Abstract
Lipoprotein glomerulopathy (LPG) is characterized by the accumulation of lipoprotein thrombi within glomerular capillaries. This rare disorder is associated with various types of mutations in the apolipoprotein E gene (apoE). Herein, we present a case of LPG with a combination of apoE Chicago (Arg147Pro) and apoE (Glu3Lys) mutations. A 51-year-old Japanese woman presented with severe (3+) proteinuria. The initial renal biopsy showed glomerular capillary dilation and occlusion with lipid granules, a specific characteristic of LPG. Phenotype, genotype, and apoE DNA sequence analyses detected 2 mutations as described above within the same allele. Although both mutations had already been reported in 1 case of LPG each, this is the first time that the combination of the 2 mutations was identified in the same case. Familial analysis detected the same mutations in the patient's mother. However, she has not suffered LPG thus far. In addition, a re-analysis of the previous LPG case with apoE (Glu3Lys) also identified the apoE Chicago mutation, as was observed in our case. Treatment with fenofibrate and irbesartan was initiated, and urinary protein excretion ceased within 1 year; recurrence was not observed after an additional 2 years of follow-up. A second biopsy after 2 years showed great improvement, with lipoprotein thrombi identified only in 2 of 18 glomeruli.
Keywords: apoE (Glu3Lys), apoE Chicago, Fenofibrate, Lipoprotein glomerulopathy, Proteinuria, Renal biopsy
Introduction
Lipoprotein glomerulopathy (LPG) is a kidney disease characterized by the accumulation of lipoprotein thrombi in the glomeruli. Since the first report of LPG in a patient in Japan in 1989 [1], approximately 150 cases and 15 different mutations in apoE have been reported to date [2]. Lipoprotein structural abnormalities due to apoE gene mutations are thought to play a causative role in LPG; however, the pathogenesis and pathogenic mechanisms of LPG have not yet been fully elucidated. In these mutations, apoE2 Chicago (Arg147Pro) was identified in a Mexican man with LPG living in the USA [3]. In contrast, apoE (Glu3Lys) usually shows a minor isoform E5 by isoelectric focusing and induces hyperlipidemia [4, 5, 6]. Moreover, the association between this mutation and classic E2 (Arg158Cys) was described in a previous case report of LPG [7].
Here, we report a case of LPG with apoE2 Chicago and apoE5 (Glu3Lys) mutations in the same allele. Treatment with fenofibrate showed a marked reduction in urinary protein excretion and lipoprotein thrombi by sequential renal biopsy.
Case Report
A 51-year-old Japanese woman was admitted for evaluation of proteinuria in 2011. She had a history of appendicitis at 12 years of age, cholelithiasis at 30 years of age, myoma at 46 years of age, and at least a 5-year history of dyslipidemia. Proteinuria (1+) had been first identified during a medical checkup 3 years prior and was ignored until increasing to 3+ in 2011. Her parents and brothers suffered from dyslipidemia but had no history of renal disease.
On admission, her height and weight were 161 cm and 49 kg, respectively, and her blood pressure was 137/94 mm Hg. On physical examination, slight pitting edema was observed; however, there were no xanthomas. Urinary protein excretion was 4.12 g/g Cre, and the serum triglyceride level was high. She did not exhibit nephrotic syndrome. The other laboratory findings are shown in Table 1. A computed tomography scan showed neither atrophy nor enlargement of the kidneys.
Table 1.
