Abstract
The effect of a splitting rule on random forests (RF) is systematically studied for regression and classification problems. A class of weighted splitting rules, which includes as special cases CART weighted variance splitting and Gini index splitting, are studied in detail and shown to possess a unique adaptive property to signal and noise. We show for noisy variables that weighted splitting favors end-cut splits. While end-cut splits have traditionally been viewed as undesirable for single trees, we argue for deeply grown trees (a trademark of RF) end-cut splitting is useful because: (a) it maximizes the sample size making it possible for a tree to recover from a bad split, and (b) if a branch repeatedly splits on noise, the tree minimal node size will be reached which promotes termination of the bad branch. For strong variables, weighted variance splitting is shown to possess the desirable property of splitting at points of curvature of the underlying target function. This adaptivity to both noise and signal does not hold for unweighted and heavy weighted splitting rules. These latter rules are either too greedy, making them poor at recognizing noisy scenarios, or they are overly ECP aggressive, making them poor at recognizing signal. These results also shed light on pure random splitting and show that such rules are the least effective. On the other hand, because randomized rules are desirable because of their computational efficiency, we introduce a hybrid method employing random split-point selection which retains the adaptive property of weighted splitting rules while remaining computational efficient.
Keywords: CART, end-cut preference, law of the iterated logarithm, splitting rule, split-point
1 Introduction
One of the most successful ensemble learners is random forests (RF), a method introduced by Leo Breiman (Breiman, 2001). In RF, the base learner is a binary tree constructed using the methodology of CART (Classification and Regression Tree) (Breiman et al., 1984); a recursive procedure in which binary splits recursively partition the tree into homogeneous or near-homogeneous terminal nodes (the ends of the tree). A good binary split partitions data from the parent tree-node into two daughter nodes so that the ensuing homogeneity of the daughter nodes is improved from the parent node. A collection of ntree > 1 trees are grown in which each tree is grown independently using a bootstrap sample of the original data. The terminal nodes of the tree contain the predicted values which are tree-aggregated to obtain the forest predictor. For example, in classification, each tree casts a vote for the class and the majority vote determines the predicted class label.
RF trees differ from CART as they are grown nondeterministically using a two-stage randomization procedure. In addition to the randomization introduced by growing the tree using a bootstrap sample, a second layer of randomization is introduced by using random feature selection. Rather than splitting a tree node using all p variables (features), RF selects at each node of each tree, a random subset of 1 ≤ mtry ≤ p variables that are used to split the node where typically mtry is substantially smaller than p. The purpose of this two-step randomization is to decorrelate trees and reduce variance. RF trees are grown deeply, which reduces bias. Indeed, Breiman’s original proposal called for splitting to purity in classification problems. In general, a RF tree is grown as deeply as possible under the constraint that each terminal node must contain no fewer than nodesize ≥ 1 cases.
The splitting rule is a central component to CART methodology and crucial to the performance of a tree. However, it is widely believed that ensembles such as RF which aggregate trees are far more robust to the splitting rule used. Unlike trees, it is also generally believed that randomizing the splitting rule can improve performance for ensembles. These views are reflected by the large literature involving hybrid splitting rules employing random split-point selection. For example, Dietterich (2000) considered bagged trees where the split-point for a variable is randomly selected from the top 20 split-points based on CART splitting. Perfect random trees for ensemble classification (Cutler and Zhao, 2001) randomly chooses a variable and then chooses the split-point for this variable by randomly selecting a value between the observed values from two randomly chosen points coming from different classes. Ishwaran et al. (2008, 2010) considered a partially randomized splitting rule for survival forests. Here a fixed number of randomly selected split-points are chosen for each variable and the top split-point based on a survival splitting rule is selected. Related work includes Geurts et al. (2006) who investigated extremely randomized trees. Here a single random split-point is chosen for each variable and the top split-point is selected.
The most extreme case of randomization is pure random splitting in which both the variable and split-point for the node are selected entirely at random. Large sample consistency results provides some rationale for this approach. Biau, Devroye, and Lugosi (2008) proved Bayes-risk consistency for RF classification under pure random splitting. These results make use of the fact that partitioning classifiers such as trees approximate the true classification rule if the partition regions (terminal nodes) accumulate enough data. Sufficient accumulation of data is possible even when partition regions are constructed independently of the observed class label. Under random splitting, it is sufficient if the number of splits kn used to grow the tree satisfies kn/n → 0 and kn → ∞. Under the same conditions for kn, Genuer (2012) studied a purely random forest, establishing a variance bound showing superiority of forests to a single tree. Biau (2012) studied a non-adaptive RF regression model proposed by Breiman (2004) in which split-points are deterministically selected to be the midpoint value and established large sample consistency assuming kn as above.
At the same time, forests grown under CART splitting rules have been shown to have excellent performance in a wide variety of applied settings, suggesting that adaptive splitting must have benefits. Theoretical results support these findings. Lin and Jeon (2006) considered mean-squared error rates of estimation in nonparametric regression for forests constructed under pure random splitting. It was shown that the rate of convergence cannot be faster than M−1(log n) −(p−1) (M equals nodesize), which is substantially slower than the optimal rate n−2q/(2q+p) [q is a measure of smoothness of the underlying regression function; Stone (1980)]. Additionally, while Biau (2012) proved consistency for non-adaptive RF models, it was shown that successful forest applications in high-dimensional sparse settings requires data adaptive splitting. When the variable used to split a node is selected adaptively, with strong variables (true signal) having a higher likelihood of selection than noisy variables (no signal), then the rate of convergence can be made to depend only on the number of strong variables, and not the dimension p. See the following for a definition of strong and noisy variables which shall be used throughout the manuscript [the definition is related to the concept of a “relevant” variable discussed in Kohavi and John (1997)].
Definition 1
If X is the p-dimensional feature and Y is the outcome, we call a variable X ⊆ X noisy if the conditional distribution of Y given X does not depend upon X. Otherwise, X is called strong. Thus, strong variables are distributionally related to the outcome but noisy variables are not.
In this paper we formally study the effect of splitting rules on RF in regression and classification problems (Sections 2 and 3). We study a class of weighted splitting rules which includes as special cases CART weighted variance splitting and Gini index splitting. Such splitting rules possess an end-cut preference (ECP) splitting property (Morgan and Messenger, 1973; Breiman et al., 1984) which is the property of favoring splits near the edge for noisy variables (see Theorem 4 for a formal statement). The ECP property has generally been considered an undesirable property for a splitting rule. For example, according to Breiman et al. (Chapter 11.8; 1984), the delta splitting rule used by THAID (Morgan and Messenger, 1973) was introduced primarily to suppress ECP splitting.
Our results, however, suggest that ECP splitting is very desirable for RF. The ECP property ensures that if the ensuing split is on a noisy variable, the split will be near the edge, thus maximizing the tree node sample size and making it possible for the tree to recover from the split downstream. Even for a split on a strong variable, it is possible to be in a region of the space where there is near zero signal, and thus an ECP split is of benefit in this case as well. Such benefits are realized only if the tree is grown deep enough—but deep trees are a trademark of RF. Another aspect of RF making it compatible with the ECP property is random feature selection. When p is large, or if mtry is small relative to p, it is often the case that many or all of the candidate variables will be noisy, thus making splits on noisy variables very likely and ECP splits useful. Another benefit occurs when a tree branch repeatedly splits on noise variables, for example if the node corresponds to a region in the feature space where the target function is flat. When this happens, ECP splits encourage the tree minimal node size to be reached rapidly and the branch terminates as desired.
While the ECP property is important for handling noisy variables, a splitting rule should also be adaptive to signal. We show that weighted splitting exhibits such adaptivity. We derive the optimal split-point for weighted variance splitting (Theorem 1) and Gini index splitting (Theorem 8) under an infinite sample paradigm. We prove the population split-point is the limit of the empirical split-point (Theorem 2) which provides a powerful theoretical tool for understanding the split-rule [this technique of studying splits under the true split function has been used elsewhere; for example Buhlmann and Yu (2002) looked at splitting for stumpy decision trees in the context of subagging]. Our analysis reveals that weighted variance splitting encourages splits at points of curvature of the underlying target function (Theorem 3) corresponding to singularity points of the population optimizing function. Weighted variance splitting is therefore adaptive to both signal and noise. This appears to be a unique property. To show this, we contrast the behavior of weighted splitting to the class of unweighted and heavy weighted splitting rules and show that the latter do not possess the same adaptivity. They are either too greedy and lack the ECP property (Theorem 7), making them poor at recognizing noisy variables, or they have too strong an ECP property, making them poor at identifying strong variables. These results also shed light on pure random splitting and show that such rules are the least desirable. Randomized adaptive splitting rules are investigated in Section 4. We show that certain forms of randomization (Theorem 10) are able to preserve the useful properties of a splitting rule while significantly reducing computational effort.
1.1 A simple illustration
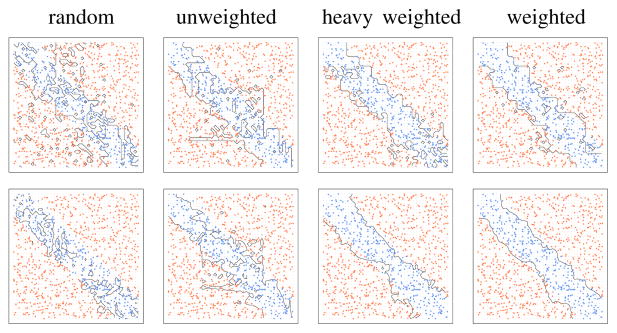
As a motivating example, n = 1000 observations were simulated from a two-class problem in which the decision boundary was oriented obliquely to the coordinate axes of the features. In total p = 5 variables were simulated: the first two were defined to be the strong variables defining the decision boundary; the remaining three were noise variables. All variables were simulated independently from a standard normal distribution. The first row of panels in Figure 1 displays the decision boundary for the data under different splitting rules for a classification tree grown to purity. The boundary is shown as a function of the two strong variables. The first panel was grown under pure random splitting (i.e., the split-point and variable used to split a node were selected entirely at random), the remaining panels used unweighted, heavy weighted and weighted Gini index splitting, respectively (to be defined later). We observe random splitting leads to a heavily fragmented decision boundary, and that while unweighted and heavy weighted splitting perform better, unweighted splitting is still fragmented along horizontal and vertical directions, while heavy weighted splitting is fragmented along its boundary.
Figure 1.
Synthetic two-class problem where the true decision boundary is oriented obliquely to the coordinate axes for the first two features (p = 5). Top panel is the decision boundary for a single tree with nodesize = 1 grown under pure random splitting, unweighted, heavy weighted and weighted Gini index splitting (left to right). Bottom panel is the decision boundary for a forest of 1000 trees using the same splitting rule as the panel above it. Black lines indicate the predicted decision boundary. Blue and red points are the observed classes.
The latter boundaries occur because (as will be demonstrated) unweighted splitting possesses the strongest ECP property, which yields deep trees, but its relative insensitivity to signal yields a noisy boundary. Heavy weighted splitting does not possess the ECP property, and this reduces overfitting because it is shallower, but its boundary is imprecise because it also has a limited ability to identify strong variables. The best performing tree is weighted splitting. However, all decision boundaries, including weighted splitting, suffer from high variability—a well known deficiency of deep trees. In contrast, consider the lower row which displays the decision boundary for a forest of 1000 trees grown using the same splitting rule as the panel above it. There is a noticeable improvement in each case; however, notice how forest boundaries mirror those found with single trees: pure random split forests yield the most fragmented decision boundary, unweighted and heavy weighted are better, while the weighted variance forest performs best.
This demonstrates, among other things, that while forests are superior to single trees, they share the common property that their decision boundaries depend strongly on the splitting rule. Notable is the superior performance of weighted splitting, and in light of this we suggest two reasons why its ECP property has been under-appreciated in the CART literature. One explanation is the potential benefit of end-cut splits requires deep trees applied to complex decision boundaries—but deep trees are rarely used in CART analyses due to their instability. A related explanation is that ECP splits can prematurely terminate tree splitting when nodesize is large: a typical setting used by CART. Thus, we believe the practice of using shallow trees to mitigate excess variance explains the lack of appreciation for the ECP property. See Torgo (2001) who discussed benefits of ECP splits and studied ECP performance in regression trees.
