8.
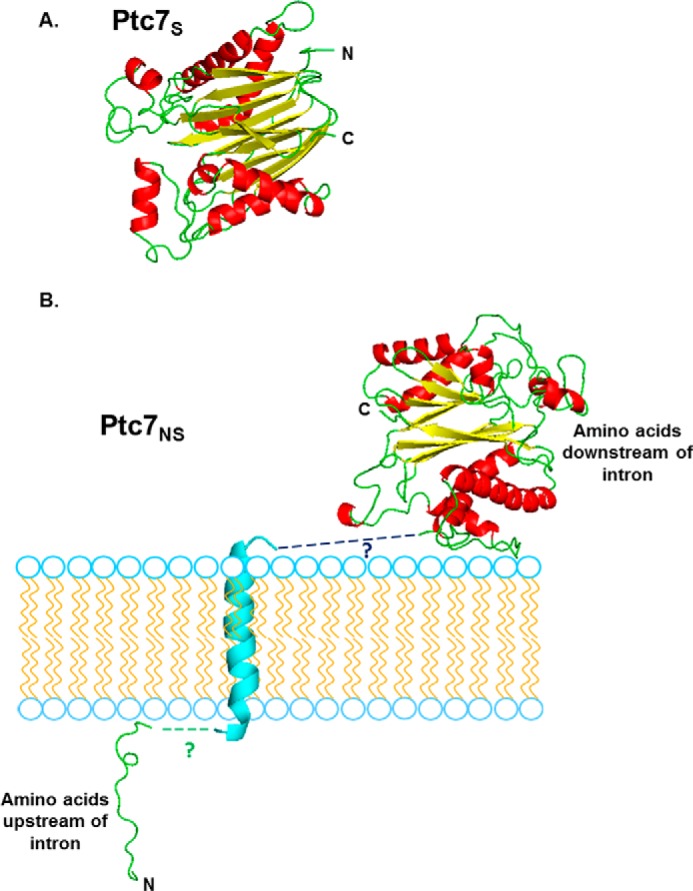
Structural predictions of mitochondrial Ptc7s and nuclear membrane traversing Ptc7ns. A, PHYRE2 homology modeling of mature mitochondrial Ptc7s, which is experimentally determined to start at amino acid Gly39 (46). 85% of residues modeled at >90% confidence (15% of residues modeled ab initio). The N terminus and C terminus of the protein are shown. B, PHYRE2 homology modeling of nuclear membrane Ptc7ns. The predicted trans-membrane helix encoded by the intron is shown in cyan. 86% of residues modeled at >90% confidence (14% of residues modeled ab initio. To show the interaction with the nuclear membrane, the N-terminal loop residing on the one side of the nuclear membrane is proposed to be linked to the modeled transmembrane helix, which is then proposed to be linked to the rest of the Ptc7 protein that is predicted to reside on the alternate side of the nuclear membrane. The nine black dashes connecting the helix to the larger portion of the protein represent nine amino acids in the intron that were in an unmodeled region.
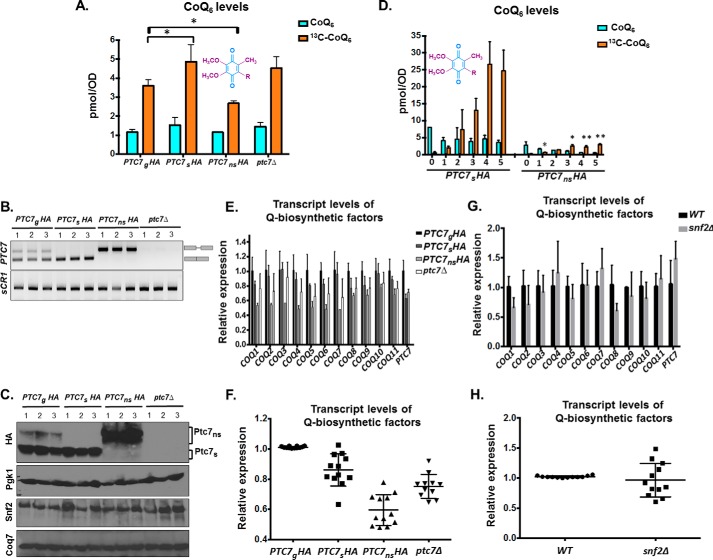
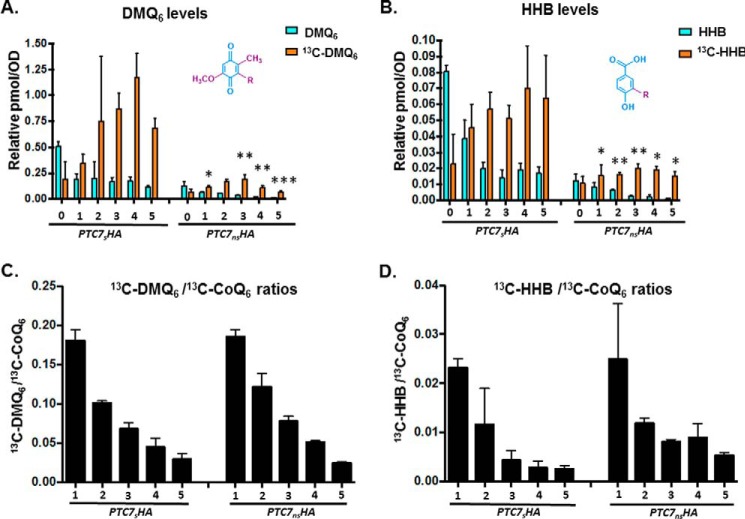
To determine the effect of each Ptc7 isoform on CoQ6 synthesis, we assayed CoQ6 levels in cells expressing both forms of Ptc7, Ptc7s only, Ptc7ns only, or neither (ptc7Δ). As reported previously, there is no significant change in CoQ6 synthesis levels in the ptc7Δ mutant (12, 30). However, exclusive expression of Ptc7s leads to an increase in CoQ6 synthesis, whereas exclusive expression of Ptc7ns leads to a decrease in CoQ6 synthesis (Fig. 9A). The relative RNA levels from each strain are shown (Fig. 9B). Moreover, there are no significant changes observed in the protein levels of Snf2 or Coq7, the target of Ptc7 activity (Fig. 9C), in these strains. Whereas each of these isoforms was expressed within the endogenous context and from the endogenous PTC7 promoter, protein levels of the Ptc7ns appeared to be increased relative to the other isoforms (Fig. 9, B and C), perhaps due to a cellular feedback mechanism that increases expression or enhances stability of Ptc7ns.