Laboratory findings
| Urine | |
|---|---|
| Protein, g/g × Cre | 4.12 |
| Peripheral blood | |
|---|---|
| Red blood cells, ×104/µL | 437 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.8 |
| Leukocyte,/µL | 5,300 |
| Platelet, ×104/µL | 19.8 |
| Total protein, g/dL | 6.3 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.6 |
| Blood urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 11 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 5.3 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 247 |
| HDL-c, mg/dL | 34 |
| LDL-c, mg/dL | 89 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 420 |
| ApoE, mg/dL | 9.2 |
Pathological Findings
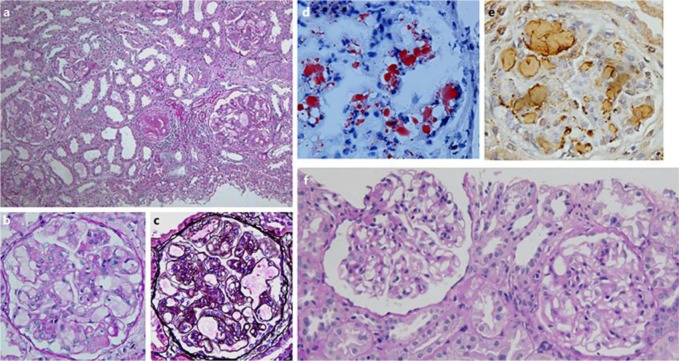
A renal biopsy specimen was processed in August 2011 using standard methods, and in the sections for light microscopy, the renal cortex was found to contain 11 glomeruli, 2 of which showed sclerosis. The remaining glomeruli were enlarged by distinct dilatation of the capillary lumina, which were filled with thrombus-like substances that stained slightly with periodic acid-Schiff. Some glomeruli exhibited moderate mesangial cell proliferation and increased mesangial matrix, and double contours of the capillary wall were partially observed. No crescents or adhesion in glomeruli were found (Fig. 1a–c). A direct immunofluorescence showed no deposition of IgG, IgA, IgM, C1q, C3, or fibrinogen in glomeruli. Staining with Oil red O showed lipid droplets in the capillary lumina, which were stained positive for apoE (Fig. 1d, e). Electron microscopic findings showed capillary dilation and occlusion with numerous lamellated lipid granules. Thin basement membranes with swollen endothelial cells were also observed. The histological findings and the results of apoE analysis (described below) satisfied the diagnostic criteria for LPG [8].
Fig. 1.
Light microscopic findings of renal biopsy specimens. The glomeruli were enlarged by distinct dilatation of the capillary lumina, which were filled with thrombus-like substances (a, b). c PAM staining. The thrombus-like substances were stained positive with Oil Red O (d) and for apoE (e). f The thrombus-like substances were absent on the second biopsy.
Treatment and Prognosis
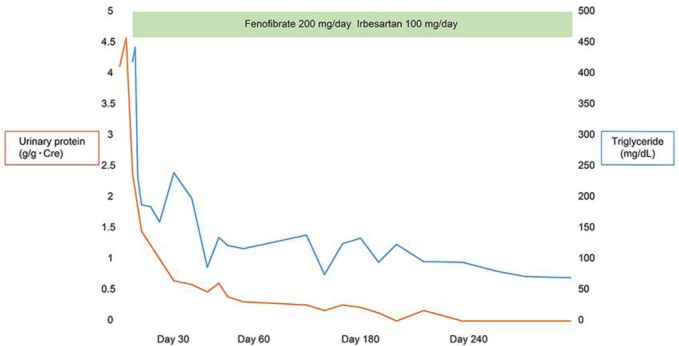
Treatment with fenofibrate and irbesartan was initiated. Two weeks later, serum triglycerides and urinary protein excretion were reduced to 200 mg/dL and 1 g/g Cre, respectively. Two months later, the former was within the normal range, and the latter was reduced to less than 0.5 g/g Cre. Eight months later, urinary protein excretion ceased and did not recur thereafter (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Clinical course. Treatment with fenofibrate and irbesartan was initiated. Two months later, serum triglycerides were within the normal range, and urinary protein excretion was reduced to less than 0.5 g/g Cre. Eight months later, urinary protein excretion ceased and did not recur thereafter.
In a second biopsy in August 2013, the specimen contained 22 glomeruli, 4 of which were obsolescent. Two of the glomeruli were filled with thrombi, but thrombi were absent in the other glomeruli (Fig. 1f).
Analysis of apoE mutations
Patient and Family
To diagnose LPG and identify apoE mutations, the serum apoE phenotype, genotype, and apoE DNA sequences of the patient, her mother, and her 2 brothers were analyzed.
Serum apoE phenotypes were analyzed by isoelectric focusing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (IEF), as previously reported [9, 10]. The patient and her brothers were E3/4, and their mother was E4/4 (Fig. 3a).
Fig. 3.