2 Regression forests
We begin by first considering the effect of splitting in regression settings. We assume the learning (training) data is ℒ = {(X1, Y1),…, (Xn, Yn)} where (Xi, Yi)1≤i≤n are i.i.d. with common distribution ℙ. Here, Xi ∈ ℝp is the feature (covariate vector) and Yi ∈ ℝ is a continuous outcome. A generic pair of variables will be denoted as (X, Y) with distribution ℙ. A generic coordinate of X will be denoted by X. For convenience we will often simply refer to X as a variable. We assume that
| (1) |
where f : ℝp → ℝ is an unknown function and (εi)1≤i≤n are i.i.d., independent of (Xi)1≤i≤n, such that 𝔼(εi) = 0 and where 0 < σ2 < ∞.
2.1 Theoretical derivation of the split-point
In CART methodology a tree is grown by recursively reducing impurity. To accomplish this, each parent node is split into daughter nodes using the variable and split-point yielding the greatest decrease in impurity. The optimal split-point is obtained by optimizing the CART splitting rule. But how does the optimized split-point depend on the underlying regression function f? What are its properties when f is flat, linear, or wiggly? Understanding how the split-point depends on f will give insight into how splitting affects RF.
Consider splitting a regression tree T at a node t. Let s be a proposed split for a variable X that splits t into left and right daughter nodes tL and tR depending on whether X ≤ s or X > s; i.e., tL = {Xi ∈ t, Xi ≤ s} and tR = {Xi ∈ t, Xi > s}. Regression node impurity is determined by within node sample variance. The impurity of t is
where Ȳt is the sample mean for t and N is the sample size of t. The within sample variance for a daughter node is
where ȲtL is the sample mean for tL and NL is the sample size of tL (similar definitions apply to tR). The decrease in impurity under the split s for X equals
where p̂(tL) = NL/N and p̂(tR) = NR/N are the proportions of observations in tL and tR, respectively.
Remark 1
Throughout we will define left and right daughter nodes in terms of splits of the form X ≤ s and X > s which assumes a continuous X variable. In general, splits can be defined for categorical X by moving data points left and right using the complementary pairings of the factor levels of X (if there are L distinct labels, there are 2L−1 − 1 distinct complementary pairs). However, for notational convenience we will always talk about splits for continuous X, but our results naturally extend to factors.
The tree T is grown by finding the split-point s that maximizes Δ̂(s, t) (Chapter 8.4; Breiman et al., 1984). We denote the optimized split-point by ŝN. Maximizing Δ̂(s, t) is equivalent to minimizing
| (2) |
In other words, CART seeks the split-point ŝN that minimizes the weighted sample variance. We refer to (2) as the weighted variance splitting rule.
To theoretically study ŝN, we replace Δ̂(s, t) with its analog based on population parameters:
where Δ(t) is the conditional population variance
and Δ(tL) and Δ(tR) are the daughter conditional variances
and p(tL) and p(tR) are the conditional probabilities
One can think of Δ(s, t) as the tree splitting rule under an infinite sample setting. We optimize the infinite sample splitting criterion in lieu of the data optimized one (2). Shortly we describe conditions showing that this solution corresponds to the limit of ŝN. The population analog to (2) is
| (3) |
Interestingly, there is a solution to (3) for the one-dimensional case (p = 1). We state this formally in the following result.
Theorem 1
Let ℙt denote the conditional distribution for X given that X ∈ t. Let ℙtL(·) and ℙtR(·) denote the conditional distribution of X given that X ∈ tL and X ∈ tR, respectively. Let t = [a, b]. The minimizer of (3) is the value for s maximizing
| (4) |
If f(s) is continuous over t and ℙt has a continuous and positive density over t with respect to Lebesgue measure, then the maximizer of (4) satisfies
| (5) |
This solution is not always unique and is permissible only if a ≤ s ≤ b.
In order to justify our infinite sample approach, we now state sufficient conditions for ŝN to converge to the population split-point. However, because the population split-point may not be unique or even permissible according to Theorem 1, we need to impose conditions to ensure a well defined solution. We shall assume that Ψt has a global maximum. This assumption is not unreasonable, and even if Ψt does not meet this requirement over t, a global maximum is expected to hold over a restricted subregion t′ ⊂ t. That is, when the tree becomes deeper and the range of values available for splitting a node become smaller, we expect Ψt′ to naturally satisfy the requirement of a global maximum. We discuss this issue further in Section 2.2.
Notice in the following result we have removed the requirement that f is continuous and replaced it with the lighter condition of square-integrability. Additionally, we only require that ℙt satisfies a positivity condition over its support.
Theorem 2
Assume that f ∈ ℒ2(ℙt) and 0 < ℙt{X ≤ s} < 1 for a < s < b where t = [a, b]. If Ψt(s) has a unique global maximum at an interior point of t, then the following limit holds as N → ∞
Note that s∞ is unique.
2.2 Theoretical split-points for polynomials
In this section, we look at Theorems 1 and 2 in detail by focusing on the class of polynomial functions. Implications of these findings to other types of functions are explored in Section 2.3. We begin by noting that an explicit solution to (5) exists when f is polynomial if X is assumed to be uniform.
Theorem 3
Suppose that . If ℙt is the uniform distribution on t = [a, b], then the value for s that minimizes (3) is a solution to
| (6) |
where Uj = cj/(j + 1) + acj+1/(j + 2) + ⋯ + aq−j cq/(q + 1) and Vj = cj/(j + 1) + bcj+1/(j + 2) + ⋯ + bq−j cq/(q + 1). To determine which value is the true maximizer, discard all solutions not in t (including imaginary values) and choose the value which maximizes
| (7) |
Example 1
As a first illustration, suppose that f(x) = c0 + c1x for x ∈ [a, b]. Then, U0 = c0 + ac1/2, V0 = c0 + bc1/2 and U1 = V1 = c1/2. Hence (6) equals
If c1 ≠ 0, then s = (a + b)/2; which is a permissible solution. Therefore for simple slope-intercept functions, node-splits are always at the midpoint.
Example 2
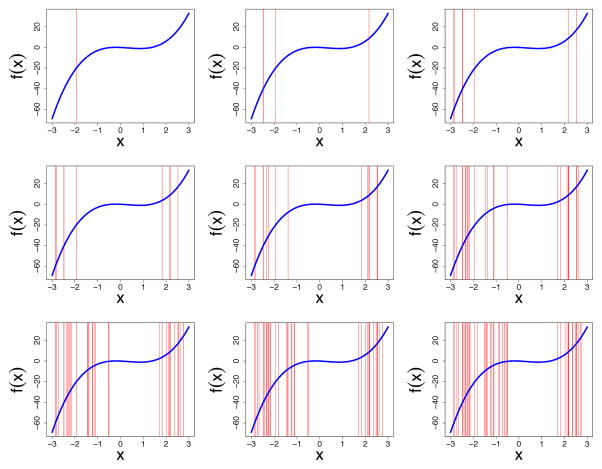
Now consider a more complicated polynomial, f(x) = 2x3 − 2x2 − x where x ∈ [−3, 3]. We numerically solve (6) and (7). The solutions are displayed recursively in Figure 2. The first panel is the optimal split over the root node [−3, 3]. There is one distinct solution s = −1.924. The second panel is the optimal split over the daughters arising from the first panel. The third panel are the optimal splits arising from the second panel, and so forth.
Figure 2.
Theoretical split-points for X under weighted variance splitting (displayed using vertical red lines) for f(x) = 2x3 − 2x2 − x (in blue) assuming a uniform [−3, 3] distribution for X.
The derivative of f is f′(x) = 6x2 − 4x − 1. Inspection of the derivative shows that f is increasing most rapidly for −3 ≤ x ≤ −2, followed by 2 ≤ x ≤ 3, and then −2 < x < 2. The order of splits in Figure 2 follows this pattern, showing that node splitting tracks the curvature of f, with splits occurring first in regions where f is steepest, and last in places where f is flattest.
Example 2 (continued)
Our examples have assumed a one-dimensional (p = 1) scenario. To test how well our results extrapolate to higher dimensions we modified Example 2 as follows. We simulated n = 1000 values from
| (8) |
using f as in Example 2, where (εi)1≤i≤n were i.i.d. N(0, σ2) variables with σ = 2 and (Xi)1≤i≤n were sampled independently from a uniform [−3, 3] distribution. The additional variables (Ui,k)1≤k≤D were also sampled independently from a uniform [−3, 3] distribution (we set d = 10 and D = 13). The first 1 ≤ k ≤ d of the Ui,k are signal variables with signal C1 = 3, whereas we set C2 = 0 so that Ui,k are noise variables for d + 1 ≤ k ≤ D. The data was fit using a regression tree under weighted variance splitting. The data-optimized split-points ŝN for splits on X are displayed in Figure 3 and closely track the theoretical splits of Figure 2. Thus, our results extrapolate to higher dimensions and also illustrate closeness of ŝN to the population value s∞.
Figure 3.
Data optimized split-points ŝN for X (in red) using weighted variance splitting applied to simulated data from the multivariate regression model (8). Blue curves are f(x) = 2x3 − 2x2 − x of Figure 2.
The near-exactness of the split-points of Figures 2 and 3 is a direct consequence of Theorem 2. To see why, note that with some rearrangement, (7) becomes
where Aj, Bj are constants that depend on a and b. Therefore Ψt is a polynomial. Hence it will achieve a global maximum over t or over a sufficiently small subregion t′.
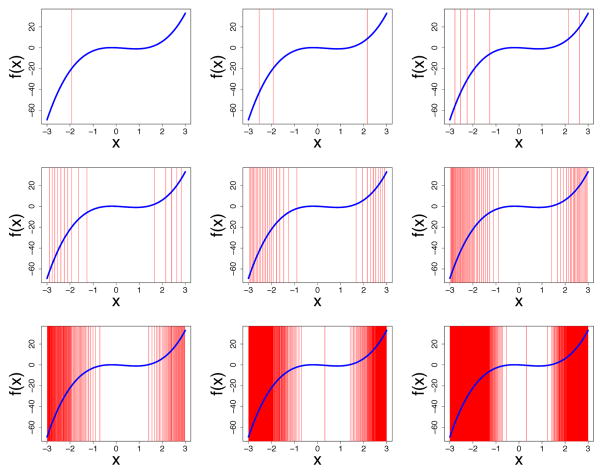
To further amplify this point, Figure 4 illustrates how Ψt′(s) depends on t′ for f(x) of Example 2. The first subpanel displays Ψt(s) over the entire range t = [−3, 3]. Clearly it achieves a global maximum. Furthermore, when [−3, 3] is broken up into contiguous subregions t′, Ψt′(s) becomes nearly concave (last three panels) and its maximum becomes more pronounced. Theorem 2 applies to each of these subregions, guaranteeing ŝN converges to s∞ over them.
Figure 4.
The first two panels are Ψt(s) and its derivative for f(s) = 2s3−2s2− s where t = [−3, 3]. Remaining panels are Ψt′(s) for t′ = [−3,−1.9], t′ = [−1.9, 1.5], t′ = [1.5, 3]. Blue vertical lines in first subpanel identify stationary points of Ψt(s).
2.3 Split-points for more general functions
The contiguous regions in Figure 4 (panels 3,4 and 5) were chosen to match the stationary points of Ψt (see panel 2). Stationary points identify points of inflection and maxima of Ψt and thus it is not surprising that Ψt′ is near-concave when restricted to such t′ subregions. The points of stationarity, and the corresponding contiguous regions, coincide with the curvature of f. This is why in Figures 2 and 3, optimal splits occur first in regions where f is steepest, and last in places where f is flattest.
