Abstract
Background
Many Trichoderma species are applied as biofungicides and biofertilizers to agricultural soils to enhance crop growth. These filamentous fungi have the ability to reduce plant diseases and promote plant growth and productivity through overlapping modes of action including induced systemic resistance, antibiosis, enhanced nutrient efficiency, and myco-parasitism. Trichoderma species are prolific producers of many small metabolites with antifungal, antibacterial, and anticancer properties. Volatile metabolites of Trichoderma also have the ability to induce resistance to plant pathogens leading to improved plant health. In this study, Arabidopsis plants were exposed to mixtures of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by growing cultures of Trichoderma from 20 strains, representing 11 different Trichoderma species.
Results
We identified nine Trichoderma strains that produced plant growth promoting VOCs. Exposure to mixtures of VOCs emitted by these strains increased plant biomass (37.1–41.6 %) and chlorophyll content (82.5–89.3 %). Trichoderma volatile-mediated changes in plant growth were strain- and species-specific. VOCs emitted by T. pseudokoningii (CBS 130756) were associated with the greatest Arabidopsis growth promotion. One strain, T. atroviride (CBS 01-209), in our screen decreased growth (50.5 %) and chlorophyll production (13.1 %). Similarly, tomatoes exposed to VOCs from T. viride (BBA 70239) showed a significant increase in plant biomass (>99 %), larger plant size, and significant development of lateral roots. We also observed that the tomato plant growths were dependent on the duration of the volatile exposure. A GC–MS analysis of VOCs from Trichoderma strains identified more than 141 unique compounds including several unknown sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, and tetraterpenes.
Conclusions
Plants grown in the presence of fungal VOCs emitted by different species and strains of Trichoderma exhibited a range of effects. This study demonstrates that the blend of volatiles produced by actively growing fungi and volatile exposure time in plant development both influence the outcome of volatile-mediated interactions. Only some of our growth promoting strains produced microbial VOCs known to enhance plant growth. Compounds such as 6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one were not common to all promoting strains. We found that biostimulatory strains tended to have a larger number of complex terpenes which may explain the variation in growth induced by different Trichoderma strains.
Keywords: Volatile organic compounds, Trichoderma, Plant growth, Arabidopsis thaliana, Solanum lycopersicum, Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, Plant–microbe interactions
Background
The genus Trichoderma is one of the most widely researched genera of filamentous fungi with numerous applications in agriculture, industry, and the environment [1, 2]. Several Trichoderma species have the ability to reduce plant diseases and promote plant growth and productivity by utilizing overlapping modes of action including induced systemic resistance [3, 4], antibiosis [5], enhanced nutrient efficiency [6], and myco-parasitism [7, 8]. In agriculture, Trichoderma species are robust biological control agents and are often added to soils to increase crop yields and control soil-borne pathogen worldwide. It has been estimated that in India alone, more than 250 Trichoderma-based formulations are sold commercially [9–11]. Moreover, since Trichoderma species possess innate resistance to many chemicals used in agriculture such as fungicides, they are readily integrated into pest management practices [12].
Trichoderma species are prolific producers of many small metabolites with medical and agricultural significance [13, 14]. Secondary metabolites such as peptaibols and polyketides exhibit antifungal, antibacterial, and anticancer properties; induce resistance to plant pathogens; or serve as toxins [14, 15]. Volatile metabolites, also known as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), have low molecular mass, high vapor pressure (>0.01 kPa), low boiling point, and low polarity [16]. They are chemically diverse and include hydrocarbons, aromatics, amines, thiols, and terpenes [17, 18]. Relatively little is known about the metabolic origin of these compounds in fungi but in plants, similar volatiles are produced as breakdown products of fatty acids, others are biotransformation products of molecules produced in central metabolism while the terpenes are secondary metabolites [19, 20].
Furthermore, there are limited studies focused on Trichoderma VOCs and their impact on plant growth. For example, the coconut odor volatile, 6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one (6PP), is one of the earliest volatile compounds to be characterized from Trichoderma; however, it was studied for its use as a “nature identical flavouring” in the food industry [21, 22]. It was not until 2008 that the effects of 6PP on plant growth and disease symptoms were examined. Adding 6PP (0.166–1 mg/l) to plant growth media or directly applying a 6PP solution to plant leaves induced growth promotion and reduced disease symptoms [23]. Recently, our laboratory has reported the ability of mixtures of VOCs from Trichoderma viride to stimulate plant growth in the absence of pathogen attack or physical contact with the plant. Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to T. viride-derived VOCs had increased plant size, fresh weight, chlorophyll, root growth, and number of flowers even in the absence of pathogen threat [24]. The volatile-mediated plant growth promotion was dependent on Trichoderma species, culture, developmental stage of the plants, and duration of the exposure [24, 25].
Many species of Trichoderma are useful biocontrol organisms known to enhance crop yields when added to soils. Our recent studies demonstrate that T. viride and T. atroviride may be able to increase plant vigor by emitting volatile blends. The aims of this study were to demonstrate that Trichoderma VOCs are a major factor in plant growth promotion, identify potential strains, and identify compounds or combination of compounds that could be directly applied to induce plant growth. To this end, we assessed Arabidopsis growth and development when plants were grown in a shared atmosphere with VOCs emitted by 20 Trichoderma strains from 11 different species. We also replicated the VOC-induced growth enhancement effects with the economically important crop, Solanum lycopersicum (tomato). Finally, we characterized the volatile profiles emitted by strains using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) analysis and assessed trends shared among positively acting Trichoderma strains.
Methods
Cultivation of fungal strains
Trichoderma strains were obtained from Dr. Amy Y. Rossman at USDA-ARS, Beltsville, MD. See Table 1 for strain number, as well as the original location and substrates from which the strains were isolated. Cultures were maintained on potato dextrose agar (PDA) or malt extract agar (MEA) (Difco) at 27 ± 2 °C in the dark with >80 % humidity. For the volatile-exposure bioassay, the fungus was grown in a 35 × 10 mm Petri dish containing 4 ml of MEA and incubated for 5 days at 27 ± 2 °C.
Table 1.
