Abstract
IMPORTANCE
With the advent of highly effective antiretroviral therapy and improved survival, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–infected people are living longer and are now at an increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). There is an urgent need to identify novel risk factors and primary prevention approaches for CVD in HIV. Although depression is prevalent in HIV-infected adults and is associated with future CVD in the general population, its association with CVD events has not been examined in the HIV-infected population.
OBJECTIVE
To examine whether depressive disorders are prospectively associated with incident acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in a large cohort of adults with HIV.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS
Included in this cohort study were 26 144 HIV-infected veterans without CVD at baseline (1998–2003) participating in the US Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Aging Cohort Study from April 1, 2003, through December 31, 2009. At baseline, 4853 veterans (19%) with major depressive disorder (MDD; International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision [ICD-9] codes 296.2 and 296.3) and 2296 (9%) with dysthymic disorder (ICD-9 code 300.4) were identified. The current analysis was conducted from January 2015 to November 2015.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES
Incident AMI (defined by discharge summary documentation, enzyme/electrocardiography evidence of AMI, inpatient ICD-9 code for AMI (410), or AMI as underlying cause of death [International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision code 121]) between the enrollment date and December 31, 2009.
RESULTS
The mean (SD) age of those with MDD was 47.3 (7.9) years and for those without MDD was 48.2 (9.7) years. During 5.8 years of follow-up, 490 AMI events (1.9%) occurred. Baseline MDD was associated with incident AMI after adjusting for demographics (hazard ratio [HR], 1.31; 95% CI, 1.05–1.62), CVD risk factors (HR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.04–1.60), and HIV-specific factors (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.05–1.62). Further adjustment for hepatitis C, renal disease, substance abuse, and hemoglobin level (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.00–1.56) and antidepressant use (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 0.87–1.42) attenuated associations. Baseline dysthymic disorder was not associated with incident AMI.
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE
We report novel evidence that HIV-infected adults with MDD have a 30% increased risk for AMI than HIV-infected adults without MDD after adjustment for many potential confounders. Our findings raise the possibility that MDD may be independently associated with incident atherosclerotic CVD in the HIV-infected population.
With the advent of highly effective antiretroviral therapy (ART), the lifespan of individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is improving.1 Unfortunately, these ART-treated, HIV-infected individuals remain at a higher risk for chronic comorbidities, with cardiovascular disease (CVD) being the leading cause of death in this population.2 Case in point is a recent cohort study that reported that HIV-infected adults have a 50% greater risk for acute myocardial infarction (AMI) than their HIV-uninfected counterparts.3 Multiple factors, some that have not yet been identified, likely account for this excess CVD risk.
In the general population, prospective studies from the past 30 years provide evidence that depression is independently associated with incident atherosclerotic CVD.4,5 Metaanalyses have revealed that adults with depressive disorders, such as major depressive disorder (MDD) or dysthymic disorder, have a 40% to 60% increased risk for developing CVD than those without these conditions, even after adjustment for CVD risk factors.4,5 Notably, this longitudinal association has been detected in both men and women and in various age and race/ethnicity groups, and it is comparable in strength with that of traditional CVD risk factors.6,7 To our knowledge, the strongest evidence that depressive disorders are risk factors for CVD comes from a follow-up study of a randomized clinical trial in which depression treatment, delivered before CVD onset, was found to halve the risk for incident CVD events of older primary care patients with depression.8
Given the greater risk for CVD of HIV-infected adults and adults with depression separately and the high prevalence (24%–40%) of depressive disorders in those with HIV,9,10a key remaining question is the following: Is depression independently associated with incident atherosclerotic CVD in the HIV-infected population? The answer to this question could have important clinical implications, as this line of research could identify a novel target (depression) and approach (depression treatment) to CVD primary prevention among HIV-infected adults. Currently, little is known about the depression-incident CVD association in adults with HIV. To address this knowledge gap, we examined the prospective association of MDD and dysthymic disorder with incident AMI among 26 144 HIV-infected veterans in the Veterans Aging Cohort Study (VACS). In addition to MDD, dysthymic disorder warrants attention in this context, as it is understudied11 and its milder but long-term course12 might have implications for CVD risk.
Methods
Participants
The VACS is a prospective, multisite cohort of HIV-infected and age-, race/ethnicity-, and clinical site–matched uninfected adults enrolled in the same calendar year in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system. Participants in VACS have been continually selected for inclusion since 1998 by using an existing validated algorithm from the VA national electronic medical record system.13,14 For the selected participants, data are extracted from several sources. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, and pharmacy data are obtained from the immunology case registry, the National Pharmacy Benefits Management database, the Decision Support System, the National Patient Care Database, and the VA electronic medical record health factor data set. Cardiovascular disease data are obtained from Medicare, Medicaid, and VA fee-for-service data and from the Ischemic Heart Disease–Quality Enhancement Research Initiative.15 Death data are obtained from the VA vital status file, the Social Security Administration death master file, the Beneficiary Identification and Records Locator Subsystem, and the Veterans Health Administration Medical Statistical Analysis Systems inpatient data sets.3 Finally, cause of death data are obtained from the National Death Index. The University of Pittsburgh, Yale University, and West Haven VA Medical Center institutional review boards approved this study; we obtained a waiver of consent from West Haven VA Medical Center and the Yale School of Medicine to minimize a loss of privacy and to facilitate this low-risk research given the large sample of HIV-infected veterans. The current analysis was conducted from January 2015 to November 2015.