We now argue in general, regardless of whether f is a polynomial, that the maximum of Ψt depends heavily on the curvature of f. To demonstrate this, it will be helpful if we modify our distributional assumption for X. Let us assume that X is uniform discrete with support 𝒳 = {αk}1≤k≤K. This is reasonable because it corresponds to the data optimized split-point setting. The conditional distribution of X over t = [a, b] is
It follows (this expression holds for all f):
| (9) |
Maximizing (9) results in a split-point s∞ such that the squared sum of f is large either to the left of s∞ or right of s∞ (or both). For example, if there is a contiguous region where f is substantially high, then Ψt will be maximized at the boundary of this region.
Example 3
As a simple illustration, consider the step function f(x) = 1{x>1/2} where x ∈ [0, 1]. Then,
When s ≤ 1/2, the maximum of Ψt is achieved at the largest value of αk less than or equal to 1/2. In fact, Ψt is increasing in this range. Let α− = max{αk : αk ≤ 1/2} denote this value. Likewise, let α+ = min{αk : αk > 1/2} denote the smallest αk larger than 1/2 (we assume there exists at least one αk > 1/2 and at least one αk ≤ 1/2). We have
The following bound holds when s ≥ α̂+ > 1/2:
Therefore the optimal split point is s∞ = α−: this is the value in the support of X closest to the point where f has the greatest increase; namely s = 1/2. Importantly, observe that s∞ coincides with a change in the sign of the derivative of Ψt. This is because Ψt increases over s ≤ 1/2, reaching a maximum at α−, and then decreases at α+. Therefore s ∈ [α−, α+) is a stationary point of Ψt.
Example 4
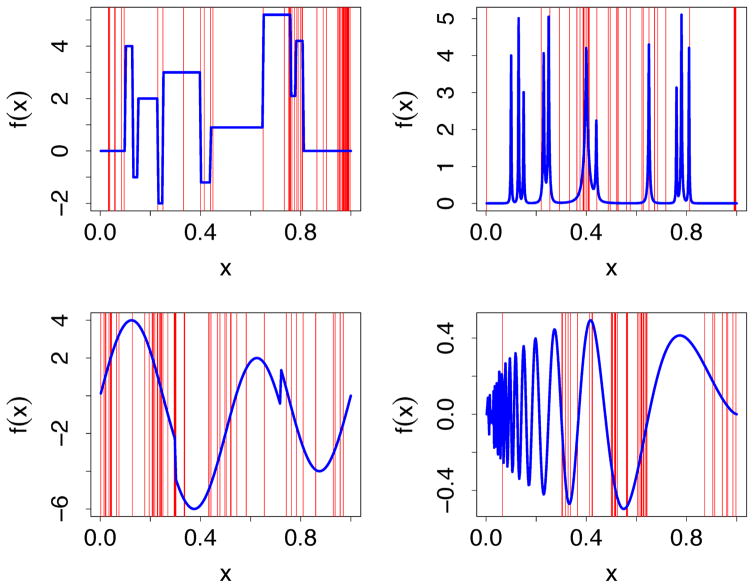
As further illustration that Ψt depends on the curvature of f, Figure 5 displays the optimized split-points ŝN for the Blocks, Bumps, HeaviSine and Doppler simulations described in Donoho and Johnstone (1994). We set n = 400 in each example, but otherwise followed the specifications of Donoho and Johnstone (1994), including the use of a fixed design xi = i/n for X. Figure 6 displays the derivative of Ψt for t = [0, 1], where Ψt was calculated as in (9) with 𝒳 = {xi}1≤i≤n. Observe how splits in Figure 5 generally occur within the contiguous intervals defined by the stationary points of Ψt. Visual inspection of Ψt′ for subregions t′ confirmed Ψt′ achieved a global maximum in almost all examples (for Doppler, Ψt′ was near-concave). These results, when combined with Theorem 2, provide strong evidence that ŝN closely approximates s∞.
Figure 5.
Data optimized split-points ŝN for X (in red) using weighted variance splitting for Blocks, Bumps, HeaviSine and Doppler simulations (Donoho and Johnstone, 1994). True functions are displayed in blue.
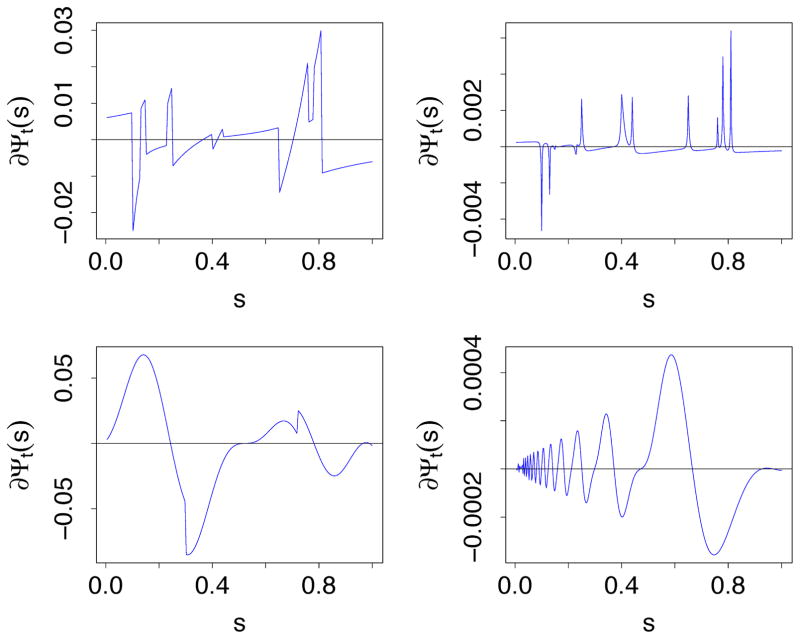
Figure 6.
Derivative of Ψt(s) for Blocks, Bumps, HeaviSine and Doppler functions of Figure 5, for Ψt(s) calculated as in (9).
We end this section by noting evidence of ECP splitting occurring in Figure 5. For example, for Blocks and Bumps, splits are observed near the edges 0 and 1 even though Ψt has no singularities there. This occurs, because once the tree finds the discernible boundaries of the spiky points in Bumps and jumps in the step functions of Blocks (by discernible we mean signal is larger than noise), it has exhausted all informative splits, and so it begins to split near the edges. This is an example of ECP splitting, a topic we discuss next.
2.4 Weighted variance splitting has the ECP property
Example 1 showed that weighted variance splits at the midpoint for simple linear functions f(x) = c0 + c1x. This midpoint splitting behavior for a strong variable is in contrast to what happens for noisy variables. Consider when f is a constant, f(x) = c0. This is the limit as c1 → 0 and corresponds to X being a noisy variable. One might think weighted variance splitting will continue to favor midpoint splits, since this would be the case for arbitrarily small c1, but it will be shown that edgesplits are favored in this setting. As discussed earlier, this behavior is referred to as the ECP property.
Definition 2
A splitting rule has the ECP property if it tends to split near the edge for a noisy variable. In particular, let ŝN be the optimized split-point for the variable X with candidate split-points x1 < x2 < · · · < xN. The ECP property implies that ŝN will tend to split towards the edge values x1 and xN if X is noisy.
To establish the ECP property for weighted variance splitting, first note that Theorem 1 will not help in this instance. The solution (5) is
which holds for all s. The solution is indeterminate because Ψt(s) has a constant derivative. Even a direct calculation using (9) will not help. From (9),
The solution is again indeterminate because Ψt(s) is constant and therefore has no unique maximum.
To establish the ECP property we will use a large sample result due to Breiman et al. (Chapter 11.8; 1984). First, observe that (2) can be written as
Therefore minimizing D̂(s, t) is equivalent to maximizing
| (10) |
Consider the following result (see Theorem 10 for a generalization of this result).
Theorem 4
(Theorem 11.1; Breiman et al., 1984). Let (Zi)1≤i≤N be i.i.d. with finite variance σ2 > 0. Consider the weighted splitting rule:
| (11) |
Then for any 0 < δ < 1/2 and any 0 < τ < ∞:
| (12) |
and
| (13) |
Theorem 4 shows (11) will favor edge splits almost surely. To see how this applies to (10), let us assume X is noisy. By Definition 1, this implies that the distribution of Y given X does not depend on X, and therefore Yi ∈ tL has the same distribution as Yi ∈ tR. Consequently, Yi ∈ tL and Yi ∈ tR are i.i.d. and because order does not matter we can set Z1 = Yi1, …, ZN = YiN where i1, …, iN are the indices of Yi ∈ t ordered by Xi ∈ t. From this, assuming Var(Yi) < ∞, we can immediately conclude (the result applies in general for p ≥ 1):
Theorem 5
Weighted variance splitting possesses the ECP property.
2.5 Unweighted variance splitting
Weighted variance splitting determines the best split by minimizing the weighted sample variance using weights proportional to the daughter sample sizes. We introduce a different type of splitting rule that avoids the use of weights. We refer to this new rule as unweighted variance splitting. The unweighted variance splitting rule is defined as
| (14) |
The best split is found by minimizing D̂U(s, t) with respect to s. Notice that (14) can be rewritten as
The following result shows that rules like this, which we refer to as unweighted splitting rules, possess the ECP property.
Theorem 6
Let (Zi)1≤i≤N be i.i.d. such that . Consider the unweighted splitting rule:
| (15) |
Then for any 0 < δ < 1/2:
| (16) |
and
| (17) |
2.6 Heavy weighted variance splitting
We will see that unweighted variance splitting has a stronger ECP property than weighted variance splitting. Going in the opposite direction is heavy weighted variance splitting, which weights the node variance using a more aggressive weight. The heavy weighted variance splitting rule is
| (18) |
The best split is found by minimizing D̂H(s, t). Observe that (18) weights the variance by using the squared daughter node size, which is a power larger than that used by weighted variance splitting.
Unlike weighted and unweighted variance splitting, heavy variance splitting does not possess the ECP property. To show this, rewrite (18) as
This is an example of a heavy weighted splitting rule. The following result shows that such rules favor center splits for noisy variables. Therefore they are the greediest in the presence of noise.
Theorem 7
Let (Zi)1≤i≤N be i.i.d. such that . Consider the heavy-weighted splitting rule:
| (19) |
Then for any 0 < δ < 1/2:
| (20) |
and
| (21) |
2.7 Comparison of split-rules in the one-dimensional case
The previous results show that the ECP property only holds for weighted and unweighted splitting rules, but not heavy weighted splitting rules. For convenience, we summarize the three splitting rules below:
Definition 3
Splitting rules of the form (11) are called weighted splitting rules. Those like (15) are called unweighted splitting rules, while those of the form (19) are called heavy weighted splitting rules.
Example 5
To investigate the differences between our three splitting rules we used the following one-dimensional (p = 1) simulation. We simulated n = 100 observations from
where Xi was drawn independently from a uniform distribution on [−3, 3] and εi was drawn independently from a standard normal. We considered three scenarios: (a) noisy (c0 = 1, c1 = 0); (b) moderate signal (c0 = 1, c1 = 0.5); and (c) strong signal (c0 = 1, c1 = 2).
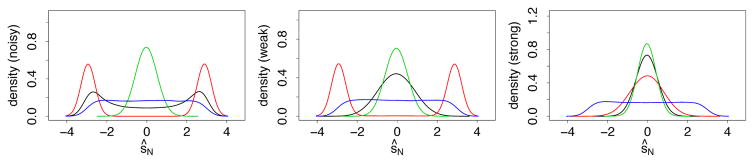
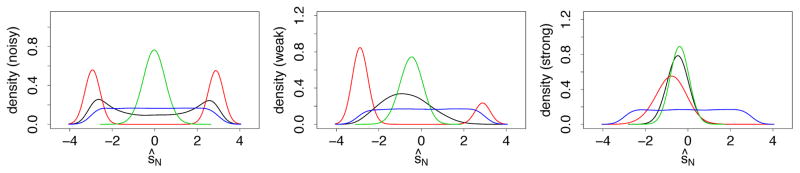
The simulation was repeated 10,000 times independently. The optimized splitpoint ŝN under weighted, unweighted and heavy weighted variance splitting was recorded in each instance. We also recorded ŝN under pure random splitting where the splitpoint was selected entirely at random. Figure 7 displays the density estimate for ŝN for each of the four splitting rules. In the noisy variable setting, only weighted and unweighted splitting exhibit ECP behavior. When the signal increases moderately, weighted splitting tends to split in the middle, which is optimal, whereas unweighted splitting continues to exhibit ECP behavior. Only when there is strong signal, does unweighted splitting finally adapt and split near the middle. In all three scenarios, heavy weighted splitting splits towards the middle, while random splitting is uniform in all instances.
