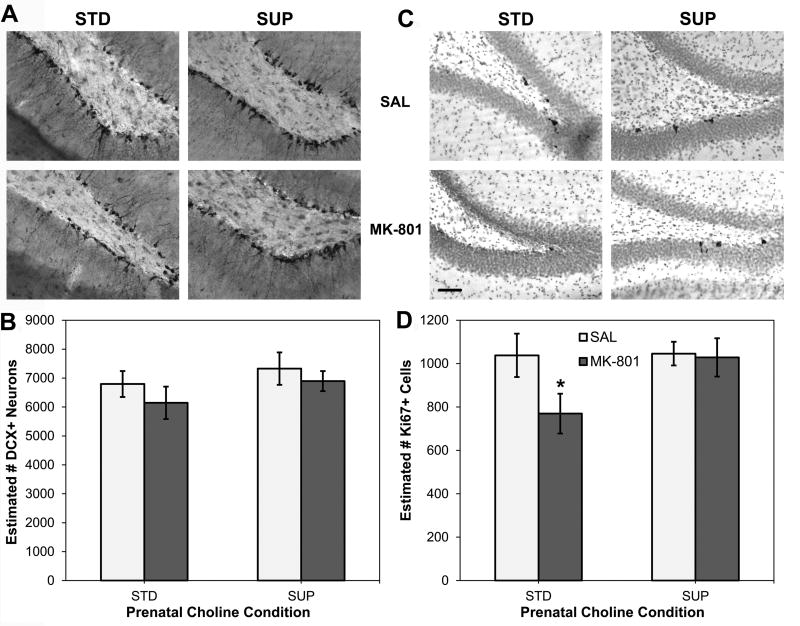
Figure 5.
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cell proliferation as a function of prenatal dietary condition and high dose MK-801 or saline administration. Photomicrographs of doublecortin (DCX) immunohistochemistry to mark new, immature neurons from representative rats from each condition are shown in (A). There were no significant changes to numbers DCX+ neurons in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus with either MK-801 administration or prenatal choline supplementation (B). Photomicrographs of Ki67 immunohistochemistry to mark dividing cells from representative rats from each condition are shown in (C). MK-801 administration significantly reduced the numbers of Ki67+ cells in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and this effect was prevented by prenatal choline supplementation (D). Photomicrographs are 200× magnification and bar in STD-MK-801 image in (C) represents 25 µm and applies to all images. *p<0.05 versus STD-SAL and SUP-MK-801.