For the present report, we selected all adults with HIV enrolled in the VACS (N = 27 350), defined as at least 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) codes for HIV in the VA Immunology Case Registry.13 The baseline enrollment date was the participant’s first clinic visit on or after April 1, 2003. As described in our earlier work,3 all veterans with prevalent CVD (n = 1206) were excluded using ICD-9 code data from Medicare, Medicaid, and VA fee-for-service files during the baseline period (1998 to the participant’s baseline enrollment date). Our final sample included 26 144 HIV-infected adults, who were followed up from their baseline enrollment date to either an AMI event, death, or the last follow-up date on December 31, 2009.
Depressive Disorders
Participants in VACS with a diagnosis of either MDD (ICD-9 codes 296.2 or 296.3) or dysthymic disorder (ICD-9 code 300.4) during baseline were identified as depression cases. Specifically, a participant with at least 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient ICD-9 codes in their VA national electronic medical record was classified as positive for either depressive disorder. Major depressive disorder (0 = no MDD and 1 = MDD) was our primary exposure variable, and dysthymic disorder (0 = no dysthymic disorder and 1 = dysthymic disorder) was our exploratory exposure variable.
Incident Acute Myocardial Infarction
The definition of our primary outcome, incident AMI, was identical to that of Freiberg and colleagues.3 Acute myocardial infarction events were identified using VA, Medicare, and death certificate data between enrollment date and December 31, 2009. Acute myocardial infarction events occurring within the VA and those transferred from non-VA hospitals were determined by discharge summary documentation. These events were initially extracted by trained abstractors and subsequently adjudicated by reviewing physician notes and medical records for (1) evidence of elevated serum markers of myocardial damage, including elevated troponin I, troponin T, or creatine kinase– myocardial band (thresholds for positive markers were defined by the assay used), or (2) electrocardiographic findings (ST-segment elevation was defined as 1 mV or higher elevation in ≥2 contiguous leads and/or left bundle branch block). Acute myocardial infarction events occurring at non-VA hospitals that were not transferred to a VA facility were detected using an inpatient ICD-9 code (410) for AMI in Medicare data or VA fee-for-service data files. Fatal AMI events occurring within the VA, those transferred from non-VA hospitals, and those occurring at non-VA hospitals not transferred to a VA facility were defined as an International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision code for AMI (I21.0-.9) as the first-listed underlying cause of death in death certificate data.
Covariates
Four groups of covariates were included in our analyses. First, the demographic factors were age, sex (0 = male, 1 = female), and race/ethnicity (white [reference], African American, Hispanic, or other), which were all determined through administrative data. Second, the cardiovascular risk factors were hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor (statin) use, which were all assessed using clinical, laboratory, and/or pharmacy record data collected closest to the baseline date. Blood pressure was defined as the average of 3 routine outpatient clinical measurements. Hypertension was categorized as no hypertension (blood pressure <140/90 mm Hg and no antihypertensive medication [reference]), controlled hypertension (<140/90 mm Hg with antihypertensive medication), or uncontrolled hypertension (≥140/90 mm Hg).16 Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels were categorized as less than 100 mg/dL (reference), 100 to 129 mg/dL, 130 to 159 mg/dL, or 160mg/dL or more (to convert to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0259). High-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels were categorized as 60 mg/dL or more (reference), 40 to 59mg/dL, or less than 40mg/dL (to convert to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0259). Triglyceride levels were categorized as less than 150mg/dL (reference) or 150mg/dL or more (to convert to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0113). Diabetes (yes/no) was identified using a previously validated metric that incorporates glucose measurements, antidiabetic agent use, and/or at least 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient ICD-9 codes for diabetes.17 Statin use was defined as a prescription receipt from pharmacy records within 180 days of the participant’s baseline enrollment date. Third, the HIV-specific factors were CD4 cell count, HIV-1 RNA level, and ART regimen. Data on CD4 cell counts (≥500/mm3 [reference], 200–499/mm3, or <200/mm3) and HIV-1 RNA levels (<500 copies/mL [reference] or ≥500 copies/mL) were collected at baseline. Baseline ART data were obtained through pharmacy data and categorized by type of regimen within 180 days of the baseline enrollment date. Regimen was coded as nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) plus protease inhibitors (reference), NRTIs plus nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), other regimen, or no ART regimen. Fourth, the other covariates were hepatitis C infection, renal disease, history of abuse of or dependence on alcohol or cocaine, and hemoglobin levels. Hepatitis C virus seropositivity (yes/no) was defined as a positive hepatitis C virus antibody test result or at least 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient ICD-9 codes for this diagnosis.18 Renal disease was assessed using outpatient and clinical laboratory data collected closest to baseline and was categorized as estimated glomerular filtration rate of 60 mL/min/1.73 m3 or more (reference), 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m3, or less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m3. History of abuse of or dependence on alcohol or cocaine were separately defined using ICD-9 codes.19Hemoglobin levels were categorized as 14 g/dL or more (reference), 12 to 13.9 g/dL, 10 to 11.9 g/dL, or less than 10g/dL (to convert to g/L, multiply by 10).