Figure 7.
Density for ŝN under weighted variance (black), unweighted variance (red), heavy weighted variance (green) and random splitting (blue) where f(x) = c0+c1x for c0 = 1, c1 = 0 (left:noisy), c0 = 1, c1 = 0.5 (middle: weak signal) and c0 = 1, c1 = 2 (right: strong signal).
The example confirms our earlier hypothesis: weighted splitting is the most adaptive. In noisy scenarios it exhibits ECP tendencies but with even moderate signal it shuts off ECP splitting enabling it to recover signal.
Example 4 (continued)
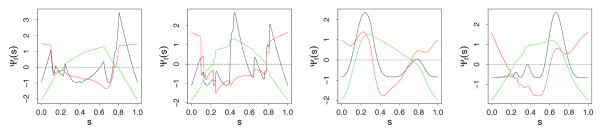
We return to Example 4 and investigate the shape of Ψt under the three splitting rules. As before, we assume X is discrete with support 𝒳 = {1/n, 2/n, …, 1}. For each rule, let Ψt denote the population criterion function we seek to maximize. Discarding unnecessary factors, it follows that Ψt can be written as follows (this holds for any f):
Ψt functions for Blocks, Bumps, HeaviSine and Doppler functions of Example 4 are shown in Figure 8. For weighted splitting, Ψt consistently tracks the curvature of the true f (see Figure 5). For unweighted splitting, Ψt is maximized near the edges, while for heavy weighted splitting, the maximum tends towards the center.
Figure 8.
Ψt(s) for Blocks, Bumps, HeaviSine and Doppler functions of Example 4 for weighted (black), unweighted (red) and heavy weighted (green) splitting.
2.8 The ECP statistic: multivariable illustration
The previous analyses looked at p = 1 scenarios. Here we consider a more complex p > 1 simulation as in (8). To facilitate this analysis, it will be helpful to define an ECP statistic to quantify the closeness of a split to an edge. Let ŝN be the optimized split for the variable X with values x1 < x2 < · · · < xN in a node t. Then, ŝN = xj for some 1 ≤ j ≤ N – 1. Let j(ŝN) denote this j. The ECP statistic is defined as
The ECP statistic is motivated by the following observations. The closest that ŝN can be to the right most split is when j(ŝN) = N – 1, and the closest that ŝN can be to the left most split is when j(ŝN) = 1. The second term on the right chooses the smallest of the two distance values and divides by the total number of available splits, N – 1. This ratio is bounded by 1/2. Subtracting it from 1/2 yields a statistic between 0 and 1/2 that is largest when the split is nearest an edge and smallest when the split is away from an edge.
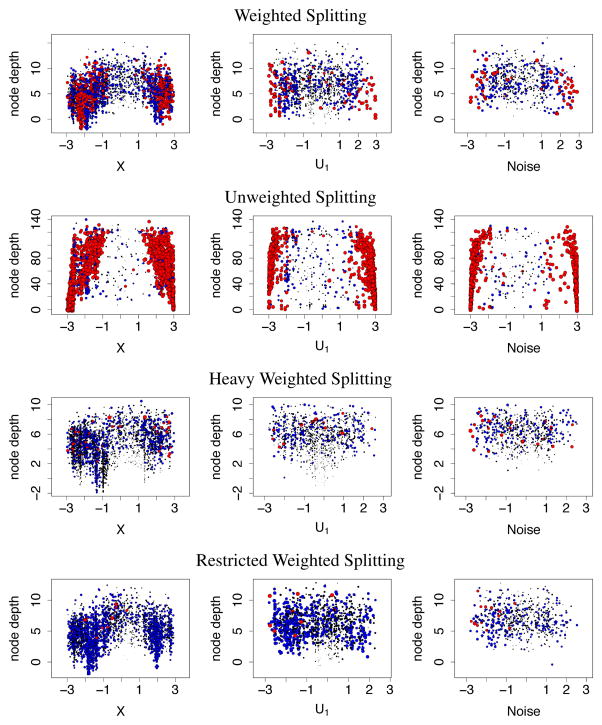
n = 1000 values were sampled from (8) using 25 noise variables (thus increasing the previous D = 13 to D = 35). Figure 9 displays ecp(ŝN) values as a function of node depth for X (non-linear variable with strong signal), U1 (linear variable with moderate signal), and Ud+1 (a noise variable) from 100 trees. Large points in red indicate high ECP values, smaller points in blue are moderate ECP values, and small black points are small ECP values.
Figure 9.
ECP statistic, ecp(ŝN), from simulation (8). Circles are proportional to ecp(ŝN). Black, blue and red indicate low, medium and high ecp(ŝN) values.
For weighted splitting (top panel), ECP values are high forX near −1 and 1.5. This is because the observed values of Y are relatively constant in the range [−1, 1.5] which causes splits to occur relatively infrequently in this region, similar to Figure 3, and endcut splits to occur at its edges. Almost all splits occur in [−3, −1) and (1.5, 3] where Y is non-linear in X, and many of these occur at relatively small depths, reflecting a strong X signal in these regions. For U1, ECP behavior is generally uniform, although there is evidence of ECP splitting at the edges. The uniform behavior is expected, because U1 contributes a linear term to Y, thus favoring splits at the midpoint, while edge splits occur because of the moderate signal: after a sufficient number of splits, U1’s signal is exhausted and the tree begins to split at its edge. For the noisy variable, strong ECP behavior occurs near the edges −3 and 3.
Unweighted splitting (second row) exhibits aggressive ECP behavior for X across much of its range (excluding [−1, 1.5], where again splits of any kind are infrequent). The predominate ECP behavior indicates that unweighted splitting has difficulty in discerning signal. Note the large node depths due to excessive end-cut splitting. For U1, splits are more uniform but there is aggressive ECP behavior at the edges. Aggressive ECP behavior is also seen at the edges for the noisy variable. Heavy weighted splitting (third row) registers few large ECP values and ECP splitting is uniform for the noisy variable. Node depths are smaller compared to the other two rules.
The bottom panel displays results for restricted weighted splitting. Here weighted splitting was applied, but candidate split values x1 < · · · < xN were restricted to xL < · · · < xU for L = [Nδ] and U = [N(1 – d)] where 0 < δ < 1/2 and [z] rounds z to the nearest positive integer. This restricts the range of split values so that splits cannot occur near (or at) edges x1 or xN and thus by design discourages end-cut splits. A value of δ = .20 was used (experimenting with other δ values did not change our results in any substantial way). Considering the bottom panel, we find restricted splitting suppresses ECP splits, but otherwise its split-values and their depth closely parallel those for weighted splitting (top panel).
To look more closely at the issue of split-depth, Table 1 displays the average depth at which a variable splits for the first time. This statistic has been called minimal depth by Ishwaran et al. (2010, 2011) and is useful for assessing a variable’s importance. Minimal depth for unweighted splitting is excessively large so we focus on the other rules. Focusing on weighted, restricted weighted, and heavy weighted splitting, we find minimal depth identical for X, while minimal depth for linear variables are roughly the same, although heavy weighted splitting’s value is smallest—which is consistent with the rules tendency to split towards the center, which favors linearity. Over noise variables, minimal depth is largest for weighted variance splitting. It’s ECP property produces deeper trees which pushes splits for noise variables down the tree. It is notable how much larger this minimal depth is compared with the other two rules—and in particular, restricted weighting. Therefore, combining the results of Table 1 with Figure 9, we can conclude that restricted weighted splitting is closest to weighted splitting, but differs by its inability to produce ECP splits. Because of this useful feature, we will use restricted splitting in subsequent analyses to assess the benefit of the ECP property.
Table 1.
Depth of first split on X, linear variables , and noise variables from simulation of Figure 9. Average values for and are displayed.
| X nonlinear | linear | noise | |
|---|---|---|---|
| weighted | 1.9 | 4.1 | 7.1 |
| unweighted | 5.9 | 26.6 | 34.1 |
| heavy weighted | 1.9 | 3.8 | 6.2 |
| restricted weighted | 1.9 | 3.9 | 6.4 |
2.9 Regression benchmark results
We used a large benchmark analysis to further assess the different splitting rules. In total, we used 36 data sets of differing size n and dimension p (Table 2). This included real data (in capitals) and synthetic data (in lower case). Many of the synthetic data were obtained from the mlbench R-package (Leisch and Dimitriadou, 2009) (e.g., data sets listed in Table 2 starting with “friedman” are the class of Friedman simulations included in the package). The entry “simulation.8” is simulation (8) just considered. A RF regression (RF-R) analysis was applied to each data set using parameters (ntree, mtry, nodesize) = (1000, [p/3]+, 5) where [z]+ rounds z to the first largest integer. Weighted variance, unweighted variance, heavy weighted variance and pure random splitting rules were used for each data set. Additionally, we used the restricted weighted splitting rule described in the previous section (δ = .20). Meansquared- error (MSE) was estimated using 10-fold cross-validation. In order to facilitate comparison of MSE across data, we standardized MSE by dividing by the sample variance of Y. All computations were implemented using the randomForestSRC R-package (Ishwaran and Kogalur, 2014).
Table 2.
MSE performance of RF-R under different splitting rules. MSE was estimated using 10-fold validation and has been standardized by the sample variance of Y and multiplied by 100.
