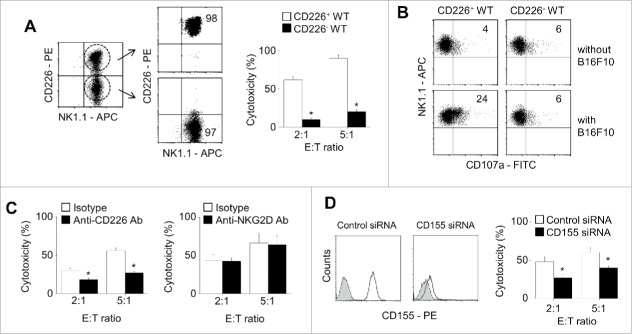
Figure 2.
CD226-negative NK cells show impaired cytotoxicity. (A) CD226+ and CD226− NK cells were purified from total splenic NK cells using flow cytometry and their cytotoxicity against B16F10 cells was determined by the LDH assay (n = 3, *p < 0.01). (B) To analyze exocytosis, NK and B16F10 cells were co-cultured for 2 h in the presence of anti-CD107a-FITC antibody. CD107+ expression level on CD226+ and CD226− NK cells was determined using flow cytometry (n = 3). (C) NK cells were treated with isotype, anti-CD226, or anti-NKG2D neutralizing antibodies (10 μg/ml) for 2 h. Cytotoxicity of NK cells against B16F10 cells was determined by the LDH assay (n = 3, *p < 0.01). (D) B16F10 cells were treated with negative control or CD155 siRNAs. CD155 expression level was determined by using flow cytometry and cytotoxicity of NK cells against B16F10 cells was determined by the LDH assay (n = 3, *p < 0.01).