We also examined the influence of 2 candidate behavioral mediators and antidepressant medication use on the depression-incident AMI association. Candidate behavioral mediators were baseline smoking and body mass index (BMI, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared), assessed using the VA electronic medical record health factor data collected through standardized clinical reminders to VA clinicians.20 Smoking was categorized as never (reference), current, or past, and BMI was dichotomously categorized (<30 [reference] or ≥30). Baseline antidepressant use was defined as documentation of a filled prescription for a selective serotonin uptake inhibitor (SSRI) or tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) from VA pharmacy records during the baseline period.
Statistical Analysis
We conducted t tests for continuous variables and χ2 tests for categorical variables (or their nonparametric counterparts) to test for MDD group differences for all covariates. To examine the prospective association of depressive disorders with incident AMI, we constructed 2 sets of Cox proportional hazards models—1 set for our primary exposure variable, MDD, and 1 set for our exploratory exposure variable, dysthymic disorder. For each set, we ran4models: (1) demographics adjusted, (2) model 1 plus CVD risk factors, (3) model 2 plus HIV-specific factors, and (4) model 3 plus other covariates. We also conducted supplementary analyses to examine the influence of candidate behavioral mediators (baseline smoking and BMI) and antidepressant use (baseline SSRI and TCA use) by adding each factor individually tomodel4. Finally, we conducted sensitivity analyses to examine the effect of efavirenz use on any observed associations by replacing the ART regimen variable with an efavirenz-only variable in models 3 and 4.
Results
The characteristics of HIV-infected participants without baseline CVD, stratified by MDD status, are presented in Table 1. Significant group differences were detected for all characteristics, except LDL cholesterol, statin use, and HIV-1 RNA levels. During baseline, 4853 adults (19%) with MDD and 2296 adults (9%) with dysthymic disorder were identified. During 5.8 median years of follow-up, 490 incident AMI events (1.9%) occurred, of which 226 (46%) were within or were transferred to VA facilities, 218 (45%) were outside the VA and never transferred to VA facilities, and 46 (9%) were AMI deaths.
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics of HIV-Infected Participants in the VACS by MDD Statusa
| Characteristic | No. (%) | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No MDD (n = 21 291) |
MDD (n = 4853) |
||
| Demographic Factors | |||
| Age, mean (SD), y | 48.2 (9.7) | 47.3 (7.9) | <.001 |
| Male | 20 805 (97.7) | 4627 (95.3) | <.001 |
| Race/ethnicity | |||
| White | 7916 (37.2) | 2079 (42.8) | <.001 |
| African American | 10 245 (48.1) | 2210 (45.5) | |
| Hispanic | 1471 (6.9) | 395 (8.1) | |
| Other | 1657 (7.8) | 169 (3.5) | |
| Cardiovascular Risk Factors | |||
| Hypertensionb | |||
| None | 14 246 (67.7) | 3319 (68.9) | .004 |
| Controlled | 1431 (6.8) | 365 (7.6) | |
| Uncontrolled | 5379 (25.5) | 1131 (23.5) | |
| Diabetes | 2794 (13.1) | 773 (15.9) | <.001 |
| Lipidsb | |||
| LDL cholesterol level, mg/dL | |||
| <100 | 7118 (46.1) | 1701 (46.4) | .96 |
| 100–129 | 4579 (29.7) | 1095 (29.9) | |
| 130–159 | 2459 (15.9) | 575 (15.7) | |
| ≥160 | 1270 (8.2) | 298 (8.1) | |
| HDL cholesterol level, mg/dL | |||
| ≥60 | 1789 (11.2) | 393 (10.1) | .04 |
| 40–59 | 6100 (38.0) | 1437 (37.0) | |
| <40 | 8149 (50.8) | 2056 (52.9) | |
| Triglycerides level ≥150 mg/dL | 8250 (46.8) | 2090 (49.5) | .002 |
| Statin use | 1361 (6.4) | 325 (6.7) | .44 |
| HIV-Specific Factors | |||
| CD4 cell count, mm3b | |||
| ≥500 | 5393 (31.5) | 1329 (34.9) | <.001 |
| 200–499 | 6857 (40.0) | 1551 (40.7) | |
| <200 | 4884 (28.5) | 929 (24.4) | |
| HIV-1 RNA levelsb | |||
| ≥500 copies/mL | 9819 (55.2) | 2229 (56.4) | .16 |
| ART regimen | |||
| NRTI plus PI | 4324 (20.3) | 1071 (22.1) | .02 |
| NRTI plus NNRTI | 4708 (22.1) | 1035 (21.3) | |
| Other regimen | 1405 (6.6) | 345 (7.1) | |
| No ART | 10 852 (51.0) | 2402 (49.5) | |
| Other Covariates | |||
| Hepatitis C infection | 6917 (32.5) | 2093 (43.1) | <.001 |
| Renal diseaseb | |||
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | |||
| ≥60 | 18 564 (93.7) | 4397 (94.6) | .047 |
| 30–59 | 1011 (5.1) | 200 (4.3) | |
| <30 | 242 (1.2) | 49 (1.1) | |
| Abuse or dependence | |||
| Alcohol | 2269 (10.7) | 1356 (27.9) | <.001 |
| Cocaine | 1786 (8.4) | 1122 (23.1) | <.001 |
| Hemoglobin levels, g/dLb | |||
| ≥14 | 10 734 (55.4) | 2614 (57.6) | <.001 |
| 12–13.9 | 6150 (31.7) | 1436 (31.6) | |
| 10–11.9 | 1815 (9.4) | 379 (8.4) | |
| <10 | 679 (3.5) | 112 (2.5) | |
| Candidate Behavioral Mediators | |||
| Smoking status, %b | |||
| Current | 11 442 (57.8) | 3227 (69.9) | <.001 |
| Past | 2727 (13.8) | 502 (10.9) | |
| Never | 5640 (28.5) | 888 (19.2) | |
| BMI ≥30b | 2867 (13.7) | 782 (16.3) | <.001 |
| Antidepressant Medication | |||
| SSRI use | 4813 (22.6) | 3565 (73.5) | <.001 |
| TCA use | 3099 (22.1) | 1423 (29.3) | <.001 |
Abbreviations: ART, antiretroviral therapy; BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; MDD, major depressive disorder; NNRTI, nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor; NRTI, nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor; PI, protease inhibitor; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TCA, tricyclic antidepressant; VACS, Veterans Aging Cohort Study.
