Abstract
T2R38 has been shown to be a specific bacterial detector implicated in innate immune defense mechanism of human upper airway. Several clinical studies have demonstrated that this receptor is associated with the development of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). T2R38 was previously reported to bind to homoserine lactones (HSL), quorum sensing molecules specific of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and other gram negative species. Nevertheless, these bacteria are not the major pathogens found in CRS. Here we report on the identification of bacterial metabolites acting as new agonists of T2R38 based on a single cell calcium imaging study. Two quorum sensing molecules (Agr D1 thiolactone from Staphylococcus Aureus and CSP-1 from Streptococcus Pneumoniae) and a list of 32 bacterial metabolites from pathogens frequently implicated in CRS were tested. First, we observed that HSL failed to activate T2R38 in our experimental system, but that the dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), used as a solvent for these lactones may, by itself, account for the agonistic effect previously described. Secondly, we showed that both Agr D1 thiolactone and CSP-1 are inactive but that at least 7 bacterial metabolites (acetone, 2-butanone, 2-pentanone, 2-methylpropanal, dimethyl disulfide, methylmercaptan, γ-butyrolactone) are able to specifically trigger this receptor. T2R38 is thus much more broadly tuned for bacterial compounds than previously thought.
Introduction
The taste type 2 receptors (T2Rs or Tas2Rs) receptors correspond to a subfamily of GPCRs initially found to be expressed in vertebrate’s tongue and to be dedicated to the perception of bitterness in food [1–3]. Recently, the expression of T2Rs has also been reported in different cell types and in different parts of the body such as airways, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, white blood cells, heart, breast, thyroid, skin, testes [4]. The physiological relevance of these extra-oral expressions of T2Rs remains largely uninvestigated. However, recent studies provided evidences for the role of some of these receptors in the detection of bacterial products, more particularly in the upper airways. T2Rs were first detected in solitary chemosensory cells in the mouse nasal mucosa and the application of bitter compounds or bacterial quorum-sensing molecules on the nasal mucosa activate protective reflexes through stimulation of the trigeminal nerve while decreasing the respiratory rate [5,6]. Bacterial quorum-sensing molecules can also modify innate airway defense mechanisms in rat [7]. In human lower airways, T2Rs are located on motile cilia of epithelial cells and their stimulation increases ciliary beat frequency [8]. Therefore, this class of receptor constitute a potential target for the management of airway diseases.
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is an important public health issue with significant repercussions on patient’s quality of life and a substantial socioeconomic impact [9]. The pathophysiology of CRS remains unknown, but host-microbial interactions seem to play a leading role [10]. Several data demonstrate the implication of some T2Rs in CRS. In humans, a bitter taste receptor (T2R38) present in the sinus epithelium was reported to detect acyl homoserine lactone [11], a specific metabolic product of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and other gram negative species that plays a role in the bacterial quorum sensing [12,13]. The activation of T2R38 drives NO production, leading to an increased mucociliary clearance and to direct antibacterial effects [11]. T2R38 have two major haplotypes, a functional (PAV) and a non functional (AVI), underlying taste sensitivity to phenylthiocarbamide [14,15]. CRS-affected patients bearing the recessive homozygous genotype have more chance to suffer sinonasal gram-negative bacterial infection [11] and require sinus surgery more frequently [16]. On another hand, patients affected by polyp free CRS who share the dominant homozygote status (PAV/PAV) for T2R38 have better surgical outcome after sinus surgery than the other genotypes [17]. Moreover, a genomic study involving several hundreds of patient has identified a significant association between a T2R38 coding SNP (I296V) and CRS. T2R38 functionality was further associated with sinonasal symptoms in healthy adults [18] and in cystic fibrosis patients [19]. All these data support the implication of T2R38 in CRS.
Since the causal agents of chronic rhinosinusitis are not limited to Pseudomonas Aeruginosa or even to gram negative bacteria, it is of interest to determine whether T2R38 can play the role of a broader detector of bacterial compounds. In this study, two quorum sensing molecules, from Staphylococcus Aureus and Steptococcus Pneumoniae, and a list of 32 bacterial compounds from pathogens implicated in rhinosinusitis were tested as potential agonists of T2R38, using an in vitro calcium-based functional assay.
Material and methods
Plasmid construction and cell line generation
The coding sequences of either the functional (PAV, GenBank accession number AY258597.1) and non-functional (AVI, GenBank accession number AF494231.1) were amplified from human genomic DNA by polymerase chain reaction.
These coding sequences were cloned in a pEFIB backbone vector in translational fusion with the coding sequence of a leader sequence corresponding to the 45 first amino acids of the rat somatostatin receptor subtype 3 [20]. The constructs were verified by sequencing. The coding sequence of RTP4 (Genbank accession number AY562238.1) was amplified from human spleen cDNA and cloned a pCI backbone vector.