| n | p | WT | WT* | UNWT | HVWT | RND | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | 111 | 5 | 26.66 | 27.54 | 25.05 | 29.90 | 41.83 |
| Automobile | 193 | 24 | 7.60 | 8.28 | 7.43 | 8.02 | 24.23 |
| Bodyfat | 252 | 13 | 33.09 | 33.62 | 33.65 | 34.51 | 46.12 |
| BostonHousing | 506 | 13 | 14.71 | 15.62 | 16.37 | 15.06 | 31.26 |
| CMB | 899 | 4 | 106.79 | 103.11 | 99.39 | 100.60 | 89.54 |
| Crime | 47 | 15 | 58.92 | 57.31 | 58.30 | 58.39 | 74.69 |
| Diabetes | 442 | 10 | 53.74 | 54.14 | 58.80 | 54.18 | 58.74 |
| DiabetesI | 442 | 64 | 53.36 | 54.51 | 67.03 | 53.89 | 77.18 |
| Fitness | 31 | 6 | 65.59 | 64.95 | 65.20 | 67.01 | 82.55 |
| Highway | 39 | 11 | 39.42 | 42.37 | 37.82 | 43.51 | 67.35 |
| Iowa | 33 | 9 | 60.44 | 64.15 | 58.20 | 64.50 | 81.22 |
| Ozone | 203 | 12 | 27.61 | 28.15 | 24.81 | 29.46 | 32.31 |
| Pollute | 60 | 15 | 46.52 | 46.75 | 44.82 | 49.32 | 66.66 |
| Prostate | 97 | 8 | 44.98 | 44.51 | 45.11 | 46.60 | 48.93 |
| Servo | 167 | 19 | 23.42 | 23.61 | 17.34 | 30.71 | 46.18 |
| Servo asfactor | 167 | 4 | 36.22 | 36.11 | 33.18 | 34.58 | 54.04 |
| Tecator | 215 | 22 | 17.18 | 17.68 | 19.37 | 18.64 | 50.63 |
| Tecator2 | 215 | 100 | 34.39 | 35.22 | 37.64 | 36.14 | 55.61 |
| Windmill | 1114 | 12 | 31.88 | 32.24 | 35.22 | 32.89 | 36.68 |
| simulation.8 | 1000 | 36 | 22.74 | 23.94 | 43.77 | 27.88 | 79.64 |
| expon | 250 | 2 | 47.90 | 47.80 | 45.49 | 54.29 | 60.89 |
| expon.noise | 250 | 17 | 60.27 | 63.18 | 66.60 | 88.86 | 95.60 |
| friedman1 | 250 | 10 | 26.46 | 28.10 | 37.41 | 33.50 | 56.57 |
| friedman1.bigp | 250 | 250 | 44.10 | 46.37 | 78.39 | 52.86 | 98.56 |
| friedman2 | 250 | 4 | 28.72 | 31.42 | 30.22 | 32.24 | 43.52 |
| friedman2.bigp | 250 | 254 | 33.23 | 35.70 | 50.51 | 37.72 | 97.85 |
| friedman3 | 250 | 4 | 34.78 | 38.33 | 35.93 | 39.53 | 53.68 |
| friedman3.bigp | 250 | 254 | 40.73 | 49.50 | 61.14 | 54.24 | 99.06 |
| noise | 250 | 500 | 103.51 | 103.41 | 102.30 | 103.15 | 100.48 |
| sine | 250 | 2 | 41.01 | 39.85 | 53.56 | 38.27 | 58.80 |
| sine.noise | 250 | 5 | 68.06 | 70.13 | 91.04 | 64.56 | 87.27 |
| AML | 116 | 629 | 27.19 | 27.27 | 27.31 | 28.05 | 42.45 |
| DLBCL | 240 | 740 | 30.94 | 32.18 | 32.61 | 34.86 | 55.12 |
| Lung | 86 | 713 | 30.16 | 31.69 | 34.95 | 33.01 | 67.16 |
| MCL | 92 | 881 | 13.46 | 14.01 | 13.16 | 14.47 | 33.78 |
| VandeVijver78 | 78 | 475 | 15.48 | 15.57 | 15.50 | 16.18 | 30.81 |
Splitting rule abbreviations: weighted (WT), restricted weighted (WT*), unweighted (UNWT), heavy weighted (HVWT), pure random splitting (RND).
To systematically compare performance we used univariate and multivariate non-parametric statistical tests described in Demsar (2006). To compare two splitting rules we used the Wilcoxon signed rank test applied to the difference of their standardized MSE values. To test for an overall difference among the various procedures we used the Iman and Davenport modified Friedman test (Demsar, 2006). The exact p-value for the Wilcoxon signed rank test are recorded along the upper diagonals of Table 3. The lower diagonal values record the corresponding test statistic where small values indicate a difference. The diagonal values of the table record the average rank of each procedure and were used for the Friedman test.
Table 3.
Performance of RF-R under different splitting rules. Upper diagonal values are Wilcoxon signed rank p-values comparing two procedures; lower diagonal values are the corresponding test statistic. Diagonal values record overall rank.
| WT | WT* | UNWT | HVWT | RND | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 1.83 | 0.0004 | 0.0459 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 |
| WT* | 117 | 2.47 | 0.2030 | 0.0004 | 0.0000 |
| UNWT | 206 | 251 | 2.69 | 0.8828 | 0.0000 |
| HVWT | 93 | 118 | 323 | 3.28 | 0.0000 |
| RND | 17 | 10 | 16 | 10 | 4.72 |
The modified Friedman test of equality of ranks yielded a p-value < 0.00001, thus providing strong evidence of difference between the methods. Overall, weighted splitting had the best overall rank, followed by restricted weighted splitting, unweighted splitting, heavy weighted splitting, and finally pure random splitting. To compare performance of weighted splitting to each of the other rules, based on the p-values in Table 3, we used the Hochberg step-down procedure (Demsar, 2006) which controls for multiple testing. Under a familywise error rate (FWER) of 0.05, the test rejected the null hypothesis that performance of weighted splitting was equal to one of the other methods. This demonstrates superiority of weighted splitting. Other points worth noting in Table 3 are that while unweighted splitting’s overall rank is better than heavy weighted splitting, the difference appears marginal and considering Table 2 we see there is no clear winner. In moderate-dimensional problems unweighted splitting is generally better, while heavy weighted splitting is sometimes better in high dimensions. The high-dimensional scenario is interesting and we discuss this in more detail below (Section 2.9.1). Finally, it is clearly evident from Table 3 that pure random splitting is substantially worse than all other rules. Considering Table 2, we find its performance deteriorates as p increases. One exception is “noise” which is a synthetic data set with all noisy variables: all methods perform similarly here. In general, its performance is on par with other rules only when n is large and p is small (e.g. CMB data).
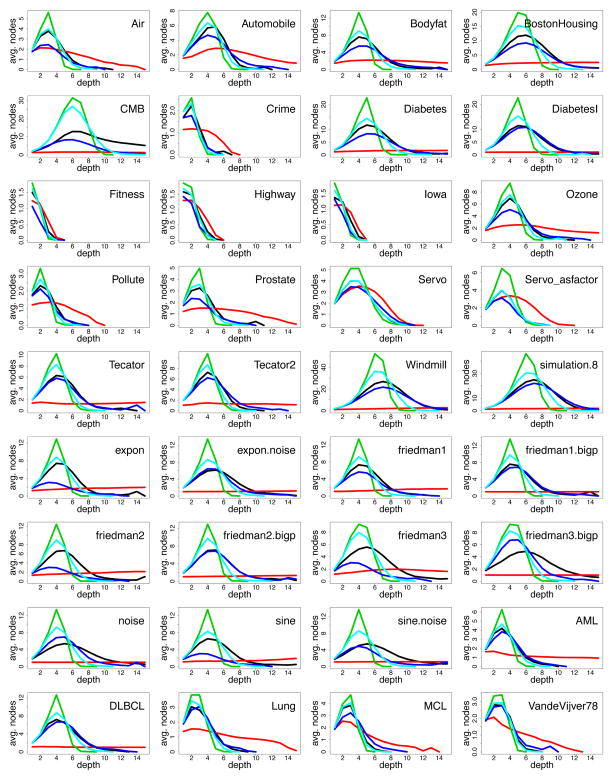
Figure 10 displays the average number of nodes by tree depth for each splitting rule. We observe the following patterns:
Figure 10.
Average number of nodes by tree depth for weighted variance (black), restricted weighted (magenta), unweighted variance (red), heavy weighted variance (green) and random (blue) splitting for regression benchmark data from Table 2.
Heavy weighted splitting (green) yields the most symmetric node distribution. Because it does not possess the ECP property, and splits near the middle, it grows shallower balanced trees.
Unweighted splitting (red) yields the most skewed node distribution. It has the strongest ECP property and has the greatest tendency to split near the edge. Edge splitting promotes unbalanced deep trees.
Random (blue), weighted (black), and restricted weighted (magenta) splitting have node distributions that fall between the symmetric distributions of heavy weighted splitting and the skewed distributions of unweighted splitting. Due to suppression of ECP splits, restricted weighted splitting is the least skewed of the three and is closest to heavy weighted splitting, whereas weighted splitting due to ECP splits is the most skewed of the three and closest to unweighted splitting.
2.9.1 Impact of high dimension on splitting
To investigate performance differences in high dimensions, we ran the following two additional simulations. In the first, we simulated n = 250 observations from the linear model
| (22) |
where (εi)1≤i≤n were i.i.d. N(0, 1) and (Xi)1≤i≤n, (Ui,k)1≤i≤n were i.i.d. uniform[0, 1]. We set C0 = 1, C1 = 2 and C2 = 0. The Ui,k variables introduce noise and a large value of d was chosen to induce high dimensionality (see below for details). Because of the linearity in X, a good splitting rule will favor splits at the midpoint for X. Thus model (22) will favor heavy weighted splitting and weighted splitting, assuming the latter is sensitive enough to discover the signal. However, the presence of a large number of noise variables presents an interesting challenge. If the ECP property is not beneficial, then heavy weighted splitting will outperform weighted splitting; otherwise weighted splitting will be better (again, assuming it is sensitive enough to find the signal). The same conclusion also applies to restricted weighted splitting. As we have argued, this rule suppresses ECP splits and yet retains the adaptivity of weighted splitting. Thus, if weighted splitting outperforms restricted weighted splitting in this scenario, we can attribute these gains to the ECP property. For our second simulation, we used the “friedman2.bigp” simulation of Table 2.
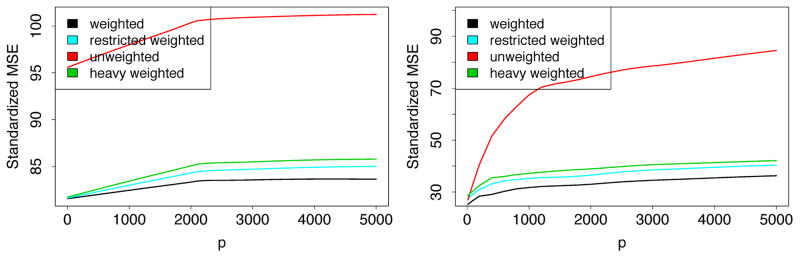
The same forest parameters were used as in Table 2. To investigate the effect of dimensionality, we varied the total number of variables in small increments. The left panel of Figure 11 presents the results for (22). Unweighted splitting has poor performance in this example, possible due to its overly strong ECP property. Restricted weighted splitting is slightly better than heavy weighted splitting, but weighted splitting has the best performance and its relative performance compared with heavy weighted and restricted weighted splitting increases with p. As we have discussed, we can attribute these gains as a direct consequence of ECP splitting. The right panel of Figure 11 presents the results for “friedman2.bigp”. Interestingly the results are similar, although MSE values are far smaller due to the strong non-linear signal.
Figure 11.
Standardized MSE (×100) for high dimensional linear simulation (22) (left panel) and non-linear simulation “friedman2.bigp” (right panel) as a function of p. Performance assessed using an independent test-set (n = 5000).
3 Classification forests
Now we consider the effect of splitting in multiclass problems. As before, the learning data is ℒ = (Xi, Yi)1≤i≤n where (Xi, Yi) are i.i.d. with common distribution ℙ. Write (X, Y) to denote a generic variable with distribution ℙ. Here the outcome is a class label Y ∈ {1, …, J} taking one of J ≥ 2 possible classes.
We study splitting under the Gini index, a widely used CART splitting rule for classification. Let ϕ̂j(t) denote the class frequency for class j in a node t. The Gini node impurity for t is defined as
As before, Let tL and tR denote the left and right daughter nodes of t corresponding to cases {Xi ≤ s} and {Xi > s}. The Gini node impurity for tL is
where ϕ̂j(tL) is the class frequency for class j in tL. In a similar way define Γ̂(tR). The decrease in the node impurity is
The quantity
is the Gini index. To achieve a good split, we seek the split-point maximizing the decrease in node impurity: equivalently we can minimize Ĝ(s, t) with respect to s. Notice that because the Gini index weights the node impurity by the node size, it can be viewed as the analog of the weighted variance splitting criterion (2).
To theoretically derive ŝN, we again consider an infinite sample paradigm. In place of Ĝ(s, t), we use the population Gini index
| (23) |
where Γ(tL) and Γ(tR) are the population node impurities for tL and tR defined as
where ϕj(tL) = ℙ{Y = j|X ≤ s, X ∈ t} and ϕj(tR) = ℙ{Y = j|X > s, X ∈ t}.
The following is the analog of Theorem 1 for the two-class problem.
Theorem 8
Let ϕ(s) = ℙ{Y = 1|X = s}. If ϕ(s) is continuous over t = [a, b] and ℙt has a continuous and positive density over t with respect to Lebesgue measure, then the value for s that minimizes (23) when J = 2 is a solution to
| (24) |
Theorem 8 can be used to determine the optimal Gini split in terms of the underlying target function, ϕ(x). Consider a simple intercept-slope model
| (25) |
Assume ℙt is uniform and that f(x) = c0 + c1x. Then, (24) reduces to
Unlike the regression case, the solution cannot be derived in closed form and does not equal the midpoint of the interval [a, b].