SI conversion factors: To convert HDL and LDL cholesterol to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0259; hemoglobin to grams per liter, multiply by 10; and triglycerides to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0113.
N = 26 144.
All variables had complete data except the following (numbers presented separately for no MDD and MDD categories, respectively): hemoglobin levels: 19 378 and 4541; BMI: 20 906 and 4794; CD4 cell count: 17 134 and 3809; HDL cholesterol: 16 038 and 3886; HIV-1 RNA: 17 792 and 3951; hypertension: 21 056 and 4815; LDL cholesterol: 15 426 and 3669; renal disease: 19 817 and 4646; smoking status: 19 809 and 4618; and triglycerides: 17 615 and 4223.
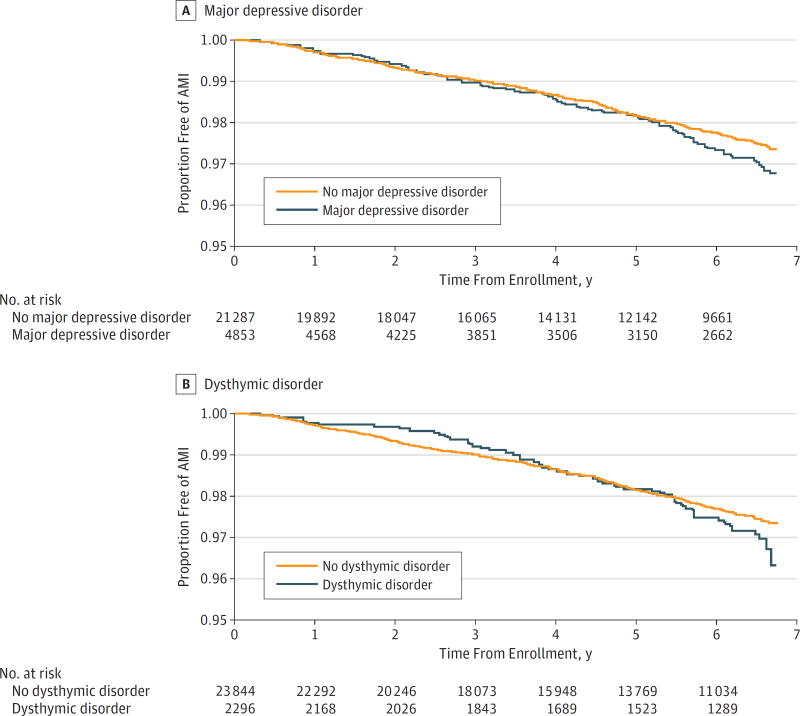
Kaplan-Meier survival curves in the Figure illustrate time to first incident AMI event and depict similar curves for those with vs without MDD until year 3, after which the MDD group demonstrates a steeper slope (Figure, A). Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for demographic factors (model 1) revealed that HIV-infected adults with MDD, vs those without MDD, had a 31% increased risk of incident AMI (hazard ratio [HR], 1.31; 95% CI, 1.05–1.62; P = .02) (Table 2). Major depressive disorder remained significantly associated with AMI after further adjustment for CVD risk factors (model 2) and HIV-specific factors (model 3), as HIV-infected adults with MDD had a 29% (HR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.04–1.60; P = .02) and 30% (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.05–1.62; P = .02) increased risk for incident AMI, respectively. The MDD–incident AMI association was not significant (P = .053) after additional adjustment for other covariates (model 4); however, the HR of 1.25 (95% CI, 1.00–1.56) demonstrates that there was little change in the magnitude of this association. In contrast, dysthymic disorder was not significantly associated with incident AMI in any of the models (Figure, B and all models in Table 2; model 1: HR, 1.26, 95% CI, 0.95–1.67; model 2: HR, 1.27, 95% CI, 0.95–1.69; model 3: HR, 1.28, 95% CI, 0.96–1.71; and model 4: HR, 1.20; 95% CI, 0.90–1.61; all P > .08), although the HRs were only slightly smaller than those for MDD. It is worth noting that our statistical power was lower in the models examining dysthymic disorder, vs those examining MDD, because of the smaller percentage of participants with the former diagnosis (9% vs 19%). Of the covariates in model 4, age, race/ethnicity, hypertension, diabetes, LDL cholesterol level, triglycerides level, CD4 cell count, hepatitis C infection, renal disease, and hemoglobin level were significantly associated with incident AMI (Table 2).
Figure. Depression-Incident Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Survival Curves.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves illustrating the time to first AMI over 5.8 median years of follow-up for human immunodeficiency virus–infected veterans (A) with vs without major depressive disorder and (B) with vs without dysthymic disorder.