The Gα16gustducin44 sequence was generated by swapping the last 132 nucleotides of the G α16 with the corresponding terminal sequence of the Gα-gustducin [21] and was cloned in a pIRES-Puro plasmid. This vector was transfected in the Peakrapid cell line (ATCC reference: CRL-2828™; purchased from LGC Standards SARL, Molsheim, FRANCE), HEK293 cell line derivative, cultured in EMEM culture medium (reference BE12-136F; Lonza, Vervier, BELGIUM) supplemented with 10% of foetal bovine serum (Sigma-Aldrich, Bornem, Belgium) and 1 μg/ml of Puromycin to allow the selection of recombinant cell populations. Cell clones expressing the Gα16gustducin44 were selected and the clone presenting the best functional response of T2R38 to phenylthicarbamide was used for the study (see below).
Single cell calcium imaging
The Peakrapid cell line expressing stably a chimeric Gα16gustducin44 G protein [21] was used. 40 000 cells were seeded in each well of a black/clear poly-D-lysine cellware pre-coated 96-well plate (Biocoat®, Becton-Dickinson, Erembodegem, Belgium) and transiently transfected with 50 ng of plasmid DNA containing the receptor sequence or not (empty vector) and with 50 ng of chaperone protein RTP4 per well. Forty hours after transfection, cells were incubated with the calcium-sensitive dye Fluo4 (Life Technologies, Oregon, USA) solubilized at 10 μg/ml in a buffer containing EMEM (150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 1.2 mM MgCl2, 10 mM glucose), 10 mM HEPES, 0.01% (v/v) Pluronic F127, 0.1% (w/v) bovine serum albumin. After 1 h incubation at 37°C, cells were rinsed twice with the same buffer without Fluo4 and left in 50 μl buffer (prior ligand injection). Measurement were performed on a platform based on a motorized Axiobserver Z1 fluorescence microscope piloted by a Axiovision software (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) as described previously [22]. For each selected well, images were taken 1 per second, during 30 seconds. 50 μl of the buffer containing the ligand twice concentrated was injected on the 2nd second of the time lapse record.
After time lapse record, the number of responding cells in each injected well was determined using ImageJ 1.34 (Rasband, W.S., ImageJ, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA, http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/1997-2004), and expressed as the percentage of the surface of a microscope field covered by activated cells with respect to the total surface of the field covered by confluent cells. Automated determination of the surface occupied by responding cells is easier to perform than a cell counting. The resulting percentage of positive surface provided a convenient estimation of the percentage of responding cells, as observed by comparing the percentage of positive surface and percentage of responsive cells determined by direct counting, in the same experiment. In agreement with the literature [23], the percentage of responding cells was proportional to the agonist concentration. During experiment in each plate, at least 2 wells were tested with phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) at 0.1 mM, which is one of the best characterized agonist of T2R38 in the literature. The activation of T2R38 by PTC allows normalization of the result of other tested molecules. The results were thus expressed as the percentage of PTC activation. In scaling calcium imaging assays using this latter receptor, concentration-responses curves were performed and data were fitted to a four parameter logistic equation: . Min and max are the minimum and the maximum values of the percentage of cell-activated surface respectively, y is the percentage of cell-activated surface at the x concentration and nH is the Hill coefficient. While setting up the assay, concentration-response curves with PTC were performed, yielding to an EC50 value of 9.7 ± 0.4 μM (mean ± SEM of n = 3 experiments) (S2 Fig), similar to Behrens et al [24].
The results were confirmed by three independent experiments.
Bacterial compounds
Two quorum-sensing molecules respectively from Staphylococcus Aureus and Steptococcus Pneumoniae were used: Agr D1 thiolactone (YSTc(CDFIM)) from Eurogentec (Seraing, Belgium) and CSP-1 (competence stimulating peptide -1) (EMRLSKFFRDFILQRKK) from Cellmano Biotech Limited (Hefei, China).
To reproduce results from the literature [11], two others quorum-sensing molecules from gram negative bacteria, N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone (C4HSL) and N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (C12HSL), were purchased respectively from Cayman Chemichal (Tallinn, Estonia) and from Sigma—Aldrich (Schnelldorf, Germany).
32 volatile metabolites of pathogens (S1 Fig) were selected from the literature [25–28]. All compounds were dissolved in buffer solution, except C4HSL dissolved in buffer solution, DMSO or ethanol, C12HSL dissolved in DMSO or ethanol, and Agr D1 thiolactone dissolved in DMSO.
All compounds were tested first at a high concentration (100 mM). If the result was non specific, lower concentration (1:2 dilution) were tested until a specific or no calcium response was found.
Statistical analysis
To compare the levels of activation of T2R38 experiments and the controls, Mann-Whitney U tests were computed in R v3.2.3. P-values were then adjusted to account for multiple testing, using the function p.adjust with method = "fdr" to compute the false discovery rates.