Figure 9.
Ptc7 isoforms have differing and opposing effects on CoQ6 synthesis. A, levels of steady-state CoQ6 (12C-CoQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized CoQ6 (13C6-CoQ6, orange bars) in strains expressing distinct Ptc7 isoforms (PTC7gHA, genomic, both isoforms expressed; PTC7sHA, exclusively expresses the isoform from spliced mRNA; PTC7nsHA, exclusively expresses the isoform from nonspliced pre-mRNA) and ptc7Δ. Labeling with 13C6-4HB was allowed to proceed for 3 h. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test; *, p < 0.05). B, expression and splicing of PTC7 for samples corresponding to A. PCR products representing the spliced and nonspliced forms are indicated. C, steady-state levels of HA-tagged Ptc7 proteins were determined by immunoblotting for samples corresponding to A. Proteins derived from the nonspliced and spliced forms of the PTC7 RNA are denoted as Ptc7ns and Ptc7s, respectively. Pgk1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1) served as a loading control. Immunoblots for Snf2 and Coq7 are also included. D, levels of steady-state (12C-CoQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized (13C6-CoQ6, orange bars) CoQ6 in PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005). E, RT-qPCR measurement of COQ1–COQ11 and PTC7 transcript levels between strains expressing different Ptc7 isoforms (PTC7gHA, genomic, both isoforms expressed; PTC7sHA, exclusively expresses the isoform from spliced mRNA; PTC7nsHA, exclusively expresses the isoform from nonspliced pre-mRNA) and ptc7Δ. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars, S.D. F, summary analysis of transcript levels of Q-biosynthetic factors from E. G, RT-qPCR measurement of COQ1-COQ11 and PTC7 transcript levels between WT and snf2Δ yeast. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates. Error bars, S.D. H, summary analysis of transcript levels of Q-biosynthetic factors from G.
The steady-state and de novo synthesized levels of CoQ6 were also measured in a 5-h time course with the yeast strains expressing either Ptc7ns or Ptc7s. Both steady-state and de novo CoQ6 biosynthesis are significantly lower in Ptc7ns strain than in the Ptc7s and in fact appear to be actively repressed, suggesting that the two isoforms of Ptc7 have differing and opposing effects on CoQ6 biosynthesis (Fig. 9D). In addition, the exclusive presence of Ptc7s causes increased de novo biogenesis of 13C-CoQ6 as compared with the exclusive presence Ptc7ns (Fig. 9D). Whereas the positive effect of Ptc7s on CoQ6 biosynthesis is consistent with the mechanisms of Ptc7 action described previously, it is clear that Ptc7ns has a repressive effect on CoQ6 biosynthesis (compare Ptc7ns and ptc7Δ in Fig. 9A). To begin to elucidate the mechanism of this repression, we assayed the mRNA transcript levels of genes encoding components of the CoQ6 biosynthetic complex (viz. COQ1–11 and PTC7). On average, there is little change in the expression of the complex upon deletion of Snf2 (Fig. 9, G and H) or with the exclusive expression of Ptc7s or ptc7Δ. However, exclusive expression of Ptc7ns is associated with pronounced down-regulation of every member of the CoQ-synthome (Fig. 9, E and F). Although the mechanism by which these components are down-regulated is unclear, it is interesting that Ptc7ns has previously been localized to the nuclear membrane (10), hinting at a novel role for this isoform in expression of the RNAs encoding the CoQ-synthome. Two possible mechanisms by which nucleus-localized Ptc7ns may affect synthesis of the CoQ-synthome are via direct action on nucleus-localized Coq7 or via indirect effects on gene expression. It is important to mention here that to the best of our knowledge, no reports have demonstrated nuclear localization of, or a nuclear role for, Coq7 in S. cerevisiae.
Interestingly, yeast strains engineered to express either Ptc7s or Ptc7ns still retain the ability to grow on medium containing a non-fermentable carbon source, as do ptc7Δ null mutants (data not shown). This is consistent with our prior observations that ∼1–10% of CoQ6 levels are sufficient for comparable growth on medium containing a nonfermentable carbon source. It has been postulated that residual CoQ6 levels are observed due to the overlapping activities of Ptc5 and/or Ptc6, and in fact the ptc5Δptc7Δ double null mutant has impaired growth under conditions of temperature stress (11, 31). It is also worth noting that unlike the deletion of SNF2, the conversion efficiencies or ratios between the early components of the pathway (DMQ6 or HHB) and CoQ6 do not vary between strains exclusively expressing either Ptc7 isoform (Fig. 10, C and D). This is because although there are significant changes in the levels of de novo synthesized DMQ6 as well as HHB when comparing Ptc7s to Ptc7ns (Fig. 10, A and B), Ptc7s is synthesizing higher levels of de novo CoQ6, DMQ6, and HHB, compared with overall lower levels of these same lipids in Ptc7ns (Fig. 10, C and D). Thus, the overall conversion efficiencies (ratios) between both isoforms are comparable (Fig. 10, C and D). This is consistent with our interpretation that the absence of Snf2 contributes to the metabolic state of the cell in other ways in addition to its role in regulation of the Ptc7 isoforms.
Figure 10.