Trichoderma strains screened for volatile-induced growth promotion
| Strain # | Trichoderma species | Strain code | Location | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T. aggressivum | DAOM222156 | ON, Canada | Mushroom casing |
| 2 | T. aggressivum | IMI 393970 | PA, USA | Mushroom compost |
| 3 | T. asperellum | CBS 433.97 | Beltsville, MD, USA | Soil, sclerotia buried in sesame plot |
| 4 | T. asperellum | GJS 02-65 | Douala, Loum, Cameroon | Soil, Xanthosoma sagittifolium roots and soil |
| 5 | T. atroviride | CBS 351.93 | NC, USA | Soil, forest |
| 6 | T. atroviride | GJS 01-209 | Cameroon | Palm |
| 7 | T. atroviride | JWB | New Orleans, LA, USA | Building, Hurricane Katrina damaged |
| 8 | T. brevicompactum | CBS 109720 | NY, USA | Soil, under Helianthus |
| 9 | T. harzianum | CBS 226.95 | United Kingdom | Soil |
| 10 | T. harzianum | CBS 227.95 | United Kingdom | Soil |
| 11 | T. inhamantum | CBS 273.78 | Colombia | Soil, maize field |
| 12 | H. koningii | CBS 989.97 | MD, USA | Decorticated wood (T. koningii type specimen) |
| 13 | T. longibrachiatum | CBS 118642 | Mexico | Soil |
| 14 | T. longibrachiatum | TR97 | OH, USA | Soil |
| 15 | T. pseudokoningii | CBS 480.91 | Australia | Wood, decayed |
| 16 | T. pseudokoningii | CBS 130756 | Australia | Wood, decorticated |
| 17 | T. stromaticum | GJS 00-127 | Bahia, Brazil | Theobroma cacao, pod |
| 18 | T. virens | DAOM167651 | GA, USA | Soil, cultivated |
| 19 | T. viride | BBA 70239 | Denmark | Building, water damaged |
| 20 | T. viride | GJS 04-379 | Brazil | Soil |
Abbreviations of culture collections and collectors as follows: BBA Biologisches Bundesanstalt, Berlin, Germany; CBS Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht, The Netherlands; DAOM Canadian Collection of Fungal Cultures, Ottawa, Canada; GJS Gary J. Samuels collection (Culture collection of the United States Department of Agriculture, Systematic Botany and Mycology Lab, Beltsville, MD, USA); IMI International Mycological Institute (New Zealand); JWB Joan W. Bennett collection (Rutgers, New Brunswick, NJ, USA); TR Earl Nelson collection (USDA-ARS, Beltsville)
Plant materials and growth conditions
Arabidopsis thaliana seeds (ecotype Columbia-7) were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (Columbus, OH). The seeds were surface-sterilized in 95 % ethanol for 30 s followed by a 20 % bleach solution for 30 min with constant agitation. Five surface-sterilized seeds were sown onto a 100 × 15 mm partitioned Petri dish (also known as split or I-plate) or 60 × 15 mm Petri dish containing Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium (pH 5.7) with vitamins, 3 % sucrose, and 0.03 % phytagel (Phytotechnology Laboratories, KS). Seeds were stratified at 4 °C for 3 days prior to volatile exposure.
Seeds of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. cv. Ponderosa) were purchased commercially. Seeds were surface sterilized with 70 % ethanol for 30 s and a 15 % bleach solution for 20 min with constant agitation. Prior to the exposure assay, two surface-sterilized seeds were sown onto a 473 ml volume sterile culture vessel (SteriCon, PhytoTechnology Laboratories, KS) containing 100 ml of MS media (1 % sucrose, 0.03 % phytagel, and pH 5.7).
Plant-Trichoderma volatile-exposure bioassay
Exposures of Arabidopsis plants to Trichoderma VOCs were performed using a double plate-within-a-plate system according to previously described methods [25]. Briefly, a small Petri plate (35 × 10 mm) containing sporulating Trichoderma grown on MEA was placed into a larger partitioned Petri dish (100 × 15 mm) containing five stratified A. thaliana seeds. They were grown together in a shared atmosphere in a growth chamber with a 16 h photoperiod at 23 ± 1 °C, 45 % relative humidity, and 180 µmol m−2 s−1 light for 14 days. For controls, plants were exposed to the fungal growth medium alone.
To expose tomato seeds, a Petri plate (35 × 10 mm) containing the Trichoderma culture was placed inside a sterile foil container (50 ml volume); together they were then placed inside the culture vessel containing sterilized seeds. Tomato seeds were germinated in the presence of Trichoderma VOCs and grown with one another in a shared atmosphere in a growth chamber with a 16-h photoperiod at 25 ± 1 °C for 21 days. At the end of the VOC exposure periods, the Arabidopsis and Solanum plants were removed from the exposure conditions, photographed, and the fresh weight of plant shoots and total chlorophyll content were measured. Total chlorophyll content of plants exposed to Trichoderma VOCs was determined by submerging the shoot overnight in 1 ml of 80 % acetone in the dark at 4 °C. The total chlorophyll content (chlorophyll a and b) was calculated from the equation [(8.02)(A663) + (20.2)(A645)]V/1000 × W, where V is volume and W is plant fresh weight [24]. The chlorophyll data were expressed in relation to the fresh weight of the plant shoot. Five replicates were used per volatile exposure condition, and the experiments were repeated three times. Quantitative results were expressed as standard error of the mean and analyzed using R Statistical Software (version 3.2.3 Wooden Christmas Tree). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Student’s t test were performed for plant exposure quantitative data.
CO2 assays
Total CO2 production by Trichoderma was measured using a CO2 meter (CO2Meter Inc. Osmond Beach, FL) at 8 h intervals for the duration of the experiment. Trapping experiments were performed in the plate-within-a-plate system where plants and fungi were grown in a shared atmosphere as described above. In separate experiments, a sterile cotton ball containing 3 ml of 0.1 M KOH was placed onto a sterile polypropylene cap (13 mm diameter). Then the cap containing the cotton ball was placed into an empty region of the plate containing the fungal culture. At the end of the exposure period, the cotton ball was fully dried and the dry weight of K2CO3 was obtained.
VOC analysis by headspace GC–MS
For headspace volatile analysis, Trichoderma cultures were grown in a 500 ml glass flask containing 250 ml of MEA with a 16 h photoperiod at 27 ± 2 °C for 7 days. VOC capture and analysis were conducted as described previously using a purge and trap method [25]. Headspace samples taken from sterile MEA served as negative controls. The headspace of the flask was purged at 100 ml per min for 4 h. The VOCs were adsorbed on 6 cm Tenax columns (Scientific Instrument Services, Ringoes, NJ), recorded and analyzed with a Varian 3400 gas chromatograph (GC) mated to a Finnigan Mat 8230 mass spectrometer (MS). The GC was equipped with a 60 m, Equity-5 (SigmaAldrich Corp., St. Louis, MO) column: 0.32 mm diameter, 1 mm film thickness. The compounds were desorbed onto a −20 °C cryotrap with a TD-4 short path thermal desorption apparatus (Scientific Instrument Services, Ringoes, NJ). The GC conditions were: 10:1 split, helium carrier at 20 psi, oven temperature from −20 to 280 °C at 10 °C per min. The MS conditions were: positive ion mode, electron impact spectra at 70 eV. The MS of the peaks were determined by their scatter pattern. Internal standards (d-6 benzene, d-8 toluene, and d-8 naphthalene) were used to normalize the peak areas. The linear regression coefficient was used to calculate the concentrations in the samples from peak areas obtained in the chromatographs. Compounds were identified by comparison of spectra obtained from the Trichoderma samples with those from a reference library (NIST 08 Mass Spectra Library, National Institute of Standards and Technology). GC–MS analysis was conducted in triplicates for each strain.