Table 2.
Cox Proportional Hazards Regression Models Examining the Association Between Baseline Depressive Disorders and Incident AMIa
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Factors | Model 1 + CVD Risk Factors | Model 2 + HIV-Specific Factors | Model 3 + Other Covariatesb | |
| MDD | ||||
| No MDD | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| MDD | 1.31 (1.05–1.62)c | 1.29 (1.04–1.60)c | 1.30 (1.05–1.62)c | 1.25 (1.00–1.56) |
| Dysthymic disorder | ||||
| No dysthymic disorder | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| Dysthymic disorder | 1.26 (0.95–1.67) | 1.27 (0.95–1.69) | 1.28 (0.96–1.71) | 1.20 (0.90–1.61) |
Abbreviations: AMI, acute myocardial infarction; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HR, hazard ratio; MDD, major depressive disorder.
N = 26 140.
Model 4 includes the following covariates: age (HR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.45–1.77), sex (female: HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.38–1.57), race/ethnicity (African American: HR, 0.65, 95% CI, 0.53–0.80; Hispanic: HR, 0.56, 95% CI, 0.38–0.84; and other: HR, 0.86, 95% CI, 0.58–1.29), hypertension (controlled: HR, 1.70, 95% CI, 1.25–2.30; uncontrolled: HR, 1.72, 95% CI, 1.41–2.10), diabetes (HR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.16–1.77), dyslipidemia (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: 100–129 mg/dL: HR, 1.15, 95% CI, 0.90–1.49; 130–159 mg/dL: HR, 1.40, 95% CI, 1.05–1.86; and ≥160 mg/dL: 1.78, 95% CI: 1.28–2.48; HDL cholesterol: 40–59 mg/dL: HR, 1.06, 95% CI, 0.74–1.51; <40 mg/dL: HR, 0.97, 95% CI, 0.67–1.41; and triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL: 1.29, 95% CI, 1.07–1.57), statin use (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.71–1.29), CD4 cell counts (200–499mm3: HR, 1.20, 95% CI, 0.93–1.55; and <200 mm3: HR, 1.40, 95% CI, 1.02–1.92), HIV-1 RNA values (≥500 copies/mL: HR, 1.10; 95% CI, 0.89–1.35), antiretroviral therapy regimen (nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors plus nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors: HR, 1.06, 95% CI, 0.83–1.37; other: HR, 0.86, 95% CI, 0.57–1.28; and no antiretroviral therapy use: HR, 1.05, 95% CI, 0.83–1.34), hepatitis C infection (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.07–1.58), renal disease (estimated glomerular filtration rate: 30–59 mL/min/1.73m2: HR, 1.53, 95% CI, 1.14–2.06; and <30 mL/min/1.73m2: HR, 3.17, 95% CI, 1.94–5.18), history of alcohol (HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 0.94–1.73) and cocaine (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.61–1.27) abuse or dependence, and hemoglobin levels (12–13.9 g/dL: HR, 1.11, 95% CI, 0.89–1.39; 10–11.9 g/dL: HR, 1.61, 95% CI, 1.18– 2.19; and <10 g/dL: HR, 1.08, 95% CI, 0.57– 2.02).
P > .05.
Supplementary analyses adjusting model 4 for the candidate behavioral mediators showed that the MDD–incident AMI association continued to fall short of significance when baseline smoking variables were added (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.98–1.53; P = .08) but became significant when baseline BMI was added (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.00–1.56; P = .049) (Table 3). Current smoking (HR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.22–1.97; P < .001), but not past smoking (HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.70–1.31; P = .78) or BMI (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.61–1.04; P = .10), was associated with incident AMI. The MDD–incident AMI association remained nonsignificant (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 0.87–1.42; P = .37) after adjusting model 4 for baseline SSRI and TCA use (Table 3). Use of SSRIs (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.00–1.52; P = .048), but not TCAs (HR, 1.10; 95% CI, 0.88–1.37; P = .41), was associated with incident AMI. Sensitivity analyses—in which the ART regimen variable replaced the efavirenz-only variable—showed that the pattern of results and the magnitude of effects did not change for either MDD or dysthymic disorder (eTable in the Supplement).
Table 3.
Cox Proportional Hazards Regression Models Examining the Influence of Candidate Behavioral Mediators and Antidepressant Medication on the MDD–Incident AMI Associationa
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 4 + Smokingb | Model 4 + Body Mass Indexb | Model 4 + SSRI and TCA Useb | |
| MDD | |||
| No MDD | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| MDD | 1.22 (0.98–1.53) | 1.25 (1.00–1.56)b | 1.12 (0.87–1.42) |
| Smoking | |||
| Current | 1.55 (1.22–1.97)c | NA | NA |
| Past | 0.57 (0.70–1.31) | NA | NA |
| BMI | NA | 0.80 (0.61–1.04) | NA |
| SSRI | NA | NA | 1.23 (1.00–1.52)c |
| TCA | NA | NA | 1.10 (0.88–1.37) |
Abbreviations: AMI, acute myocardial infarction, BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); HR, hazard ratio; MDD, major depressive disorder; NA, not applicable; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TCA, tricyclic antidepressant.
N = 26 140.
Candidate behavioral mediators and antidepressant medication were added individually to model 4, which included the following covariates: age, sex, race/ethnicity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, statin use, CD4 cell count, HIV-1 RNA level, antiretroviral therapy regimen, hepatitis C infection, renal disease, history of abuse or dependence of alcohol and cocaine, and hemoglobin level.
