Figure 4. Effect of casticin on cell proliferation and apoptosis of LX2 cells.
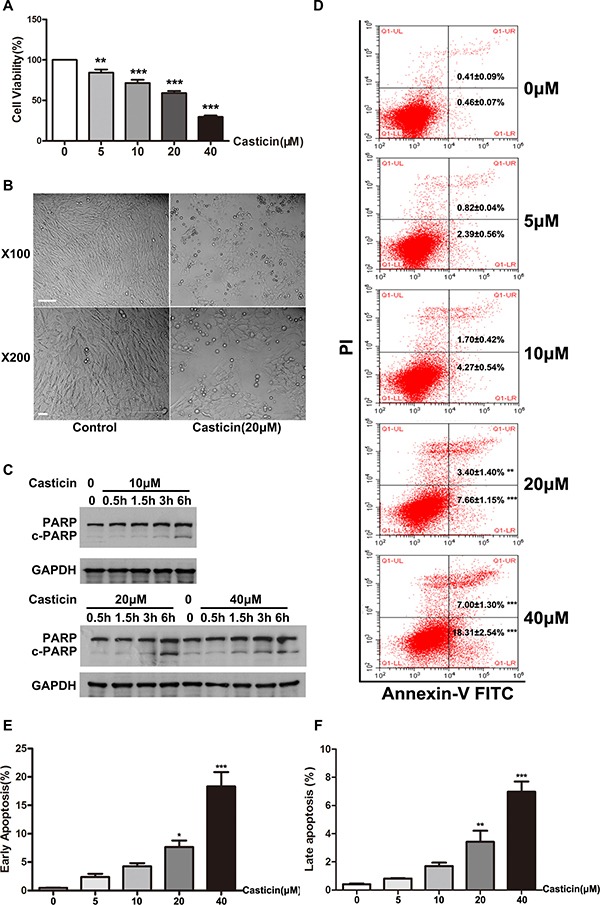
(A) Cell proliferation was determined by CCK-8 assay. LX2 cells plated in 96-well plates were treated with casticin (5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM or 40 μM) in growth medium containing serum for 48 h. (B) LX2 cells were cultured for 24 h, then incubated with casticin (20 μM) for up to 12 h. Representative phase-contrast photomicrographs of LX2 cells after incubation with equivoluminal DMSO or 20 μM casticin for 12 h are shown (original magnification 100× and 400×). (C) LX2 cells were cultured for 24 h, then treated with casticin (10 μM, 20 μM or 40 μM) for 0.5 h, 1.5 h, 3 h or 6 h. Cell lysates were subjected to western blot analysis to assess the cleavage of PARP. (D–F) LX2 cells were cultured for 24 h, then incubated with casticin (20 μM) for up to 12 h. Then casticin-induced cell apoptosis as measured by Annexin V–FITC and PI staining.
