Abstract
Objectives
The main purpose of the study was to assess the validity between the Fitbit and ActiGraph GT3X+ accelerometer. The specific aims were to determine the: (1) concurrent validity between the various models of the Fitbit and the GTX3+ accelerometer as the criterion measure for: number of steps and active minutes averaged over a single-day and 7-day period; (2) validity of the two devices with the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) for the number of daily active minutes performed.
Methods
Fifty-three subjects wore a Fitbit and ActiGraph concurrently for 7 days. Data were analysed using correlation coefficients, t-tests to assess mean comparisons and Bland-Altman plots to determine agreement between the Fitbit and the ActiGraph.
Results
The correlations between the Fitbit and ActiGraph for steps per day and per 7 days were r=0.862 and 0.820, respectively with significant mean differences between both devices. Bland-Altman analyses revealed agreement between the Fitbit and the ActiGraph for 7-day active minutes only. The correlations between the Fitbit and ActiGraph for active minutes per day and per 7 days were r=0.695 and r=0.658, respectively, with no significant mean differences between both devices. No significant correlations were found between the IPAQ and the other two devices.
Conclusions
The data produced by the Fitbit were consistent with the ActiGraph when the means of each device were compared over the 1-day and 7-day time periods. However, Bland-Altman analyses revealed that the Fitbit agreed with the ActiGraph when used to measure physical activity levels over a 7-day span only.
Keywords: Physical activity, tracker, validity, accelerometer
What are the findings?
The Fitbit may not be a valid indicator of steps per day.
The number of active minutes generated by the Fitbit is comparable with the minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity generated by the ActiGraph over a 7-day period.
Use of the Fitbit to measure active minutes over a 1-day period does not agree with the minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity recorded by the ActiGraph.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the future?
Active minutes of physical activity promote improvements in health and fitness. The Fitbit can accurately measure active minutes when used over a 7-day period.
Health and fitness professionals should use the Fitbit to track and measure health-enhancing physical activities for individuals for at least this time period.
Use of the Fitbit to track steps per day or active minutes for a 1-day period may not be appropriate.
Introduction
Physical activity (PA) is one of the most important tasks to improve physical and mental health.1 In 2008, the US government issued minimum daily recommendations for aerobic and muscle strengthening activities for all individuals.2 These recommendations require the inclusion of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) to enhance overall health. Moderate PA is defined as skeletal muscle contractions that produce energy expenditures that are greater than or equal to 3 and less than 6 metabolic equivalents (METS) and vigorous PA is any activity that produces greater than 6 METS.3
Numerous instruments have been devised to measure PA in the free-living environment that range from self-report questionnaires to devices such as pedometers, heart rate monitors and accelerometers. ActiGraph is one of the leading manufacturers of accelerometers, with applications that are suitable for researchers and clinical scientists to estimate PA levels via regression equations. These equations have been validated using gold standard laboratory measures, such as doubly labelled water and calorimetry.4–8
The GT3X+ model is a triaxial accelerometer produced by ActiGraph that may be worn on the hip, thigh, ankle or wrist. It can provide data on energy expenditure, time spent in various static positions and intensity levels of PA. Previous validation studies on the GT3X+ have been conducted on healthy and clinical paediatric, adult and geriatric populations. Remoortel et al and Garcıa-Masso et al noted strong correlations (r=0.79 and 0.86, respectively) between the GT3X+ and a portable indirect calorimeter as individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Remoortel et al) and paraplegia (Garcia-Masso et al) performed a standardised protocol of activities of daily living.5 9 Based on this and other published reports, the GT3X+ is one of the more accurate research-grade instruments used to assess free-living PA.4–6 10
Fitbit manufactures over 10 different consumer-based PA trackers, several of which use triaxial accelerometry to capture activity counts that are displayed either on a wrist-worn unit or via a compatible cellular phone or personal computer.
The Fitbit provides data to the consumer like the ActiGraph, but with a user-friendly application. The validity of the Fitbit to measure energy expenditure, step count and PA under free-living conditions have been examined. Tully et al noted a high correlation between the Fitbit Zip (r>0.91) and the GT3X+ and Yamax CW700 pedometer.11 They noted a significant difference between the Fitbit Zip and the GT3X+ with the Fitbit Zip systematically recording a higher number (7477 (Fitbit) vs 6774 (GT3X+)) of steps per day. Gomersall et al10 compared the Fitbit One to the GTX3. The correlations for the Fitbit One ranged from 0.72 to 0.90 for estimated steps per day and time spent performing MVPA per day that the Fitbit manufacturers defines as ‘active minutes’. In this study, the Fitbit One overestimated daily steps by 8% and underestimated MVPA time by 46%. Paul et al12 measured the 7-day step count of 32 community-dwelling adults using either the Fitbit One or Zip and the ActiGraph worn simultaneously. They found that the Fitbit models had excellent agreement (ICC2,1=0.94) with the ActiGraph despite the Fitbit overestimating their subjects’ step count by 716.7 per day.