P > .05.
Discussion
We report novel evidence suggesting that MDD is independently associated with AMI in the HIV-infected population, similar to the general population. In our sample of more than 26 000 veterans with HIV, we found that MDD at baseline was associated with an increased risk for incident AMI over 5.8years of follow-up. Specifically, after adjustment for demographics, CVD risk factors, and HIV-specific factors, HIV-infected adults with MDD had a 30% greater risk for having an AMI than did HIV-infected adults without MDD. This elevation in AMI risk was slightly attenuated to 25% (P = .053) after further adjustment for other covariates, namely, hepatitis C infection, renal disease, alcohol/cocaine abuse or dependence, and hemoglobin levels. In contrast to MDD, baseline dysthymic disorder was not associated with incident AMI.
To our knowledge, this is the first large study to examine the association between depression and incident atherosclerotic CVD among adults with HIV. In a study by Parruti and colleagues,21 no association between depression symptom severity and vascular events in HIV was observed. However, because only 19 vascular events occurred during follow-up in their cohort of 210 HIV-infected patients, they likely had low power to detect an association. Although our findings do not agree with those of Parruti et al,21 they are in line with a separate analysis we conducted of the VACS data. Specifically, we found that MDD was independently associated with incident heart failure among HIV-infected adults.22 Furthermore, the effect we observed in the present study is consistent with findings in the general population, albeit smaller in magnitude. To illustrate, in a meta-analysis of 16 studies, depression was associated with a 57% increased risk for CVD.5 Last, our findings are compatible with the literature demonstrating that depression is also independently associated with CVD prognosis in cardiac patients without HIV.23–25
While the factors explaining the MDD–incident CVD association in HIV are unknown, several candidates exist. First, the mechanisms thought to play a role in the general population could also operate in HIV. Potential biological mechanisms are systemic inflammation,26 autonomic nervous system dysfunction,27 hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation,28 and altered platelet function.29 Elevated markers of inflammation and coagulation have also been found to be associated with CVD events in those with HIV.30–33 Thus, it is possible that the presence of MDD further exacerbates the persistent inflammatory and coagulatory activation already present in HIV, resulting in higher CVD event rates. Potential behavioral mechanisms underlying the MDD–incident CVD association are poor health behaviors (eg, smoking and sedentary lifestyle) and treatment nonadherence,34 including lower adherence to CVD primary prevention efforts (eg, statins).35 Adjusting for smoking in our analyses only slightly attenuated the observed association and adjusting for BMI did not change it, suggesting that these factors may not be operating as mediators (Table 3). However, we examined baseline smoking and BMI and not changes in these factors during follow-up. Treatment nonadherence in those with HIV may play a larger role because lower adherence to HIV therapies or CVD primary prevention efforts could promote CVD. In fact, depression has been shown to reduce adherence to HIV/AIDS treatment.36 Thus, it is possible that the presence of MDD reduces adherence to both HIV- and CVD-related interventions, leading to higher CVD event rates. Finally, because social isolation is common in depression37 and has been found to be associated with incident CVD38 and all-cause mortality,39 it is yet another candidate mechanism that could underlie the MDD–incident CVD association.
In addition to these mechanistic pathways, the use of certain medications could partially explain the MDD–incident CVD association in HIV-infected adults. For instance, use of the HIV antiretroviral efavirenz has been linked to depression, higher risk for suicidality,40 and AMI events.41 However, efavirenz use is an unlikely explanation of the MDD–incident AMI association that we observed. First, efavirenz use was lower in those with vs without MDD (25% vs 30%, P < .001). Second, rerunning models 3 and 4 after adding an efavirenz-only variable as a covariate demonstrated the same pattern of results and magnitude of effects.
The limitations of our study should be noted. First, because our depressive disorder variables were based on electronic medical record ICD-9 codes, some misclassification certainly occurred (ie, patients with unrecognized depressive disorders were classified as not having these conditions). However, such misclassification would bias our results to the null and potentially attenuate the association between depressive disorders and incident AMI. Second, because of the lower rates of dysthymic disorder relative to MDD, our models involving this exposure variable may be underpowered and, thus, may have failed to detect important associations. Third, because a comprehensive assessment of lifetime depression history is not available for the VACS, we could not evaluate the influence of the number and/or duration of past depressive episodes on AMI risk. Fourth, we could not examine the effect of depression status and depression treatment exposure during the follow-up period on AMI risk or the reported associations, as data regarding these factors are not currently available for the VACS. Fifth, our analysis could not examine the association between depression and CVD death nor differentiate between AMI death and sudden cardiac death. Sixth, our analyses did not include baseline aspirin use because aspirin use is often purchased over the counter and therefore incompletely captured in the VA pharmacy records. Last, given that more than 95% of our sample included male veterans, future studies are needed to determine whether our findings generalize to women and non-VA populations.
Conclusions
With the advent of ART and improved survival, HIV-infected people are living longer and are now at an increased risk for CVD.1,42 Thus, there is an urgent need to identify risk factors and primary prevention approaches for CVD in HIV. We report novel evidence that HIV-infected adults with MDD have a greater risk for AMI than HIV-infected adults without MDD after adjustment for many potential confounders. Our findings raise the possibility that, similar to the general population, MDD may be independently associated with incident atherosclerotic CVD in the HIV-infected population. Considering the dearth of research in this area, future epidemiologic and mechanistic studies that include women and non-VA populations with HIV are needed. Furthermore, there is a need for clinical trials designed to evaluate the effect of high-quality depression treatment on CVD risk markers and incident events in HIV-infected adults with depression. Ultimately, this line of research could have substantial clinical ramifications; it could identify a novel and prevalent CVD risk factor (depression) and a new CVD primary prevention approach (depression treatment), which in turn could help to reduce CVD morbidity and mortality in adults with HIV.
