Abstract
Racism, whether defined at individual, interpersonal, or structural levels, is associated with poor health among Blacks. This association may arise because exposure to racism causes poor health, but geographic mobility patterns pose an alternative explanation—namely, Black individuals with better health and resources can move away from racist environments. We examine evidence for selection effects using nationally representative, longitudinal data (1990–2009) from the Panel Study on Income Dynamics (N=33,852). We conceptualized state-level racial animus as an ecologic measure of racism and operationalized it as the percent of racially-charged Google search terms in each state. Among those who move out of state, Blacks reporting good self-rated health are more likely to move to a state with less racial animus than Blacks reporting poor self-rated health (p = .01), providing evidence for at least some selection into environments with less racial animus. However, among Blacks who moved states, over 80% moved to a state within the same quartile of racial animus, and fewer than 5% resided in states with the lowest level of racial animus. Geographic mobility patterns are therefore likely to explain only a small part of the relationship between racial animus and self-rated health. These results require replication with alternative measures of racist attitudes and health outcomes.
Keywords: neighborhood/place, quality of life, psychological stress, migration
Racial disparities in health are well documented [1–4], and multiple explanations for these disparities have been posited, including socioeconomic status [5–7] and differential preventative care usage [8–10]. Because racial disparities persist after accounting for these factors [11–14], researchers have looked toward other risk indicators, including racism [15, 16]. Proposed pathways for how racism impacts health include adverse living conditions due to segregation [17] and the stress of experiencing racism [18].
Racism occurs at multiple levels, ranging from individual to structural [19–21]. Most research has focused on racism at the individual and interpersonal levels, which predict adverse health outcomes among Blacks (reviewed in: [22]). Structural racism—which refers to the totality of macrolevel systems, including both institutions and ideologies, that work through various social processes to generate, sustain, and legitimize inequities among racial and ethnic groups [23–25]—can also contribute to racial disparities in health [19, 26]. Racist attitudes, measured at the community level, have been conceptualized as a critical manifestation of racist ideology that not only reflect but also shape other indicators of structural racism, such as policy regimes. An emerging literature suggests that community-level racial animus may also be a risk factor for poor health among Blacks [27–30].
However, mobility patterns pose an alternative explanation for a causal role of area-based racial animus on health [31]—namely, that individuals with better health have more opportunities to exit more racist environments. Thus, according to this selection hypothesis, Blacks have worse health in highly racist environments not because areas with high levels of racism cause poor health directly (i.e., social causation), but because Blacks in poor health are less able to leave racist environments (i.e., social selection).
Few studies have examined whether selective mobility related to health and race can explain the relationship between racism and health among Blacks. Because socioeconomic inequality is one consequence of racism, studies of mobility patterns by race and socio-economic indicators can be informative. Geronimus et al. [31] recently documented little evidence that associations between neighborhood poverty and health are attributable to selective mobility. The authors showed that the U.S. population is generally highly mobile and that mobility is more common among healthy people; however, the net movement patterns are relatively stable and there was little evidence for migration differences among races. This study, however, did not include a measure of racism.
The present study was designed to address the question of social causation versus social selection as a predictor of Black-White disparities in self-rated health through examining 6 associations that together may help to adjudicate between these two competing explanations. For either explanation, we anticipate finding the following: (1) There are disparities in the incidence of poor self-rated health by race; and (2) state-level racism is associated with the development of poor self-rated health. For any exposure to be a determinant of health disparities, the marginalized group must either be more exposed than the dominant group, and/or the exposure must affect the marginalized group more than the dominant group. We test both: (3) Blacks are more likely than Whites to live in states with high levels of racism, and/or exposure to state-level racism has a differential effect on self-rated health of Blacks compared with Whites.
To evaluate evidence for the social selection hypothesis, we test: (4) whether individuals reporting good self-rated health are more mobile, and whether they are more likely to move to other states; and (5) whether Blacks reporting good self-rated health are more likely to move to states with lower levels of racism than Blacks reporting poor self-rated health; the same relation should not be observed for Whites (otherwise, according to this hypothesis, no Black-White difference in self-rated health by state-level racism would be produced). These two associations would support the selection hypothesis that healthy Black individuals move away from places with high levels of racism, leaving behind people prone to being or becoming sicker. In contrast, if (6) among individuals who do not move, state-level racism predicts the development of poor self-rated health among Blacks, but not Whites, this would provide evidence in support of the social causation hypothesis, which posits that racial animus itself causes poor self-rated health among Blacks.
METHODS
Sample
The Panel Study on Income Dynamics (PSID) is a nationally representative, longitudinal study of households in the U.S. [32]. We analyzed patterns of movement among respondents aged 18–96 who were interviewed in 1990 through 2009. Surveys were administered every year between 1990 and 1996, and every two years starting in 1997. We included self-identified Black and White respondents who were head of household throughout the study period and had a state of residence listed from 1990 to 2009. While health data has been collected since 1984, we chose 1990 as the baseline year as there were few respondents with poor health prior to 1990. In total, there are 16,580 respondents; 10,954 (66.1%) are White, and 5,626 are Black (33.9%). Of these, 11,163 respondents moved at least once, whereas 1,174 respondents never moved during these years (4,243 observations were missing movement information). Eligibility requirements differed per analysis and study aim (Table 1).
