| Summary: |
The present
invention relates to compounds useful for the treatment of diseases
such as B-cell malignancies including leukemias, lymphomas, myeloma,
inflammatory disorders, and so forth. The pharmaceutical agents inhibit
the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB)-inducing kinase (also known
as MAP3K14 or NIK kinase). NF-κB is a transcription factor that
regulates the expression of various genes involved in immune response,
apoptosis, carcinogenesis, cell proliferation, and adhesion. NIK is
a serine/threonine kinase, which regulates two NF-κB signaling
pathways; the canonical and the noncanonical. The canonical pathway,
also known as the “alternative” NF-κB pathway,
mediates downstream signals of a subset of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
receptor family such as BR3/BAFF-R, CD40, and CD27. However, the noncanonical
NF-κB pathway is involved in bone metabolism, B cell survival
and maturation, lymphocyte recruitment, and so forth. |
| The noncanonical NF-κB pathway is selectively activated
by ligands such as CD40, B-cell activating factor (BAFF), TNF-related
weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK), and lymphotoxin β receptor
ligands. As a result, NIK expression is tightly regulated, and under
nonstimulated conditions, the NIK protein levels are very low. However,
when stimulated by ligands, the activated receptors now compete for
TNF receptor associated factors (TRAFs), which dissociates the TRAF-NIK
complexes and leads to increased levels of NIK, which is seen in many
disease processes. There are reports that have shown that blocking
the NF-κB signaling pathway in cancer cell lines causes cells
to stop proliferating, become more sensitive to anticancer therapies,
and eventually die. Furthermore, NIK is dysregulated in multiple myeloma
because of diverse genetic abnormalities. In addition, NIK has been