The Fitbit has also been tested under laboratory conditions. Gusmer et al reported strong correlations between the Fitbit Ultra and ActiGraph GT1M for step count during slow walking (r=0.974, p<0.001) and brisk walking (r=0.996, p<0.001) tasks on a treadmill for young adults.13 The energy expenditure between the two devices were moderately correlated (r=0.584, p=0.011) during the slow walking task. Diaz et al14 assessed the reliability and validity of three Fitbit One devices worn simultaneously (two placed on the right hip and one placed on the left hip) and two wrist-worn Fitbit Flex devices (worn on each wrist) with indirect calorimetry and actual step counts via a video during a four-stage treadmill test. They found the correlations ranged between 0.97 to 0.99 between both devices of the Fitbit and the observed step counts with mean differences that ranged between −3.1 and −0.3 steps for the Fitbit One and −26.3 to −2.9 steps for the Fitbit Flex. The correlations between the Fitbit One and the Fitbit Flex were 0.86 and 0.88, respectively, with indirect calorimetry.
Self-reported measures such as the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) offer a convenient, low cost method to quantify the volume of various types of PA performed. The IPAQ's use for population-based epidemiological studies is well supported; however, its reported criterion-referenced validity to accurately assess PA levels when compared with instrumented methods is moderate to low. Wanner et al15 performed a cross-sectional study to validate the IPAQ long form with the GT3X+ among individuals aged 18–84 years who speak three different languages and residing in Switzerland. They found the highest correlations (r=0.41) for vigorous PA and sitting time (r=0.42), noting that the IPAQ overestimated PA but underestimated sitting time. Garriguet et al16 reported a correlation of 0.20 between the IPAQ and the Actical accelerometer for measuring time spent performing MVPA, which is a large discrepancy from the previous study. Kim et al17 performed a meta-analysis that used 21 studies published between the year 2004 and 2010 to determine the convergent validity between the IPAQ and other instruments that measure PA. They pooled 152 studies to generate mean effect sizes between the IPAQ and other self-report instruments, pedometers and accelerometers across five different PA categories. Overall, they found small to medium effect sizes with the highest and lowest pooled correlations found for vigorous and moderate PA, respectively.
The purpose of this cross-sectional study was to determine the criterion validity among the various models of the Fitbit and IPAQ using the ActiGraph GT3X+ as the reference measure.
Methods
Subjects
This cross-sectional study design recruited 53 subjects (women: 44; men: 9) from two university settings from January to June of 2016. Ethic approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Boards of Texas Woman's University and the University of New England. Each subject needed to have their own Fitbit with their respective smartphone application to be included in the study. After consenting to participation, each subject was issued an ActiGraph GT3X+ triaxial accelerometer (ActiGraph, Pensacola, Florida, USA). Accelerometers were initialised using Actilife 6 software (ActiGraph) using the subject’s date of birth, sex, weight, height, race/ethnicity and dominant hand. The sampling rate was selected at 30 Hz.
Instruments
Subjects were instructed to wear the accelerometer for 1 week using the belt clip provided on the right side of their waist during all waking hours at the same time they wore their Fitbit on their non-dominant arm. The subjects returned the accelerometer after 1 week, and the activity data from their Fitbit application was recorded in a spreadsheet. The data of interest from the Fitbit were steps per day, steps per 7 days (7 day average), active minutes per day and active minutes 7 day total.
The accelerometer data were downloaded using the Actilife software, and a clinical report was created by using a Troiano algorithm for data filtering and Freedson equations for estimation of energy expenditure and cut-offs of PA.18–20 A valid day was considered as 600 min (10 hours) of wear time, which is a higher threshold than previously reported in the literature.4 Fitbit uses the term ‘active minutes’ to denote minutes spent performing MVPA; this term will be used interchangeably with MVPA minutes throughout this manuscript.21
The IPAQ long form was used to measure PA by measuring hours and/or minutes performing PA and days per week performing activities at a moderate to vigorous intensity.22 PA was reported in and was scored using standardised IPAQ scoring protocols to yield total MET-minutes of PA per week.