Table 1.
Sample characteristics.
| Characteristics | N White Subjects | % White Subjects | N Black Subjects | % Black Subjects | Total | % Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head of household, White or Black, Baseline state of residence provided, baseline age category provided | 10,954 | - | 5,626 | - | 16,580 | - |
| Reported ever moving | 7,173 | 65.48% | 3,991 | 70.94% | 11,163 | 67.33% |
| Reported never moving | 845 | 7.71% | 329 | 5.85% | 1,174 | 7.08% |
| Moved, but reported staying in state | 5,416 | 49.44% | 3,429 | 60.95% | 8,845 | 53.35% |
| Moved, reported going out of state | 1,757 | 16.04% | 562 | 9.99% | 2,319 | 13.99% |
| Provided health information | 3,958 | 36.13% | 2,104 | 37.40% | 6,062 | 36.56% |
| Provided baseline education information | 10,773 | 98.35% | 5,481 | 97.42% | 16,254 | 98.03% |
| Moved to different quartile + complete covariate information | 724 | 6.61% | 295 | 5.24% | 1,019 | 6.15% |
| Stayed within quartile + complete covariate information | 3,234 | 29.52% | 1,809 | 32.15% | 5,043 | 30.42% |
Measures
State-level racism
We operationalized state-level racism as the amount of racial animus at the state level, using the percentage of racially-charged Google search terms in each state from 2004–2007 [33]. This variable was calculated as the proportion of total Google searches containing the “N-word” (singular or plural), measured at the media market level and aggregated to the state level. To account for Google searches that may make use of the “N-word” but not be motivated by racist attitudes, this measure includes Google controls that normalize search volume for “African American,” for the N-word as ending in “a/ah” (as the word almost always appears in popular music), and for profane language [33, 34]. Data were unavailable for Alaska.
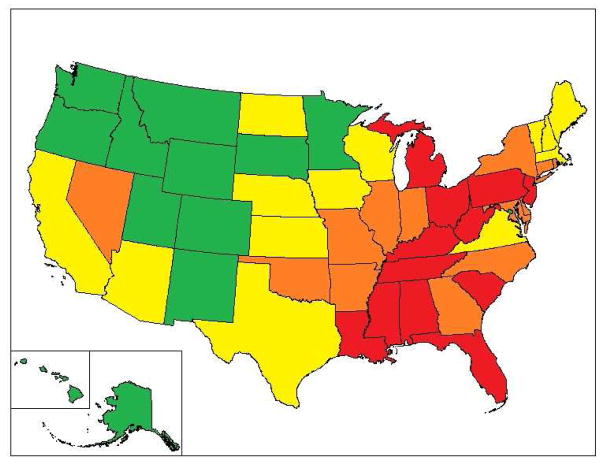
We divided this measure into four categories of state-level racial animus, grouping the states into approximate quartiles, with 12–13 states per category of state-level racism based on the ranking. Figure 1 shows the states in each category of state-level racism. There are fewer respondents in states in the lowest quartile (1,719, or 11.0%) and the greatest number of respondents in states in the highest quartile (5,876, or 37.5%).
Figure 1.
State-level racism using number of racially-charged Google search terms.
Notes. Red = highest quartile (most racist); orange = middle-high quartile; yellow = middle-low quartile; green = lowest quartile (least racist)
This measure, and the use of Google search terms to estimate state characteristics, has been validated in several ways. First, internet queries of health conditions have been used for disease surveillance, including influenza outbreaks, and some studies have suggested that these internet measures are a stronger predictor than pharmacy records [35, 36]. Second, the state-level racial animus measure strongly predicted the differential in 2008 votes for Barack Obama, versus 2004 votes for John Kerry [33]. Third, to further establish construct validity, we examined correlations between the Google search measure and 8 self-reported items measuring racist attitudes based on the General Social Survey (GSS) for the years 1990 and 2000. The overall correlation was strong and statistically significant (r=0.45, p<0.01).
One potential threat to validity is if state-level racial animus changed over time so that the Google measure does not reflect racial animus in 1990. To address this, we ranked each state with available data from the Google search measure and the GSS items from those showing the most racial animus to those showing the least for each of the items; we then computed an average ranking. The correlations between the rankings as determined by each individual item, as well as the aggregate for 1990 and 2000, are shown in Online Table 1. There was a high correlation between state rankings over time from the GSS and the state ranking using the Google search term measure (Cronbach coefficient α=0.63 using aggregates for 1990 and 2000), indicating stability for state-level racism across the last 30 years.
We chose not to use the GSS as a measure because data on racist attitudes from the GSS were missing from 13 states in 1990 and 2000, and this would have resulted in a loss of statistical power as well as potential for bias. Additionally, the Google measure may be a more valid indicator of racism than the self-report measures used in the GSS, as socially unacceptable attitudes like racism may be less censored when expressed in private online.