It is straightforward to extend Theorem 2 to the classification setting, thus justifying the use of an infinite sample approximation. The square-integrability condition will hold automatically due to boundedness of ϕ(s). Therefore only the positive support condition for ℙt and the existence of a unique maximizer for Ψt is required, where Ψt(s) is
Under these conditions it can be shown that ŝN converges to the unique population split-point, s∞, maximizing Ψt(s).
Remark 2
Breiman (1996) also investigated optimal split-points for classification splitting rules. However, these results are different than ours. He studied the question of what configuration of class frequencies yields the optimal split for a given splitting rule. This is different because it does not involve the classification rule and therefore does not address the question of what is the optimal split-point for a given ϕ(x). The optimal split-point studied in Breiman (1996) may not even be realizable.
3.1 The Gini index has the ECP property
We show that Gini splitting possesses the ECP property. Noting that
and that , we can rewrite the Gini index as
where Nj,L = Σi∈tL 1{Yi=j} and Nj,R = Σi∈tR 1{Yi=j}. Observe that minimizing Ĝ(s, t) is equivalent to maximizing
| (26) |
In the two-class problem, J = 2, it can be shown this is equivalent to maximizing
which is a member of the class of weighted splitting rules (11) required by Theorem 4 with Zi = 1{Yi=1}.
This shows Gini splitting has the ECP property when J = 2, but we now show that the ECP property applies in general for J ≥ 2. The optimization problem (26) can be written as
where Zi(j) = 1{Yi=j}. Under a noisy variable setting, Zi(j) will be identically distributed. Therefore we can assume (Zi(j))1≤i≤n are i.i.d. for each j. Because the order of Zi(j) does not matter, the optimization can be equivalently described in terms of , where
We compare the Gini index for an edge split to a non-edge split. Let
For a left-edge split
Apply Theorem 4 with τ = J to each of the J terms separately. Let An,j denote the first event in the curly brackets and let Bn,j denote the second event (i.e. Bn,j = {j* = j}). Then An,j occurs with probability tending to one, and because Σj ℙ(Bn,j) = 1, deduce that the entire expression has probability tending to 1. Applying a symmetrical argument for a right-edge split completes the proof.
Theorem 9
The Gini index possesses the ECP property.
3.2 Unweighted Gini index splitting
Analogous to unweighted variance splitting, we define an unweighted Gini index splitting rule as follows
| (27) |
Similar to unweighted variance splitting, the unweighted Gini index splitting rule possesses a strong ECP property.
For brevity we prove that (27) has the ECP property in two-class problems. Notice that we can rewrite (27) as follows
where Zi = 1{Yi=1} (note that ). This is a member of the class of unweighted splitting rules (15). Apply Theorem 6 to deduce that unweighted Gini splitting has the ECP property when J = 2.
3.3 Heavy weighted Gini index splitting
We also define a heavy weighted Gini index splitting rule as follows
Similar to heavy weighted splitting in regression, heavy weighted Gini splitting does not possess the ECP property. When J = 2, this follows directly from Theorem 7 by observing that
which is a member of the heavy weighted splitting rules (19) with .
3.4 Comparing Gini split-rules in the one-dimensional case
To investigate the differences between the Gini splitting rules we used the following one-dimensional two-class simulation. We simulated n = 100 observations for ϕ(x) specified as in (25) where f(x) = c0 + c1x and X was uniform [−3, 3]. We considered noisy, moderate signal, and strong signal scenarios, similar to our regression analysis of Figure 7. The experiment was repeated 10,000 times independently.
Figure 12 reveals a pattern similar to Figure 7. Once again, weighted splitting is the most adaptive. It exhibits ECP tendencies, but in the presence of even moderate signal it shuts off ECP splitting. Unweighted splitting is also adaptive but with a more aggressive ECP behavior.
Figure 12.
Density for ŝN under Gini (black), unweighted Gini (red), heavy weighted Gini (green) and random splitting (blue) for ϕ(x) specified as in (25) for J = 2 with f(x) = c0 + c1x for c0 = 1, c1 = 0 (left: noisy), c0 = 1, c1 = 0.5 (middle: weak signal) and c0 = 1, c1 = 2 (right: strong signal).
3.5 Multiclass benchmark results
To further assess differences in the splitting rules we ran a large benchmark analysis comprised of 36 data sets of varying dimension and number of classes (Table 4). As in our regression benchmark analysis of Table 2, real data sets are indicated with capitals and synthetic data in lower case. The latter were all obtained from the mlbench R-package (Leisch and Dimitriadou, 2009). A RF classification (RF-C) analysis was applied to each data set using the same forest parameters as Table 2. Pure random splitting as well as weighted, unweighted and heavy weighted Gini splitting was employed. Restricted Gini splitting, defined as in the regression case, was also used (δ = .20).
Table 4.
Brier score performance (×100) of RF-C under different splitting rules. Performance was estimated using 10-fold validation. To interpret the Brier score, the benchmark value of 25 represents the performance of a random classifier.
| n | p | J | WT | WT* | UNWT | HVWT | RND | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothyroid | 2000 | 24 | 2 | 1.16 | 1.11 | 1.58 | 1.05 | 1.85 |
| SickEuthyroid | 2000 | 24 | 2 | 2.30 | 2.58 | 2.52 | 2.56 | 5.90 |
| SouthAHeart | 462 | 9 | 2 | 20.04 | 20.03 | 20.52 | 19.16 | 18.77 |
| Prostate | 158 | 20 | 2 | 15.78 | 16.97 | 15.33 | 16.45 | 16.69 |
| WisconsinBreast | 194 | 32 | 2 | 18.11 | 17.78 | 18.70 | 17.77 | 17.49 |
| Esophagus | 3127 | 28 | 2 | 18.52 | 18.35 | 18.80 | 18.52 | 18.21 |
| BreastCancer | 683 | 10 | 2 | 2.56 | 2.51 | 2.45 | 2.55 | 2.49 |
| DNA | 3186 | 180 | 3 | 3.09 | 3.03 | 3.09 | 4.28 | 13.76 |
| Glass | 214 | 9 | 6 | 5.88 | 6.00 | 6.96 | 6.17 | 7.66 |
| HouseVotes84 | 232 | 16 | 2 | 5.94 | 5.95 | 3.09 | 3.01 | 5.77 |
| Ionosphere | 351 | 34 | 2 | 5.61 | 7.17 | 5.04 | 6.90 | 11.37 |
| 2dnormals | 250 | 2 | 2 | 7.12 | 6.96 | 7.25 | 7.11 | 7.52 |
| cassini | 250 | 2 | 3 | 1.06 | 1.20 | 0.73 | 1.21 | 4.86 |
| circle | 250 | 2 | 2 | 5.92 | 6.97 | 6.35 | 7.69 | 11.30 |
| cuboids | 250 | 3 | 4 | 0.71 | 0.86 | 1.07 | 0.73 | 3.91 |
| ringnorm | 250 | 20 | 2 | 11.03 | 14.98 | 9.23 | 17.33 | 18.46 |
| shapes | 250 | 2 | 4 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 1.26 | 0.80 | 4.85 |
| smiley | 250 | 2 | 4 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 2.97 |
| spirals | 250 | 2 | 2 | 2.67 | 5.11 | 2.30 | 5.52 | 12.98 |
| twonorm | 250 | 20 | 2 | 8.62 | 8.67 | 6.53 | 8.71 | 10.50 |
| threenorm | 250 | 20 | 2 | 16.92 | 17.54 | 18.55 | 17.90 | 19.82 |
| waveform | 250 | 21 | 3 | 9.53 | 9.54 | 10.62 | 9.61 | 12.83 |
| xor | 250 | 2 | 2 | 4.85 | 4.26 | 10.90 | 2.99 | 12.01 |
| PimaIndians | 768 | 8 | 2 | 15.97 | 16.09 | 16.39 | 16.34 | 16.70 |
| Sonar | 208 | 60 | 2 | 13.32 | 13.01 | 18.29 | 12.87 | 18.51 |
| Soybean | 562 | 35 | 15 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.69 | 1.24 | 1.69 |
| Vehicle | 846 | 18 | 4 | 7.52 | 7.54 | 9.44 | 7.80 | 10.03 |
| Vowel | 990 | 10 | 11 | 2.58 | 2.71 | 4.96 | 2.91 | 4.61 |
| Zoo | 101 | 16 | 7 | 1.44 | 1.43 | 1.47 | 1.64 | 2.30 |
| aging | 29 | 8740 | 3 | 16.60 | 16.42 | 16.42 | 17.02 | 21.86 |
| brain | 42 | 5597 | 5 | 8.08 | 8.37 | 8.03 | 8.49 | 13.16 |
| colon | 62 | 2000 | 2 | 12.95 | 13.03 | 12.99 | 12.43 | 19.43 |
| leukemia | 72 | 3571 | 2 | 4.08 | 4.06 | 4.24 | 4.09 | 17.26 |
| lymphoma | 62 | 4026 | 3 | 2.75 | 2.84 | 2.67 | 2.82 | 8.90 |
| prostate | 102 | 6033 | 2 | 7.62 | 7.62 | 7.39 | 7.69 | 20.84 |
| srbct | 63 | 2308 | 4 | 3.23 | 3.35 | 2.88 | 4.35 | 14.33 |
Splitting rule abbreviations: weighted (WT), restricted weighted (WT*), unweighted (UNWT), heavy weighted (HVWT), pure random splitting (RND).
Performance was assessed using the Brier score (Brier, 1950) and estimated by 10-fold cross-validation. Let p̂i,j := p̂ (Yi = j|Xi, ℒ) denote the forest predicted probability for event j = 1, …, J for case (Xi, Yi) ∈ 𝒯, where 𝒯 denotes a test data set. The Brier score was defined as
The Brier score was used rather than misclassification error because it directly measures accuracy in estimating the true conditional probability ℙ{Y = j|X}. We are interested in the true conditional probability because a method that is consistent for estimating this value is immediately Bayes risk consistent but not vice-versa. See Gyorfi et al. (Theorem 1.1, 2002).
Tables 4 and 5 reveal patterns consistent with Tables 2 and 3. As in Table 2, random splitting is consistently poor with performance degrading with increasing p. The rank of splitting rules in Table 5 is consistent with Table 3, however statistical significance of pairwise comparisons are not as strong. The Hochberg step-down procedure comparing weighted splitting to each of the other methods did not reject the null hypothesis of equality between between weighted and unweighted splitting at a 0.05 FWER, however increasing the FWER to 16%, which matches the observed p-value for unweighted splitting, led to all hypotheses being rejected. The modified Friedman test of difference in ranks yielded a p-value < 0.00001, thus indicating a strong difference in performance of the methods. We can conclude that splitting rules generally exhibit the same performance as in the regression setting, but performance gains for weighted splitting are not as strong.