Exclusive expression of Ptc7 isoforms dramatically alters levels of CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway intermediates DMQ6 and HHB, yet overall conversion efficiency between both isoforms is comparable. A, levels of steady-state DMQ6 (12C-DMQ6, blue bars) and de novo synthesized DMQ6 (13C6-DMQ6, orange bars) in PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005). B, levels of steady-state HHB (12C-HHB, blue bars) and de novo synthesized HHB (13C6-HHB, orange bars) in PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test between corresponding bars for PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005). C, ratio of 13C6-DMQ6/13C6-CoQ6 in PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Ratios were derived from levels of 13C6-CoQ6, as shown in Fig. 7D. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. The 0-h time point is excluded, because the ratio is not indicative of pathway conversion. D, ratio of 13C6-HHB/13C6-CoQ6 in PTC7sHA and PTC7nsHA yeast cells were determined at the designated hours after labeling with 13C6-4HB. Ratios were derived from levels of 13C6-CoQ6, as shown in Fig. 7D. Error bars, S.D. of n = 3 biological replicates. The 0-h time point is excluded, because the ratio is not indicative of pathway conversion.
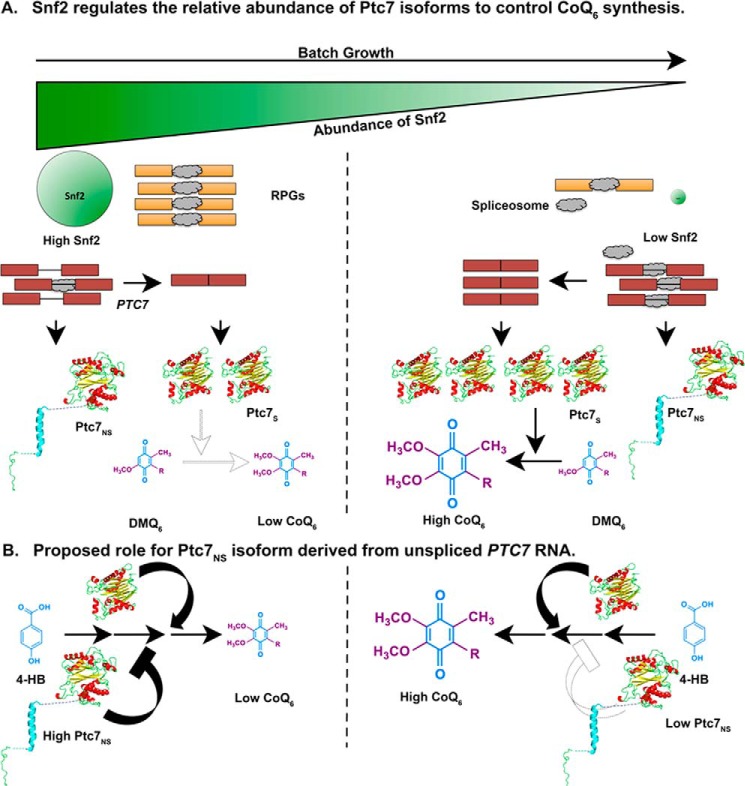
These data reveal a novel role for Snf2 in respiration and specifically in the transition from a largely fermentative mode of metabolism to a largely respiratory one in S. cerevisiae, as shown by the model in Fig. 11. Under conditions of high nutrient availability, Snf2-dependent transcription of intron-rich RPGs sequesters spliceosomes away from transcripts with weak splice sites, such as PTC7. As a consequence, both isoforms of the Ptc7 protein are expressed at appreciable levels, and their opposing effects on CoQ6 synthesis ensure that CoQ6 is maintained at a relatively low level. As the nutrients in the medium are depleted, the levels of Snf2 and, consequently, RPG transcripts, decrease concurrently, freeing up spliceosomes to act on PTC7. This leads to better splicing of PTC7 and a shift in the relative abundances of the two protein isoforms, which eventually leads to an increase in CoQ6 synthesis.
Figure 11.
Model for a novel role for Snf2 in respiration, and in the transition from a primarily fermentative mode of metabolism to a primarily respiratory mode of metabolism. A, during S. cerevisiae batch growth, the abundance of Snf2 decreases in conjunction with depletion of nutrients in the medium. RPGs under the control of Snf2 are down-regulated, allowing redistribution of spliceosomes to other poorly spliced transcripts. Splicing of the PTC7 transcript increases, enhancing the ratio of Ptc7s/Ptc7ns and overall levels of Ptc7s. These changes in Ptc7 isoform levels lead to increased conversion of DMQ6 and increased synthesis of CoQ6. The darker arrow represents a greater effect or reaction conversion, whereas a lighter arrow represents a smaller effect or reaction conversion. B, Ptc7ns has a repressive effect on CoQ6 biosynthesis. CoQ6 levels are low or high, depending on the levels of the Ptc7ns isoform relative to Ptc7s. Similar to A, darker arrows and bars denote a larger effect, whereas lighter arrows and bars denote a smaller effect.
Discussion
Whereas it has been broadly acknowledged that chromatin states and chromatin factors influence splicing outcomes in various organisms, identifying the functional importance of such regulation under biologically relevant conditions remains a challenge. We have shown previously that down-regulation of Snf2, the core ATPase component of the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex, in response to nutrient depletion leads to a change in cellular splicing outcomes due to down-regulation of RPGs and subsequent redistribution of spliceosomes (5, 6). We show here that Snf2-dependent changes in splicing of PTC7 during yeast growth, combined with the general conditions in the cell in the absence of Snf2, causes a shift in the ratio of two distinct isoforms of the Ptc7 protein that have distinct and opposing effects on CoQ6 biosynthesis. This change in the ratio of the isoforms is concomitant with an increase in CoQ6 levels in the cell, preparing for the transition from a largely fermentative to a respiratory mode of metabolism.