Self-rated health
At each interview wave, respondents were asked to report whether their health was “excellent, very good, good, fair, or poor.” Self-rated health (SRH) is a validated indicator of health distress and the presence of disease [37, 38], and it differentiates heightened mortality risk [39–41]. We defined a respondent as having “poor health” if they self-rated poor or fair health in at least two consecutive interviews. Further, respondents were defined as having “good health” if they self-reported good, very good, or excellent health in at least two consecutive interviews and never reported poor SRH in two consecutive interviews. After applying these criteria, data for SRH were available for 6,062 respondents.
Movement across states
Respondents were asked at each interview whether or not they had moved since the last interview and their current state of residence. We analyzed three different movement outcomes. The first assessed any movement during the study period, coded dichotomously as “moved” (7,173 Whites [65.48%]; 3,991 Blacks [70.94%]) and “did not move” (845 Whites [7.71%]; 329 Blacks [5.85%]). The second assessed movement out of state among movers, also coded dichotomously; respondents whose final state of residence was the same state as at baseline were defined as “stayed in same state” (N=8,845 [53.35%]), while those who listed a different final state of residence were defined as “moved to another state” (N=2,319 [13.99%]). The third movement outcome assessed state-level racism categories, comparing quartiles for baseline state of residence with final state of residence among movers; this enabled us to examine whether those who moved relocated to states with different levels of racism.
Covariates
Individual-level covariates, which were obtained from PSID data, included: individual health in 1990 (2 categories: poor vs. good); age in 1990 (4 categories: 18–29, 30–39, 40–49, and 50+); and education level in 1990 (3 categories: less than high school, high school or equivalent degree, at least some college). The Google measure of racial animus was also used as a covariate in analyses that included movement as the outcome. Two state-level covariates were used: (1) state-level poverty (percentage of the population below the poverty line in 1990) and (2) state-level median income (both obtained from the U.S. Census Bureau). Because of collinearity between these two measures (r=0.65), we included only state-level median income, which showed the strongest associations with self-rated health.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SAS Statistical Software (version 9.4), using complex survey procedures. We estimated the proportion of respondents who developed poor SRH using cross-tabulation. Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate all time-varying associations, and interactions between race and state-level racial animus in predicting poor SRH were tested on the multiplicative scale with cross-product terms. Individuals who did not develop poor SRH were censored based on the year that they were lost to follow up or the end of the study period. Analyses using time-invariant outcomes were estimated using logistic regression.
We performed sensitivity analyses based on years of follow-up in the study (Online Figure 1, Online Tables 2 – 8). On average, there were 8.7 years of follow up in the lowest racial animus group (min 1 year, max 20; SD=6.6) and 6.7 years of follow up in the highest racial animus group (min 1 year, max 20; SD=6.1). Among Whites, there were on average 6.4 years of follow up; among Blacks, there were on average 5.7 years. Given racial differences in the distributions of study participants, we replicated all analyses stratified two ways: first, among those with less than 7 years of follow up, and second, among those with more than 10. We present results in the paper based on the total sample, and stratified analyses as online supplements, as the results did not change.
RESULTS
First, we present evidence for associations that should be present for both the social selection and social causation explanations: (1) there are disparities in SRH by race; (2) state-level racism is associated with the development of poor SRH; and (3) Blacks are more likely than Whites to live in states with high levels of racism, and/or exposure to state-level racism has a differential effect on SRH among Blacks compared with Whites.
(1) Are there disparities in incident poor SRH by race?
Blacks were more likely to develop poor SRH than Whites and at a faster rate, providing evidence for racial disparities in incident poor SRH (Figure 3). Blacks had 1.54 times (95% CI: 1.39–1.71) the adjusted hazard of poor SRH compared with Whites (Table 2).
Table 2.
Hazard ratios of the association between race (Black vs. White) and self-rated health* by each confounder.
| Hazard ratios | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| Unadjusted association | 1.67 | 1.34 – 2.07 |
|
| ||
| Associations after adjustment for each covariate separately | ||
| Age in 1990 | 1.74 | 1.69 – 1.91 |
| State racial animus 1990 | 1.62 | 1.29 – 2.02 |
| Education in 1990 | 1.54 | 1.22 – 1.93 |
| Median state income in 1990 | 1.63 | 1.30 – 2.05 |
|
| ||
| Fully adjusted association | 1.54 | 1.39 – 1.71 |
Notes. We defined a respondent as having poor health if he/she self-rated poor or fair health in at least two consecutive interviews, starting in 1991 through 2009.
(2) Is racism at the U.S. state level associated with the development of poor SRH?
Blacks (Table 3) in the most racist states were more likely to develop poor SRH than were Blacks in the least racist states (58.6% vs. 50.5%, respectively). Among both Blacks and Whites, living in states with higher levels of racism was positively associated with developing poor SRH. Blacks in the highest-racism states had 1.20 (95% CI: .95–1.50) times the hazard of reporting poor SRH as those in the lowest-racism states (Table 3), with higher magnitude hazard ratios observed for those in the middle-high and middle-low quartiles. These conclusions were similar for initial and final state of residence (see Online Tables 2 and 3). Among Whites, those in higher-racism states were also more likely to develop poor SRH (AHR for highest racism states 1.33, 95% CI: 1.20–1.47).
