Abstract
Although uncommon, rotator cuff tears that occur medially at the musculotendinous junction can result from acute trauma, anatomic force imbalance, or medial row cuff failure following a previous rotator cuff repair. The quality of the torn muscle and tendon along with the length of the remnant tendon stump should be considered before deciding on the most appropriate repair technique. When muscle and tendon quality are sufficient, the tear can often be repaired directly to the remnant tendon stump and compressed onto the greater tuberosity. If the remnant tendon stump is degenerative, of insufficient length, or lacks tendon in which to place sutures, an allograft patch can be used to augment the repair. When the quality of the remaining muscle and tendon are poor or when the muscle is retracted too far medially and is nonmobile, a bridging technique such as superior capsule reconstruction is preferable. The purpose of this report is to (1) highlight that medial cuff failure can occur both primarily and after previous repair; (2) define and classify the 3 major tear patterns that are encountered, and (3) describe the authors' preferred techniques for medial cuff repair that specifically address each of the major tear patterns.
Although tears near the musculotendinous junction (MTJ) are common in some areas of the body, they infrequently involve the rotator cuff where the majority of tears present with detachment of the footprint from the greater tuberosity. Only a small number of case reports of have described the treatment of rotator cuff tears near the MTJ—many of these reports specifically refer to the infraspinatus1, 2, 3 whereas others refer specifically to the supraspinatus.4, 5, 6 Although the precise etiologies of medial cuff tears are not fully understood, they are likely to be multifactorial and may include any combination of acute or chronic trauma with established subacromial impingement.4, 5, 6
In general, rotator cuff tendon repair techniques aim to restore the anatomic rotator cuff footprint,7 achieve adequate footprint compression,8 minimize gap formation,9 and maximize ultimate load-to-failure.10 With tears at the MTJ, repair techniques rely more on soft tissue–to–soft tissue fixation as opposed to soft tissue to bone. Although we have seen an overall reduction in repair failures with anatomic constructs that follow the aforementioned biomechanical criteria,11 there are still some retears. One of the mechanisms of failure may be related to biologic insufficiency of the repaired cuff tendon (e.g., failure at the suture-tendon interface).12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 Specifically, repair constructs that have sutures at the MTJ have introduced a new failure mechanism characterized by suture cut-out at or near the MTJ.4, 5, 6
Medial tears of the rotator cuff that occur at the MTJ can occur primarily (without prior surgery), or secondarily after previous rotator cuff repair (secondary or type 2 failures). Both pose relevant treatment challenges. Primary failure usually occurs from a traumatic injury to the shoulder. Secondary injuries occur after previous surgery. Cho et al. described this type of failure and classified it as a type 2 failure where the tendon fails medially, close to the MTJ.12, 19, 20, 21, 22 Secondary medial cuff failure near the MTJ after repair (type 2 failure) has been associated with the placement of knots and abrasive suture materials near the MTJ, thus potentially resulting in acute or chronic subacromial knot impingement, medial stress concentration, tendon strangulation, and/or suture cut-out in this area.12, 19, 20, 21, 22 When failure occurs, the tendon/muscle is found to be torn medial to the previous repair site whereas the cuff tendon insertion remains intact and well fixed to the greater tuberosity.
Surgical treatment of these tears is challenging because of the short or absent medial tendon stump; the lack of sufficient tendon medially, the susceptibility of sutures to tear through degenerated tissues or the medial muscle fibers at the MTJ, the difficulty in restoring the length-tension relation of the cuff tendon without overtensioning the repair site, and the lack of sufficient clinical outcomes data to guide surgical decision making. As a result, when surgeons encounter these types of tears, there is little information to guide them.4, 5, 6 The purpose of this report is to highlight that (1) medial cuff failure can occur both primarily and secondarily after previous repair; (2) to define and classify the 3 major tear patterns that are encountered, and (3) to describe our preferred techniques for medial cuff repair that specifically address each of the major tear patterns.