Results
Strain specific volatile-mediated plant growth promotion
Twenty Trichoderma strains (Table 1) were screened. Following 14 days of exposure, plants were collected for measurement of fresh weight and total chlorophyll content of plant shoots (see Fig. 1). We defined a strain as growth promoting if both the plant fresh shoot weight and total chlorophyll content were significantly higher than controls. We identified nine strains representing six different species that promoted Arabidopsis growth: T. aggressivum (strains DAOM222156 and IMI 393970); T. asperellum (GJS 02-65); T. harzianum (CBS 226.95); T. longibrachiatum (strains CBS 118642 and TR97); T. pseudokoningii (strains CBS 480.91 and CBS 130756); and T. viride (GJS 04-379). Plant growth was enhanced by exposure to the nine strains including T. viride (BBA 70239) which is shown as a representative in Fig. 2b. The strongest volatile-mediated plant effects were observed in T. aggressivum (IMI 393970) with an increase of 37.1 % in fresh shoot weight and 82.5 % in chlorophyll and in T. pseudokoningii (CBS 130756) with an increase of 41.6 and 89.3 %, respectively. In contrast T. atroviride (CBS 01-209) emitted inhibitory VOCs, leading to small plants with a 13.1 % decrease in fresh shoot weight and 50.5 % decrease in chlorophyll. In addition to a reduction in fresh weight, we observed localized death in leaves (Fig. 2c). Half of the strains screened in this study did not alter the growth of Arabidopsis plants under our test conditions and looked similar to control plants (Fig. 2a).
Fig. 1.
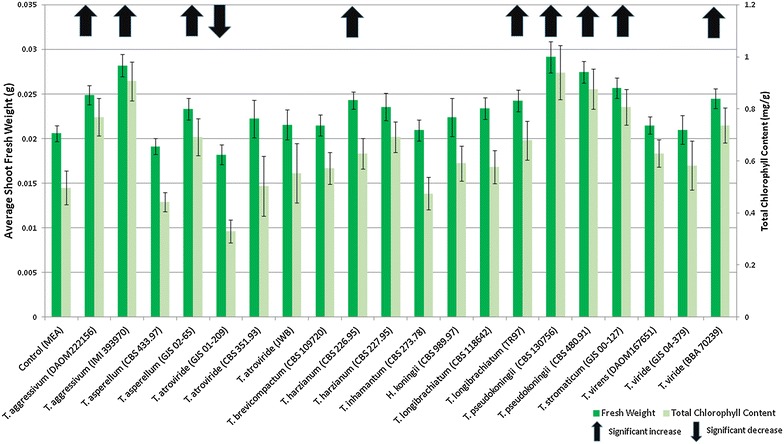
Average fresh weight and total chlorophyll content of Arabidopsis thaliana plants grown in a shared atmosphere with 20 different strains of Trichoderma for 14 days. Controls were grown without fungi. (n = 25, ANOVA P = 0.001)
Fig. 2.
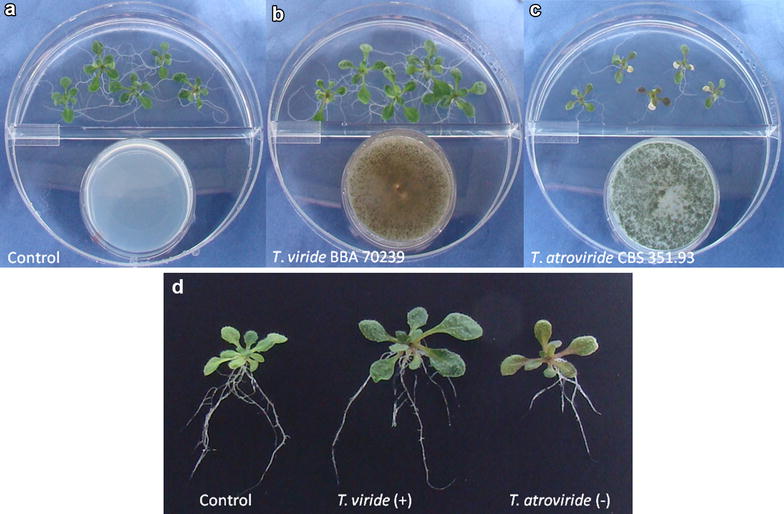

Growth of Arabidopsis thaliana in a shared atmosphere with Trichoderma for 14 days. a Control plants exposed to MEA medium, b plants exposed to T. viride (BBA 70239) are larger, c plants exposed to T. atroviride (CBS 351.93) are smaller, and d Arabidopsis plants removed from growth medium following 14-day Trichoderma volatile exposure
We measured CO2 production by Trichoderma using a CO2 monitor and did not find a significant difference between CO2 production by the fungi and ambient air in our testing conditions. We observed similar CO2 levels between ambient and Trichoderma air ranging between 400 and 600 ppm of CO2 throughout the duration of our experiment. In addition, trapping Trichoderma-derived CO2 with 0.1 M KOH solution did not remove the observed volatile-induced beneficial effects. We observed a 41 % increase in chlorophyll for plants exposed to Trichoderma VOCs and KOH solution (0.68 mg/g) compared to negative control grown only in KOH (0.4 mg/g).
The effects of Trichoderma volatiles on tomato shoot and root growths
We selected the Arabidopsis growth promoting strain, T. viride (BBA 70239) and measured plant growth to assess its effects on tomato growth after 14 and 21 days of exposure. We selected this strain because it grew prolifically, sporulated readily, and was identified as a strain that did not produce the plant growth promoting compound, 6PP. Tomato seedlings exposed to T. viride VOCs were larger in size (Fig. 3), with increases in the lateral root development (Fig. 3c). The fresh root weight was 61.2 % greater than controls. Similarly, tomato plants exposed to T. viride VOCs for 14 days had a significant increase in biomass (41.2 %) and chlorophyll concentration (70.7 %). Extending the duration of volatile exposure to 21 days led to a larger increase in both tomato fresh weight (99.7 %) and chlorophyll (100.1 %) (Fig. 4).
Fig. 3.