Table 3.
Hazard ratios for the association between state-level racial animus of final state of residence and the development of poor self-rated health in Blacks and Whites.
| Model 1: White | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
| Poor Health* | Total N | HR | 95% C.I. | AHR** | 95% C.I. | |
|
| ||||||
| Highest quartile of state-level racial animus | 43.4% | 1687 | 1.39 | 1.28 – 1.51 | 1.33 | 1.20 – 1.47 |
| Middle high | 39.3% | 956 | 1.16 | 1.08 – 1.23 | 1.13 | 1.04 – 1.22 |
| Middle low | 37.1% | 1373 | 1.17 | 1.08 – 1.27 | 1.19 | 1.07 – 1.32 |
| Lowest quartile of state-level racial animus | 34.2% | 630 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
|
| ||||||
| Model 2: Blacks | ||||||
|
| ||||||
| Poor Health* | Total N | HR | 95% CI | AHR** | 95% CI | |
|
| ||||||
| Highest quartile of state-level racial animus | 58.6% | 1334 | 1.20 | .97 – 1.48 | 1.20 | .95 – 1.50 |
| Middle high | 57.0% | 927 | 1.17 | .922 – 1.50 | 1.31 | 1.05 – 1.63 |
| Middle low | 59.3% | 597 | 1.23 | .99 – 1.42 | 1.43 | 1.12 – 1.82 |
| Lowest quartile of state-level racial animus | 50.5% | 93 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
|
| ||||||
| Multiplicative interaction between state-level racial animus and race | Most racist | Middle high | Middle low | Least racist | ||
|
| ||||||
| p-value | 0.95 | 0.25 | 0.13 | Ref | ||
Notes.
We defined a respondent as having poor health if he/she self-rated poor or fair health in at least two consecutive interviews, starting in 1991 through 2009.
Adjusted for health status in 1990, age, education level in 1990, and state-level median income in 1990.
HR=Hazard Ratio; AHR=Adjusted Hazard Ratio; CI=Confidence Interval.
(3) Are Blacks more likely than Whites to live in states with high levels of racism? Does exposure to state-level racism have a differential effect on the SRH of Blacks compared with Whites?
Blacks were more likely than Whites to reside in more racist states (Table 4). For initial state of residence, 44.0% of Blacks lived in the highest-racism states, compared to 34.3% of Whites; conversely, only 3.7% of Blacks lived in the lowest-racism states, compared to 14.6% of Whites. These distributions were similar based on final state of residence. As Table 3 indicates, there was no indication that state-level racism has a differential effect on SRH among Blacks compared to Whites, as tests of the interaction between state-level racial animus and race were not statistically significant. Thus, state-level racism is associated with poor SRH for both Blacks and Whites.
Table 4.
Association between race and state-level racial animus: 1990 and 2009.
| Based on initial state of residence | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| Blacks N (%) | Whites N (%) | Total N | |
| Highest quartile of state-level racial animus | 44.0% | 34.3% | 5876 |
| Middle high | 32.3% | 21.3% | 3912 |
| Middle low | 20.1% | 2.98% | 4165 |
| Lowest quartile of state-level racial animus | 3.7% | 14.6% | 1719 |
| Total | 5202 | 10470 | 15672 |
| Based on final state of residence | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| Blacks N (%) | Whites N (%) | Total N | |
| Highest quartile of state-level racial animus | 44.2% | 34.1% | 5081 |
| Middle high | 32.2% | 21.7% | 3429 |
| Middle low | 20.4% | 29.4% | 3549 |
| Lowest quartile of state-level racial animus | 3.3% | 14.8% | 1453 |
| Total | 4714 | 8798 | 13512 |
Next, we examined the evidence for the social selection hypothesis.
(4a) Does SRH predict any moving (in or out of state)?
We first examined SRH as a predictor of any movement (Table 5). Most individuals (67.3%) in the study sample moved at least once. Individuals reporting good SRH were not more likely to move than individuals reporting poor SRH (Blacks: AOR = 1.03, 95% CI: 0.78–1.36; Whites: AOR = 2.17, 95% CI: 0.98–4.81).
Table 5.
Self-rated health at baseline predicting whether individuals moved (in or out of state) after 1990, by race.
| Baseline health predicting any movement after 1990, Whites | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| Never moved N (%) | Moved at least once N (%) | Total N | OR | 95% CI | AOR* | 95% CI | |
| Good | 4.7% | 95.3% | 2957 | 2.24 | 0.78 – 6.44 | 2.17 | 0.98 – 4.81 |
| Fair/Poor | 10.0% | 90.0% | 610 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Total | 201 | 3366 | 3567 | ||||
| Baseline health predicting any movement after 1990, Blacks | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| Health in 1990 | Never moved N (%) | Moved at least once N(%) | Total N | OR | 95% CI | AOR* | 95% CI |
| Good | 5.6% | 94.4% | 1162 | 1.32 | 1.02 – 1.72 | 1.03 | .78 – 1.36 |
| Fair/Poor | 7.3% | 93.7% | 744 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Total | 119 | 1787 | 1906 | ||||
Notes. Adjusted for age, education level in 1990, and state-level median income in 1990.