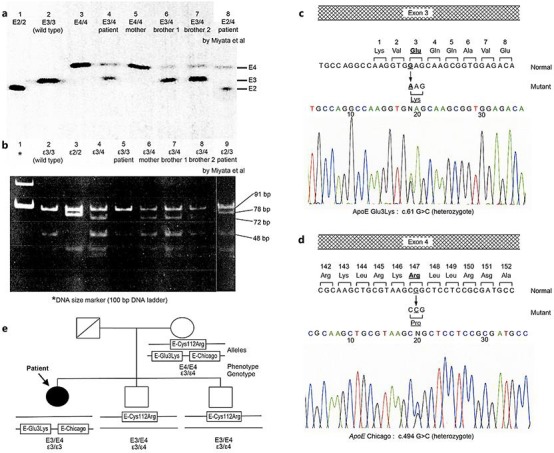
a ApoE phenotype determined by isoelectric focusing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (IEF). Lane 1 (E2/2), lane 2 (E3/3, wild-type), and lane 3 (E4/4) are samples; lane 4 (E3/3) is the patient; lane 5 (E4/4) is the mother, lanes 6 and 7 (E3/4) are the 2 brothers; and lane 8 (E2/4) is a re-analysis of a previous patient. b apoE genotype examined by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). PCR-amplified DNA of apoE, including codons 112 and 158, was digested with HhaI. Lane 1 shows the DNA size marker (100-bp DNA ladder); lane 2 (ε3/3, wild-type), lane 3 (ε2/2), and lane 4 (ε3/4) are samples; lane 5 (ε3/3) is the patient, lanes 6, 7, and 8 (ε3/4) are the mother and the 2 brothers; lane 9 (ε2/3) is a re-analysis of a previous patient. c, d Sequence analysis of PCR-amplified DNA of apoE in the patient. c In exon 3, the normal allele contained the sequence GAG coding for amino acid 3, glutamine. The mutant allele contained the substituted sequence AAG, coding for amino acid 3, lysine. d In exon 4, the normal allele contained the sequence CGG coding for amino 147, arginine. The mutation allele contained the substituted sequence CCG, coding for amino acid 147, proline. e The patient's family tree. Since 3 apoE mutations expressed in the patient's mother were observed in the patient (E-Glu3Lys and E-Chicago [Arg147Pro]) and the 2 brothers (E4 [Cys112Arg]), we confirmed that E-Glu3Lys and E-Chicago were on one allele, and E4 (Cys112Arg) was on the other allele.
The apoE genotype was determined by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, as described previously [9, 10]. Genomic DNA was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using oligonucleotide primers (sense 5′-ACGCGGGCACGGCTGTCCAAGGA-3′ and antisense 5′-TCGCGGGCCCCGGCCTGGTACAC-3′). The PCR products were digested with the restriction enzyme HhaI. Genotype ε3/3 in the patient was identified by 91- and 48-bp fragments, and genotype ε3/4 in her mother and brothers was detected by the addition of a 72-bp fragment (Fig. 3b). Accordingly, there were differences between phenotype and genotype in the patient and her mother.
Sequencing of apoE DNA was performed as follows. Three fragments of genomic DNA containing all coding sequence of mature apoE were amplified by PCR with the following primers for apoE: 5′-GCTTTCCAAGTGATTAAACCGACT-3′ and 5′-AGAGCTAAAGCCAGGAGTCAG-3′ for exon 3; and 5′-CCTCTTGGGTCTCTCTGGCT-3′ and 5′-CTGCTCCTTCACCTCGTCCA-3′, 5′-GCAGTACCGCGGCGAGGTGCAGG-3′ and 5′-GATCGTGCCACTGCACTCTA-3′ for exon 4. The amplified DNA fragments were purified using a PCR purification kit (Qiagen, Germany) and directly sequenced with a Genetic Analyzer 3130xl DNA sequencer (Thermo Fisher, USA) using a BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit (Thermo Fisher). For the patient, we identified a heterozygous missense mutation (G to A) in exon 3, leading to an amino acid substitution Lys (AAG) for Glu (GAG) at codon 3 (Fig. 3c); another missense mutation (G to C) in exon 4 resulted in a substitution of Pro (CCG) for Arg (CGG) at codon 147 (Fig. 3d). Both mutations were also found in her mother (data not shown). Moreover, since her mother and 2 brothers had a heterozygous Cys112Arg showing classical E4, we confirmed in the patient's family that the mutations Glu3Lys and Arg147Cys were on one allele, whereas Cys112Arg was on the other (Fig. 3e). Although Glu3Lys and Arg147Cys usually result in E5 and E2 in IEF, respectively, the coexistence of both mutations in the same allele may induce E4 through interaction of the electric charges. Additionally, both mutations could not influence ordinary fragmentation by HhaI, resulting in genotype ε3/3 in RFLP.