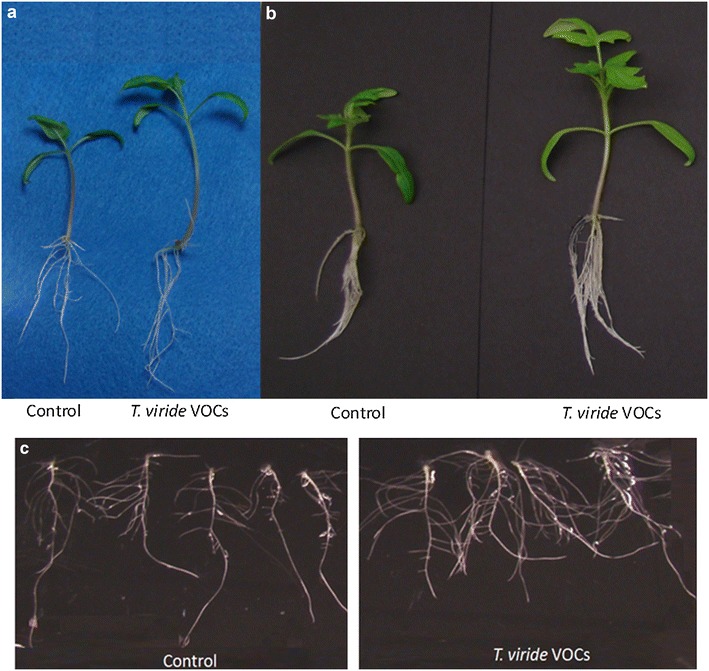

Tomato seedlings exposed to T. viride (BBA 70239) VOCs for a 14 days and b 21 days. c Roots of tomatoes exposed to Trichoderma VOCs for 21 days. Average fresh root weight of tomato seedlings exposed to Trichoderma VOCs for 21 days (0.135 ± 0.01 g) compared to controls (0.084 ± 0.018 g)
Fig. 4.
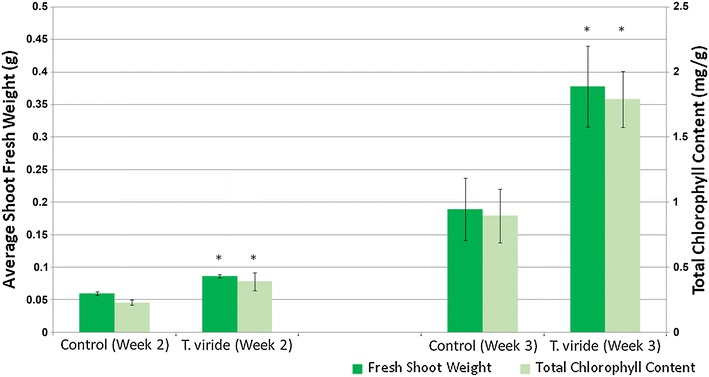
Shoot fresh weight and total chlorophyll content of tomato seedlings following 14- and 21-day-exposure to T. viride (BBA 70239) VOCs (n = 10, P = 0.01)
Identification of VOCs produced by Trichoderma
Trichoderma strains were grown separately on MEA for 7 days, and then the headspace was collected for 4 h and analyzed by GC–MS. Trichoderma strains differed in types and abundance of volatiles detected by headspace analysis. A total of 141 unique volatile compounds were detected at least twice per strain (Table 2). They encompassed hydrocarbons, alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, alkanes, alkenes, esters, aromatic compounds, heterocyclic compounds, and various terpenes. C8 and C10 compounds were dominant, making up 17.01 and 15.64 %, respectively, of the VOCs identified in this study. We also found unknown monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and tetraterpenes with molecular weights of 204, 222, 272 and 290 (data not presented). No terpenes were detected in headspace samples from MEA controls.
Table 2.
Headspace volatile collection of Trichoderma strains (100 ml/min, purge rate, 4 h, 1 µg Int. Std. by P&T-TD-GC–MS)
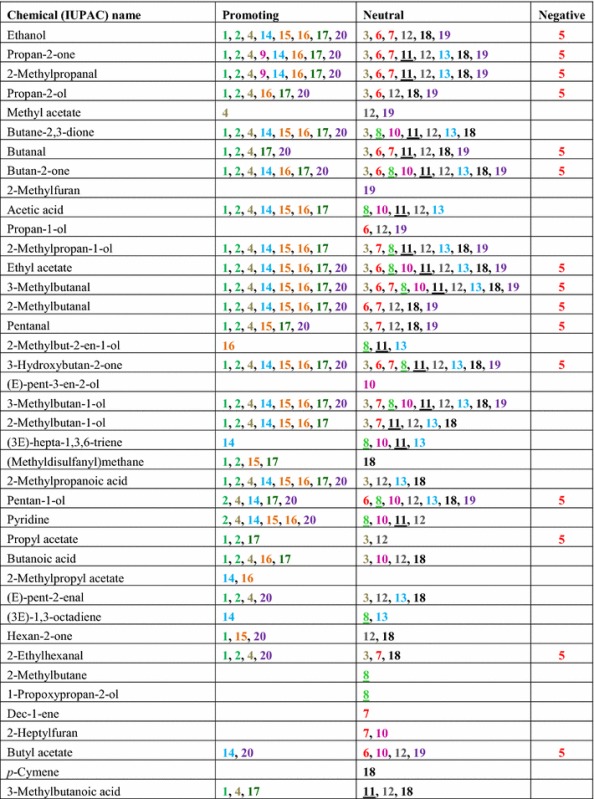
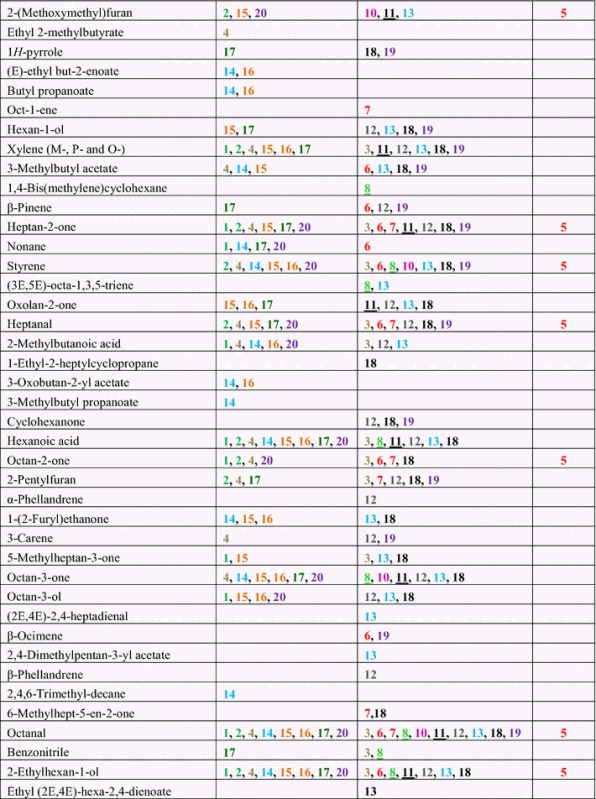
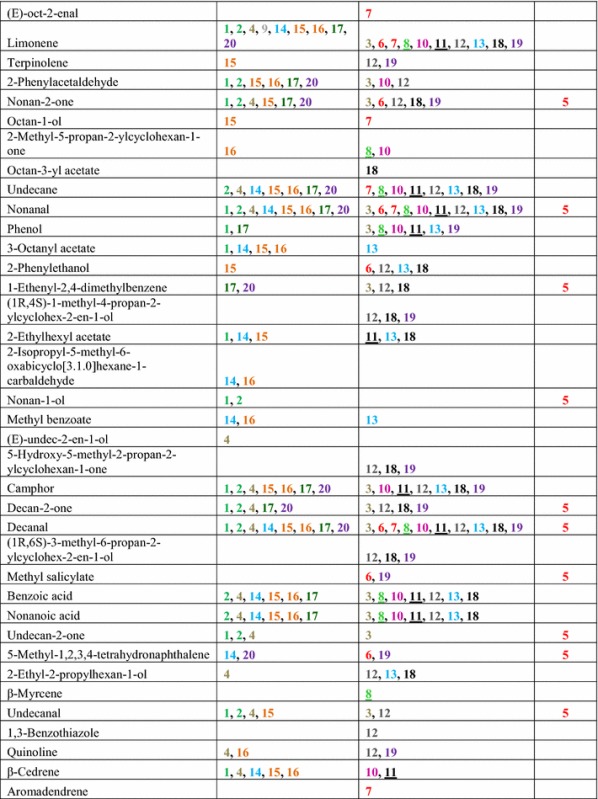
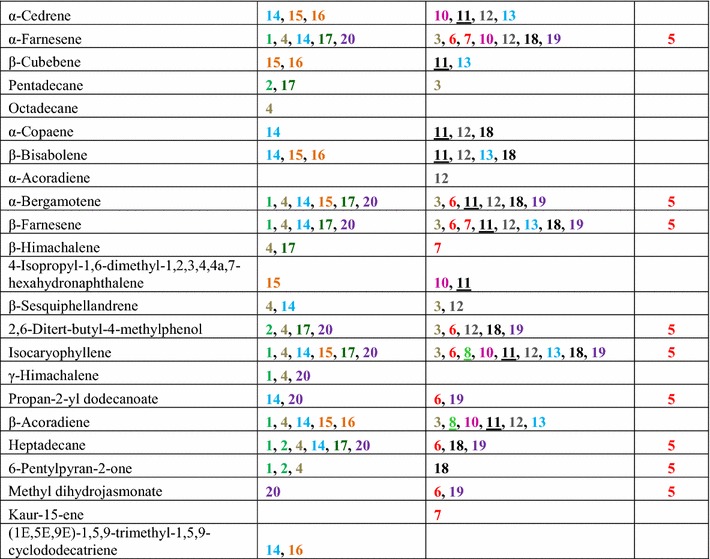
See Table 1 for strain number information. Same species are color coded
A Venn diagram representing the complete volatile profile of Trichoderma strains identified by GC–MS is presented in Fig. 5. Positively acting (‘promoting’) strains lead to significant increases in overall plant biomass and chlorophyll while “inhibiting” strains lead to reduced size, biomass, and chlorophyll. “Neutral” strains did not significantly alter plant growth following volatile exposure. Approximately 27.7 % of the compounds identified were produced by 14 or more strains (Fig. 5; Table 2). Of these, only four compounds (3-methylbutanal, octanal, nonanal, and decanal) were found in all strains. Other commonly produced VOCs included acetoin and 2-butanone (found in 18 strains), 3-methyl-1-butanol (found in 17), and 2-methyl-1-propanol and acetone (both found in 16). Several terpenes were commonly identified including limonene (18 strains), β-caryophyllene (16 strains), β-farnesene (14 strains), and 2-norpinene (13 strains). The largest number of compounds (39 %) was shared between those that induced growth promotion and those that did not significantly impact growth.