OR=Odds Ratio; AOR=Adjusted Odds Ratio; CI=Confidence Interval.
(4b) Does SRH predict moving to another state?
Table 6 shows results for moving out of state. In contrast to our analyses for moving at all (in or out of state), those reporting good SRH were more likely than those reporting poor SRH to move out of state (than to stay in state or not move), among Blacks (AOR = 1.26, 95% CI: 1.08–1.49) but not among Whites (AOR = 1.31, 95% CI: .98–1.75). Results were significant for both groups when we examined only those who ever moved at least once (Blacks: AOR = 1.20, 95% CI: 1.02–1.42; Whites: AOR = 1.31, 95% CI: 1.15–1.51). In summary, reporting ever moving is not associated with health among our study participants, but among those who do move, movement out of state is associated with good SRH. However, 75.5% of Whites and 85.9% of Blacks who moved stayed in the same state.
Table 6.
Self-rated health in 1990 predicting whether individuals moved out of state after 1990, by race.
| Baseline health predicting different final state than initial state, Whites | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| Never moved out of state N (%) | Moved at least once out of state N (%) | Total N | OR | 95% CI | AOR* | 95% CI | |
| Good | 78.2% | 21.8% | 3243 | 1.38 | .95 – 2.02 | 1.31 | .98 – 1.75 |
| Fair/Poor | 83.2% | 16.8% | 715 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Total | |||||||
| Baseline health predicting different final state than initial state, Blacks | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| Health in 1990 | Never moved out of state N (%) | Moved at least once out of state N(%) | Total N | OR | 95% CI | AOR* | 95% CI |
| Good | 83.1% | 16.9% | 1283 | 1.32 | 1.16 – 1.50 | 1.26 | 1.08 – 1.49 |
| Fair/Poor | 86.6% | 13.4% | 821 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Total | |||||||
|
|
|||||||
| Test for multiplicative interaction of race and movement | p-value | ||||||
|
| |||||||
| .98 | |||||||
| Baseline health predicting different final state than initial state among those who have ever moved, Whites | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| Moved but not out of state N (%) | Moved at least once out of state N (%) | Total N | OR | 95% CI | AOR* | 95% CI | |
| Good | 78.2% | 21.8% | 2817 | 1.37 | 1.14 – 1.65 | 1.31 | 1.15 – 1.51 |
| Fair/Poor | 83.1% | 16.9% | 549 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Total | |||||||
| Baseline health predicting different final state than initial state among those who have ever moved, Blacks | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| Health in 1990 | Moved but not out of state N (%) | Moved at least once out of state N(%) | Total N | OR | 95% CI | AOR* | 95% CI |
| Good | 83.1% | 16.9% | 1097 | 1.30 | 1.15 – 1.48 | 1.20 | 1.02 – 1.42 |
| Fair/Poor | 86.5% | 13.5% | 690 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Total | |||||||
|
|
|||||||
| Test for multiplicative interaction of race and movement | p-value | ||||||
|
| |||||||
| .84 | |||||||
Notes. Adjusted for age, education level in 1990, and state-level median income in 1990.
OR=Odds Ratio; AHR=Adjusted Odds Ratio; CI=Confidence Interval.
(5) Are Blacks and Whites reporting good SRH in 1990 more likely to move to other states with lower levels of racism than those reporting poor SRH in 1990?
Table 7 shows the proportion of movers that moved to a state that was the same, higher, or lower in quartile of racial animus as the state they were in at baseline. Among Blacks, those reporting good SRH were 1.30 (95% CI: 1.07–1.58) times as likely to move to a state lower in racial animus compared with those reporting poor SRH; the same association was not observed for Whites (AOR = 1.05, 95% CI: 0.76–1.45). In summary, among those who move out of state, those reporting good SRH are more likely to move to a state with lower levels of racial animus than those reporting poor SRH among Blacks but not Whites, providing some support for social selection.
Table 7.
Among all movers, the association between baseline self-rated health and movement across racism categories, by race.
| Higher quartile of state-level racial animus | Same quartile of state- level racial animus | Lower quartile of state-level racial animus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Among Whites | |||
| Good health at baseline (N = 3,234) | 5.1% | 81.1% | 13.8% |
| Poor health at baseline (N=715) | 1.4% | 84.5% | 14.1% |
| P<.0001 | |||
| Among Blacks | |||
| Good health at baseline (N = 1,283) | 2.6% | 84.2% | 13.3% |
| Poor health at baseline (N = 281) | 1.8% | 88.8% | 9.4% |
| P = .01 | |||
Finally, we examined the evidence for the social causation hypothesis. If living in a state with high levels of racial animus was causally associated with development of poor SRH, the association should be present among those who never moved.
(6) Among individuals who do not move and reported good SRH at baseline, is racism at the U.S. state level predictive of the development of poor SRH among Blacks, but not Whites?
Among Blacks, those in states at the highest quartile of racial animus were not significantly more likely to develop poor SRH (AHR = 1.91, 95% CI: 0.45–8.05) compared with those in the lowest quartile (Table 8). The sensitivity analysis for years of follow-up was not performed, as there were too few respondents for sub-analyses.