Results
DMSO is an agonist of T2R38 and questions the agonistic effect of C4HSL and C12HSL
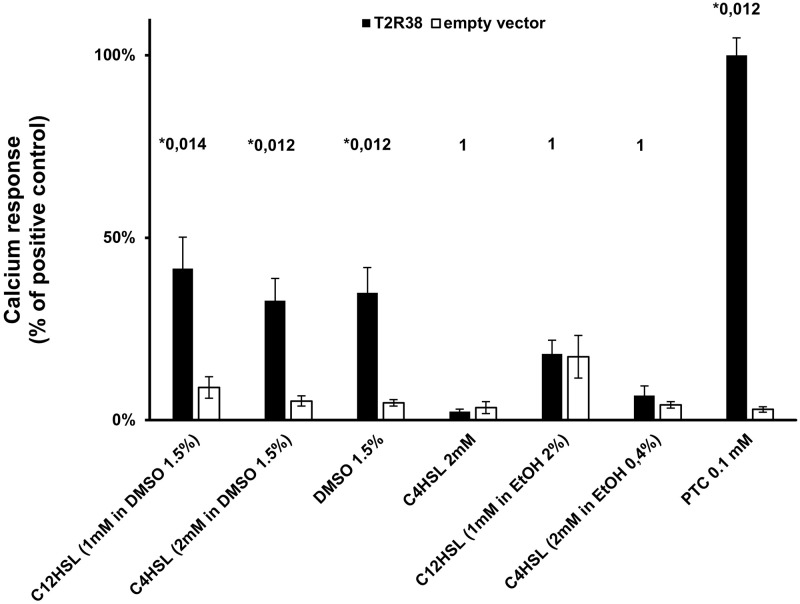
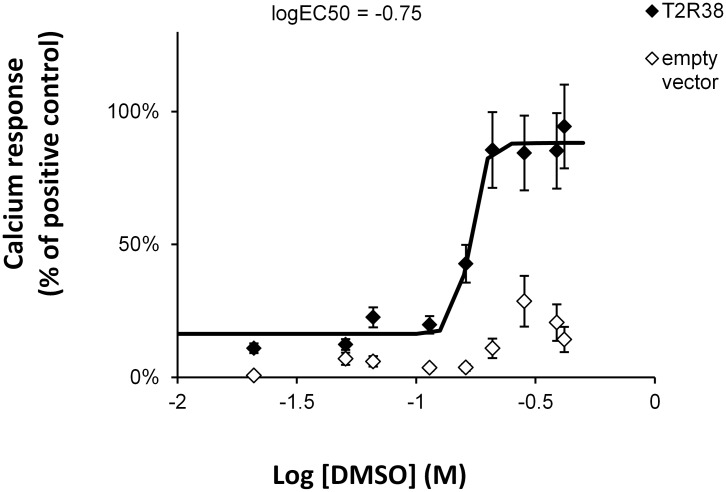
With the intent of exploring the receptivity of T2R38 for bacterial products, we first tried to reproduce previous results showing that C4HSL and C12HSL activate specifically T2R38 [11]. Our experimental system relied on a transient expression of the receptor Peakrapid cells (a derivative of HEK293 cell line) that stably expressed the chimeric protein Gα16gus44. This model allows an efficient coupling of bitter taste receptors activation to an IP3-dependent increase of cytosolic calcium increase [21]. Regarding the poor water solubility of C4HSL and C12HSL, we used DMSO as a solvent as described by Lee and coworkers [11]. When dissolved in DMSO 1.5% (209 mM), C4HSL and C12HSL elicited an average calcium response of respectively 33% and 42% of the one induced by 0.1 mM of PTC used as a positive control (Fig 1). To verify the specificity of the response, the vehicle solution alone was also tested. Unexpectedly, DMSO 1.5% (209 mM) alone induced a T2R38-dependent calcium response of the same intensity. A lower dilutions of 0.1 mM of C12HSL with either 0.3% or 0.15% percent of DMSO in the incubation buffer, did not trigger any specific activation of the receptor (S3 Fig). This surprising observation seriously questioned of the ability of HSLs to trigger the receptor in our experimental system and clearly contrasted with the results of the inspiring study of Lee et al. [11]. Indeed, it showed a calcium response elicited by both C4HSL and C12HSL in primary culture of sinus epithelial cells from patients homozygote for the active T2R38 (PAV) allele but not from patients heterozygote or homozygote for the inactive (AVI) allele. The triggering of a T2R38-mediated calcium response upon stimulation with the HSLs was also observed in HEK293 cells expressing G16gus44, i.e. an experimental system equivalent to ours. Therefore, we tried alternative modes of solubilization of the lactones. C4HSL can be solubilized in the aqueous buffer, but did not elicit a response of T2R38 when assayed at 2 mM, i.e. the same final concentration than used when solubilized in DMSO. Likewise, ethanol-solubilized C4HSL and C12HSL did not trigger a specific activation of T2R38. These results indicate that C4HSL and C12HSL are not agonists of the receptor in our hands. Relying on the description of HSLs solubilization (stock solution at 1:1,000 in DMSO) in the publication of Lee et al [11], we calculated that the amount of DMSO introduced in experiments might reach up to 3% (422 mM) or more, i.e. a concentration that could fully account for the activation of T2R38. This first conclusion is further supported by the concentration-response analysis performed with DMSO on T2R38 (Fig 2). It demonstrated an EC50 value of 178 mM. The images of the calcium response are shown in the supplementary data (S4 Fig). The specific interaction of DMSO with T2R38 is also illustrated by the absence of effect of this molecule on the non-functional haplotype of T2R38 (AVI) (S5 Fig).
Fig 1. DMSO is an agonist of T2R38 which questions the agonistic effect of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone (C4HSL) and N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (C12HSL).