shown to exacerbate disease conditions in chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD), diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and so forth.
Thus, the present invention is directed to a series of pharmaceutical
compounds such as Formula (I) for the prevention or treatment of diseases
such as cancer, obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. |
| Important Compound Classes: |
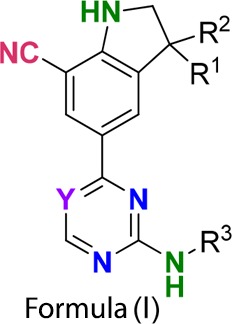 |
| Key Structures: |
The inventors
described synthetic procedures and listed structures of 240 compounds
of Formula (I) including the following representative examples: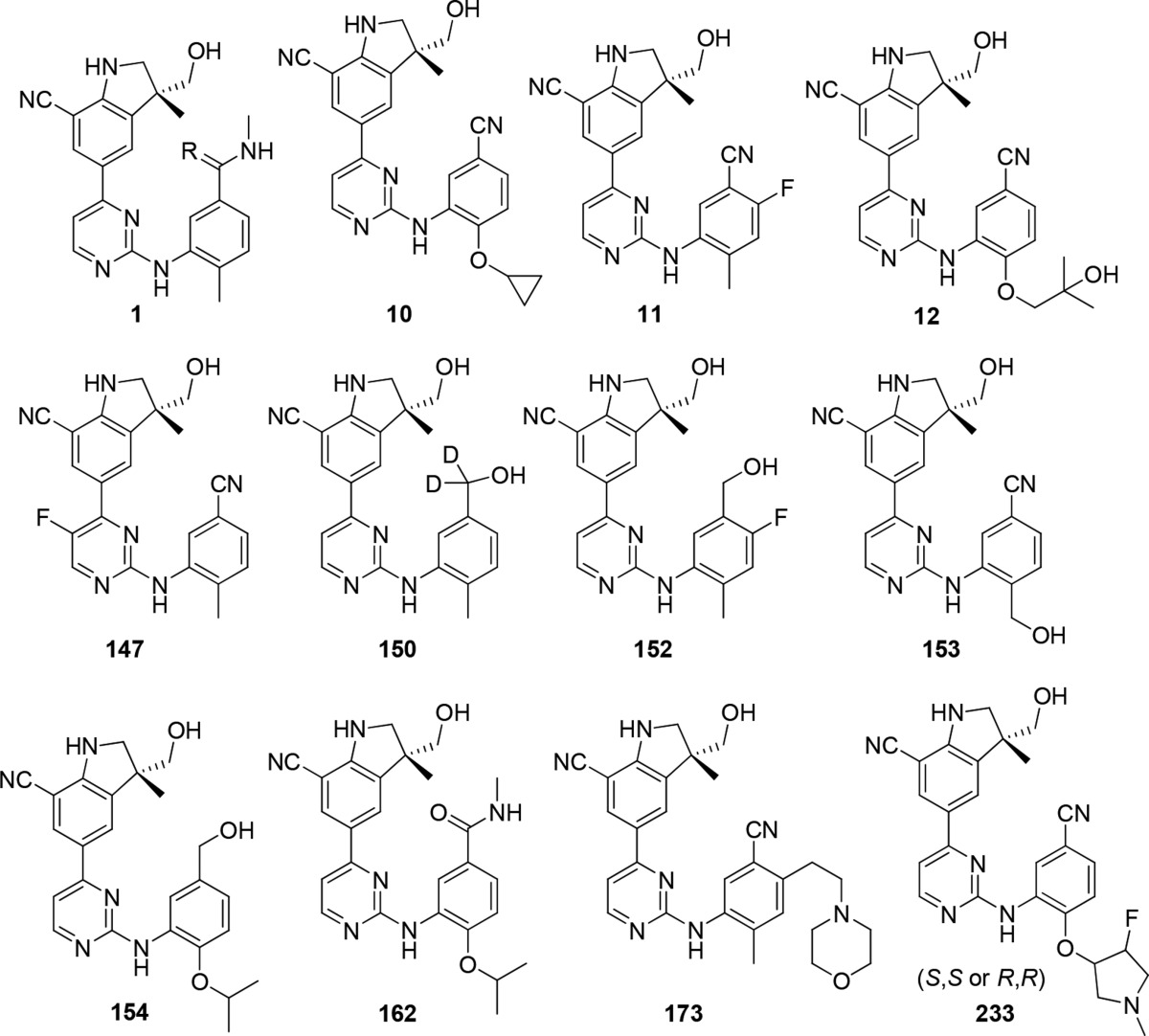
|
| Recent Review Articles: |
1. Castanedo G. M.; Blaquiere N.; Beresini M.; Bravo B.; Brightbill H.; Chen J.; Cui H.-F.; Eigenbrot C.; Everett C.; Feng J.; Godemann R.; Gogol E.; Hymowitz S.; Johnson A.; Kayagaki N.; Kohli P. B.; Knüppel K.; Kraemer J.; Krüger S.; Loke P.; McEwan P.; Montalbetti C.; Roberts D. A.; Smith M.; Steinbacher S.; Sujatha-Bhaskar S.; Takahashi R.; Wang X.; Wu L. C.; Zhang Y.; Staben S. T.. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 627. |
| 2. Limerick G.; Tang X.; Lee W. S.; Mohamed A.; Al-Aamiri A.; Wadsworth W. G.. Neuroscience 2017, 1–81. |
| 3. Rapino F.; Abhari B. A.; Jung M.; Fulda S.. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, 1692. |
| Biological Assay: |
There were
three biological assays used in this patent:
-
(1)
The NIK/MAP3K14 autophosphorylation
activity was measured
using the Alpha Screen (αscreen) format (PerkinElmer). The compounds
were tested for inhibition of the autophosphorylation of recombinant
human NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK/MAP3K14) activity. Assays were
carried out in 384-well Alphaplates (PerkinElmer).
-
(2)
Compounds of interest were tested
in P-IKKα levels of L363 (NIK translocated multiple myeloma)
cells. The human L363 cells (ATCC) were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium,
which was supplemented with GlutaMax and 10% fetal calf serum (PAA).