Patient Selection
The decision to pursue rotator cuff repair in general is dependent on a number of patient-centered variables, such as symptoms, demographics, comorbidities, physical goals, and the expected outcomes of surgery, among others. Although many of the physical examination findings and biologic features are similar to those found in more common rotator cuff tear variants, there are several pathobiologic features of medial cuff tears that are important indicators of repairability, including the chronicity of the tear, the degree of retraction, the amount of fatty infiltration, the global tissue quality, the quality of the tissue in the medial stump, the length of the remnant tendon stump laterally, the bone quality of the glenoid and greater tuberosity, the acromion morphology, and, in cases of secondary MTJ tears, the number and location of suture anchors used for the previous cuff repair. Three major patterns of MTJ tears occur. Type A tears occur when the tendon and muscle are both healthy and adequate. This tear pattern is seen frequently with primary tears that occur and are treated acutely. Most cases of type A medial cuff tears can be repaired primarily and fixed to the greater tuberosity using a double-row technique. Type B tears occur when there is a healthy muscle laterally, but the remaining medial tendon is short and retracted. When healthy muscle tissue and poor tendon quality is encountered in these type B tears, the medial stump is advanced laterally and an allograft patch can be used to augment the repair. Type C tears occur when the tears become chronic. In such cases, there may be tendon remaining at the footprint but the muscle is retracted, is of insufficient length, and has fatty infiltration (i.e., Goutallier grade 3 or 4). In such cases, the native medial rotator cuff tissue cannot be repaired primarily and some type of reconstructive procedure must be employed such as the recently described superior capsule reconstruction (SCR) procedure, latissimus dorsi tendon transfer, or reverse shoulder arthroplasty. The authors' present preferred approach is the SCR, as it is proving to be a viable and reproducible surgical option for patients with type C tears who are otherwise poor candidates for reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA) or tendon transfer.23, 24, 25
Surgical Techniques
Patient Positioning and Anesthesia
After placement of a regional interscalene block and induction of general anesthesia, the patient is placed in a modified beach-chair position and the operative extremity is situated in a pneumatic arm holder (Tenet T-Max Beach Chair and Spider arm positioner; Smith & Nephew, Memphis, TN). The operative shoulder and axilla are prepared and draped using sterile techniques.
Diagnostic Arthroscopy
Diagnostic arthroscopy is first performed after establishing a posterior viewing portal and an anterior working portal through the rotator interval. The long head of the biceps tendon, biceps-labral complex, glenoid labrum, articular cartilage, and undersurface of the torn rotator cuff are thoroughly evaluated and concomitant pathologies are addressed as necessary. An anterolateral portal is established and subacromial bursectomy is performed to optimize visualization. In cases of secondary tears with medial cuff failure after previous repair, careful inspection of the undersurface of the acromion and its relation with the greater tuberosity with intraoperative dynamic passive elevation is recommended because these tears have been associated with both acute and chronic subacromial knot impingement and the presence of a corresponding impingement lesion.26 Where necessary, subacromial decompression is performed using an arthroscopic shaver (Synergy Resection Shaver Console and APS II Handpiece; Arthrex, Naples, FL) and, in cases of dynamic impingement during passive elevation, additional acromioplasty and release of the coracoacromial ligament is performed through an accessory posterolateral portal. A Bigliani type 1 acromion is created. When the critical shoulder angle is large, a lateral acromioplasty is also performed.27 When present and symptomatic, the long head of the biceps tendon is released from the superior labrum and open subpectoral tenodesis is performed, after completion of the cuff repair. Attention is then turned to repairing the torn rotator cuff.
Classification
Tears can be classified as primary (no prior surgery: type 1 tear) or secondary (occurring after prior rotator cuff repair: type 2 retear) and simultaneously by their tear patterns (Table 1). Accurate diagnosis of the tear pattern is crucial as this determines the optimal management strategy (Table 1).
Table 1.