Table 8.
Association between state-level racism and development of poor self-rated health among a cohort of individuals in good health at baseline who never moved, by race.
| Whites (N=275) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||
| State- level racial animus | % developing poor health | HR | 95% CI | AHR* | 95% CI |
| Highest quartile | 80.7% | 1.19 | .91 – 1.56 | 1.34 | 1.05 – 1.71 |
| Middle high | 73.8% | .95 | .74 – 1.21 | .92 | .65 – 1.29 |
| Middle low | 66.7% | 1.19 | .90 – 1.56 | 1.15 | .92 – 1.45 |
| Lowest quartile | 60.5% | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
|
| |||||
| Blacks (N=169) | |||||
|
| |||||
| State- level racial animus | % developing poor health | HR | 95% CI | AHR* | 95% CI |
|
| |||||
| Highest quartile | 74.7% | 1.34 | .37 – 4.88 | 1.91 | .45 – 8.05 |
| Middle high | 75.5% | 1.28 | .32 – 5.12 | 2.21 | .52 – 9.42 |
| Middle low | 79.3% | 1.47 | .31 – 6.96 | 2.91 | .59 – 14.41 |
| Lowest quartile | 50.0% | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
Notes.
Adjusted for age, education level in 1990, and state-level median income in 1990.
HR=Hazard Ratio; ARR=Adjusted Hazard Ratio; CI=Confidence Interval.
Because the states at the highest quartile of racial animus were also the states with the largest number of Black residents, we performed sensitivity analyses on all Cox models including 1990 census estimates of state-level percentage Black population [42] as a covariate to adjust for potential confounding. We found that our estimated adjusted hazards ratios did not change in significance, direction, or interpretation.
DISCUSSION
Evidence suggests exposure to racism predicts adverse health outcomes among Blacks [16], including racial animus that varies across US states [26, 43]. There are at least two potential explanations for these findings. The social causation hypothesis posits that exposure to racism causes poor health among Blacks, whereas the social selection hypothesis attributes the observed association between racism and poor health to Blacks in good health selecting into low-racism environments, leaving behind those prone to poor health. Few studies have empirically evaluated the evidence for the selection hypothesis.
Using data from a longitudinal, nationally representative study, we began to address this gap in the literature. Results indicated that among those who move out of state, Blacks reporting good self-rated health are more likely to move to a state with less racial animus than Blacks reporting poor self-rated health, providing evidence for at least some selection into environments with less racial animus. However, only 14% of all subjects who moved ever reported leaving the state. Further, among Blacks who moved states, over 80% moved to a state within the same quartile of racial animus, and fewer than 5% resided in states with the lowest level of racial animus. These findings suggest that it is highly unlikely that selection alone can account for a racial disparity in SRH of the magnitude that we observed in this sample (the adjusted hazard ratio for poor health was more than 50% higher for Blacks than Whites). We therefore conclude that while selection is occurring, it only contributes to a small part of the observed racial differences in SRH. This conclusion is largely consistent with findings from Geronimus et al. [31], despite differences between the two studies.
Among the subsample that did not move over the course of the study, Blacks in states with high levels of racial animus were not significantly more likely to develop poor SRH than those in states with low levels of racial animus, adjusting for relevant confounders, providing little support for social causation. Prior research examining the relationship between community-level racist attitudes and the health of Blacks has generally found support for these relationships, but these studies are either cross-sectional or, if longitudinal, have rarely conducted analyses among non-movers [27, 28]. We note, however, that our results trend in the same direction, with a fairly large effect size: while 75% of Blacks in the highest-racism states developed poor SRH, only half of those in the lowest-racism states did. The lack of statistically significant results may be due to low statistical power, as these analyses were only conducted among 329 Blacks (5.85% of all Black subjects), or to differences between our measure of racial animus and those used in other studies, which have tended to use explicit self-reported measures of attitudes.
The history of mobility patterns among Black Americans has been shaped by the enduring legacy of segregation, ranging from institutional policies by the federal government to discrimination by local housing authorities and landlords [17]. Blacks continue to face barriers to mobility imposed by institutional factors that are more likely to affect Blacks than Whites, such as housing restrictions based on imprisonment history, as well as by cultural norms or interpersonal attitudes [44]. Americans move for a variety of reasons, including economic opportunities or to be close to family or better schools; those in good health, however, may be more able to take advantage of these opportunities [31]. In the case of Blacks Americans, these may come into conflict with each other; moving to a place with less segregation, for example, could mean moving away from a place with a great amount of family stability. Understanding the mechanisms that underlie the relationship between racism, health, and geographic mobility can help us to better evaluate the impact of these social processes on creating and perpetuating disparities.
Though health is not the only driver of geographic mobility, our aim was not to explain all the reasons for mobility among Blacks and Whites. This study was designed to answer a narrow research question: we were interested in quantifying the relative contribution of social selection processes that may underlie observations of an association between markers of societal racism and health. In this analysis, we found patterns consistent with the predictions of social selection, though these alone did not account for the disparities in SRH.