Supplementary Material
Key Points.
Question
Is depression independently associated with incident atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–infected population?
Findings
In this cohort study of 26 144 veterans without CVD, HIV-infected adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) had a greater risk for acute myocardial infarction than HIV-infected adults without MDD after adjustment for many potential confounders.
Meaning
Major depressive disorder may be an independent predictor of incident atherosclerotic CVD in the HIV-infected population.
Acknowledgments
Funding/Support: The Veterans Aging Cohort Study was funded by grant U10 AA 13566 from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and Veterans Health Administration Public Health Strategic Health Core Group. This analysis was funded in part by grant R01HL126557 from the National Institutes of Health.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Footnotes
Author Contributions: Dr Freiberg had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Concept and design: Khambaty, Stewart, Gupta, Bedimo, Crane, Gibert, Justice, Freiberg.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Khambaty, Stewart, Gupta, Chang, Bedimo, Budoff, Butt, Leaf, Rimland, Tindle, So-Armah, Justice, Freiberg.
Drafting of the manuscript: Khambaty, Stewart, Leaf, Freiberg.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Stewart, Gupta, Chang, Bedimo, Budoff, Butt, Crane, Gibert, Leaf, Rimland, Tindle, So-Armah, Justice, Freiberg.
Statistical analysis: Chang, Leaf.
Obtaining funding: Stewart, Gupta, Justice, Freiberg.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Gupta, Budoff, Leaf, Rimland, Tindle, So-Armah, Justice.
Study supervision: Stewart, Gupta, Budoff, Leaf, Justice, Freiberg.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: All authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Dr Bedimo has received grants and/or other forms of funding from Merck & Co, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Theratechnologies, and Gilead Sciences. Dr Budoff has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and General Electric. Dr Butt has received grants from Gilead and AbbVie. Dr So-Armah has received grants from the National Institutes of Health. No other disclosures were reported.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the position or policy of the US Department of Veterans Affairs.
Previous Presentation: This study was presented in part at the 2014 Annual Meeting of the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; March 5, 2014; Boston, Massachusetts.
References
- 1.Porter K, Babiker A, Bhaskaran K, et al. CASCADE Collaboration. Determinants of survival following HIV-1 seroconversion after the introduction of HAART. Lancet. 2003;362(9392):1267–1274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(03)14570-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sackoff JE, Hanna DB, Pfeiffer MR, Torian LV. Causes of death among persons with AIDS in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: New York City. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145(6):397–406. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-6-200609190-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Freiberg MS, Chang C-CH, Kuller LH, et al. HIV infection and the risk of acute myocardial infarction. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(8):614–622. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Goodwin RD, Davidson KW, Keyes K. Mental disorders and cardiovascular disease among adults in the United States. J Psychiatr Res. 2009;43(3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Van der Kooy K, van Hout H, Marwijk H, Marten H, Stehouwer C, Beekman A. Depression and the risk for cardiovascular diseases: systematic review and meta analysis. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;22(7):613–626. doi: 10.1002/gps.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Suls J, Bunde J. Anger, anxiety, and depression as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the problems and implications of overlapping affective dispositions. Psychol Bull. 2005;131(2):260–300. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.131.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rosengren A, Hawken S, Ôunpuu S, et al. INTERHEART investigators. Association of psychosocial risk factors with risk of acute myocardial infarction in 11119 cases and 13648 controls from 52 countries (the INTERHEART Study): case-control study. Lancet. 2004;364(9438):953–962. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stewart JC, Perkins AJ, Callahan CM. Effect of collaborative care for depression on risk of cardiovascular events: data from the IMPACT randomized controlled trial. Psychosom Med. 2014;76(1):29–37. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Salomon EA, Mimiaga MJ, Husnik MJ, et al. Depressive symptoms, utilization of mental health care, substance use and sexual risk among young men who have sex with men in EXPLORE: implications for age-specific interventions. AIDS Behav. 2009;13(4):811–821. doi: 10.1007/s10461-008-9439-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kagee A, Martin L. Symptoms of depression and anxiety among a sample of South African patients living with HIV. AIDS Care. 2010;22(2):159–165. doi: 10.1080/09540120903111445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Markowitz JC, Kocsis JH, Bleiberg KL, Christos PJ, Sacks M. A comparative trial of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for “pure” dysthymic patients. J Affect Disord. 2005;89(1–3):167–175. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2005.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000. text revision. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fultz SL, Skanderson M, Mole LA, et al. Development and verification of a “virtual” cohort using the National VA Health Information System. Med Care. 2006;44(8 suppl 2):S25–S30. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000223670.00890.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Justice AC, Dombrowski E, Conigliaro J, et al. Veterans Aging Cohort Study (VACS): overview and description. Med Care. 2006;44(8 suppl 2):S13–S24. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000223741.02074.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Every NR, Fihn SD, Sales AE, Keane A, Ritchie JR QUERI IHD Executive Committee. Quality Enhancement Research Initiative in ischemic heart disease: a quality initiative from the Department of Veterans Affairs. Med Care. 2000;38(6 suppl 1):I49–I59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42(6):1206–1252. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Butt AA, Fultz SL, Kwoh CK, Kelley D, Skanderson M, Justice AC. Risk of diabetes in HIV infected veterans pre- and post-HAART and the role of HCV coinfection. Hepatology. 2004;40(1):115–119. doi: 10.1002/hep.20289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goulet JL, Fultz SL, McGinnis KA, Justice AC. Relative prevalence of comorbidities and treatment contraindications in HIV-mono-infected and HIV/HCV-co-infected veterans. AIDS. 2005;19(suppl 3):S99–S105. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000192077.11067.e5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kraemer KL, McGinnis KA, Skanderson M, et al. Alcohol problems and health care services use in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected and HIV-uninfected veterans. Med Care. 2006;44(8 suppl 2):S44–S51. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000223703.91275.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McGinnis KA, Brandt CA, Skanderson M, et al. Validating smoking data from the Veteran’s Affairs Health Factors dataset, an electronic data source. Nicotine Tob Res. 2011;13(12):1233–1239. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntr206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Parruti G, Vadini F, Sozio F, et al. Psychological factors, including alexithymia, in the prediction of cardiovascular risk in HIV infected patients: results of a cohort study. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.White JR, Chang C-CH, So-Armah KA, et al. Depression and human immunodeficiency virus infection are risk factors for incident heart failure among veterans: Veterans Aging Cohort Study. Circulation. 2015;132(17):1630–1638. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Glassman AH, Shapiro PA. Depression and the course of coronary artery disease. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(1):4–11. doi: 10.1176/ajp.155.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kirkman MS, Briscoe VJ, Clark N, et al. Diabetes in older adults. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(12):2650–2664. doi: 10.2337/dc12-1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schütt M, Fach EM, Seufert J, et al. DPV Initiative and the German BMBF Competence Network Diabetes Mellitus. Multiple complications and frequent severe hypoglycaemia in ‘elderly’ and ‘old’ patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2012;29(8):e176–e179. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2012.03681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Howren MB, Lamkin DM, Suls J. Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. 2009;71(2):171–186. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181907c1b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Carney RM, Freedland KE, Veith RC. Depression, the autonomic nervous system, and coronary heart disease. Psychosom Med. 2005;67(suppl 1):S29–S33. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000162254.61556.d5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vreeburg SA, Hoogendijk WJ, van Pelt J, et al. Major depressive disorder and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: results from a large cohort study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(6):617–626. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bruce EC, Musselman DL. Depression, alterations in platelet function, and ischemic heart disease. Psychosom Med. 2005;67(suppl 1):S34–S36. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000164227.63647.d9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Duprez DA, Neuhaus J, Kuller LH, et al. INSIGHT SMART Study Group. Inflammation, coagulation and cardiovascular disease in HIV-infected individuals. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Deeks SG. HIV infection, inflammation, immunosenescence, and aging. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:141–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-042909-093756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kuller LH, Tracy R, Belloso W, et al. INSIGHT SMART Study Group. Inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers and mortality in patients with HIV infection. PLoS Med. 2008;5(10):e203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sandler NG, Wand H, Roque A, et al. INSIGHT SMART Study Group. Plasma levels of soluble CD14 independently predict mortality in HIV infection. J Infect Dis. 2011;203(6):780–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lett HS, Blumenthal JA, Babyak MA, et al. Depression as a risk factor for coronary artery disease: evidence, mechanisms, and treatment. Psychosom Med. 2004;66(3):305–315. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000126207.43307.c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Berntson J, Stewart KR, Vrany E, Khambaty T, Stewart JC. Depressive symptoms and self-reported adherence to medical recommendations to prevent cardiovascular disease: NHANES 2005–2010. Soc Sci Med. 2015;138:74–81. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2015.05.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gonzalez JS, Batchelder AW, Psaros C, Safren SA. Depression and HIV/AIDS treatment nonadherence: a review and meta-analysis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;58(2):181–187. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31822d490a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nabi H, Hall M, Koskenvuo M, et al. Psychological and somatic symptoms of anxiety and risk of coronary heart disease: the health and social support prospective cohort study. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(4):378–385. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.07.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Denollet J, Freedland KE, Carney RM, de Jonge P, Roest AM. Cognitive-affective symptoms of depression after myocardial infarction: different prognostic importance across age groups. Psychosom Med. 2013;75(7):701–708. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e31829dbd36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Greysen SR, Horwitz LI, Covinsky KE, Gordon K, Ohl ME, Justice AC. Does social isolation predict hospitalization and mortality among HIV+ and uninfected older veterans? J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61(9):1456–1463. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mollan KR, Smurzynski M, Eron JJ, et al. Association between efavirenz as initial therapy for HIV-1 infection and increased risk for suicidal ideation or attempted or completed suicide: an analysis of trial data. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/M14-0293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Durand M, Sheehy O, Baril J-G, Lelorier J, Tremblay CL. Association between HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy, and risk of acute myocardial infarction: a cohort and nested case-control study using Québec’s public health insurance database. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;57(3):245–253. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31821d33a5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Triant VA, Lee H, Hadigan C, Grinspoon SK. Increased acute myocardial infarction rates and cardiovascular risk factors among patients with human immunodeficiency virus disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(7):2506–2512. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.