Previous studies have presented contradictory evidence regarding the involvement of PTC7 in CoQ6 biosynthesis. Ptc7 is required for the dephosphorylation of Coq7, thus transitioning Coq7 to its “active” form, which is able to catalyze the penultimate step of the CoQ6 pathway. This led to the prediction that the ptc7Δ strain would demonstrate decreased CoQ6 synthesis, as assayed by quantification of lipids from purified mitochondria (11). Surprisingly, although Ptc7 supports general respiratory function, the absence of PTC7 does not lead to a deficiency in CoQ6 levels, as assayed in lipid extracts of whole cells (12) (Fig. 9A). The studies here help to resolve this apparent contradiction. Studies with the ptc7Δ cells fail to address the opposing roles that the two Ptc7 isoforms have in the cell under WT conditions. Only cells with the capacity to express both Ptc7s and Ptc7ns can accurately reflect the full extent of Ptc7 function. We demonstrate that exclusive expression of Ptc7ns has a significant repressive effect on CoQ6 biosynthesis (Fig. 9, A and D). Notably, the rates of conversions from precursors in the pathway to the final product remained unchanged, indicating down-regulation of the entire pathway (Fig. 10, C and D). Consistent with this, we observe down-regulation of almost all of the components of the CoQ6 biosynthetic complex upon exclusive expression of Ptc7ns (Fig. 9F). The mechanism by which Ptc7ns affects RNA expression is as yet unknown, and investigations to understand the same are ongoing.
PTC7 is not the only known example of a gene in S. cerevisiae encoding functional proteins from both the nonspliced pre-mRNA as well as the “mature” spliced mRNA (10). We recently reported translation of unspliced GCR1 pre-mRNA leading to a functional Gcr1 protein, although in this case, translation starts from within the retained intron (7). Whereas the read-through nature of the intron is conserved across most Saccharomycetaceae species, the intron is excised in the same species (analysis of publicly available RNA-seq data sets; data not shown), rendering it likely that both forms of the protein are necessary and functional. This is illustrated in the case of Tetrapisispora blattae, which, like S. cerevisiae, underwent a whole genome duplication event; but unlike S. cerevisiae, which lost the duplications of most of its genes, T. blattae retains two copies of the PTC7 gene. Interestingly, the two PTC7 genes in T. blattae subfunctionalized into a gene that encodes a mitochondrial PP2C (Ptc7b, from a spliced transcript of PTC7b containing a stop codon within its intron) and a second gene encoding a PP2C predicted to localize to the nuclear envelope (Ptc7a, from an nonspliced transcript of PTC7a (32). This conservation further suggests that both protein isoforms derived from the PTC7 transcript in S. cerevisiae are functional. Cells lacking Ptc7ns show increased sensitivity to latrunculin A treatment, compared with strains expressing both isoforms of Ptc7 or lacking Ptc7s (10). Such sensitivity might suggest a distinct role for Ptc7ns in actin filament formation.
It is noteworthy that nuclear roles for numerous metabolic enzymes have been described previously. The ability of metabolic enzymes to “moonlight” in the nucleus, affecting gene regulation at various steps, appears to be crucial for the ability of cells to sense and adapt to their potentially distinct nutrient environments (33). Numerous mitochondrial enzymes, such as succinate dehydrogenase, fumarase, aconitase, and malate dehydrogenase (all components of the Krebs cycle), have been shown to have significant nuclear roles in the regulation of gene expression (34–38). In some of these cases, enzymatic activity of these enzymes has been shown to be crucial to their nuclear roles (39). This precedence, combined with the evolutionarily conserved presence of an isoform of Ptc7 in the nuclear membrane, raises the possibility that a nucleus-localized phosphatase is crucial to regulation of components of the CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway. Intriguingly, CLK-1 and COQ7, the C. elegans and human homologs of Coq7, which is a target for Ptc7 in S. cerevisiae (11), have been demonstrated to localize to the nucleus and are postulated to have roles independent of CoQ biosynthesis (40). COQ7 has also been shown to associate with chromatin in HeLa cells (40), although recently this has been attributed to a transformed cell phenomenon (41). Whereas nuclear localization of Coq7 in S. cerevisiae has not been demonstrated, we suggest a potential role in nuclear gene regulation for Ptc7 via phosphatase activity on Coq7 or other unidentified targets, including conventionally nuclear and other “moonlighting” mitochondrial enzymes.
It is also possible that Ptc7 has a substrate other than Coq7 that affects expression of the CoQ6-synthome. In fact, a recent study identified with high confidence numerous differentially phosphorylated proteins in a ptc7Δ strain (12). Notably, this proteomic analysis does not distinguish between the potential effects of the two Ptc7 isoforms globally. In fact, rescue using plasmid-based expression of PTC7 (full-length) does not restore dephosphorylation levels for a number of nuclear proteins, although the increased phosphorylation of mitochondrial proteins upon deletion of PTC7 is almost completely reversed by exogenous expression of Ptc7 (12). Furthermore, it is possible that the mitochondrial role for Ptc7s is in fact covered by multiple redundancies. Ptc5 and Ptc6, two other PP2C protein phosphatases, also localize to the mitochondrial membrane, and PTC5 demonstrates a negative genetic interaction with PTC7, indicating the possibility of overlapping functions (11, 31).
Interestingly, the effect of Snf2 deletion on CoQ6 biosynthesis does not perfectly mirror the exclusive expression of Ptc7s. We postulate that this is partially due to the Snf2 affecting the flux of the entire CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway, as demonstrated by the increased conversion of early precursors. Whereas deletion of Snf2 does not, on average, change the expression of the components of the CoQ6-synthome (Fig. 9, G and H), it is possible the Snf2 may have other effects of CoQ6 flux. We are exploring these possibilities.