Fig. 5.
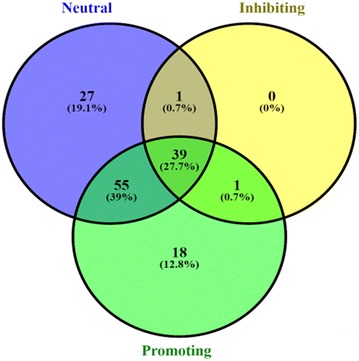
Comparison of Trichoderma volatile compounds identified by GC–MS. Compounds unique to Trichoderma strains that induced plant growth (green), inhibition (yellow), and no impact (blue)
One of the highest single concentrations of any volatile metabolite we identified in this study was 6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one [(6PP) 7559.45 ng/trap] produced by T. atroviride (GJS 01-209). This compound also was found in T. aggressivum (DAOM 222156 and IMI 393970), T. asperellum (GJS 02-65), and T. virens (DAOM 167651). Of these, only exposure to VOC mixtures from T. aggressivum and T. asperellum were associated with enhanced plant growth.
We found that 12.8 % of compounds identified were unique to plant growth promoting Trichoderma strains. They included ethyl 2-methylbutyrate and octadecane (T. asperellum GJS 02-65), 3-methylbutyl propanoate (T. longibrachiatum TR 97), and (2E,4E)-2,4-heptadienal (T. longibrachiatum CBS 118642). Compared to the neutral and inhibitory strains, plant growth promoting strains also produced a larger number of terpenes such as β-acoradiene, β-cubebene, β-cedrene, β-bisabolene, β-himachalene, and γ-himachalene. Compounds shared by growth promoting and neutral strains showed that only a minor portion of compounds (7 out of 56) were known to be produced from microorganisms while the rest are produced by both microorganisms and plants.
Discussion
Volatile-mediated interactions between plants and microbes have been gaining increased attention in agriculture [26–29]. For example, VOCs have been proposed as biological control agents leading to the reduction of plant disease [30–33]. Furthermore, it is known that beneficial rhizosphere bacteria such as Bacillus produce VOCs that enhance plant growth [34–38]. The ability of soil fungi such as Trichoderma species to produce plant growth enhancing VOCs has been recognized only relatively recently [23–25]. In this study, we screened 20 Trichoderma biocontrol strains comprising 11 species and demonstrated that nine of these strains emitted VOC mixtures that significantly improved plant growth in Arabidopsis as measured by biomass, plant size, and chlorophyll concentration. Although T. aggressivum and T. pseudokoningii emitted VOCs that influenced Arabidopsis growth positively, we do not have a sufficient number of strains for each species to claim that the species as a whole can improve plant growth. It is known that increased CO2 levels associated with microbial growth in a Petri plate system can lead to plant growth promotion [39, 40]; however, we did not find significant differences in the level of CO2 in microhabitats containing Trichoderma and ambient air. Furthermore, sequestering Trichoderma-produced CO2 by absorption in the Petri system did not reduce the growth promotion observed.