Table 5.
| WT | WT* | UNWT | HVWT | RND | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 2.22 | 0.0798 | 0.1568 | 0.0183 | 0.0000 |
| WT* | 221 | 2.58 | 0.6693 | 0.0134 | 0.0000 |
| UNWT | 242 | 305 | 2.81 | 0.9938 | 0.0000 |
| HVWT | 184 | 237 | 334 | 2.92 | 0.0000 |
| RND | 22 | 26 | 43 | 14 | 4.47 |
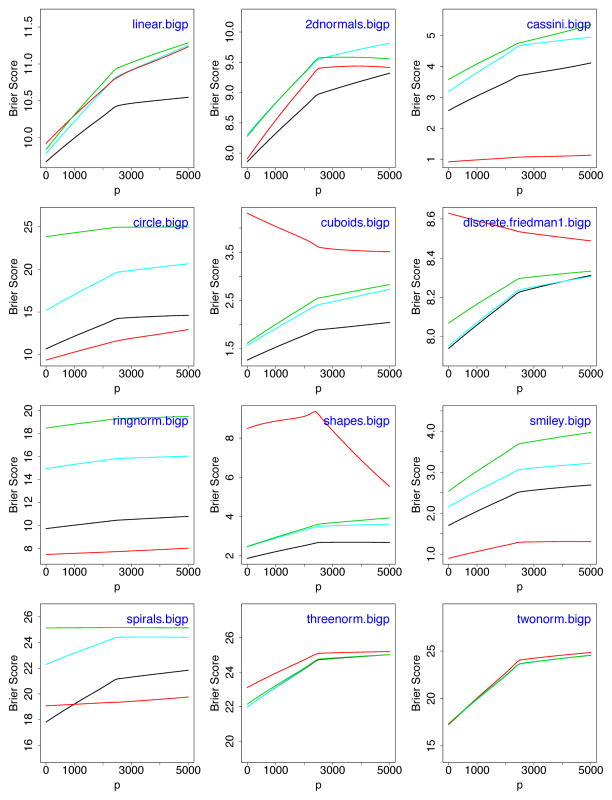
Regarding the issue of dimensionality, there appears to be no winner over the high-dimensional examples in Table 4: aging, brain, colon, leukemia, lymphoma, prostate and srbct. However, these are all microarray data sets and this could simply be an artifact of this type of data. To further investigate how p affects performance, we added noise variables to mlbench synthetic data sets (Figure 13). The dimension was increased systematically in each instance. We also included a linear model simulation similar to (22) with ϕ(x) specified as in (25) (see top left panel, “linear.bigp”). Figure 13 shows that when performance differences exist between rules, weighted splitting and unweighted splitting, which possess the ECP property, generally outperform restricted weighted and heavy weighted splitting. Furthermore, there is no example where these latter rules outperform weighted splitting.
Figure 13.
Brier score performance (×100) for synthetic high dimensional simulations as a function of p under weighted variance (black), restricted weighted (magenta), unweighted variance (red), and heavy weighted (green) Gini splitting. Performance assessed using an independent test-set (n = 5000).
4 Randomized adaptive splitting rules
Our results have shown that pure random splitting is rarely as effective as adaptive splitting. It does not possess the ECP property, nor does it adapt to signal. On the other hand, randomized rules are desirable because they are computationally efficient. Therefore as a means to improve computational efficiency, while maintaining adaptivity of a split-rule, we consider randomized adaptive splitting. In this approach, in place of deterministic splitting in which the splitting rule is calculated for the entire set of N available split-points for a variable, the splitting rule is confined to a set of split-points indexed by IN ⊆ {1, …, N}, where |IN| is typically much smaller than N. This reduces the search for the optimal split-point from a maximum of N split-points to the much smaller |IN|.
For brevity, we confine our analysis to the class of weighted splitting rules. Deterministic (non-random) splitting seeks the value 1 ≤ m ≤ N − 1 maximizing (11). In contrast, randomized adaptive splitting maximizes the split-rule by restricting m to IN. The optimal split-point is determined by maximizing the restricted splitting rule:
| (28) |
where RN = |IN| and (ZN,i)1≤i≤RN denotes the sequence of values {Zi : i ∈ IN}.
In principle, IN can be selected in any manner. The method we will study empirically selects nsplit candidate split-points at random, which corresponds to sampling RN-out-of-N values from {1, …, N} without replacement where RN = nsplit. This method falls under the general result described below, which considers the behavior of (28) under general sequences. We show (28) has the ECP property under any sequence (IN)N≥1 if the number of split-points RN increases to ∞. The result requires only a slightly stronger moment assumption than Theorem 4.
Theorem 10
Let (Zi)1≤i≤N be independent with a common mean and variance and assume supi 𝔼(|Zi|q) < ∞ for some q > 2. Let (IN)N≥1 be a sequence of index sets such that RN → ∞. Then for any 0 < δ < 1/2 and any 0 < τ < ∞:
| (29) |
and
| (30) |
Remark 3
As a special case, Theorem 10 yields Theorem 4 for the sequence IN = {1, …, N}. Note that while the moment condition is somewhat stronger, Theorem 10 does not require (Zi)1≤i≤N to be i.i.d. but only independent.
Remark 4
Theorem 10 shows that the ECP property holds if nsplit → ∞. Because any rate is possible, the condition is mild and gives justification for nsplit-randomization. However, notice that nsplit = 1, corresponding to the extremely randomized tree method of Geurts et al. (2006), does not satisfy the rate condition.
4.1 Empirical behavior of randomized adaptive splitting
To demonstrate the effectiveness of randomized adaptive splitting, we re-ran the RF-R benchmark analysis of Section 2. All experimental parameters were kept the same. Randomized weighted splitting was implemented using nsplit = 1, 5, 10. Performance values are displayed in Table 6 based on the Wilcoxon signed rank test and overall rank of a procedure.
Table 6.
Performance of weighted splitting rules from RF-R benchmark data sets of Table 2 expanded to include randomized weighted splitting for nsplit = 1, 5, 10 denoted by WT(1), WT(5), WT(10). Values recorded as in Table 3.
| WT | WT* | WT(1) | WT(5) | WT(10) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 2.08 | 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.0074 | 0.6028 |
| WT* | 117 | 3.44 | 0.0000 | 0.1974 | 0.0000 |
| WT(1) | 54 | 77 | 4.42 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| WT(5) | 165 | 416 | 637 | 2.97 | 0.0001 |
| WT(10) | 299 | 580 | 623 | 572 | 2.08 |
Table 6 shows that the rank of a procedure improves steadily with increasing nsplit. The modified Friedman test of equality of ranks rejects the null (p-value < 0.00001) while the Hochberg step-down procedure, which tests equality of weighted splitting to each of the other methods, cannot reject the null hypothesis of performance equality between weighted and randomized weighted splitting for nsplit = 10 at any reasonable FWER. This demonstrates the effectiveness of nsplit-randomization. Table 7 displays the results from applying nsplit-randomization to the classification analysis of Table 4. The results are similar to Table 6 (modified Friedman test p-value < 0.00001; step-down procedure did not reject equality between weighted and randomized weighted for nsplit = 10).
Table 7.
Performance of weighted splitting rules from RF-C benchmark data sets of Table 4. Values recorded as in Table 3.
| WT | WT* | WT(1) | WT(5) | WT(10) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 2.64 | 0.0798 | 0.0001 | 0.0914 | 0.9073 |
| WT* | 221 | 3.00 | 0.0046 | 0.7740 | 0.1045 |
| WT(1) | 97 | 156 | 3.94 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| WT(5) | 225 | 352 | 601 | 2.97 | 0.0000 |
| WT(10) | 325 | 437 | 600 | 548 | 2.44 |
Remark 5
For brevity we have presented results of nsplit-randomization only in the context of weighted splitting, but we have observed that the properties of all our splitting rules remain largely unaltered under randomization: randomized unweighted variance splitting maintains a more aggressive ECP behavior, while randomized heavy weighted splitting does not exhibit the ECP property at all.
5 Discussion
Of the various splitting rules considered, the class of weighted splitting rules, which possess the ECP property, performed the best in our empirical studies. The ECP property, which is the property of favoring edge-splits, is important because it conserves the sample size of a parent node under a bad split. Bad splits generally occur for noisy variables but they can also occur for strong variables (for example, the parent node may be in a region of the feature space where the signal is low). On the other hand, non-edge splits are important when strong signal is present. Good splitting rules therefore have the ECP behavior for noisy or weak variables, but split away from the edge when there is strong signal.
Weighted splitting has this optimality property. In noisy scenarios it exhibits ECP tendencies, but in the presence of signal, it can shut off ECP splitting. To understand how this adaptivity arises, we found that optimal splits under weighted splitting occur in the contiguous regions defined by the singularity points of the population optimization function Ψt—thus, weighted splitting tracks the underlying true target function. To illustrate this point, we looked carefully at Ψt for various functions, including polynomials and complex nonlinear functions. Empirically, we observed that unweighted splitting is also adaptive, but it exhibits an aggressive ECP behavior and requires a stronger signal to split away from an edge. However, in some instances this does lead to better performance. Thus, it is recommended to use weighted splitting in RF analyses, but an unweighted splitting analysis could also be run and the forest with the smallest test-set error retained as the final predictor. Restricted weighted splitting in which splits are restricted from occurring at the edge, and hence which suppress ECP behavior, was generally found inferior to weighted splitting and is not recommended. In general, rules which do not possess ECP behavior are not recommended.
Randomized adaptive splitting is an attractive compromise to deterministic (non-randomized) splitting. It is computationally efficient and yet does not disrupt the adaptive properties of a splitting rule. The ECP property can be guaranteed under fairly weak conditions. Pure random splitting, however, is not recommended. Its lack of adaptivity and non-ECP behavior yields inferior performance in almost all instances except large sample settings with low dimensionality. Although large sample consistency and asymptotic properties of forests have been investigated under the assumption of pure random splitting, these results show that such studies mist be viewed only as a first (but important) step to understanding forests. Theoretical analysis of forests under adaptive splitting rules is challenging, yet future theoretical investigations which consider such rules are anticipated to yield deeper insight into forests.
While CART weighted variance splitting and Gini index splitting are known to be equivalent (Wehenkel, 1996), many RF users may not be aware of their interchangeability: our work reveals both are examples of weighted splitting and therefore share similar properties (in the case of two-class problems, they are equivalent). Related to this is work by Malley et al. (2012) who considered probability machines, defined as learning machines which estimate the conditional probability function for a binary outcome. They outlined advantages of treating two-class data as a nonparametric regression problem rather than as a classification problem. They described a RF regression method to estimate the conditional probability—an example of a probability machine. In place of Gini index splitting they used weighted variance splitting and found performance of the modified RF procedure to compare favorably to boosting, k-nearest neighbors, and bagged nearest neighbors. Our results which have shown a connection between the two types of splitting rules sheds light on these findings.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Ishwaran’s work was funded in part by DMS grant 1148991 from the National Science Foundation and grant R01CA163739 from the National Cancer Institute. The author gratefully acknowledges three anonymous referees whose reviews greatly improved the manuscript.
Appendix: Proofs
Proof of Theorem 1
Let ℙε denote the measure for ε. By the assumed independence of X and ε, the conditional distribution of (X, ε) given X ≤ s and X ∈ t is the product measure ℙtL × ℙε. Furthermore, for each Borel measurable set A, we have
| (31) |
Setting Y = f(X) + ε, it follows that
where we have used (31) in the last line. Recall that 𝔼(ε) = 0 and 𝔼(ε2) = σ2. Hence
and
Using a similar argument for p(tR)Δ(tR), deduce that
| (32) |
We seek to minimize D(s, t). However, if we drop the first two terms in (32), multiply by −1, and rearrange the resulting expression, it suffices to maximize Ψt(s). We will take the derivative of Ψt(s) with respect to s and find its roots. When taking the derivative, it will be convenient to rexpress Ψt(s) as
The assumption that f(s) is continuous ensures that the above integrals are continuous and differentiable over s ∈ [a, b] by the fundamental theorem of calculus. Another application of the fundamental theorem of calculus, making use of the assumption ℙt has a continuous and positive density, ensures that ℙt{X ≤ s}−1 and ℙt{X > s}−1 are continuous and differentiable at any interior point s ∈ (a, b). It follows that Ψt(s) is continuous and differentiable for s ∈ (a, b). Furthermore, by the dominated convergence theorem, Ψt(s) is continuous over s ∈ [a, b].
Let h(s) denote the density for ℙt. For s ∈ (a, b)
Keeping in mind our assumption h(s) > 0, the two possible solutions that make the above derivative equal to zero are (5) and
| (33) |
Because Ψt(s) is a continuous function over a compact set [a, b], one of the solutions must be the global maximizer of Ψt(s), or the global maximum occurs at the edges of t.