Limitations
U.S. states differ in ways other than levels of racism. We controlled for state-level median income, but there may be other unobserved, unmeasured factors influencing both geographic mobility and self-rated health and correlated with state-level racism. Further, while individual income likely predicts an individual’s propensity to move, this information was substantially missing in the data so we did not adjust for it. Loss to follow-up was common; nearly half the sample died or dropped out over the course of the study. We used person-time methods to account for differential losses to follow up, but movement and health outcomes after losses to follow up cannot be established. We measured racial animus at the state level, but the racial climate may vary within states, which could bias our results given that most movement was in state. Our survey-weighted model did not have the capability to take into account multiple moves in and out of state. Given how common moving is, understanding the dynamics of moving at a finer geographic level may help to clarify the mechanisms driving health disparities.
Conclusion
Within the field of social epidemiology, there is great interest in how social environments shape population health. Addressing whether social factors are causally related to poor health is of central importance not only to theories of the determinants of population health, but also to interventions and public policies. While numerous studies have consistently documented the existence of health disparities and their relationship to the social determinants of health, far fewer have empirically addressed the mechanisms that operate to create and perpetuate these disparities. The current study represents an initial attempt to evaluate social selection and causation hypotheses as they relate to research on racism and racial health disparities. Our study only examined one health outcome, one measure of racial animus at the state level, and one type of social selection. Future studies are needed to replicate our results using other samples and different measures of racism and health. Moving forward, utilizing new technologies to capture measurements of ambient social attitudes, including racial animus, can help to further elucidate the mechanisms by which social processes impact health outcomes and health behaviors—as well as how and under what circumstances these attitudes may change over time.
Supplementary Material
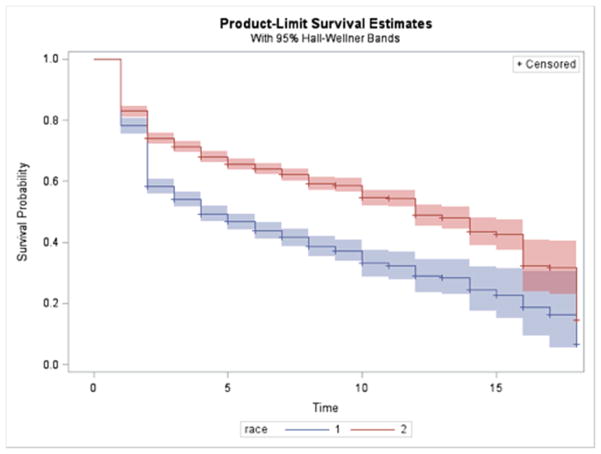
Figure 2.
Kaplan-Meier survival estimate of time to poor self-rated health among heads of household Whites (Red) and Blacks (Blue) in the Panel Study of Income Dynamics, 1990 through 2009.
Notes. p<0.0001 for the difference in curves between Blacks and Whites
Acknowledgments
Financial disclosure: The authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Conflict of interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Funding: The collection of data used in this study was partly supported by the National Institutes of Health under grant number R01 HD069609 and the National Science Foundation under award number 1157698. Authors also wish to acknowledge financial support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Health & Society Scholars program.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Contributor Information
Sarah McKetta, Department of Epidemiology, Mailman School Public Health, Columbia University, New York City, New York.
Mark L. Hatzenbuehler, Department of Sociomedical Sciences, Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University, New York City, New York
Charissa Pratt, Department of Epidemiology, Mailman School Public Health, Columbia University, New York City, New York.
Lisa Bates, Department of Epidemiology, Mailman School Public Health, Columbia University, New York City, New York.
Bruce G. Link, University of California Riverside, Riverside, California
Katherine M. Keyes, Department of Epidemiology, Mailman School Public Health, Columbia University, New York City, New York
References
- 1.Jemal A, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2001, with a special feature regarding survival. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Clegg L, et al. Cancer survival among US whites and minorities: a SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) Program population-based study. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tammemagi CM, et al. Comorbidity and survival disparities among black and white patients with breast cancer. JAMA. 2005;294(14):1765–72. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.14.1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Phelan JC, Link B. Is Racism a Fundamental Cause of Inequalities in Health? Annual Review of Sociology. 2015;41.1(2015) [Google Scholar]
- 5.Winkleby MA, et al. Socioeconomic status and health: how education, income, and occupation contribute to risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Am J Public Health. 1992;82(6):816–20. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.6.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mokdad AH, et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003;289(1):76–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Steyn K, Damasceno A. Lifestyle and Related Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases. In: Jamison DT, et al., editors. Disease and Mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa. Washington (DC): 2006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.White A, et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in colorectal cancer screening persisted despite expansion of Medicare’s screening reimbursement. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011;20(5):811–7. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Crawford ND, Jones CP, Richardson LC. Understanding racial and ethnic disparities in colorectal cancer screening: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2002 and 2004. Ethn Dis. 2010;20(4):359–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goel MS, et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in cancer screening: the importance of foreign birth as a barrier to care. J Gen Intern Med. 2003;18(12):1028–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2003.20807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Berry J, et al. Examining racial disparities in colorectal cancer care. J Psychosoc Oncol. 2009;27(1):59–83. doi: 10.1080/07347330802614840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vital signs. Vital signs: racial disparities in breast cancer severity--United States, 2005–2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012;61(45):922–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lannin DR, et al. Influence of socioeconomic and cultural factors on racial differences in late-stage presentation of breast cancer. JAMA. 1998;279(22):1801–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.279.22.1801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Geruso M. Black-white disparities in life expectancy: how much can the standard SES variables explain? Demography. 