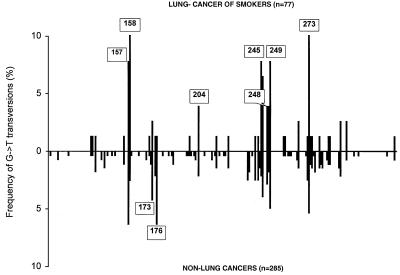
MEDICAL SCIENCES. For the article “Human lung cancer and p53: The interplay between mutagenesis and selection” by Sergei N. Rodin and Andrew S. Rodin, which appeared in number 22, October 24, 2000, of Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (97, 12244–12249; First Published October 17, 2000; 10.1073/pnas.180320897), the authors note the following correction. Fig. 2 shows erroneous spectra that do not correspond to the test result (0.979 P value as described in the text) because the lung cancer spectrum in smokers was constructed when erroneous repeats were not removed from the IARC p53 mutational database (April 1999). Also, some mutations were assigned to the wrong cancer type classes because of a spreadsheet macro programming error during the building of the chart. Fig. 2 is repeated here with the correct spectra. These corrections do not change the results or the conclusions reported in the paper.
Figure 2.
Comparison of the p53 spectra of G→T transversions from lung cancer (cases related to radon and other occupational exposures excluded) of ever smokers and cancers in non-lung tissues least accessible to smoke (see Table 1). The size of the bars represents the G→T frequency at the corresponding guanine. Hot- and “warm”-spot codons are indicated.