Data analysis
The statistical aims and hypotheses of this study were to determine the criterion validity: (1) between the various models of the Fitbit and the GTX3+ accelerometer as the criterion measure for the number of steps and active minutes averaged over a single-day and 7-day period and (2) among the various models of the Fitbit, the IPAQ long form and the GT3X+ for minutes of MVPA over a 7-day assessment period. It was hypothesised that a significant, positive relationship will exist between the Fitbit and the GT3X+ accelerometer: (1) for number of steps and active minutes averaged over a single-day and 7-day period, while a non-significant mean comparison will exist between the aforementioned variables measured by the Fitbit and the GT3X+ accelerometer; (2) with the IPAQ for minutes spent performing MVPA while a non-significant mean comparison will exist between the IPAQ with the Fitbit and the IPAQ with the GT3X+ accelerometer for minutes spent performing MVPA; and (3) with the IPAQ for minutes spent performing MVPA while a non-significant mean comparison will exist between the IPAQ with the Fitbit and the IPAQ with the GT3X+ accelerometer for minutes spent performing MVPA. All data were recorded and calculated using a spreadsheet. Calculations were performed to determine the 7-day averages for steps per day. All additional statistical analyses were performed using SPSS V.21. Descriptive statistics (mean±SD, range) were used to analyse demographic variables.
Paired t-tests were run to assess for between group differences based on device (ActiGraph and Fitbit) for each of the following conditions: steps per day (daily), steps for 7 days (7-day average), active minutes per day and active minutes 7 day total. Paired t-tests were performed to assess the between instrument differences between the ActiGraph and the IPAQ and between the Fitbit and the IPAQ for MVPA minutes over the 7-day assessment period. Pearson’s product moment correlations were used to assess the strength of the relationship for each pair-wise comparison between devices (Fitbit vs ActiGraph; ActiGraph vs IPAQ; Fitbit vs IPAQ).
Bland-Altman analyses were used to assess for the agreement between the devices and the IPAQ. Bland-Altman analyses were used to visually and statistically determine agreement between the instruments. The Bland-Altman statistical analyses require the use of simple linear regression using the mean of the data between the instruments to predict the mean differences to generate beta coefficients. These coefficients will be used to determine if any pair of instruments (Fitbit vs ActiGraph; Fitbit vs IPAQ; ActiGraph vs IPAQ) agree with each other. These analyses were done only if the between group mean comparisons were not significant and the correlation between them exceeded 0.30. All Fitbit data were analysed in aggregate format regardless of the model type used.
Results
A total of 53 subjects were enrolled; however, technical issues resulted in the loss of two subjects’ accelerometer data and one subject’s Fitbit data. Therefore, data for 50 subjects (41 female, 9 male) were included in the final analysis. Subjects were primarily graduate students, with a mean age of 28.10±9.12 years old (range 21.0–58.0); 165.3±7.1 cm tall (range 154.9–185.4) and 70.6±17.0 kg (range 44–124.7). Forty-eight of the subjects of the 50 subjects self-reported that they met the US government’s PA recommendations as noted via the IPAQ reports. The Fitbit models used for this study are in table 1.
Table 1.
Fitbit models included in study
| Charge HR | 23 |
| Charge | 10 |
| Flex | 8 |
| Surge | 5 |
| Zip | 3 |
| Alta | 1 |
Steps per day: steps per day resulted in a very strong and statistically significant correlation between the Fitbit and ActiGraph, r=0.862, p>0.001. However, there was a statistically significant difference between groups (Fitbit: 7996.22 steps/day; ActiGraph: 6630.83 steps/day) and mean difference 1365.39, t=12.407, 368, p>0.001.
Seven-day average, steps per day: weekly average steps per day resulted in a very strong and statistically significant correlation between Fitbit and ActiGraph, r=0.820, p>0.001. However, there was a statistically significant difference between groups, (Fitbit: 8345.83 steps/day, ActiGraph: 6408.12 steps/day) and mean difference 1937.71, t=10.837, 49, p>0.001.
MVPA minutes per day: MVPA minutes per day resulted in a moderate and significant correlation between the Fitbit and ActiGraph, r=0.695, p>0.001. There was no significant difference between the two devices (Fitbit: 30.23, ActiGraph: 31.04), mean difference 0.81, t=-0.640, 380, p=0.523.