2012;49(2):553–74. doi: 10.1007/s13524-011-0089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Health Disparities and Inequalities Report -- United States, 2011. MMWR. 2011;60(Supplement) http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/other/su6001.pdf. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Williams DR, Mohammed SA. Discrimination and racial disparities in health: evidence and needed research. J Behav Med. 2009;32(1):20–47. doi: 10.1007/s10865-008-9185-0. State-level racial animus and self-rated health 32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Williams DR, Collins C. Racial Residential Segregation: A fundamental cause of racial disparities in health. Public Health Reports. 2001;116:404–416. doi: 10.1093/phr/116.5.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Clark R, et al. Racism as a stressor for African Americans. A biopsychosocial model. Am Psychol. 1999;54(10):805–16. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.54.10.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Krieger N. Methods for the scientific study of discrimination and health: an ecosocial approach. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):936–44. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Krieger N, et al. Racism, sexism, and social class: implications for studies of health, disease, and well-being. Am J Prev Med. 1993;9(6 Suppl):82–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Meyer IH. Prejudice as stress: conceptual and measurement problems. Am J Public Health. 2003;93(2):262–5. doi: 10.2105/ajph.93.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Paradies Y. A systematic review of empirical research on self-reported racism and health. Int J Epidemiol. 2006;35(4):888–901. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyl056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Link B, Phelan JC. Stigma Power. Social Science and Medicine. 2014;103:24– 32. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.07.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Powell J. Structural Racism: Building upon the insights of John Calmore. North Carolina Law Review. 2008;86:791–816. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gee GC, Ford CL. STRUCTURAL RACISM AND HEALTH INEQUITIES: Old Issues, New Directions() Du Bois review: social science research on race. 2011;8(1):115–132. doi: 10.1017/S1742058X11000130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lukachko A, Hatzenbuehler ML, Keyes KM. Structural racism and myocardial infarction in the United States. Soc Sci Med. 2014;103:42–50. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.07.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kennedy BP, et al. (Dis)respect and black mortality. Ethn Dis. 1997;7(3):207–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Leitner JB, et al. Blacks’ Death Rate Due to Circulatory Diseases Is Positively Related to Whites’ Explicit Racial Bias. Psychological Science. 2016;27(10):1299–1311. doi: 10.1177/0956797616658450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chae DH, et al. Association between an Internet-Based Measure of Area Racism and Black Mortality. PLoS One. 2015 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee Y, et al. Effects of racial prejudice on the health of communities: A multilevel survival analysis. American Journal of Public Health. 2015;105:2349–2355. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Geronimus AT, Bound J, Ro A. Residential mobility across local areas in the United States and the geographic distribution of the healthy population. Demography. 2014;51(3):777–809. doi: 10.1007/s13524-014-0299-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Panel Study of Income Dynamics. Public use dataset, produced and distributed by the Survey Research Center. Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan; Ann Arbor, MI: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stephens-Davidowitz S. The Effects of Racial Animus on a Black Presidential Candidate: Using Google Search Data to Find What Surveys Miss. 2012. Available at. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stephens-Davidowitz S. The cost of racial animus on a black candidate: Evidence using Google search data. Journal of Public Economics. 2014;118:26–40. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Carneiro HA, Mylonakis E. Google trends: a web-based tool for real-time surveillance of disease outbreaks. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49(10):1557–64. doi: 10.1086/630200. State-level racial animus and self-rated health 33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ginsberg J, et al. Detecting influenza epidemics using search engine query data. Nature. 2009;457(7232):1012–4. doi: 10.1038/nature07634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kaplan GA, et al. Inequality in income and mortality in the United States: analysis of mortality and potential pathways. BMJ. 1996;312(7037):999–1003. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7037.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jylha M, Volpato S, Guralnik JM. Self-rated health showed a graded association with frequently used biomarkers in a large population sample. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59(5):465–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Benyamini Y. Why does self-rated health predict mortality? An update on current knowledge and a research agenda for psychologists. Psychol Health. 2011;26(11):1407–13. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2011.621703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Idler EL, Benyamini Y. Self-rated health and mortality: a review of twenty-seven community studies. J Health Soc Behav. 1997;38(1):21–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.DeSalvo KB, et al. Mortality prediction with a single general self-rated health question. A meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(3):267–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2005.00291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.McKinnon J. The Black Population: 2000. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Krieger N, et al. The unique impact of abolition of Jim Crow laws on reducing inequities in infant death rates and implications for choice of comparison groups in analyzing societal determinants of health. Am J Public Health. 2013;103(12):2234– 2244. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bailey ZD, et al. Structural racism and health inequities in the USA: evidence and interventions. The Lancet. 389(0077):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30569-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.