The response of T2R38 to a stimulation by quorum sensing lactone and to the solvent dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) was monitored using a Ca2+-based functional assay. Results are presented as the percentage of the response elicited by 0.1 mM of phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) used as a reference agonist. Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) activated T2R38. Controls correspond to mock transfected cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. The false discovery rates (fdr) are indicated above the columns, * indicate a significant result (fdr < 0.05).
Fig 2. Concentration response curve of Peakrapid cells expressing T2R38 after stimulation with increasing DMSO (EC50 = 178 mM).
Results are presented as the percentage of the response elicited by 0.1 mM of phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) used as a reference agonist. Controls correspond to mock transfected cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
Several bacterial metabolites activate T2R38
Published data suggest a role for T2R38 in chronic rhinosinusitis and bacterial detection [11]. In spite of our first results showing that C4HSL and C12HSL are not agonists for this receptor, we have not definitively dismissed this hypothesis and have considered other bacterial molecules as putative activators of the receptor.
First, two quorum-sensing molecules of bacterial species implicated in rhinosinusitis were tested on T2R38 (S6 Fig). Agr D1 thiolactone (from Staphylococcus Aureus) was not soluble in aqueous solution and therefore solubilized in 0.3% DMSO at a final concentration of 0.1 mM. This concentration did not show specific activation. CSP-1 (from Streptococcus Pneumoniae) was soluble at 0.5 mM in the buffer solution. The calcium response observed upon stimulation with concentrations between 0.2 to 0.5 mM was similar in both T2R38-expressing cells and in negative control, avoiding to conclude to a specific activation of the receptor.
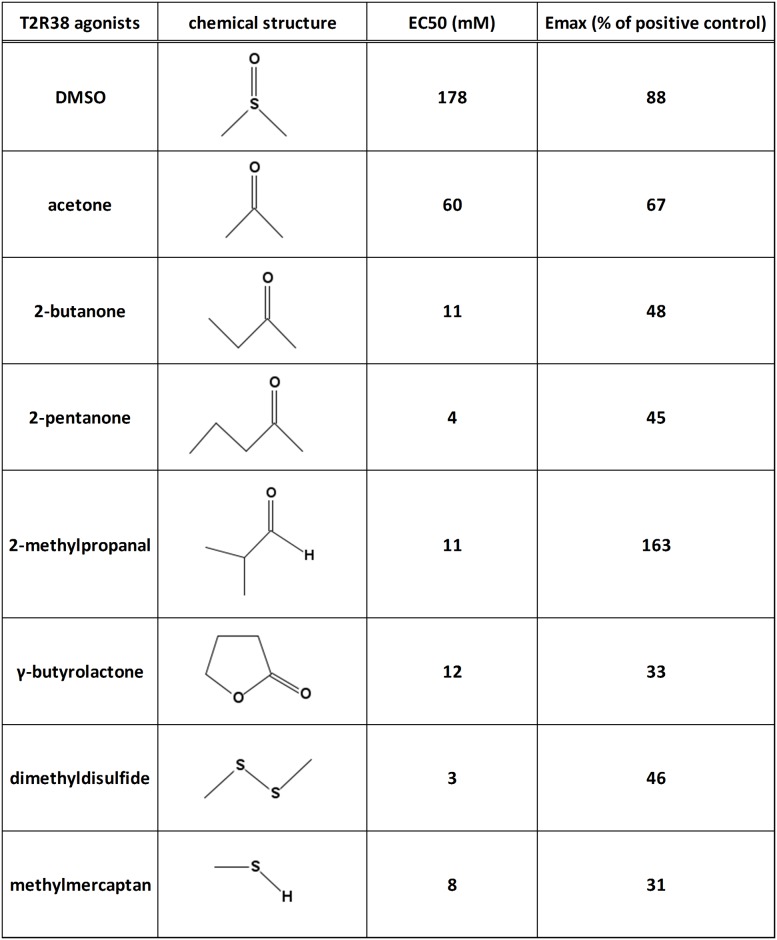
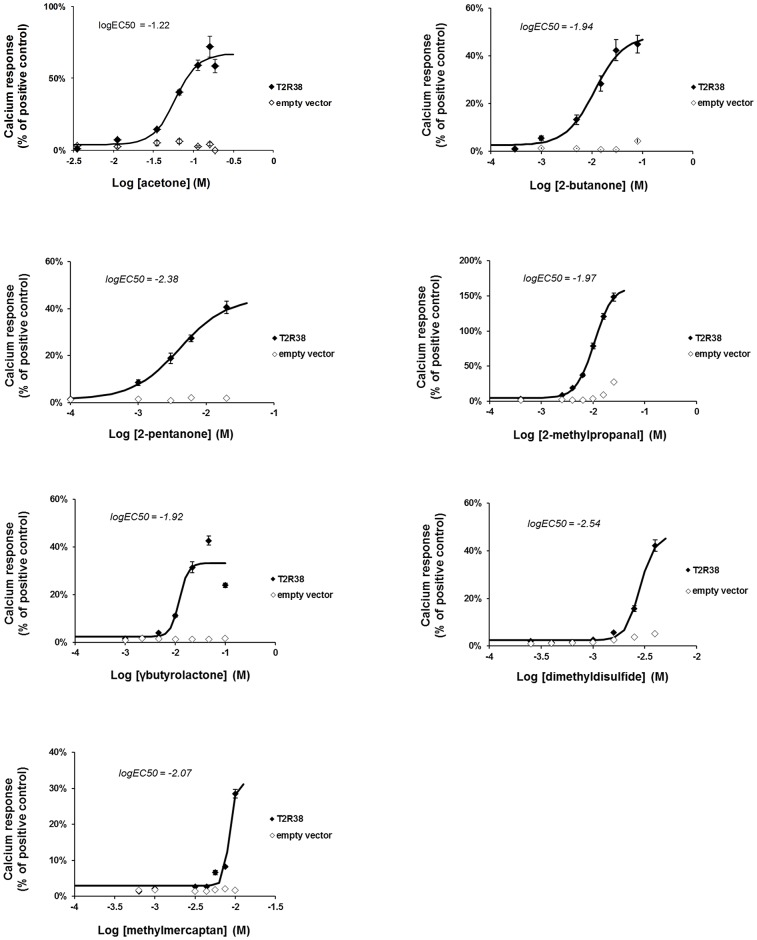
Secondly, it was of interest to determine whether common bacterial metabolites can activate T2R38. 32 volatile metabolites of pathogens (S1 Fig) were selected on the basis of the implication of the corresponding pathogen in rhinosinusitis, the level of abundance in bacterial medium [25–28] and the purchase availability. Over these 32 selected compounds, 7 produced an activation of T2R38 (Figs 3 and 4 and S7).
