Fig. 1.
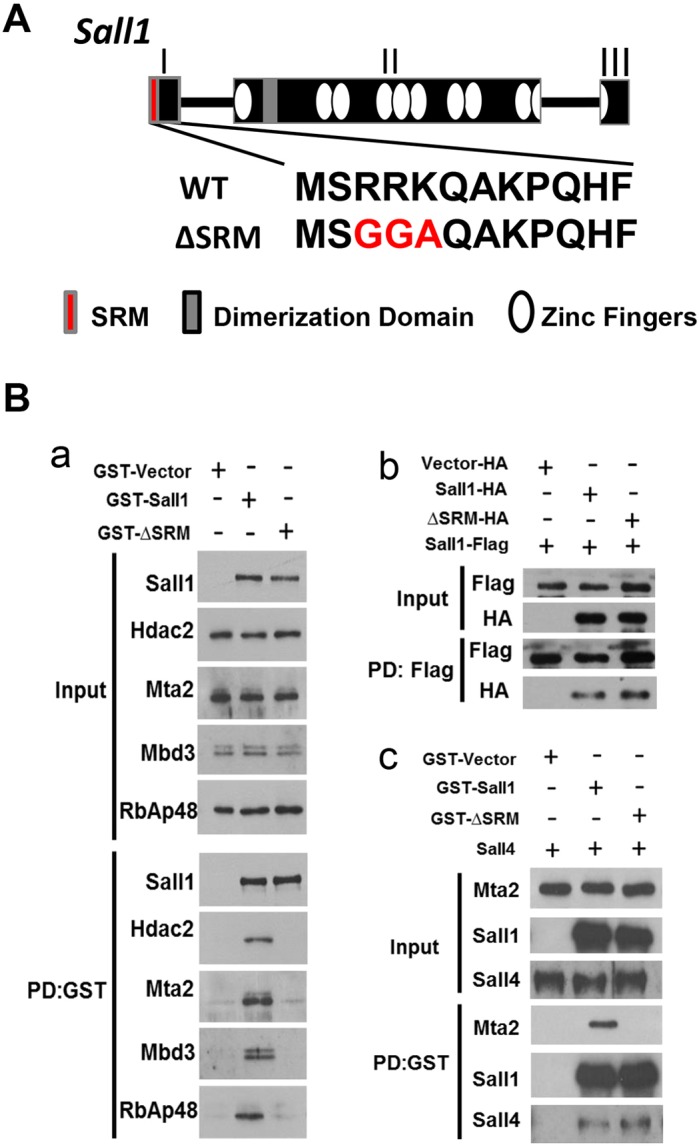
A three amino acid mutation in the SRM of Sall1 disrupts NuRD binding. (A) Schematic of the wild-type Sall1 locus with three exons (I-III). Zinc fingers are represented by white ovals; gray shaded area in exon II represents the glutamine-rich Sall family member interaction domain. The first 12 amino acids of Sall1 that interact with NuRD (Sall repression motif, SRM; shown in red) are encoded in exon I and are listed below. A three amino acid mutation (R3G, R4G, K5A) encodes ΔSRM. (B) (a) GST constructs of full-length wild-type Sall1 or ΔSRM were overexpressed in COS-1 cells, which express components of the NuRD complex endogenously, but do not express Sall1 or family members (Sall2-4). Cell lysates were precipitated with glutathione sepharose and analyzed by western blot (n=3). GST-Sall1 interacts with NuRD components Hdac2, Mta2, Mbd3 and RbAp48. However, a three amino acid mutation (ΔSRM-GST) abolishes the interaction with NuRD components Hdac2, Mta2, Mbd3 and RbAp48. (b) Flu (HA)-tagged Sall1 and ΔSRM were expressed in COS-1 cells with Flag-tagged Sall1. Cell lysates were precipitated with anti-Flag agarose and analyzed by western blot. Sall1-Flag interacts with both wild-type Sall1-HA and ΔSRM-HA (n=2). (c) GST constructs of full-length wild-type Sall1 or ΔSRM were overexpressed with Sall4 in COS-1 cells. Cell lysates were precipitated with glutathione sepharose and analyzed by western blot (n=2). ΔSRM-GST does not interact with the NuRD component Mta2; however, it still interacts with overexpressed Sall4.