Classification of Tears at the Musculotendinous Junction, by Their Tear Pattern
| Tear Pattern | Treatment |
|---|---|
| A. Tendon on footprint, short but adequate medial tendon | Complex bridging repair |
| B. Tendon on footprint, deficient medial tendon, with healthy muscle (MTJ can reach medial footprint) | Bridging repair with graft augmentation |
| C. Tendon on footprint laterally but deficient medial tendon with retracted, atrophied muscle with fatty infiltration | Interposition graft (superior capsule reconstruction), latissimus dorsi tendon transfer, or reverse total shoulder arthroplasty |
NOTE. Accurate diagnosis of the tear pattern is crucial as this determines the optimal management strategy. These tears are simultaneously classified as primary (no prior surgery: type 1 tear) or secondary (occurring after prior rotator cuff repair: type 2 retear).
Type A Medial Cuff Tears
Technique: Complex Bridging Repair
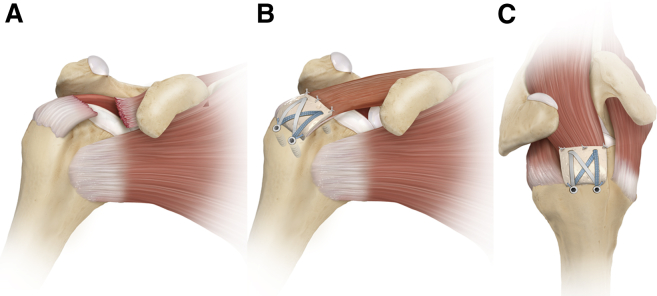
Primary medial cuff tears (type 1A MTJ tears) (Figs 1 and 2) that are treated promptly are typically amenable to repair to the lateral tendon stump as long as the final fixation construct diverts tensile stresses through the suture anchors rather than through the apposed tear edges (Fig 3). There are also many secondary type A MTJ tears that can be repaired with this method. With type A tears, there is a small amount of tendon that remains with the medial MTJ stump that aids in repair and will resist suture cutout. The remaining medial tendon stump is also typically fairly mobile and reaches the footprint. In such cases, we prefer to use an anatomic linked or bridging construct with suture tapes and sutures to decrease the chance of suture cutout after repair.
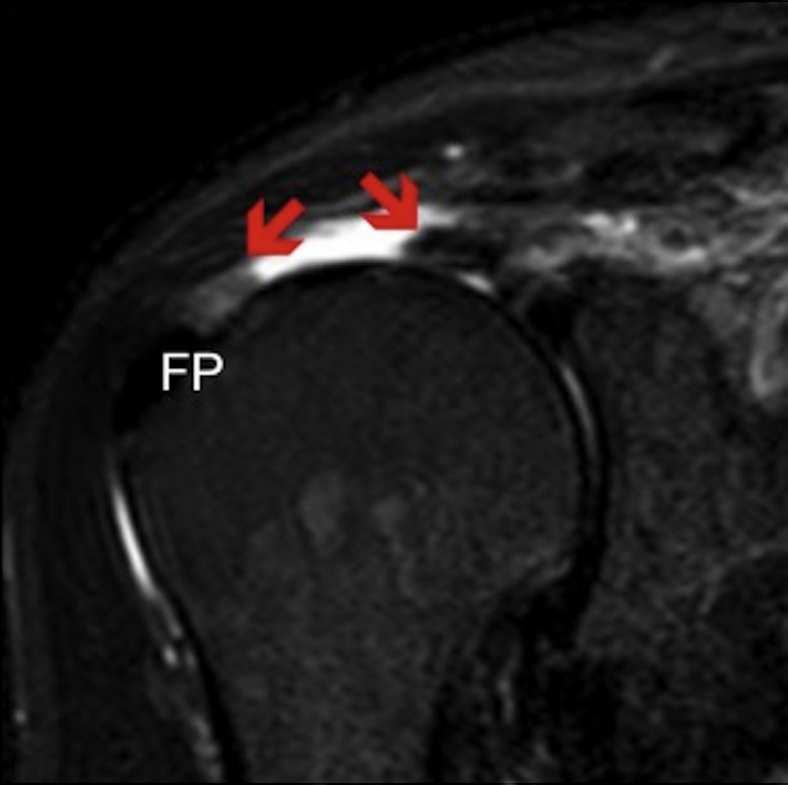
Fig 1.