Fig 3. List of the 8 new T2R38 agonists.
Emax is the percentage of the response elicited by 0.1 mM of phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) used as a reference agonist.
Fig 4. Activation of T2R38 by different bacterial metabolites.
Results are presented as the percentage of the response elicited by 0.1 mM of phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) used as a reference agonist. Controls correspond to mock transfected cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments.
It is striking to note that none of the alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters or nitrogen bearing compounds are active. To date, 21 ligands have been reported for T2R38 [29,30]. They are characterized by a high degree of diversity of unrelated chemical structures and different potencies. The most potent agonists are active at low concentrations, below 100 μM whereas the less active need to be used at more than 1 mM to trigger the receptor [29], i.e. in the same range than the agonists identified in the present study. None of them are acids in line with our data. Known ligands of T2R38 have molecular weight and cLogP values ranging from 470 to 89 and +4.04 to -2.71 respectively. The compounds identified in our study have cLogP values from +1.39 to -1.28 within the range of the known ligands and molecular weights from 94 to 48 overlapping with the range of the known ligands and extending to the low molecular weight.
Discussion
The application of bitter compounds on airways leads to various effects, such as bronchorelaxation or triggering of innate immune defenses. Recent studies have pinpointed the involvement of T2Rs in these mechanisms. More precisely, T2R38 was found to be expressed in sinonasal epithelial cells and to be activated by HSLC4 and HSLC12, two quorum sensing molecules secreted by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and other gram negative bacteria. An increase of mucociliary clearance and NO production of the upper airway epithelium would result from the triggering of this receptor [11].
In the present study, we failed to reproduce the activation of T2R38 by HSLC4 and HSLC12 in a heterologous HEK293 cell-based expression system but we observed that the receptor responds to DMSO and to other bacterial metabolites than HSLC4 and HSLC12. These results are in apparent contradiction with the conclusions of the above mentioned study of Lee and coworkers [11]. A deeper analysis of the experimental conditions reveals that HSLC12 and HSLC4 used by Lee et al in single cell calcium imaging experiments were solubilized in DMSO.
According to the Method section of the corresponding publication, HSLC12 and HSLC4 were first prepared at 1:1,000 stock solutions in DMSO and used at 100 or 200 μM. In this condition, we calculated that the final concentrations of the solvent reached 3% (for HSLC12 at 100 μM) and 3.24% to 6.48% (for HSLC4 at 100 and 200 μM respectively). At these concentrations, DMSO alone could fully account for the observed activation of the receptor. Control experiments presented in the study of Lee et al [11], showed no effect of DMSO at concentrations up to 1%, in accordance with our own results. However, a possible activation at higher concentrations in DMSO was not provided. During the course of the reviewing of our manuscript, one of the co-author of Lee et al [11] stated that HSLC12 and HSLC4 where first solubilized at 100 mM before being diluted 1:1,000 (an additional information that cannot be read in the publication), making the concentration of DMSO at 0.1% i.e, below the activation threshold. Nevertheless, our observations that ethanol-solubilized HSLC4 and HSLC12 and water-solubilized HSLC4 remained without effect on the receptor are still in contradiction with an activation of T2R38 by HSLs. However, the results obtained with heterologous expression system we used does not rule out the possibility of an interaction of T2R38 with HSLs. Indeed, the main part of the work of Lee et al, was performed on primary culture of sinus epithelial cells. Peculiar phenomena of heterodimerization, coupling with alternative G protein or signaling cascade, as well as biased agonism could occurred in this cells that would be missed by our experimental system where a single receptor is expressed and the coupling to a chimeric G protein is forced. Additional indirect arguments in favor of an interaction T2R38 with HSLs are provided by the fact that culture supernatant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa culture increases NO secretion, ciliary beat frequency and bacteria killing by primary epithelial cells from individuals that expressed a functional T2R38 (PAV/PAV) but not from those expressing the non-functional allele (AVI/AVI) [11]. Interestingly, these effects are not observed with supernatant from a mutant strain, deficient for HSLs production. Other observations made in myeloid cells and neutrophils show that HSLC12 can bind T2R38 and this binding is inhibited by an antibody to T2R38. This binding is further illustrated by pull down assays using FITC-coupled or biotin-coupled HSLC12 [31, 32].