In order to determine if we could duplicate the Trichoderma VOC response in a crop plant, we grew S. lycopersicum (tomato) seedlings in a shared atmosphere with the growth promoting strain, T. viride (BBA 70239). Exposed tomato plants also displayed significant increase in plant biomass, larger plant size, and increased lateral root development. Previously, we showed that Trichoderma-volatile induced growth promotion in Arabidopsis was dependent on the duration of exposure [25] and that early removal of the fungi lead to loss of growth promotion. In this study, we showed that a 3-week exposure had a greater proportional impact than a 2-week exposure. Moreover we observed an acceleration of the transition of vegetative phases. Prolonged exposure to microbial VOCs to trigger plant growth and development also have been observed in Bacillus [41, 42]. Together, these studies have shown the importance of the amount of volatile exposure time during different plant development phases [25, 41]. Based on the changes observed in the volatile-treated tomato seedlings, we believe that the VOC-induced acceleration of flower and fruit development warrants further investigation.
Which components of the volatile mixture emitted by growing Trichoderma strains cause the growth promotion effects? All microbial VOCs are found as complex mixtures and the volatile production is influenced by environmental conditions (i.e. nutrient content, microbial community composition, temperature, humidity, and pH), making it difficult to pinpoint either the effects of individual volatile molecules or their mechanisms of action [16, 25, 42–44]. We first looked at several individual compounds that have been identified in the literature as being stimulatory or inhibitory to plant growth. The compound 6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one (6PP), a lactone with a coconut-like odor, is commonly produced by Trichoderma and has been shown to both improve and inhibit plant growth and health at different concentrations [7, 23]. Although 6PP was produced by five Trichoderma strains in this study, the presence of 6PP was not unique to all growth promoting strains and was also found in strains that did not significantly impact plant growth. Previous reports showed that plants exposed to the volatile phase of 3-methyl-1-butanol, limonene, and acetoin lead to changes in plant size and chlorophyll concentration [34, 45] and we found that most of our strains produced 3-methyl-1-butanol, 2-methyl-1-propanol, limonene, β-farnesene, and β-caryophyllene, all known to be common microbial volatiles [17, 46–48]. However, since these compounds were found to be ubiquitous, they are not likely to be the cause of our observed growth promotion. Low concentrations of 1-hexanol, a truffle volatile, had a growth-promoting effect on Arabidopsis [38] while at higher concentrations, 1-hexanol inhibited plant growth [49] illustrating the importance of volatile concentration. The strain that caused reduction in plant growth did not produce detectable 1-hexanol in our study. Since the negatively impacting T. atroviride strain did not produce compounds unique to this strain, we suspect other factors such as concentration of individual compounds and changing volatile profile over time may have attributed to the negative effects observed in our study.
However, many of the compounds we identified are reported from plant research. Studies have shown that injured plants can influence the growth of neighboring plants through the release of certain plant VOCs that increase defense responses or growth [50, 51]. Several of the C8 compounds we found such as 3-octanol, 1-octanol, and 3-octanone have been characterized from wounded or infected plants [52–54]. Similarly, 3-carene, 2-methyl-1-butanol, butanoic acid, hexanoic acid, β-bisabolene, β-sesquiphellandrene, and β-acoradiene are released by plants under stress [55–58]. Trichoderma strains that increased plant growth and those that did not significantly alter plants both produced these VOCs. Similarly, a large number of diverse terpenes known to be produced by plants were detected in growth promoting strains. Finally, compounds unique to growth promoting strains (16 out of 18 compounds) were volatiles typically emitted from flowers and ripening fruits. Of these, octadecane, (2E,4E)-2,4-heptadienal, and (E)-pent-3-en-2-ol are emitted by plants under stress [59–61].
Even though we found several VOCs that have been studied as plant growth promoting compounds, these individual compounds alone do not explain the variation in growth induced by different Trichoderma strains. Fungi emit a large number of VOCs and the volatile profile changes as the fungi grow and mature. As with bacterial VOCs, the blend of volatiles produced and the time in plant development at which volatiles are applied, together, influence the outcome of the interactions [42]. Since we have only taken a single time point for our GC-MS analysis, we recognize that our analysis is a temporal “snap shot” that does not capture the full range of VOCs likely to have been produced by the growing Trichoderma during the course of the plant exposure experiments. There are not enough samples to be statistically absolute in the volatile profiles and the concentrations of individual compounds. Nevertheless, because we detected several compounds produced by Trichoderma strains that are well known plant metabolites produced by plants under stressful conditions, we hypothesize that the volatiles emitted by growth promoting Trichoderma strains are mimicking plant metabolites, providing plant cues that ultimately trigger growth changes.
Conclusions
In conclusion, A. thaliana grown in the presence of fungal VOCs emitted by different species and strains of Trichoderma exhibited a range of endpoints that included increased plant size, neutral effects, or more rarely, growth inhibition. Plants exposed to Trichoderma strains were generally larger in size and greener in color. Only some of our growth promoting strains produced microbial VOCs known to enhance plant growth. Compounds such as 6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one were not common to all promoting strains. We found that biostimulatory strains tended to have a larger number of complex terpenes which may explain the variation in growth induced by different Trichoderma strains. It has been pointed out by Bailey and Melnick [62] that most Trichoderma research focuses on obtaining one candidate strain for formulation into an optimal biological control agent, with little work focused on the differences between strains. This study demonstrates that the blend of volatiles produced by actively growing fungi, strain-specific volatile profile, and volatile exposure time in plant development influence the outcome of volatile-mediated interactions.
Authors’ contributions
SL performed experimental work, data analysis, and co-wrote the manuscript. MY performed the experimental work and GB performed data analysis. SL and RH were responsible for conceptualization and methodology. All authors (SL, MY, GH, RH, and JWB) contributed to generating the manuscript. JWB supervised the experimental work and co-wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Gary Samuels and Amy Rossman for their insights on Trichoderma and for providing the fungal strains. Dr. Thomas G. Hartman and Dr. Bin Khong Khoo helped in analysis and identification of fungal volatiles. Prakash Masurekar, Shannon Morath, and Sally Padhi provided intellectual input. We thank all of them for their important help in this research. SL was supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program (Grant No. 0937373) and part of the work was funded by the Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (SARE), USDA—National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) (Grant No. GNE14-084-27806). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the view of the NSF, the SARE program or the USDA.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Funding
Part of the study and data collection was funded by the Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (SARE), USDA—National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) (Grant No. GNE14-084-27806).
Abbreviations
- VOCs
volatile organic compounds
- 6PP
6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one
- GC–MS
gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
- PDA
potato dextrose agar
- MEA
malt extract agar
- MS
Murashige and Skoog
- ANOVA
analysis of variance
- GC
gas chromatograph
- MS
mass spectrometer
Contributor Information
Samantha Lee, Phone: (848) 932-6235, Email: Samantha.LeexIII@gmail.com.