A coronal T2 slice of magnetic resonance imaging showing a type 1A musculotendinous junction tear of the supraspinatus in a right shoulder. The remaining stumps and medial and lateral edges of the tear (red arrows) can be visualized. Note the lateral stump still remains attached to the footprint. (FP, footprint.)
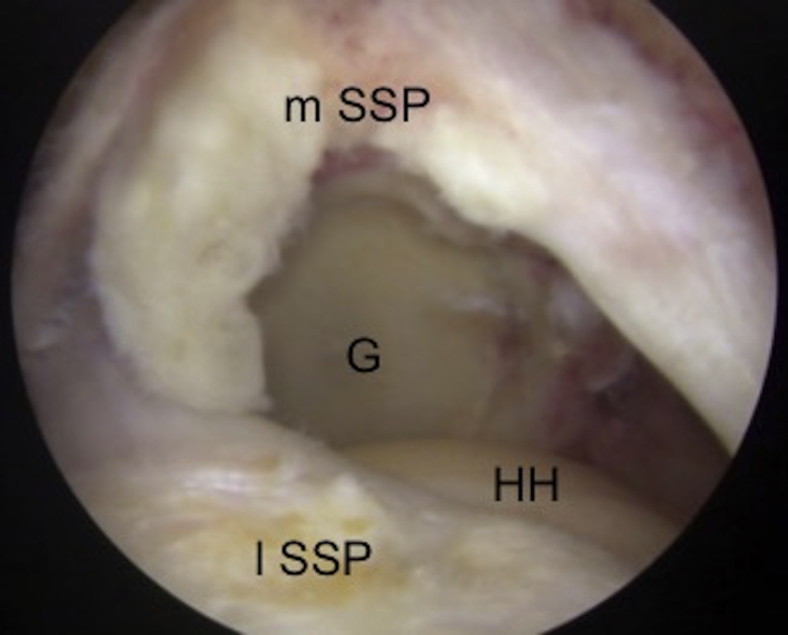
Fig 2.
Arthroscopic image of right shoulder through the posterolateral portal showing a type 1A rotator cuff tear at the musculotendinous junction of the supraspinatus. (G, glenoid; HH, humeral head; lSSP, lateral margin of torn supraspinatus; mSSP, medial margin of torn supraspinatus.)
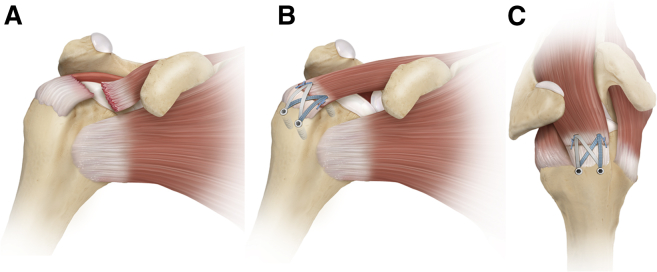
Fig 3.
Primary repair of a type A tear at the musculotendinous junction in a right shoulder. (A) Illustration with a view from the anterior aspect, showing a tear of supraspinatus (SSP) at the musculotendinous junction. (B) Illustration with the same view, showing the SSP, which is pulled laterally and compressed down with a SpeedBridge technique using medial and lateral row anchors. (C) Illustration with a view from the superolateral aspect, showing the linked double-row construct. Margin convergence sutures are used to appose the lateral tendon stump and medial muscular portion. The acromion has been removed for clarity.