Although the heterologous expression system used here does not allow to study the whole range of T2R38 interactions, it remains a valuable tool for a pharmacological characterization of the receptor and enabled to discover the agonist status of DMSO. It is of particular importance since DMSO is a common solvent and its inappropriate use (i.e. high concentration) can drive to misleading interpretations while assessing potential agonist compounds on T2R38.
DMSO is known to have a bitter taste [33] but its potency as an agonist of T2R38 in the airway is particularly low as the active concentrations (EC50 = 178 mM) are far over those of bacterial products found in the airway. It is therefore unlikely that DMSO corresponds to a natural ligand that T2R38 would be assumed to detect in the sinus. Subsequently, we investigated the agonist potential of similar molecules. Replacing the sulfur atom by a carbon gives acetone that also activates T2R38 (EC50 = 89 mM). A further lengthening of the carbon chain results in 2-butanone and 2-pentanone, two additional stronger agonists of the receptor in our hands (EC50 = 11 mM and 4 mM, respectively). Interestingly, these two latter ketones are known bacterial metabolites produced by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and other bacterial species [25].
The extension of our analysis to 32 additional volatiles metabolites of pathogens [25], selected on 1) the basis of the implication of the bacteria in rhinosinusitis, 2) the level of abundance in bacterial medium and 3) the purchase availability, led to the identification of 7 new agonists of T2R38. These molecules are not specific of a single bacterial species, but are produced by several pathogens including Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis, except maybe the 2-methylpropanal that is produced by Staphylococcus aureus but not by the other pathogens [25]. Based on the interaction of T2R38 with quorum sensing molecules of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Lee and coworkers have proposed that this receptor plays a role in the triggering of innate immunity in sinonasal pathologies. Although the results presented here question the T2R38 agonist status of HSLC4 and HSLC12, our results are still supportive of this hypothesis. Since many clinical studies suggest an involvement of T2R38 in CRS [11,16,17,18,19], it was surprising that this receptor only detected product from bacteria less frequently implicated in this sinonasal pathology. Our results strongly suggest that T2R38 has a larger range of agonists from a bacterial origin and therefore, would be tuned to detect non-selectively a broader spectrum of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, the most frequent pathogen in CRS [9].
T2R38 has been well characterized on a pharmacological point of view. At least 21 agonists have been identified so far [29,30] and are active in or below the millimolar range. The role of this receptor in the taste perception of several of these agonists has also been demonstrated by the correlation of a specific inability to taste the corresponding molecule with genetic alteration in the coding sequence of T2R38 [14,15]. It is well accepted that the main physiological role of bitterness perception consists in preventing the ingestion of toxics. It can therefore be conceived that T2Rs have been evolutionarily selected to detect those poisons at a low concentration.
The situation could be rather different when considering the role of a T2R in bacterial detection and triggering of innate immune defenses. This mechanism would serve in maintaining a stable microbiome on the sinonasal epithelium. Such system should be effective when the quorum of pathogenic bacteria reaches a critical threshold. The involved receptor would therefore be activated by bacterial metabolites at a concentration generated by a relatively dense population. Consistently, the active concentrations of the 7 bacterial metabolites reported here to agonize T2R38 are all over the millimolar range. So far, there is no report of accurate measurement of these metabolite concentrations in the sinusonasal mucus that could comfort our hypothesis. Nevertheless, in culture conditions, concentrations up to 10 mM have been reported. For example, 2-pentanone can be detected at concentrations exceeding 40 mM in Aspergillus Niger culture [34], 2-methylpropanal can reach 15 mM in Cyanobacteria culture [35] and methylmercaptan 100 mM in another bacterial culture [36]. Moreover, in an adherent film of maximal width of 100 μm on airway mucosa even small quantities could achieve such high concentration.
Our study presents several limitations. First, the results were obtained in a heterologous expression system using a single cell calcium imaging assay that may be far from physiological reality. It will be necessary to confirm the effect of the bacterial metabolites in more physiological conditions, like explants of sinonasal mucosa. Another limitation relies in the number of bacterial metabolites tested. We selected the molecules among a short list of volatile metabolites of pathogens. This is of course not comprehensive of all bacterial metabolites, and it would be worth extending this research to other released bacterial products. Likewise, we have limited our analysis to T2R38 because of the evidences provided in the literature of a role of this receptor in CRS pathogenesis. Other chemosensory receptors, bitter or olfactory, might also be involved since they are expressed in the airways [37–39]. Together, they could constitute an information network about bacterial populations.
Supporting information
(TIF)
Controls correspond to mock transfected cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 experiments (n = 6).
(TIF)
Results are presented as mean ± SD. The calcium response is relative to 100% T2R38 activation by 0.1 mM of PTC.