Melanie Yap, Email: mxy5151@psu.edu.
Gregory Behringer, Email: gregbehringer@gmail.com.
Richard Hung, Email: RichardHung8888@gmail.com.
Joan W. Bennett, Email: profmycogirl@yahoo.com
References
- 1.Schuster A, Schmoll M. Biology and biotechnology of Trichoderma. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;87:787–799. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2632-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mukherjee PK, Horwitz BA, Singh US, Mukherjee M, Schmoll M. Trichoderma in agriculture, industry and medicine: an overview. In: Mukherjee PK, Horwitz BA, Singh US, Mukherjee M, Schmoll M, editors. Trichoderma biology and applications. Boston: CAB International; 2013. pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hoitink HAJ, Madden LV, Dorrance AE. Systemic resistance induced by Trichoderma spp.: interactions between the host, the pathogen, the biocontrol agent, and soil organic matter quality. Phytopathology. 2006;96:186–189. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-96-0186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mathys J, De Cremer K, Timmermans P, Van Kerckhove S, Lievens B, Vanhaecke M, Cammue BP, De Coninck B. Genome-wide characterization of ISR induced in Arabidopsis thaliana by Trichoderma hamatum T382 against Botrytis cinerea infection. Front Plant Sci. 2012 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Howell CR. The role of antibiosis in biocontrol. In: Harman GE, Kubicek CP, editors. Trichoderma and Gliocladium. London: Taylor and Francis; 1998. pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Contreras-Cornejo HA, Macías-Rodríguez L, Cortés-Penagos C, López-Bucio J. Trichoderma virens, a plant beneficial fungus, enhances biomass production and promotes lateral root growth through an auxin-dependent mechanism in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009;149:1579–1592. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.130369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Harman GE, Howell CR, Viterbo A, Chet I, Lorito M. Trichoderma species—opportunistic, avirulent plant symbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:43–56. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Szabo M, Csepregi K, Galber M, Fekete C. Control plant-parasitic nematodes with Trichoderma species and nematode-trapping fungi: the role of chi18-5 and chi18-12 genes in nematode egg-parasitism. Biol Control. 2012;63:121–128. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2012.06.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Singh PC, Nautiyal CS. A novel method to prepare concentrated conidial biomass formulation of Trichoderma harzianum for seed application. J Appl Microbiol. 2012;113:1442–1450. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gillespie AT, Moorhouse ER. The use of fungi to control pests of agricultural and horticultural importance. In: Whipps JM, Lumsden RD, editors. Biotechnology of fungi for improving plant growth. London: Cambridge University Press; 1989. pp. 55–84. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mendoza-Mendoza A, Steyaert J, Nieto-Jacobo MF, Holyoake A, Braithwaite M, Stewart A. Identification of growth stage molecular markers in Trichoderma sp. ‘atroviride type B’ and their potential application in monitoring fungal growth and development in soil. Microbiology. 2015;161:2110–2126. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chaparro AP, Carvajal LH, Orduz S. Fungicide tolerance of Trichoderma asperelloides and T. harzianum strains. Agric Sci. 2011;2:301–307. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mathivanan N, Prabavathy VR, Vijayanandraj VR. The effect of fungal secondary metabolites on bacterial and fungal pathogens. In: Karlovsky P, editor. Secondary metabolites in soil ecology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2008. pp. 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mukherjee PK, Horwitz BA, Kenerley CM. Secondary metabolism in Trichoderma—a genomic perspective. Microbiology. 2012;158:35–45. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.053629-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Engelberth J, Koch T, Schüler G, Bachmann N, Rechtenbach J, Boland W. Ion channel-forming alamethicin is a potent elicitor of volatile biosynthesis and tendril coiling. Cross talk between jasmonate and salicylate signaling in lima bean. Plant Physiol. 2001;125:369–377. doi: 10.1104/pp.125.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Insam H, Seewald SA. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in soils. Biol Fertil Soils. 2010;46:199–213. doi: 10.1007/s00374-010-0442-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Korpi A, Jarnberg J, Pasanen AL. Microbial volatile organic compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2009;39:139–193. doi: 10.1080/10408440802291497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lemfack MC, Nickel J, Dunkel M, Preissner R, Piechulla B. VOC: a database of microbial volatiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:744–748. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kesselmeier J, Staudt M. Biogenic volatile organic compounds (VOC): an overview on emission, physiology and ecology. J Atmos Chem. 1999;33:23–88. doi: 10.1023/A:1006127516791. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dudareva N, Klempien A, Muhlemann JK, Kaplan I. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds. New Phytol. 2013;198:16–32. doi: 10.1111/nph.12145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Collins RP, Halim AF. Characterization of the major aroma constituent of the fungus Trichoderma viride (Pers.) J Agric Food Chem. 1972;20:437–738. doi: 10.1021/jf60180a010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Parker SR, Hill RA, Cutler HG. Spectrum of activity of antifungal natural products and their analogs. In: Cutler HG, Cutler SJ, editors. Biologically active natural products: agrochemicals. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1999. pp. 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vinale F, Sivasithamparam K, Ghisalberti EL, Marra R, Woo SL, Lorito M. Trichoderma-plant pathogens interactions. Soil Biol Biochem. 2008;40:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.07.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hung R, Lee S, Bennett JW. Arabidopsis thaliana as a model system for testing the effects of Trichoderma volatile organic compounds. Fungal Ecol. 2013;6:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.funeco.2012.09.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee S, Hung R, Yap M, Bennett JW. Age matters: the effects of volatile organic compounds emitted by Trichoderma atroviride on plant growth. Arch Microbiol. 2015;197:723–727. doi: 10.1007/s00203-015-1104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schulz S, Dickschat JS. Bacterial volatiles: the smell of small organisms. Nat Prod Rep. 2007;24:814–842. doi: 10.1039/b507392h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Piechulla B, Degenhardt J. The emerging importance of microbial volatile organic compounds. Plant Cell Environ. 2014;37:811–812. doi: 10.1111/pce.12254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bitas V, Kim H-S, Bennett JW, Kang S. Sniffing on microbes: diverse roles of microbial volatile organic compounds in plant health. Mol Plant Microbe Interact J. 2013;4:835–843. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-12-0249-CR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Junker RR, Tholl D. Volatile organic compound mediated interactions at the plant–microbe interface. J Chem Ecol. 2013;39:810–825. doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wheatley R, Hackett C, Bruce A, Kundzewicz A. Effect of substrate composition on production of volatile organic compounds from Trichoderma spp. inhibitory to wood decay fungi. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. 1997;39:199–205. doi: 10.1016/S0964-8305(97)00015-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bruce A, Wheatley RE, Humphris SN, Hackett CA, Florence MEJ. Production of volatile organic compounds by Trichoderma in media containing different amino acids and their effect on selected wood decay fungi. Holzforschung. 2000;54:481–486. doi: 10.1515/HF.2000.081. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Aguero LEM, Alvarado R, Martinez A, Dorta B. Inhibition of Aspergillus flavus growth and aflatoxin B1 production in stored maize grains exposed to volatile compounds of Trichoderma harzianum Rifai. Interciencia. 2008;33:219–222. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Campos VP, Pinho RSC, de Freire ES. Volatiles produced by interacting microorganisms potentially useful for the control of plant pathogens. Ciencia e Agrotec Lavras. 2010;34:525–535. doi: 10.1590/S1413-70542010000300001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ryu CM, Farag MA, Hu CH, Reddy MS, Wie HX, Pare PW, Kloepper JW. Bacterial volatiles promote growth of Arabidopsis. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 2003;100:4927–4932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0730845100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ryu CM, Farag MA, Hu CH, Reddy MS, Kloepeer JW, Pare PW. Bacterial volatiles induce systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004;134:1017–1026. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.026583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lugtenberg B, Kamilova F. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2009;63:541–556. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cortes-Barco AM, Goodwin PH, Hsiang T. Comparison of induced resistance activated by benzothiadiazole, (2R, 3R)-butanediol and an isoparaffin mixture against anthracnose of Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Pathol. 2010;59:643–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02283.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Blom D, Fabbri C, Connor EC, Schiestl FP, Klauser DR, Boller T, Eberl L, Weisskopf L. Production of plant growth modulating volatiles is widespread among rhizosphere bacteria and strongly depends on culture conditions. Environ Microbiol. 2011;13:3047–3058. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kai M, Piechulla B. Plant growth promotion due to rhizobacterial volatiles—an effect of CO2? FEBS Lett. 2009;583:3473–3477. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.09.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yang J, Kloepper JW, Ryu CM. Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2009;14:1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Xie X, Zhang H, Paré PW. Sustained growth promotion in Arabidopsis with long-term exposure to the beneficial soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis (GB03) Plant Signal Behav. 2009;4:948–953. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.10.9709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bailly A, Weisskopf L. The modulating effect of bacterial volatiles on plant growth. Plant Signal Behav. 2012;7:79–85. doi: 10.4161/psb.7.1.18418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.McNeal KS, Herbert BE. Volatile organic metabolites as indicators of soil microbial activity and community composition shifts. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 2009;73:579–588. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2007.0245. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Polizzi V, Adams A, Picco AM, Adriaens E, Lenoir J, Peteghem CV, Saegar SD, Kimpe ND. Influence of environmental conditions on production of volatiles by Trichoderma atroviride in relation with sick building syndrome. Build Environ. 2011;46:945–954. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2010.10.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hung R, Lee S, Bennett JW. Fungal volatile organic compounds and their role in ecosystems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:3395–3405. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pasanen P, Korpi A, Kalliokosi P, Pasanen AL. Growth and volatile metabolite production of Aspergillus versicolor in house dust. Environ Int. 1997;23:425–432. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(97)00027-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fiedler K, Schutz E, Geh S. Detection of microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) produced by moulds on various materials. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2001;204:111–121. doi: 10.1078/1438-4639-00094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jelen H, Blaszczyk L, Jerzy C, Rogowicz K, Strakowska J. Formation of 6-n-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one (6-PAP) and other volatiles by different Trichoderma species. Mycol Prog. 2014;13:589–600. doi: 10.1007/s11557-013-0942-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Splivallo R, Novero M, Bertea CM, Bossi S, Bonfante P. Truffle volatiles inhibit growth and induce an oxidative burst in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2007;175:417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pierik R, Mommer L, Voesenek LACJ. Molecular mechanisms of plant competition: neighbor detection and response strategies. Funct Ecol. 2013;27:841–853. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Blande JD, Holopainen JK, Niinemets Ü. Plant volatiles in a polluted atmosphere: stress response and signal degradation. Plant Cell Environ. 2014;37:1892–1904. doi: 10.1111/pce.12352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cardoza YJ, Alborn HT, Tumlinson JH. In vivo volatile emissions from peanut plants induced by simultaneous fungal infection and insect damage. J Chem Ecol. 2002;28:161–174. doi: 10.1023/A:1013523104853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tabata J, De Moraes CM, Hescher MC. Olfactory cues from plants infected by powdery mildew guide foraging by a mycophagous ladybird beetle. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mohanta TK, Occhipinti A, Atsbaha Zebelo S, Foti M, Fliegmann J, Bossi S, Maffei ME, Bertea CM. Ginkgo biloba responds to herbivory by activating early signaling and direct defenses. PLoS One. 2012;7:e32822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Snoeren TAL, Kappers IF, Broekgaarden C, Mumm R, Dicke M, Bouwmeester HJ. Natural variation of herbivore-induced volatiles in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot. 2010;61:3041–3056. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cai L, Koziel JA, O’Neal ME. Studying plant–insect interactions with solid phase microextraction: screening for airborne volatile emissions response of soybeans to the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura (Hemiptera:Aphididae) Chromatography. 2015;2:265–276. doi: 10.3390/chromatography2020265. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Joutsensaari J, Yli-Pirila P, Korhonen H, Arola A, Blande JD, Heijari J, Kivimaenpaa M, Mikkonen S, Hao L, Miettinen P, Lyytikainen-Saarenmaa P, Faiola CL, Laaksonen A, Holopainen JK. Biotic stress accelerates formation of climate-relevant aerosols in boreal forests. Atmos Chem Phys. 2015;15:12139–12157. doi: 10.5194/acp-15-12139-2015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Llorens E, Camañes G, Lapeña L, García-Agustín P. Priming by hexanoic acid induce activation of mevalonic and linolenic pathways and promotes the emission of plant volatiles. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:495. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Reisenman CE, Riffell JA, Duffy K, Pesque A, Mikles D, Goodwin B. Species-specific effects of herbivory on the oviposition behavior of the moth Manduca sexta. J Chem Ecol. 2012;39:76–89. doi: 10.1007/s10886-012-0228-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Jardine KJ, Meyers K, Abrell L, Alves EG, Yanez Serrano AM, Kesselmeier J, Karl T, Guenther A, Chambers JQ, Vickers C. Emissions of putative isoprene oxidation products from mango branches under abiotic stress. J Exp Bot. 2013;64:3697–3708. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tanaka K, Taniguchi S, Tamaoki D, Yoshitomi K, Akimitsu K, Gomi K. Multiple roles of plant volatiles in jasmonate-induced defense response in rice. Plant Signal Behav. 2014;9:e29247. doi: 10.4161/psb.29247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bailey BA, Melnick RL. The endophytic Trichoderma. In: Mukherjee PK, Horwitz BA, Singh US, Mukherjee M, Schmoll M, editors. Trichoderma: biology and applications. Boston: CABI; 2013. pp. 152–172. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.