In these cases, the torn edge at the MTJ is first debrided to remove frayed and degenerative tissue and a grasper is used to assess the tendon's mediolateral mobility. Intra- and extra-articular releases are performed as necessary to allow for adequate lateral excursion of the muscle substance in preparation for repair—this step is critical for the planning of anchor placement that ensures restoration of the resting length-tension relation of the torn cuff muscle. The footprint on the tuberosity is prepared and can be medialized 1 to 2 mm onto the articular surface to create a bony bed for healing. This step is very important to achieve healing in primary repair of tears at the MTJ. The goal is to get the medial tendon stump to heal not only to the lateral tendon stump but also to the bone of the greater tuberosity. In secondary type A MTJ tears, suture anchors, if present from the previous repair, should be removed to improve the biology at the bone-tendon interface where healing and tissue regeneration needs to occur.
Typically, a hybrid double-row bridging repair with 4 anchors is performed (2 medial and 2 lateral anchors).10, 28 Although rarely needed, additional anchors may be added when larger tears are encountered.23 After preparing the footprint and debriding 1 to 2 mm of the articular margin, the medial anchors are placed in the greater tuberosity. We recommend maintaining an anteroposterior bone bridge of about 10 mm between each medial anchor. An arthroscopic punch is used to create a bone socket to accommodate the anterior-medial anchor approximately 1 to 2 mm medial to the articular margin into the newly created footprint. A vented 4.75-mm knotless suture anchor loaded with no. 2 suture tape is placed in this anterior-medial socket (BioComposite SwiveLock anchor with FiberTape; Arthrex). With an arthroscopic grasper and suture passer (QuickPass SutureLasso; Arthrex), each limb of the suture tape is passed through the medial muscle/tendon remnant, approximately 3 to 5 mm medial to its lateral tear edge. Care should be taken to avoid passing the suture tapes too medially as this will overtension the repair. When a small stump of tendon remains just lateral to the MTJ, as is frequently the case for type A tears, care should be taken to pass the suture tapes through the residual tendon to optimize the length-tension relation of the repair. Preparation of the posterior-medial anchor is performed in an identical fashion while taking care to maintain a 10-mm bone bridge relative to the first medial anchor.
After placement of the medial anchors, nonabsorbable sutures are also shuttled at least 2 mm from each tear edge into the medial and lateral tendon stumps. The medial and lateral tear margins are then drawn together, and arthroscopic knots are tied. This creates medial to lateral, margin-convergence-to-bone stitches at each anchor. Although the number of sutures required for adequate repair depends on the size of cuff tear, we advise tying approximately 1 knot per 0.5 to 1.0 cm of anteroposterior length of repaired tissue. Typically, there are 2 sutures placed, 1 per medial anchor. Additional medial to lateral simple sutures can be placed as deemed necessary to sew the torn medial MTJ stump to the lateral tendon stump (Fig 4).
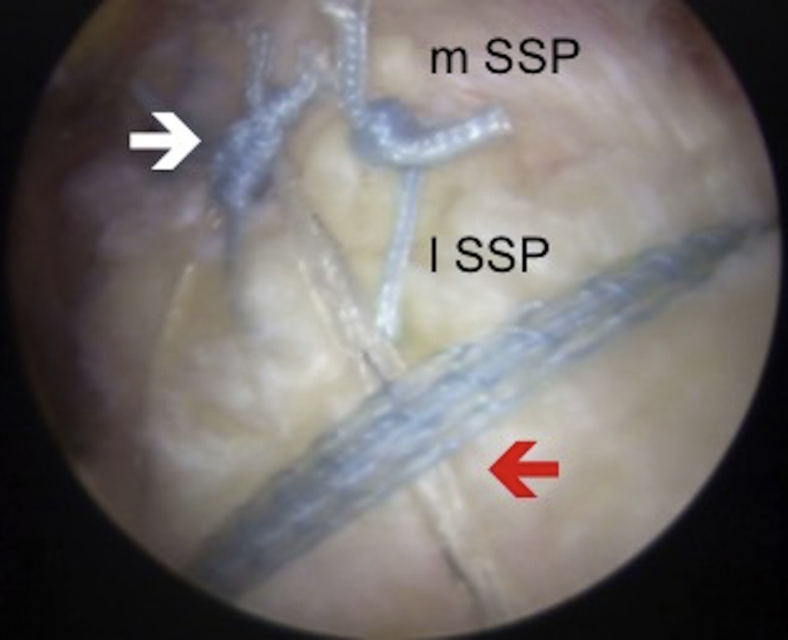
Fig 4.
