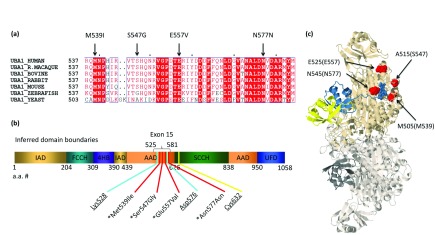
Figure 1. Uba1 conservation, domains, and modeling of XL-SMA mutations.
( a) XL-SMA variant residues show strict amino acid sequence conservation in nearly all eukaryotes from yeast to modern man. ( b) Schematic of the inferred domains of Uba1. Pathogenic variants and key residues are labeled. IAD = inactive adenylation domain, FCCH = first catalytic cysteine half domain, 4HB = 4 helix bundle, AAD = active adenylation domain, SCCH = second catalytic half domain. UFD = Ub fold domain. Known pathogenic variants marked with asterisk. Critical Adenylation and Thiolester residues are underlined. ( c) 3D protein modeling of S. cerevisiae Uba1 using Jmol modeling software. XL-SMA variants labeled in red, thiolestered Ub in yellow and non-covalently bound Ub-adenylate in blue. This figure has been reproduced and modified from Protein Data Bank public domain content (PDB ID: 4NNJ) under original permission from Schäfer et al. (2014). “Structure of the ubiquitin-activating enzyme loaded with two ubiquitin molecules.” Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70(Pt 5): 1311–1320.