Re-Analysis of the Previous LPG Case
Watanabe et al. [11] reported a case of LPG at nearly the same time as Saito et al. [1], and Miyata et al. [7] demonstrated apoE mutations in the classic E2 (Arg158Cys) and E5 (Glu3Lys) in this patient after he received kidney transplantation. Interestingly, his mother came from the same city (Kuwana, Mie Prefecture) in which our patient's mother lived, although the consanguinity was not noted between the families. Therefore, we re-analyzed apoE in the patient reported previously [7] to obtain more detailed information. DNA sequencing showed a new missense mutation leading to apoE Chicago at codon 147 as well as 2 other mutations for E2 (Arg158Cys) and E5 (Glu3Lys) previously reported [7]; this result was consistent with phenotype E2/4 (Fig. 3a, lane 8) and genotype ε2/3 (Fig. 3b, lane 9).
Discussion
In the current case, apoE (Glu3Lys) and apoE Chicago (Arg147Pro) were expressed on the same allele, and the other allele was the wild-type E3. To the best of our knowledge, only 1 case of LPG with apoE Chicago (Arg147Pro) was reported in the USA in 2006, occurring in a Mexican man [3]. Additionally, apoE (Glu3Lys) is known to be associated with hyperlipidemia in Japan [4, 5, 6] and to yield the E5 phenotype in IEF analysis. This mutation has also been reported in a previous case of LPG by Miyata et al. [7]; their report described the combination of this mutation and apoE2 (Arg158Cys) on each allele during LPG recurrence after kidney transplantation.
Since Oikawa et al. [9] discovered apoE Sendai, the first mutant associated with LPG, 15 apoE variants have been shown to have an etiological role in LPG [2]. Most of these variants exhibit structural changes around the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor site and may suppress the metabolism of lipoprotein, resulting in the development of type III hyperlipoproteinemia, as found in some carriers of homozygous apoE2/2. However, this does not explain the mechanism of kidney injury directly caused by the apoE abnormality in LPG.
Substitution of proline for arginine, as observed in apoE Chicago (Arg147Pro), is the representative mutation in LPG and loosens α helices and transforms the structure of apoE. This may change the affinity of lipoprotein for the LDL receptor or other structures of the glomerulus, e.g., heparin-binding [12, 13]. Sam et al. [3], who reported the first case of apoE Chicago, demonstrated the affinity of patient apoE to the glomerular capillaries using immunofluorescence staining. From this result, they suggested enhanced binding of the mutated apoE to glomerular capillaries, although they were not able to confirm its binding activity to LDL receptors. Georgiadou et al. [14] showed in their detailed biochemical analysis that the proline mutant is thermodynamically unstable, which may induce the coagulation of lipoprotein and cause LPG.
Additionally, some reports have shown an association of apoE5 (Glu3Lys) with hyperlipidemia [4, 5, 6]. This mutant is 2 times more active for binding to LDL receptors than wild-type apoE3 [4, 5], suggesting that hyperlipidemia results from downregulation of the LDL receptor due to high uptake of lipoproteins containing this mutant [4, 5]. Accordingly, it is likely that the coexistence of E5 (Glu3Lys) with E-Chicago (Arg147Pro) in the same allele may affect the development of LPG because the affinity of E-Chicago (Arg147Pro) to the glomerular capillaries may be indirectly influenced by downregulation of active LDL receptor binding of E5 (Glu3Lys) [4, 5]. However, there have been no studies showing the relationship between E5 (Glu3Lys) and the kidney disease other than the report by Miyata et al. [7]. Therefore, we should be careful to assess the association of E5 (Glu3Lys) with other mutations in LPG.
The patient's apoE mutations were inherited from her mother (Fig. 3e). However, her mother has not suffered LPG thus far. Although she had apoE4 (Cys112Arg) in the other allele, its role in the metabolism of lipoprotein is unknown. Additionally, the incomplete penetrance of LPG has been clinically and experimentally recognized [15, 16].
Previous cases [2, 16] showed the efficiency of fibrates but not of statins in LPG treatment, as supported by sequential renal biopsies and clinical experience. The second biopsy in our case also supported these studies. Since renal function decreased gradually in some of the reported cases, careful follow-up is still needed in our case.
In summary, we experienced a case of LPG with dual mutations in apoE (Glu3Lys) and apoE Chicago (Arg147Pro). Although both mutations had been reported in one LPG case each in prior studies, this was the first time this combination has been reported; additionally, we identified both mutations in a re-analysis of a previous case [7]. Treatment with fenofibrate succeeded in reducing serum triglycerides and urinary protein excretion to the normal ranges. Sequential renal biopsy confirmed the histological improvement.