Intriguingly, although the absence of Snf2 enhances levels of CoQ6, yeast strains lacking Snf2 have a severe growth defect on non-fermentable carbon sources, such as glycerol or acetate (26) (Fig. 1E). However, Snf2 protein is undetectable by immunoblotting during growth in medium containing glycerol or acetate as the only carbon source (data not shown). This leads us to hypothesize that before Snf2 protein is down-regulated in response to glucose depletion, it is required for the transition from a fermentative metabolic state to one that is predominantly respiratory in nature. The molecular details of the requirement for Snf2 in this transition are the subject of ongoing investigation. However, it is probably at least in part due to its reported role in the activation (de-repression) of genes whose transcription had previously been subject to glucose-mediated catabolite repression. This activation occurs once the glucose has been depleted or the yeast have been shifted to a different, non-fermentable carbon source (26). We postulate that once the gene expression profile required for adaptation to the new nutrient environment has been initiated and/or established, the requirement for Snf2 is relieved, and in fact, the down-regulation of Snf2 enhances splicing of PTC7. This transient requirement for Snf2 bears striking similarities to a previous report detailing the role of Snf2 in reversing Ume6-mediated repression at certain meiotic genes early in meiosis, before it is itself down-regulated to enable splicing of meiotic transcripts (6).
This work reveals a mechanism by which SWI/SNF acts as a nexus point in the fermentation–respiratory transition in S. cerevisiae. We also demonstrate opposing effects of isoforms of a single gene, PTC7, on the process of CoQ6 biosynthesis, via distinct mechanisms. Numerous aspects of these mechanisms remain to be studied, as well as their potential roles in the gene regulation response to other physiological conditions that yeast might experience.
Experimental procedures
Yeast strains and culture conditions
The yeast strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. All strains except W303Δcoq2 are derived from the BY background. Yeast strains were grown in YPD (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% dextrose) medium at 30 °C. Snf2 and Ptc7 null strains were maintained with a backup expression plasmid (pRS316 backbone harboring either SNF2 or PTC7). The plasmid was shuffled out by growth on 5-fluoroorotic acid before using the strains in experiments. Strains with tagged isoforms of Ptc7 were a kind gift from Dr. Ron Davis (10). These strains were back-crossed against WT or snf2Δ strains, and daughter strains used for this study are listed in Table 1. The snf2Δ strain was observed to spontaneously mutate if grown on YPD for longer than 7–8 days, acquiring suppressor mutations that made it difficult to distinguish from WT. Hence, for all experiments with snf2Δ, the plasmid containing SNF2 was shuffled out prior to each experiment, allowing a fresh snf2Δ strain with each experiment, to avoid these suppressor mutants. We found that this was absolutely instrumental to observe the proper phenotype and behavior of the snf2Δ strain.
Table 1.
Genotype and source of yeast strains
| Strain number | Name | Genotype | Source/reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| TJY6724 | WT | MATa his3Δ leu2Δ LYS2 met15Δ ura3Δ | Ref. 6 |
| TJY6727 | snf2Δ | MATα his3Δ leu2Δ ura3Δ snf2Δ::NatMX | Ref. 6 |
| TJY7114 | PTC7gHA | MATa his3Δ leu2Δ ura3Δ PTC7gHA:KanMX | This study |
| TJY7115 | snf2ΔPTC7gHA | MATa his3Δ leu2Δ ura3Δ snf2Δ::NatMX PTC7gHA:KanMX | This study |
| W303Δcoq2 | coq2Δ | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 coq2::HIS3 | Ref. 47 |
| TJY7116 | PTC7sHA | MATa his3Δ leu2Δ ura3Δ PTC7sHA:KanMX | This study |
| TJY7118 | PTC7nsHA | MATa his3Δ leu2Δ ura3Δ PTC7nsHA:KanMX | This study |
| TJY7142 | ptc7Δ | MATa his3Δ leu2Δ ura3Δ ptc7Δ:KanMX | This study |
| BY4741Δcoq9 | coq9Δ | MATα his3Δ0 leu2Δ0 met15Δ0 ura3Δ0 coq9::KANMX4 | Ref. 48 |
RNA-sequencing analyses
The RNA-sequencing data reported in this study were generated previously (6). Briefly, RNA sequencing libraries were prepared using the Illumina Truseq® V3 kit and ribosomal RNA depletion (Ribo-Zero, Illumina). Single-end, 50-nucleotide sequence reads (HiSeq 2000) were aligned to SacCer3 and spliced transcripts from the Ares Lab Yeast Intron Database version 3 (42) in a single step using STAR (43). Only the highest scoring alignments for each read were kept, allowing for at most a single tie. Reads/kb/million were computed for each gene by dividing the total number of reads that aligned entirely within the gene's exon boundaries by the gene's total exon length in kilobase pairs per million mapped reads. Reads within ICGs were categorized as exonic, spliced, or unspliced. Exonic reads map entirely within an exon, as defined by the Ares Lab Yeast Intron Database. Introns with annotated small nucleolar RNAs within the defined intron boundaries were disregarded in this analysis. Spliced reads are those that align with a gap that corresponds to an annotated intron, and unspliced reads map partially within an exon and partially within an intron with no gap. Spliced and unspliced read counts were normalized by dividing total spliced counts by the number of potential unique alignment positions that contribute to the total. For spliced reads, this is read length minus one for every intron. For unspliced read counts, this is the length of the intron plus the read length minus one. Splicing efficiency for each intron was calculated as normalized spliced counts divided by the sum of the normalized spliced and normalized unspliced counts. Changes in splicing efficiency were calculated as percentage difference over WT efficiency and plotted against expression levels (reads/kb/million) in WT. Data are available under GEO accession number GSE94404, and detailed methods were described previously (6).
RT-PCR and real-time PCR analysis
RNA was isolated from a 5-ml aliquot of cell culture corresponding to time points described in each experiment. After DNase treatment (Roche Applied Science), equal quantities of total RNA from each sample were used to make cDNA using a cDNA synthesis kit (Fermentas). To detect PTC7 splicing isoforms, primers flanking the intronic sequences were used for PCR using 1 μl of cDNA diluted 1:20. PCR products were then separated on a 2% agarose gel and imaged. RT-qPCR was done in a 10-μl reaction volume with gene-specific primers using 1 μl of cDNA diluted 1:20 using Perfecta SYBR Green Fastmix (Quanta Biosciences) and a CFX96 Touch System (Bio-Rad). All samples were analyzed in triplicate for each independent experiment. RT-qPCR was also performed for the scR1 (cytoplasmic signal recognition particle RNA subunit) RNA from each cDNA sample. Gene expression analysis was done by 2−ΔCt methods using scR1 as a reference. -Fold expression of mRNA was measured compared with WT by 2−ΔΔCt methods (44).