Seven-day total active minutes: Active minutes per day resulted in a moderate and significant correlation between the Fitbit and ActiGraph, r=0.658, p>0.001. There was no significant difference between the two devices (Fitbit: 233.26, ActiGraph: 235.32), mean difference 2.06, t=−0.144, 49, p=0.886.
Seven-day total active minutes: Fitbit versus IPAQ and ActiGraph versus IPAQ: when compared with the IPAQ for moderate to vigorous minutes per week, there were no significant correlations between either the Fitbit (r=0.157, p=0.277) or ActiGraph (r=−0.032, p=0.824). The paired t-tests revealed significant differences between the IPAQ results and both the Fitbit (t=−3.656,49, p=0.001) and ActiGraph (t=−3.426, 49, p=0.001).
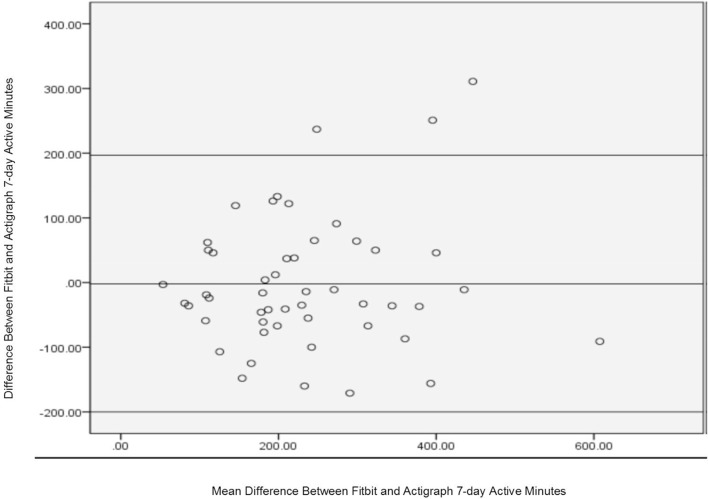
Bland-Altman analyses: 7-day total active minutes and daily total active minutes for the Fitbit versus ActiGraph were performed using two separate analyses. The Bland-Altman plot that displays the level of agreement between the 7-day total active minutes between the Fitbit and ActiGraph is shown in figure 1.
Figure 1.
7-day active minute agreement between Fitbit and Actigraph.
The beta coefficients generated by the linear regression analyses confirmed agreement between the 7-day active minutes’ data generated by the Fitbit and the ActiGraph due to non-significant level of p=0.467 (table 2).
Table 2.
Fitbit–ActiGraph 7-day mean minutes beta coefficient
| Model | Unstandardised coefficients | Standardised coefficients | |||
| B | SE | Beta | t | Sig. | |
| (Constant) | −24.560 | 33.883 | −0.725 | 0.472 | |
| Fibit–ActiGraph 7-day mean minutes | 0.096 | 0.131 | 0.105 | 0.734 | 0.467 |
Dependent variable: Fibit–ActiGraph 7-day difference in minutes.
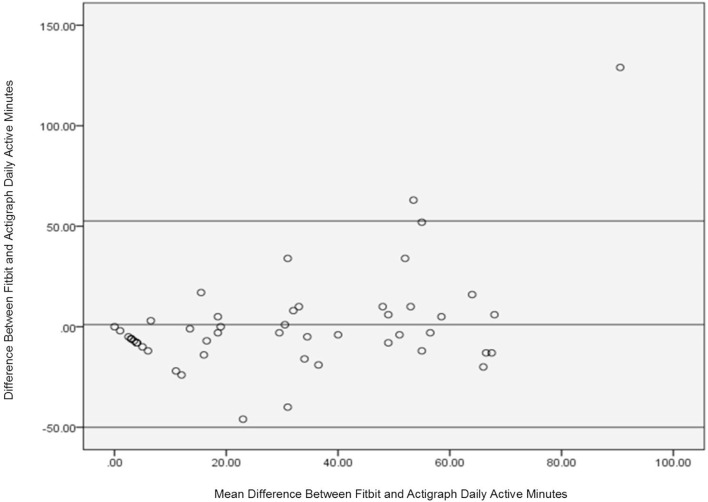
The Bland-Altman plot that displays the level of agreement between the daily total active minutes between the Fitbit and ActiGraph is shown in figure 2. The beta coefficients generated by the linear regression analyses demonstrated lack of agreement between the daily active minutes data generated by the Fitbit and the ActiGraph due to a significant difference from zero (p=0.001) (table 3).
Figure 2.
Daily active minute agreement between Fitbit and Actigraph.