-
(3)
Determination of antiproliferative
activity on JJN-3 (NIK translocated) and KMS12-BM (NIK WT) multiple
myeloma cells. The cell viability was assessed using CellTiter-Gluo
cell viability assay kit (Promega). The human JJN-3 and KMS12-BM cells
(DSMZ) were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium and supplemented with 2 mM l-glutamine and 10% fetal calf serum (PAA). Luminescence was
measured on a HTS Topcount (PerkinElmer).
|
| Biological Data: |
The
biological data obtained from testing the above representative
compounds of Formula (I) are listed in the following table: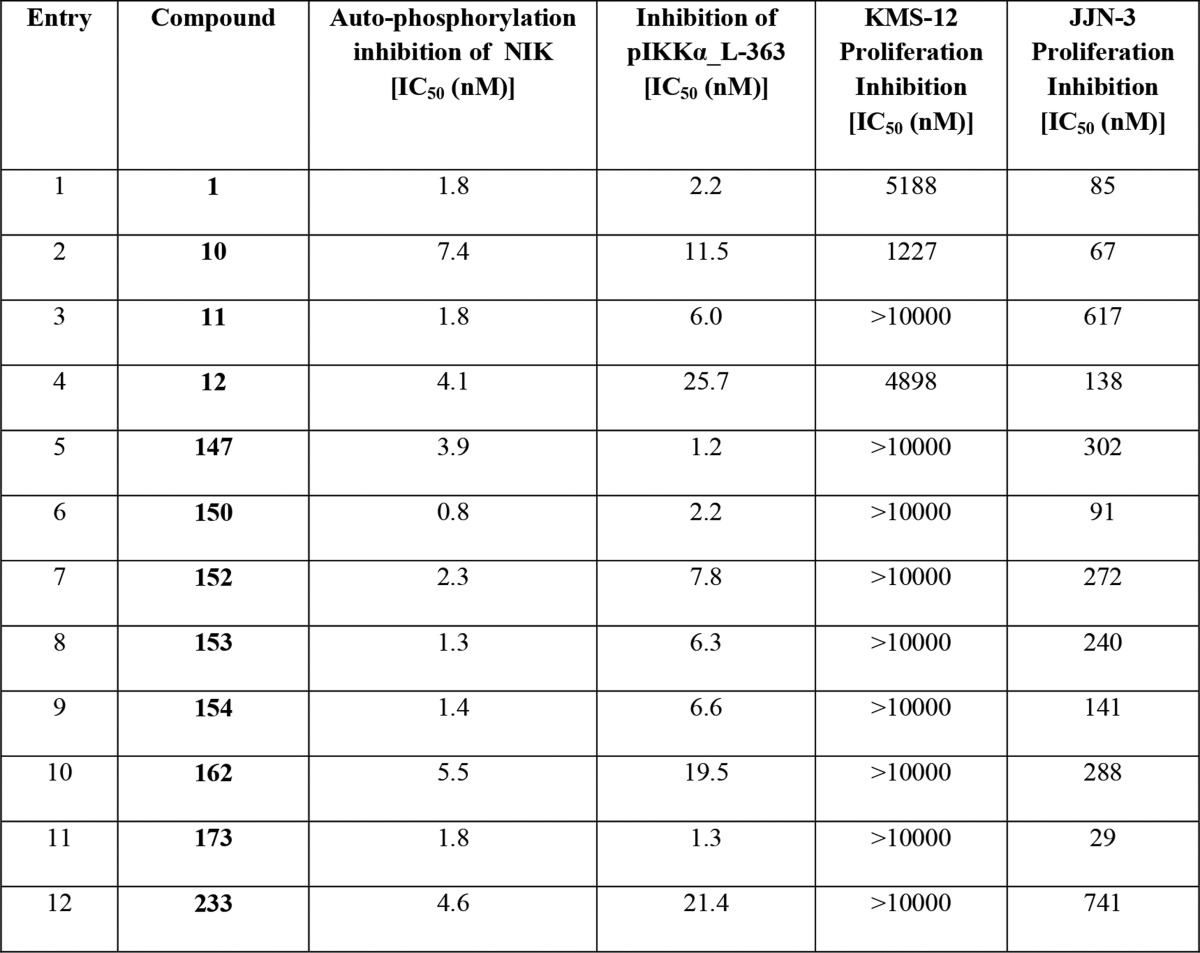
|
| Claims: |
33 Total claims |
| 27 Composition of
matter claims |
| 6 Method of use claims |