(TIF)
Cells were transfected with T2R38 plasmid (right column) and control experiments with an empty vector (left column).
(TIF)
PAV is the functional allele of the receptor. Controls correspond to cells transfected with nonfunctional allele (AVI). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. The calcium response is relative to 100% T2R38 activation by 0.1 mM of PTC.
(TIF)
Results are presented as mean ± SD. Controls correspond to mock transfected cells.
(TIF)
PAV is the functional allele of the receptor. Control is cell transfected with nonfunctional allele (AVI). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. The calcium response is relative to 100% T2R38 activation by 0.1mM of PTC. The false discovery rates (fdr) are indicated above the columns, * indicate a significant result (fdr < 0.05).
(TIF)
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Parmentier and J.Y. Springael from Institute of Interdisciplinary Research in Human and Molecular Biology, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium, and A. Botteaux from Molecular Bacteriology Laboratory, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium, for fruitful discussions. We also thank C. Moreau from ChemCom S.A., Brussels, Belgium for help in imaging analysis.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
Two authors (AV and PC) are employed by the commercial company Chemcom S.A., Brussels. The funder, Fonds Erasme, provided support in the form of salaries for author [CV], but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ section.
References
- 1.Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS. A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell. 2000. March 17;100(6):693–702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chandrashekar J, Mueller KL, Hoon MA, Adler E, Feng L, Guo W, et al. T2Rs function as bitter taste receptors. Cell. 2000. March 17;100(6):703–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Matsunami H, Montmayeur JP, Buck LB. A family of candidate taste receptors in human and mouse. Nature. 2000. April 6;404(6778):601–4. doi: 10.1038/35007072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Avau B, Depoortere I. The bitter truth about bitter taste receptors: Beyond sensing bitter in the oral cavity. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015. October 23 doi: 10.1111/apha.12621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Finger TE, Böttger B, Hansen A, Anderson KT, Alimohammadi H, Silver WL. Solitary chemoreceptor cells in the nasal cavity serve as sentinels of respiration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. July 22;100(15):8981–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1531172100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tizzano M, Gulbransen BD, Vandenbeuch A, Clapp TR, Herman JP, Sibhatu HM, et al. Nasal chemosensory cells use bitter taste signaling to detect irritants and bacterial signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. February 16;107(7):3210–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911934107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sbarbati A, Tizzano M, Merigo F, Benati D, Nicolato E, Boschi F, et al. Acyl homoserine lactones induce early response in the airway. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2009. March;292(3):439–48. doi: 10.1002/ar.20866 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shah AS, Ben-Shahar Y, Moninger TO, Kline JN, Welsh MJ. Motile cilia of human airway epithelia are chemosensory. Science. 2009. August 28;325(5944):1131–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1173869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012. March;50(1):1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamilos DL. Host-microbial interactions in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. March;133(3):640–53.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.06.049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee RJ, Xiong G, Kofonow JM, Chen B, Lysenko A, Jiang P, et al. T2R38 taste receptor polymorphisms underlie susceptibility to upper respiratory infection. J Clin Invest. 2012. November;122(11):4145–59. doi: 10.1172/JCI64240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eberhard A, Burlingame AL, Eberhard C, Kenyon GL, Nealson KH, Oppenheimer NJ. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry. 1981. April 28;20(9):2444–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bandara HM, Lam OL, Jin LJ, Samaranayake L. Microbial chemical signaling: a current perspective.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2012. August;38(3):217–49. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2011.652065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim UK, Jorgenson E, Coon H, Leppert M, Risch N, Drayna D. Positional cloning of the human quantitative trait locus underlying taste sensitivity to phenylthiocarbamide. Science. 2003. February 21;299(5610):1221–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1080190 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bufe B, Breslin PA, Kuhn C, Reed DR, Tharp CD, Slack JP, et al. The molecular basis of individual differences in phenylthiocarbamide and propylthiouracil bitterness perception. Curr Biol. 2005. February 22;15(4):322–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Adappa ND, Zhang Z, Palmer JN, Kennedy DW, Doghramji L, Lysenko A, et al. The bitter taste receptor T2R38 is an independent risk factor for chronic rhinosinusitis requiring sinus surgery. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014. January;4(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/alr.21253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Adappa ND, Farquhar D, Palmer JN, Kennedy DW, Doghramji L, Morris SA, et al. TAS2R38 genotype predicts surgical outcome in nonpolypoid chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016. January;6(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/alr.21666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Farquhar DR, Kovatch KJ, Palmer JN, Shofer FS, Adappa ND, Cohen NA. Phenylthiocarbamide taste sensitivity is associated with sinonasal symptoms in healthy adults. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. February;5(2):111–8. doi: 10.1002/alr.21437 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Adappa ND, Workman AD, Hadjiliadis D, Dorgan DJ, Frame D, Brooks S, et al. T2R38 genotype is correlated with sinonasal quality of life in homozygous ΔF508 cystic fibrosis patients. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. December 17 doi: 10.1002/alr.21675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bufe B, Hofmann T, Krautwurst D, Raguse JD, Meyerhof W. The human TAS2R16 receptor mediates bitter taste in response to beta-glucopyranosides. Nat Genet. 2002. November;32(3):397–401. doi: 10.1038/ng1014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ueda T, Ugawa S, Yamamura H, Imaizumi Y, Shimada S. Functional interaction between T2R taste receptors and G-protein alpha subunits expressed in taste receptor cells. J Neurosci. 2003. August 13;23(19):7376–80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hadad I, Veithen A, Springael JY, Sotiropoulou PA, Mendes Da Costa A, Miot F, et al. Stroma cell-derived factor-1α signaling enhances calcium transients and beating frequency in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56007 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sanz G, Schlegel C, Pernollet JC, Briand L. Comparison of odorant specificity of two human olfactory receptors from different phylogenetic classes and evidence for antagonism. Chem Senses. 2005. January;30(1):69–80. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bji002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Behrens M, Gunn HC, Ramos PC, Meyerhof W, Wooding SP. Genetic, functional, and phenotypic diversity in TAS2R38-mediated bitter taste perception. Chem Senses. 2013. July;38(6):475–84. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjt016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bos LD, Sterk PJ, Schultz MJ. Volatile metabolites of pathogens: a systematic review. PLoS Pathog. 2013. May;9(5):e1003311 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Filipiak W, Sponring A, Baur MM, Filipiak A, Ager C, Wiesenhofer H, et al. Molecular analysis of volatile metabolites released specifically by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2012. June 20;12:113 doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Filipiak W, Sponring A, Baur MM, Ager C, Filipiak A, Wiesenhofer H, et al. Characterization of volatile metabolites taken up by or released from Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae by using GC-MS. Microbiology. 2012. December;158(Pt 12):3044–53. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.062687-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Preti G, Thaler E, Hanson CW, Troy M, Eades J, Gelperin A. Volatile compounds characteristic of sinus-related bacteria and infected sinus mucus: analysis by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009. July 15;877(22):2011–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.05.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Meyerhof W, Batram C, Kuhn C, Brockhoff A, Chudoba E, Bufe B, et al. The molecular receptive ranges of human TAS2R bitter taste receptors. Chem Senses. 2010. February;35(2):157–70. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjp092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wiener A, Shudler M, Levit A, Niv MY. BitterDB: a database of bitter compounds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. January;40(Database issue):D413–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr755 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Maurer S, Wabnitz GH, Kahle NA, Stegmaier S, Prior B, Giese T, Gaida MM, Samstag Y, Hänsch GM. Tasting Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms: Human Neutrophils Express the Bitter Receptor T2R38 as Sensor for the Quorum Sensing Molecule N-(3-Oxododecanoyl)-l-Homoserine Lactone. Front Immunol. 2015. July 24;6:369 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gaida MM, Dapunt U, Hänsch GM. Sensing developing biofilms: the bitter receptor T2R38 on myeloid cells. Pathog Dis. 2016. April;74(3). pii: ftw004. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jacob Stanley W., de la Torre Jack C., Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) in Trauma and Disease, CRC Press, 2015 [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lewis HL. Caproic Acid Metabolism and the Production of 2-Pentanone and Gluconic Acid by Aspergillus niger. Journal of General Microbiology (1971), 63,203–210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Atsumi S, Higashide W, Liao JC. Direct photosynthetic recycling of carbon dioxide to isobutyraldehyde. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. December;27(12):1177–80. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Baumler DJ, Hung KF, Jeong KC, Kaspar CW. Production of methanethiol and volatile sulfur compounds by the archaeon "Ferroplasma acidarmanus". Extremophiles. 2007. November;11(6):841–51. doi: 10.1007/s00792-007-0108-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Braun T, Mack B, Kramer MF. Solitary chemosensory cells in the respiratory and vomeronasal epithelium of the human nose: a pilot study. Rhinology. 2011. December;49(5):507–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Barham HP, Cooper SE, Anderson CB, Tizzano M, Kingdom TT, Finger TE, et al. Solitary chemosensory cells and bitter taste receptor signaling in human sinonasal mucosa. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013. June;3(6):450–7. doi: 10.1002/alr.21149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Verbeurgt C, Wilkin F, Tarabichi M, Gregoire F, Dumont JE, Chatelain P. Profiling of olfactory receptor gene expression in whole human olfactory mucosa. PLoS One. 2014. May 6;9(5):e96333 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(TIF)
Controls correspond to mock transfected cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM of 3 experiments (n = 6).
(TIF)
Results are presented as mean ± SD. The calcium response is relative to 100% T2R38 activation by 0.1 mM of PTC.
(TIF)
Cells were transfected with T2R38 plasmid (right column) and control experiments with an empty vector (left column).
(TIF)
PAV is the functional allele of the receptor. Controls correspond to cells transfected with nonfunctional allele (AVI). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. The calcium response is relative to 100% T2R38 activation by 0.1 mM of PTC.
(TIF)
Results are presented as mean ± SD. Controls correspond to mock transfected cells.
(TIF)
PAV is the functional allele of the receptor. Control is cell transfected with nonfunctional allele (AVI). Results are presented as mean ± SEM. The calcium response is relative to 100% T2R38 activation by 0.1mM of PTC. The false discovery rates (fdr) are indicated above the columns, * indicate a significant result (fdr < 0.05).
(TIF)
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.