Immunoblots
Protein was isolated from cell pellets with FA-1 lysis buffer (50 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, 0.1% sodium deoxycholate, 1 mm PMSF, and protease inhibitors) with bead beating. The buffer was supplemented with protease inhibitor mixture tablet (Roche Applied Science). Total protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE. The gel was transferred to PVDF membrane, and proteins were detected with the following antibodies at the stated dilutions: anti-SNF2 antibody (yN-20, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) at a 1:200 dilution in 2% milk, anti-HA antibody (901514, BioLegend) at a 1:2000 dilution in 5% milk, anti-Pgk1 antibody (459250, Invitrogen) at a 1:3000 dilution in 5% milk, or anti-Coq7 antibody (described previously (16) at a 1:2000 dilution in 3% milk. Signal was detected with enhanced chemiluminescence (Thermo Scientific) as described by the manufacturer.
Metabolic labeling of CoQ6 with 13C6-labeled precursors
Yeast strains were grown overnight in 25 ml of YPD in a shaking incubator (30 °C, 250 rpm) and diluted to an A600 of 0.1 in 60 ml of fresh YPD the next morning. The cultures were incubated as before to an A600 of 0.5 (midlog phase) and subsequently treated with 13C6-4HB at 10 μg/ml (600 μg total) or ethanol vehicle control (0.015%, v/v). At designated time periods, cells were harvested by centrifugation at 3000 × g for 5 min, from 50-ml aliquots (used for lipid extraction) or 10-ml aliquots (used for RNA and protein analysis). Cell pellets were stored at −20 °C.
Analysis of CoQ6 and CoQ6 intermediates
Lipid extraction of cell pellets was conducted as described (18) with methanol and petroleum ether and CoQ4 as the internal standard. Lipid measurements were performed by HPLC-MS/MS and normalized to total OD. Prior to mass spectrometry analysis, all samples were treated with 1.0 mg/ml benzoquinone to oxidize hydroquinones to quinones. Mass spectrometry analyses utilized a 4000 QTRAP linear MS/MS spectrometer (Applied Biosystems), and data were acquired and analyzed using Analyst version 1.4.2 and 1.5.2 software (Applied Biosystems). Separation of lipid quinones was performed with a binary HPLC delivery system and a Luna 5μ phenyl-hexyl column (100 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm; Phenomenex). The mobile phase consisted of a 95:5 methanol/isopropyl alcohol solution with 2.5 mm ammonium formate as solution A and a 100% isopropyl alcohol solution with 2.5 mm ammonium formate as solution B. The percentage of solution B was increased linearly from 0 to 5% over 6 min, whereby the flow rate was increased from 600 to 800 μl. Initial flow rate and mobile phase conditions were changed back to initial phase conditions linearly over 3.5 min. Each sample was analyzed using multiple-reaction monitoring mode. The following precursor-to-product ion transitions were detected as well as the +17 m/z ammoniated adducts for each of the metabolic products: 13C6-HHB m/z 553.4/157.0 (ammoniated: 570.4/157.0), 12C-HHB m/z 547.4/151.0 (ammoniated: 564.4/151.0), 13C6-DMQ6 m/z 567.6/173.0 (ammoniated: 584.6/173.0), 12C-DMQ6 m/z 561.6/167.0 (ammoniated: 578.6/167.0), 13C6-CoQ6 m/z 597.4/203.1 (ammoniated: 614.4/203.1), 12C-CoQ6 m/z 591.4/197.1 (ammoniated: 608.4/197.1), and 12C-CoQ4 m/z 455.4/197.0 (ammoniated: 472.4/197.0).
Plate dilution assays
Strains were grown overnight in 5 ml of YPD and diluted to an A600 of 0.2 in sterile PBS. A 5-fold serial dilution in PBS was performed, after which 2 μl of each dilution (1×, 5×, 25×, 125×, and 625×) were spotted onto the designated carbon sources. The final A600 of the aforementioned dilution series are 0.2, 0.04, 0.008, 0.0016, and 0.00032, respectively.
PHYRE homology modeling
Phyre2 is a modeling program designed to analyze protein structure, function, and mutations (45). It is used to analyze the primary sequence of a protein and, with homology detection methods, constructs a structure that compares the protein of interest with other proteins (or motifs of proteins) with known structure. In regard to Ptc7, the full nonspliced version of the protein (Ptc7ns), which is composed of 374 amino acids and retains its 31-amino acid intron (amino acids 19–50), was analyzed. The resulting structure and alignment coverage contained 86% of residues modeled at >90% confidence, with 14% of residues modeled ab initio. Additionally, the spliced isoform of Ptc7 (Ptc7s), which is localized and processed in the mitochondria, comprised of 305 amino acids, resulting from the removal of the 31-amino acid intron and the excision of the predicted mitochondrial targeting sequence (the 38 N-terminal amino acids of Ptc7s) (46), was also modeled using the PHYRE2 intensive modeling mode. The resulting structure and alignment coverage contains 85% of residues modeled at >90% confidence, with 15% of residues modeled ab initio.
Author contributions
A. M. A. and S. V. contributed equally to this work (both conducted the majority of the experiments, analyzed the results, and wrote the paper together). A. N. and M. C. B. assisted A. M. A. in conducting experiments; A. N. assisted A. M. A. in analyzing mass spectrometry results. A. R. G. and L. N. assisted S. V. in experiments, with A. R. G. also having assisted in the background research relating to PTC7 differential splicing in the snf2Δ strain shown in Fig. 1A. S. D. aligned the RNA-sequencing data and calculated splicing efficiencies. M. C. B. and L. N. thoroughly read and edited the working draft of the paper. C. F. C. and T. L. J. oversaw all details related to the project and provided guidance on experiments, data analysis, and the writing of this paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. James Bowie (UCLA) for advice and guidance in generating the PHYRE models and in the depiction of the spliced and nonspliced versions of Ptc7. We acknowledge the UCLA Molecular Instrumentation Core proteomics facility for the use of the QTRAP4000. We thank the laboratory of Dr. Ronald W. Davis (Stanford) for generously providing the Ptc7 spliced and nonspliced isoforms.