Table 3.
Fitbit–ActiGraph daily mean minutes beta coefficient
| Model | Unstandardised coefficients | Standardised coefficients | |||
| B | SE | Beta | t | Sig. | |
| (Constant) | −13.999 | 5.588 | −2.505 | 0.016 | |
| Fibit–ActiGraph mean daily minutes | 0.488 | 0.144 | 0.439 | 3.386 | 0.01 |
Dependent variable: Fibit–ActiGraph difference in daily minutes.
Discussion
The findings of the current study indicate that the Fitbit may be an appropriate device for the measurement of active minutes when compared with a previously validated device. The Fitbit demonstrated consistency with the ActiGraph, within 1 min/day and 2 min/7 day cumulative total based on mean comparisons and correlations alone. However, the Bland-Altman analyses revealed that the Fitbit and the ActiGraph produced data that may be used interchangeably if the purpose is to measure PA levels over a span of 7 days and not just 1 day. A plausible reason may be due to the Fitbit’s tendency to produce varied measurements for a 1-day assessment, but if used to assess PA levels over several days, the device tends to produce results that are more indicative of an individual's true PA level. In addition, based on inspection of the Bland-Altman plot for the daily active minutes, one subject was an extreme outlier. This subject was retained for all analyses to enhance the generalisability of the study; however, when this subject was removed from the analysis, there was statistical agreement between the Fitbit and ActiGraph for daily active minutes.
The results for the assessment of active minutes over a 7-day period do not appear to carryover to other measures such as steps per day. While strongly correlated, there was a significant difference in steps per day; the Fitbit overestimated steps per day by 1365 steps. When assessed over a 7-day epoch, overestimation increased to 1938 steps/day. Because of this overestimation, we advise caution with the use of steps as a measure of free-living PA if using a Fitbit device. We suggest that if Fitbit steps per day data is to be used in research, an adjustment may be required. Everson et al23 in their systematic review reported high validity for consumer-based activity trackers like the Fitbit for step count when compared with accelerometry or an individual counting the subjects’ steps. This aforementioned review predominately used laboratory based studies that involved short duration walks on a treadmill, whereas our study involved overground walking under free-living conditions for a duration of 7 days, which may explain the variations found.
Error levels in reporting of PA using recall techniques have been estimated to be between 35% and 50%, due to factors including difficulty with recall ability and the desire to provide socially desirable responses.24 The findings of the current study indicated gross overestimation of MVPA on the IPAQ (+181 to 183/minutes per week, 77.0%–78.6%) when compared with the Fitbit and ActiGraph devices. These results far exceed prior reports of overestimation with recall devices; as a result, the validity of the IPAQ as a clinical tool appears to be questionable at best.
There are several limitations of this study due to: the varied models of the Fitbit used, the lack of standardised placements of the devices and the subject inclusion criteria. The different Fitbit models used by the subjects may have impacted the level of validity with the ActiGraph and IPAQ. Fitbit does not publish their proprietary algorithms used to estimate PA levels and energy expenditures that do not allow for the determination of reliability differences by model. The subjects wore the Fitbit on the non-dominant wrist and the GT3X+ on the right hip, which may have influenced the accuracy of the comparisons between both devices due to differences in accelerations between the two bodily segments. However, current best practice recommendations for accelerometers suggest placement at the right hip yields the most accurate data.24 As the comparison is of the results as the devices are worn under free-living conditions, this difference may also enhance the external validity of the results. The inclusion criterion that required each subject to own a Fitbit may have introduced selection bias. The subjects in this study may have been more physically active than individuals that do not own one, which limits the generalisability of these results. To enhance the accuracy of the IPAQ comparisons, subjects should record their PAs at the end of each day instead of relying on recall over several days. Lastly, studies that use an individual’s own Fitbit should account for the duration of ownership of the device as the passage of time may have an influence on the accuracy of the device.
Conclusions
Overall, the Fitbit demonstrated concurrent validity with the ActiGraph GT3X+ as a tool to assess active minutes in a free-living environment. This validity did not carryover to steps per day. If limited to the assessment of active minutes, the Fitbit demonstrated appropriate validity for use as a research tool in the free-living environment when used over a 7-day period. Health professionals and researchers using the Fitbit should consider using the data produced by these devices over a 7-day period to accurately track and monitor MVPA, which is the intensity needed to enhance health and fitness.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the several graduate students at the Texas Woman’s University and University of New England’s Department of Physical Therapy for their diligent work collecting data and their recruitment efforts.