Statement of Ethics
The study of the patient was approved by Institutional Ethics Committee of Yokkaichi Hazu Medical Center, and written informed consent was obtained from the patient and the patient's mother and brothers before commencement of the phenotype and gene analysis.
Disclosure Statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- 1.Saito T, Sato H, Kudo K, Oikawa S, Shibata T, Hara Y, Yoshinaga K, Sakaguchi H. Lipoprotein glomerulopathy: glomerular lipoprotein thrombi in a patient with hyperlipoproteinemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 1989;13:148–153. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(89)80134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Saito T, Matsunaga A, Ito K, Nakashima H. Topics in lipoprotein glomerulopathy: an overview. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2014;18:214–217. doi: 10.1007/s10157-013-0887-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sam R, Wu H, Yue L, Mazzone T, Schwartz MM, Arruda JA, Dunea G, Singh AK. Lipoprotein glomerulopathy: a new apolipoprotein E mutation with enhanced glomerular binding. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47:539–548. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2005.12.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dong LM, Yamamura T, Yamamoto A. Enhanced binding activity of an apolipoprotein E mutant, APO E5, to LDL receptors on human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;168:409–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wardell MR, Rall SC, Jr, Schaefer EJ, Kane JP, Weisgraber KH. Two apolipoprotein E5 variants illustrate the importance of the position of additional positive charge on receptor-binding activity. J Lipid Res. 1991;32:521–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kobayashi J, Shirai K, Murano T, Misawa Y, Tashiro J, Yoshida T, Shinomiya M. A case of hyperlipidemia with homozygous apolipoprotein E5 (Glu3–>gt;Lys). Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1583:117–121. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Miyata T, Sugiyama S, Nangaku M, Suzuki D, Uragami K, Inagi R, Sakai H, Kurokawa K. Apolipoprotein E2/E5 variants in lipoprotein glomerulopathy recurred in transplanted kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:1590–1595. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V1071590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Saito T, Matsunaga A, Oikawa S. Impact of lipoprotein glomerulopathy on the relationship between lipids and renal diseases. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47:199–211. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2005.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Oikawa S, Matsunaga A, Saito T, Sato H, Seki T, Hoshi K, Hayasaka K, Kotake H, Midorikawa H, Sekikawa A, Hara S, Abe K, Toyota T, Jingami H, Nakamura H, Sasaki J. Apolipoprotein E Sendai (Arginine 145->Proline): a new variant associated with lipoprotein glomerulopathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:820–823. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V85820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Matsunaga A, Sasaki J, Komatsu T, Tsuji E, Moriyama K, Koga T, Arakawa K, Oikawa S, Saito T, Kita T, Doi T. A novel apolipoprotein E mutation, E2 (Arg25Cys), in lipoprotein glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 1999;56:421–427. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Watanabe Y, Ozaki I, Yoshida F, Fukatsu A, Itoh Y, Matsuo S, Sakamoto N. A case of nephrotic syndrome with glomerular lipoprotein deposition with capillary ballooning and mesangiolysis. Nephron. 1989;51:265–270. doi: 10.1159/000185297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hoffmann M, Scharnagl H, Panagiotou E, Banghard W, Wieland H, März W. Diminished LDL receptor and high heparin binding of apolipoprotein E2 Sendai associated with lipoprotein glomerulopathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:524–530. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V123524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saito T, Matsunaga A, Ito K, Nakashima H. Topics in lipoprotein glomerulopathy: an review. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2014;18:214–217. doi: 10.1007/s10157-013-0887-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Georgiadou D, Stamatakis K, Efthimiadou EK, Kordas G, Gantz D, Chroni A, Stratikos E. Thermodynamic and structural destabilization of apoE3 by hereditary mutations associated with the development of lipoprotein glomerulopathy. J Lipid Res. 2013;54:164–176. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M030965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Toyota K, Hashimoto T, Ogino D, Matsunaga A, Ito M, Masakane I, Degawa N, Sato H, Shirai S, Umetsu K, Tamiya G, Saito T, Hayasaka K. A founder haplotype of APOE-Sendai mutation associated with lipoprotein glomerulopathy. J Hum Genet. 2013;58:254–258. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2013.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hu Z, Huang S, Wu Y, Liu Y, Liu X, Su D, Tao Y, Fu P, Zhang X, Peng Z, Zhang S, Yang Y. Hereditary features, treatment, and prognosis of the lipoprotein glomerulopathy in patients with the APOE Kyoto mutation. Kidney Int. 2014;85:416–424. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]