We will show that the maximizer for Ψt(s) cannot be s = a, s = b, or the solution to (33), unless (33) holds for all s and Ψs(t) is constant. It follows by definition that
where the last line holds for any a < s < b due to Jensen’s inequality. Moreover, the inequality is strict with equality occurring only when (33) holds. Thus, the maximizer for Ψt(s) is some a < s0 < b such that , or Ψt(s) is a constant function and (33) holds for all s. In the first case, s0 = ŝN. In the latter case, the derivative of Ψt(s) must be zero for all s and (5) still holds, although it has no unique solution.
Proof of Theorem 2
Let X̃, X1,..., XN be i.i.d. with distribution ℙt. By the strong law of large numbers
| (34) |
Next we apply the strong law of large numbers to Δ̂(tL). First note that
The right-hand side is finite because σ2 < ∞ and f2 is integrable (both by assumption). A similar argument shows that 𝔼(1{X̃≤s}Y) < ∞. Appealing once again to the strong law of large numbers, deduce that for s ∈ (a, b)
where we have used that the denominators in the above expression are strictly positive by our positivity assumption for ℙt. Noting that the last line above equals Var(Y |X ≤ s,X ∈ t), it follows that
The above convergence can be shown to be uniform on compact sets [a′, b′] ⊂ (a, b) by appealing to a uniform law of large numbers. For example, the Glivenko-Cantelli theorem immediately guarantees that convergence of (34) is uniform over [a, b]. See Chapter 2 of Pollard (1984) for background on uniform convergence of empirical measures. Applying a symmetrical argument for the right daughter node tR, deduce that
The minimizer of D(s, t) is equivalent to the maximizer of Ψt(s). The conclusion follows by Theorem 2.7 of Kim and Pollard (1990) because Ψt has a unique global maximum (by assumption) and ŝN = Op(1) (because a ≤ s ≤ b).
Proof of Theorem 3
By Theorem 1, and using the fact that ℙt is a uniform distribution, the global minimum to (3) is the solution to
| (35) |
where for a ≤ α < β ≤ b. Multiply the right-hand side by (s − a)(b − s), and substituting f(x) and solving, yields
Divide by (s − a)(b − s). Deduce that the right-hand side is
where u = s/a and v = s/b (if a = 0 the identity continues to hold under the convention that 0j/0j = 1). With some rearrangement deduce (6).
To determine which solution from (35) minimizes (3), choose that value which maximizes (4). Algebraic manipulation allows one to express (4) as (7).
Proof of Theorem 4
The following is a slightly modified version of the proof given in Breiman et al. (1984). We provide a proof not only for the convenience of the reader, but also because parts of the proof will be reused later.
To start, we first show there is no loss of generality in assuming 𝔼(Z1) = 0. Let and where μ = 𝔼(Z1). Then
which is equivalent to maximizing
Therefore, we can assume 𝔼(Z1) = 0. Hence, and . Let C > 0 be an arbitrary constant. Kolmogorov’s inequality asserts that for independent variables (Ui)1≤i≤n with 𝔼(Ui) = 0
Let . Because Zi are independent with mean zero, deduce that
Similarly,
Therefore,
| (36) |
Let . By the law of the iterated logarithm (LIL) (Hartman and Wintner, 1941)
which implies that for any 0 < θ < 2 and any integer m0 > 2
Hence for m0 chosen such that δC log(logm0) > 2/θ
| (37) |
Because C can be made arbitrarily small, deduce from (37) and (36) that (12) holds. A symmetrical argument yields (13).
Proof of Theorem 6
We will assume 𝔼(Z1) = 0 and later show that the assumption holds without loss of generality. Let . With a little bit of rearrangement we obtain
where
are i.i.d. with mean zero, and
We will maximize AN,m+BN,m which is equivalent to minimizing ζN,m. This analysis will reveal that BN,m is uniformly smaller than AN,m asymptotically. The desired result follows from the asymptotic behavior of AN,m.
We begin with BN,m. We consider its behavior away from an edge. Let and . Arguing as in the proof of Theorem 4, we have for any C > 0
Applying a similar argument for , deduce that
Therefore we have established that
| (38) |
Now consider AN,m. We first consider its behavior away from an edge. Let , which is finite by our assumption . Let and . Let C > 0 be an arbitrary constant. By Kolmogorov’s inequality
Using a similar argument for ,
| (39) |
Now we consider the behavior of AN,m near an edge. As in the proof of Theorem 4, let . Choose and let m0 > 2 be an arbitrary integer. Even though S̃m can be negative, we can deduce from the LIL that for any sequence rm ≥ 1
| (40) |
We will need a bound for the following quantity
By Kolmogorov’s inequality, for any constant K >0,
| (41) |
The following lower bounds hold:
| (42) |
The last line follows from ℙ(AB) = ℙ(A) − ℙ(ABc) ≥ ℙ(A) − ℙ(Bc) for any two sets A and B. Choose m0 large enough so that
Then the first term on the last line of (42) is bounded below by
which converges to 1 due to (40) with rm = lm/l0, where . Mean-while, the second term on the last line of (42) can be made arbitrarily close to 0 by selecting K large enough due to (41). Deduce that (42) can be made arbitrarily close to 1, and because C can be made arbitrarily small, it follows from (39) and (42) that
| (43) |
The limits (16) and (17) follow by combining results from above. To prove (16), note by (38) we have
Combining this with (43) yields (16). The limit (17) follows by symmetry. Therefore, this concludes the proof under the assumption 𝔼(Z1) = 0. To show such an assumption holds without loss of generality, let μ = 𝔼(Z1) and define
Rewrite ζN,m as follows
Simplifying, it follows that
and therefore μ = 0 can be assumed without loss of generality.
Proof of Theorem 7
We can assume without loss of generality that 𝔼(Z1) = 0 (the proof is similar to the proof used for Theorem 6 given above). Let . Some rearrangement yields
where AN,m = −σ2(m2 + (N − m)2)/N + Nσ2,
are i.i.d. with mean zero and finite variance (finiteness holds by our assumption of a fourth moment), and
In place of minimizing φN,m we will maximize AN,m + BN,m + CN,m. We will show that AN,m is the dominant term by showing
The result will follow from the asymptotic behavior of AN,m.
For brevity we only provide a sketch of the proof since many of the technical details are similar to that used in the proof of Theorem 6. We start with a bound for CN,m. By the LIL
A similar analysis for the second term in CN,m, yields
Now we bound BN,m. Applying the LIL
Applying a similar analysis for the second term in BN,m, deduce that
To complete the proof we show that AN,m is the dominating term. Collecting terms,
The function g(m) = −2(m − N/2)2 is concave (quadratic) in m with a unique maximum at m = N/2. Furthermore,
Thus, AN,N/2 ≫ maxm |BN,m| + maxm CN,m is the dominating term. Because the optimal split point must be an integer, its value lies in the range m ∈ [N/2−1,N/2+1]. Deduce (20) and (21).
Proof of Theorem 8
For each measurable set A
Because ϕ1(tL)(1 − ϕ1(tL)) = ϕ2(tL)(1 − ϕ2(tL)), it follows that
Using a similar argument for p(tR)Γ(tR), deduce that
| (44) |
Notice that this has a similar form to (32) with ϕ(x) playing the role of f(x) (the first term on the right of (44) and the first two terms on the right of (32) play no role). Indeed, we can simply follow the remainder of the proof of Theorem 1 to deduce the result.
Proof of Theorem 10
The proof is nearly identical to Theorem 4 except for the modifications required to deal with triangular arrays. Assume without loss of generality that 𝔼(Zi) = 0. Let and . Splits away from an edge are handled as in Theorem 4 with ZN,i substituted for Zi and RN substituted for N. It follows for any constant C > 0
| (45) |
Now we consider the contribution of a split from a left edge split. To do so, we make use of a LIL for weighted sums. We use Theorem 1 of Lai and Wei (1982). Using their notation, we write , where aN,i = 1 for i ∈ IN, and aN,i = 0 otherwise. The values aN,i comprise a double array of constants {aN,i: N ≥ 1,−∞ < i < ∞}. By part (iii) of Theorem 1 of Lai and Wei (1982), for any 0 < θ < 2
where . Now arguing as in the proof of Theorem 4, this implies
| (46) |
Because C can be made arbitrarily small, deduce from (46) and (45) that (29) holds. The limit (30) for a right-edge split follows by symmetry.
References
- Biau G. Analysis of a random forests model. J Machine Learning Research. 2012;13:1063–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Biau G, Devroye L, Lugosi G. Consistency of random forests and other classifiers. J Machine Learning Research. 2008;9:2039–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman L. Technical note: some properties of splitting criteria. Machine Learning. 1996;24:41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman L. Random forests. Machine Learning. 2001;45:5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman L. Technical Report 670. University of California, Statistics Department; 2004. Consistency for a simple model of random forests. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman L, Friedman JH, Olshen RA, Stone CJ. Classification and Regression Trees. Belmont, California: 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Brier GW. Verification of forecasts expressed in terms of probabilities. Monthly Weather Review. 1950;78:1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Buhlmann P, Yu B. Analyzing bagging. Ann Statist. 2002;30(4):927–961. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler A, Zhao G. Pert - perfect random tree ensembles. Computing Science and Statistics. 2001;33:490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Demsar J. Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Machine Learning Research. 2006;7:1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich TG. An experimental comparison of three methods for constructing ensembles of decision trees: bagging, boosting, and randomization. Machine Learning. 2000;40:139–157. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho DL, Johnstone IM. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika. 1994;81:425–455. [Google Scholar]
- Geurts P, Ernst D, Wehenkel L. Extremely Randomized Trees. Machine Learning. 2006;63:3–42. [Google Scholar]
- Genuer R. Variance reduction in purely random forests. J Nonparam Statist. 2012;24(3):543–562. [Google Scholar]
- Gyorfi L, Kohler M, Krzyzak A, Walk H. A Distribution-Free Theory of Non-parametric Regression. Springer; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P, Wintner A. On the law of the iterated logarithm. Amer J Math. 1941;63:169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ishwaran H, Kogalur UB, Blackstone EH, Lauer MS. Random survival forests. Ann Appl Stat. 2008;2:841–860. [Google Scholar]
- Ishwaran H, Kogalur UB, Gorodeski EZ, Minn AJ, Lauer MS. High-dimensional variable selection for survival data. J Amer Stat Assoc. 2010;105:205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Ishwaran H, Kogalur UB, Chen X, Minn AJ. Random survival forests for high-dimensional data. Statistical Analysis and Data Mining. 2011;4:115–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ishwaran H, Kogalur UB. randomForestSRC: Random Forests for Survival, Regression and Classification (RF-SRC) R package version 1.4.0. 2014 http://cran.r-project.org.
- Kohavi R, John G. Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence. 1997;97:273–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kim J, Pollard D. Cube root asymptotics. Ann Stat. 1990;18:191–219. [Google Scholar]
- Lai TL, Wei CZ. A law of the iterated logarithm for double arrays of independent random variables with applications to regression and time series models. Ann Prob. 1982;19:320–335. [Google Scholar]
- Leisch F, Dimitriadou E. R package version 1.1–6. 2009. mlbench: Machine Learning Benchmark Problems. [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y, Jeon Y. Random forests and adaptive nearest neighbors. J Amer Statist Assoc. 2006;101:578–590. [Google Scholar]
- Malley JD, Kruppa J, Dasgupta A, Malley KG, Ziegler A. Probability machines: consistent probability estimation using nonparametric learning machines. Methods Inform Med. 2012;1:51. doi: 10.3414/ME00-01-0052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan JN, Messenger RC. THAID: a Sequential Search Program for the Analysis of Nominal Scale Dependent Variables. Survey Research Center, Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan; 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Pollard D. Convergence of Stochastic Processes. Springer-Verlag; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Stone CJ. Optimal rates of convergence for nonparametric estimators. Ann Stat. 1980;8:1348–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Torgo L. A study on end-cut preference in least squares regression trees. Progress in Artificial Intelligence Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 2001;2258:104–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wehenkel L. On uncertainty measures used for decision tree induction. Proceedings of the International Congress on Information Processing and Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge based Systems, IPMU96; 1996. pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]