Footnotes
Contributors: Drs WB and BS supervised the data collection and secured ethical approval for the study.
Funding: The University of New England Office of Research provided the funding.
Competing interests: None declared.
Ethics approval: Texas Woman’s University and University of New England Institutional Review Boards.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Physical Activity Basics, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health, Office of the Secretary, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Physical Activity Guidelines, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pescatello LS. American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. PhiladelphiaWolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health, 2014:456. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aadland E, Ylvisåker E. Reliability of the Actigraph GT3X+ Accelerometer in Adults under Free-Living Conditions. PLoS One 2015;10:e0134606 10.1371/journal.pone.0134606 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.García-Massó X, Serra-Añó P, García-Raffi LM, et al. Validation of the use of Actigraph GT3X accelerometers to estimate energy expenditure in full time manual wheelchair users with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2013;51:898–903. 10.1038/sc.2013.85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Crouter SE, Kuffel E, Haas JD, et al. Refined two-regression model for the ActiGraph accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2010;42:1029–37. 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181c37458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rothney MP, Schaefer EV, Neumann MM, et al. Validity of physical activity intensity predictions by ActiGraph, Actical, and RT3 accelerometers. Obesity 2008;16:1946–52. 10.1038/oby.2008.279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Crouter SE, Churilla JR. Bassett DR,Jr. Estimating energy expenditure using accelerometers. Eur J Appl Physiol 200698601.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Van Remoortel H, Raste Y, Louvaris Z, et al. Validity of six activity monitors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a comparison with indirect calorimetry. PLoS One 2012;7:e39198 10.1371/journal.pone.0039198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gomersall SR, Ng N, Burton NW, et al. Estimating Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in a Free-Living Context: A Pragmatic Comparison of Consumer-Based Activity Trackers and ActiGraph Accelerometry. J Med Internet Res 2016;18:e239 10.2196/jmir.5531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tully MA, McBride C, Heron L, et al. The validation of Fibit Zip physical activity monitor as a measure of free-living physical activity. BMC Res Notes 2014;7:952–7. 10.1186/1756-0500-7-952 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Paul SS, Tiedemann A, Hassett LM, et al. Validity of the Fitbit activity tracker for measuring steps in community-dwelling older adults. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 2015;1:e000013 10.1136/bmjsem-2015-000013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gusmer RJ, Bosch TA, Watkins AN, et al. Comparison of FitBit Ultra to ActiGraph GT1M for Assessment of Physical Activity in Young Adults During Treadmill Walking. Open Access J Sports Med 2014;8:11–15. 10.2174/1874387001408010011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Diaz KM, Krupka DJ, Chang MJ, et al. Fitbit: An accurate and reliable device for wireless physical activity tracking. Int J Cardiol 2015;185:138–40. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.03.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wanner M, Probst-Hensch N, Kriemler S, et al. Validation of the long international physical activity questionnaire: Influence of age and language region. Prev Med Rep 2016;3:250–6. 10.1016/j.pmedr.2016.03.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garriguet D, Tremblay S, Colley RC. Comparison of Physical Activity Adult Questionnaire results with accelerometer data. Health Rep 2015;26:11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kim Y, Park I, Kang M. Convergent validity of the international physical activity questionnaire (IPAQ): meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr 2013;16:440–52. 10.1017/S1368980012002996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Troiano RP. Large-scale applications of accelerometers: new frontiers and new questions. Med Sci Sports Exerc 200739:1501 10.1097/mss.0b013e318150d42e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Freedson PS, Melanson E, Sirard J. Calibration of the computer science and applications, inc. Accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998;30:777–81. 10.1097/00005768-199805000-00021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Freedson PS, Lyden K, Kozey-Keadle S, et al. Evaluation of artificial neural network algorithms for predicting METs and activity type from accelerometer data: validation on an independent sample. J Appl Physiol 2011;111:1804–12. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00309.2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ferguson T, Rowlands AV, Olds T, et al. The validity of consumer-level, activity monitors in healthy adults worn in free-living conditions: a cross-sectional study. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2015;12:42 10.1186/s12966-015-0201-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003;35:1381–95. 10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Evenson KR, Goto MM, Furberg RD. Systematic review of the validity and reliability of consumer-wearable activity trackers. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2015;12:159 10.1186/s12966-015-0314-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ward DS, Evenson KR, Vaughn A, et al. Accelerometer use in physical activity: best practices and research recommendations. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2005;37:S582–8. 10.1249/01.mss.0000185292.71933.91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]