This work was supported by National Science Foundation Grants MCB-1330803 and 1518316, and by NIGMS, National Institutes of Health, Grant GM-085474; the Whitcome Pre-doctoral Fellowship in Molecular Biology (to S. V.); and Ruth L. Kirschstein National Service Award GM-007185 (to M. B). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
RNA-seq data are available in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under accession number GSE94404.
- ICG
- intron-containing gene
- RPG
- ribosomal protein gene
- ns
- non-spliced
- s
- spliced
- CoQ
- coenzyme Q
- DMQ6
- 5-demethoxy-Q6
- 4HB
- 4-hydroxybenzoic acid
- HHB
- 3-hexaprenyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid
- qPCR
- quantitative PCR
- TOR
- target of rapamycin.
References
- 1. Naftelberg S., Schor I. E., Ast G., and Kornblihtt A. R. (2015) Regulation of alternative splicing through coupling with transcription and chromatin structure. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 84, 165–198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Johnson T. L., and Vilardell J. (2012) Regulated pre-mRNA splicing: the ghostwriter of the eukaryotic genome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1819, 538–545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Pleiss J. A., Whitworth G. B., Bergkessel M., and Guthrie C. (2007) Rapid, transcript-specific changes in splicing in response to environmental stress. Mol. Cell 27, 928–937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ares M. Jr., Grate L., and Pauling M. H. (1999) An handful of intron-containing genes produces the lion's share of yeast mRNA. RNA 5, 1138–1139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Munding E. M., Shiue L., Katzman S., Donohue J. P., and Ares M. Jr. (2013) Competition between pre-mRNAs for the splicing machinery drives global regulation of splicing. Mol. Cell 51, 338–348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Venkataramanan S., Douglass S., Galivanche A. R., and Johnson T. L. (2017) The chromatin remodeling complex Swi/Snf regulates splicing of meiotic transcripts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 10.1093/nar/gkx373 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Hossain M. A., Claggett J. M., Edwards S. R., Shi A., Pennebaker S. L., Cheng M. Y., Hasty J., and Johnson T. L. (2016) Posttranscriptional regulation of Gcr1 expression and activity is crucial for metabolic adjustment in response to glucose availability. Mol. Cell 62, 346–358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Hossain M. A., Rodriguez C. M., and Johnson T. L. (2011) Key features of the two-intron Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene SUS1 contribute to its alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 8612–8627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Jiang L., Whiteway M., Ramos C. W., Rodriguez-Medina J. R., and Shen S.-H. (2002) The YHR076W gene encodes a type 2C protein phosphatase and represents the seventh PP2C gene in budding yeast. FEBS Lett. 527, 323–325 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Juneau K., Nislow C., and Davis R. W. (2009) Alternative splicing of PTC7 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae determines protein localization. Genetics 183, 185–194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Martín-Montalvo A., González-Mariscal I., Pomares-Viciana T., Padilla-López S., Ballesteros M., Vazquez-Fonseca L., Gandolfo P., Brautigan D. L., Navas P., and Santos-Ocaña C. (2013) The phosphatase Ptc7 induces coenzyme Q biosynthesis by activating the hydroxylase Coq7 in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 28126–28137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Guo X., Niemi N. M., Hutchins P. D., Condon S. G., Jochem A., Ulbrich A., Higbee A. J., Russell J. D., Senes A., Coon J. J., and Pagliarini D. J. (2017) Ptc7p dephosphorylates select mitochondrial proteins to enhance metabolic function. Cell Rep. 18, 307–313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Turunen M., Olsson J., and Dallner G. (2004) Metabolism and function of coenzyme Q. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1660, 171–199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Doimo M., Desbats M. A., Cerqua C., Cassina M., Trevisson E., and Salviati L. (2014) Genetics of coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Mol. Syndromol. 5, 156–162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Quinzii C. M., Emmanuele V., and Hirano M. (2014) Clinical presentations of coenzyme Q10 deficiency syndrome. Mol. Syndromol. 5, 141–146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Tran U. C., and Clarke C. F. (2007) Endogenous synthesis of coenzyme Q in eukaryotes. Mitochondrion 7, S62–S71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. González-Mariscal I., García-Testón E., Padilla S., Martín-Montalvo A., Pomares Viciana T., Vazquez-Fonseca L., Gandolfo Domínguez P., and Santos-Ocaña C. (2014) The regulation of coenzyme Q biosynthesis in eukaryotic cells: all that yeast can tell us. Mol. Syndromol. 5, 107–118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Allan C. M., Awad A. M., Johnson J. S., Shirasaki D. I., Wang C., Blaby-Haas C. E., Merchant S. S., Loo J. A., and Clarke C. F. (2015) Identification of Coq11, a new coenzyme Q biosynthetic protein in the CoQ-synthome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 7517–7534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Padilla S., Jonassen T., Jiménez-Hidalgo M. A., Fernández-Ayala D. J., López-Lluch G., Marbois B., Navas P., Clarke C. F., and Santos-Ocaña C. (2004) Demethoxy-Q, an intermediate of coenzyme Q biosynthesis, fails to support respiration in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and lacks antioxidant activity. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25995–26004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Padilla S., Tran U. C., Jiménez-Hidalgo M., López-Martín J. M., Martín-Montalvo A., Clarke C. F., Navas P., and Santos-Ocaña C. (2009) Hydroxylation of demethoxy-Q6 constitutes a control point in yeast coenzyme Q6 biosynthesis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 66, 173–186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Whitehouse I., Flaus A., Cairns B. R., White M. F., Workman J. L., and Owen-Hughes T. (1999) Nucleosome mobilization catalysed by the yeast SWI/SNF complex. Nature 400, 784–787 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Liu X., Li M., Xia X., Li X., and Chen Z. (2017) Mechanism of chromatin remodelling revealed by the Snf2-nucleosome structure. Nature 544, 440–445 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Dutta A., Gogol M., Kim J. H., Smolle M., Venkatesh S., Gilmore J., Florens L., Washburn M. P., and Workman J. L. (2014) Swi/Snf dynamics on stress-responsive genes is governed by competitive bromodomain interactions. Genes Dev. 28, 2314–2330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Dutta A., Sardiu M., Gogol M., Gilmore J., Zhang D., Florens L., Abmayr S. M., Washburn M. P., and Workman J. L. (2017) Composition and function of mutant Swi/Snf complexes. Cell Rep. 18, 2124–2134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Gabunilas J., and Chanfreau G. (2016) Splicing-mediated autoregulation modulates Rpl22p expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 12, e1005999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Neigeborn L., and Carlson M. (1984) Genes affecting the regulation of SUC2 gene expression by glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 108, 845–858 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Martín-Montalvo A., González-Mariscal I., Padilla S., Ballesteros M., Brautigan D. L., Navas P., and Santos-Ocaña C. (2011) Respiratory-induced coenzyme Q biosynthesis is regulated by a phosphorylation cycle of Cat5p/Coq7p. Biochem. J. 440, 107–114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Martin D. E., Soulard A., and Hall M. N. (2004) TOR regulates ribosomal protein gene expression via PKA and the Forkhead transcription factor FHL1. Cell 119, 969–979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Wang A., Mouser J., Pitt J., Promislow D., and Kaeberlein M. (2016) Rapamycin enhances survival in a Drosophila model of mitochondrial disease. Oncotarget 7, 80131–80139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. González-Mariscal I., Martín-Montalvo A., Ojeda-González C., Rodríguez-Eguren A., Gutiérrez-Rios P., Navas P., and Santos-Ocaña C. (2017) Balanced CoQ6 biosynthesis is required for lifespan and mitophagy in yeast. Microb. Cell 4, 38–51 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Sharmin D., Sasano Y., Sugiyama M., and Harashima S. (2014) Effects of deletion of different PP2C protein phosphatase genes on stress responses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 31, 393–409 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Marshall A. N., Montealegre M. C., Jiménez-Lopez C., Lorenz M. C., and van Hoof A. (2013) Alternative splicing and subfunctionalization generates functional diversity in fungal proteomes. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Boukouris A. E., Zervopoulos S. D., and Michelakis E. D. (2016) Metabolic enzymes moonlighting in the nucleus: metabolic regulation of gene transcription. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41, 712–730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. De P., and Chatterjee R. (1962) Evidence of nucleolar succinic dehydrogenase activity. Exp. Cell Res. 27, 172–173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. De P., and Chatterjee R. (1962) Nucleolar localization of succinic dehydrogenase in human malignant cells with MTT. Experientia 18, 562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Yogev O., Yogev O., Singer E., Shaulian E., Goldberg M., Fox T. D., and Pines O. (2010) Fumarase: a mitochondrial metabolic enzyme and a cytosolic/nuclear component of the DNA damage response. PLoS Biol. 8, e1000328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Jung S. J., Seo Y., Lee K. C., Lee D., and Roe J. H. (2015) Essential function of Aco2, a fusion protein of aconitase and mitochondrial ribosomal protein bL21, in mitochondrial translation in fission yeast. FEBS Lett. 589, 822–828 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Lee S. M., Kim J. H., Cho E. J., and Youn H. D. (2009) A nucleocytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase regulates p53 transcriptional activity in response to metabolic stress. Cell Death Differ. 16, 738–748 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. McEwen B. S., Allfrey V. G., and Mirsky A. E. (1963) Studies on energy-yielding reactions in thymus nuclei. J. Biol. Chem. 238, 2571–2578 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Monaghan R. M., Barnes R. G., Fisher K., Andreou T., Rooney N., Poulin G. B., and Whitmarsh A. J. (2015) A nuclear role for the respiratory enzyme CLK-1 in regulating mitochondrial stress responses and longevity. Nat Cell Biol. 17, 782–792 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Liu J. L., Yee C., Wang Y., and Hekimi S. (2017) A single biochemical activity underlies the pleiotropy of the aging-related protein CLK-1. Sci. Rep. 7, 859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Grate L., and Ares M. Jr. (2002) Searching yeast intron data at Ares lab Web site. Methods Enzymol. 350, 380–392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Dobin A., Davis C. A., Schlesinger F., Drenkow J., Zaleski C., Jha S., Batut P., Chaisson M., and Gingeras T. R. (2013) STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Livak K. J., and Schmittgen T. D. (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods 25, 402–408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Kelley L. A., Mezulis S., Yates C. M., Wass M. N., and Sternberg M. J. (2015) The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 10, 845–858 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Vögtle F. N., Wortelkamp S., Zahedi R. P., Becker D., Leidhold C., Gevaert K., Kellermann J., Voos W., Sickmann A., Pfanner N., and Meisinger C. (2009) Global analysis of the mitochondrial N-proteome identifies a processing peptidase critical for protein stability. Cell 139, 428–439 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Ashby M. N., Kutsunai S. Y., Ackerman S., Tzagoloff A., and Edwards P. A. (1992) COQ2 is a candidate for the structural gene encoding para-hydroxybenzoate:polyprenyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 4128–4136 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Winzeler E. A., Shoemaker D. D., Astromoff A., Liang H., Anderson K., Andre B., Bangham R., Benito R., Boeke J. D., Bussey H., Chu A. M., Connelly C., Davis K., Dietrich F., Dow S. W., et al. (1999) Functional characterization of the S. cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science 285, 901–906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]