Genetics. In the article “Genetic definition of a protein-splicing domain: Functional mini-inteins support structure predictions and a model for intein evolution” by Victoria Derbyshire, David W. Wood, Wei Wu, John T. Dansereau, Jacob Z. Dalgaard, and Marlene Belfort, which appeared number 21, October 14, 1997 of Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (94, 11,466–11,471), the authors request that the higher-contrast versions of Fig. 3 be noted below.
Figure 3.
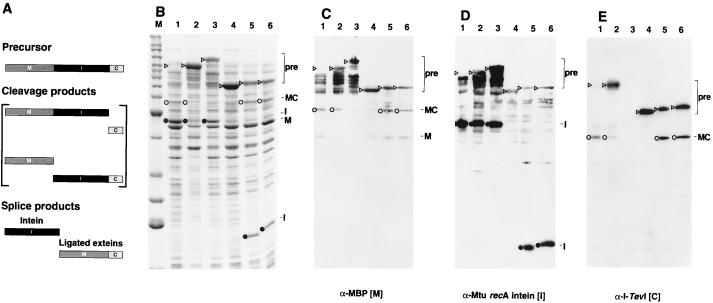
Splicing in vivo. (A) Schematic of the MIC in-frame fusion. Precursor, cleavage, and splice products are shown. (B) Twelve percent Coomassie-stained SDS polyacrylamide gel of cell lysates of MIC constructs induced at 37°C for 3 h. Lane M, molecular mass marker bands (Benchmark, GIBCO/BRL) from the bottom up correspond to 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 120, 160, and 220 kDa (bold numbers correspond to the two high-intensity bands). Lanes: 1, full-length MIC; 2, MIC25, a slow-splicing mutant derivative of full-length MIC (D.W.W. et al., unpublished results); 3, MIT with TS as C-terminal extein; 4, 101Δ405(A7) (Fig. 2, construct 3); 5, 110Δ383 (Fig. 2, construct 6); 6, 114Δ372 (Fig. 2, construct 8). ▹, precursor (MIC or MIT); ○, ligated exteins (MC); •, intein. Arrowheads in lane 1 mark position of precursor. (C) Western blot of 12% SDS polyacrylamide gel with maltose binding protein antiserum. (D) Western blot of 12% SDS polyacrylamide gel with Mtu recA intein antiserum. (E) Western blot of 10% SDS polyacrylamide gel with I-TevI antiserum. The assignments were verified on a 12% gel (data not shown). Background bands from cross-reactivity to the polyclonal antisera are also evident in C–E. Lanes and symbols are as in B.