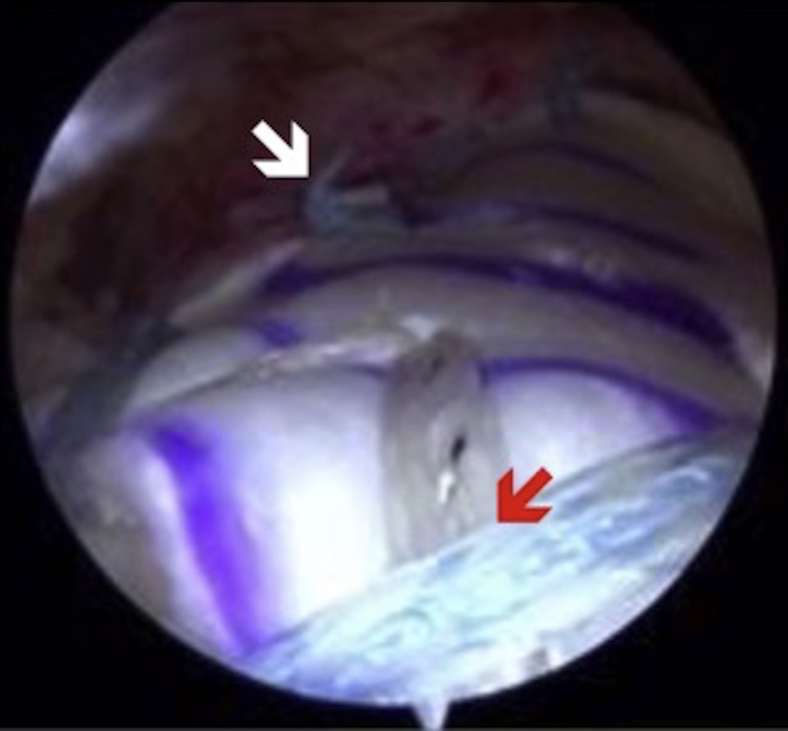
Arthroscopic image of right shoulder through the lateral portal showing repair of the rotator cuff with a linked double-row SpeedBridge (Arthrex) construct (red arrow). Additional tendon-to-tendon sutures (white arrow) were placed to appose the lateral stump and the articular margin. (lSSP, lateral margin of torn supraspinatus; mSSP, medial margin of torn supraspinatus.)
After reducing and suturing the medial and lateral tear margins, a lateral row of anchors is placed to bridge the tapes over the repair construct. An arthroscopic punch is used to prepare the anterior-lateral bone socket approximately 15 mm lateral to the corresponding medial anchor. One limb of suture tape from each medial anchor is retrieved through the anterolateral portal and preloaded into the eyelet of the anterior-lateral anchor. Gentle tension is applied through the suture tapes to reduce and compress the cuff tissue against the greater tuberosity. While maintaining adequate tension, the anterior-lateral anchor is guided into place using a driver and rotated clockwise to achieve bony fixation. The remaining suture limbs are cut, thus completing anterior-lateral anchor insertion. This procedure is repeated for placement of the posterior-lateral anchor while maintaining a minimum 15-mm distance from both the posterior-medial and anterior-lateral anchors. The tapes help disperse the force over a greater surface area and decrease the risk of cutout and at the same time serve as a bioscaffold for new tissue growth. From our experience with second look arthroscopy and from postoperative magnetic resonance images, the suture tapes act as biological scaffolds for new tissue growth that aid in healing. Furthermore, the linked and crossed nature of the construct improves the biomechanics by dispersing forces across the whole repair construct to minimize point loading, maximize self-reinforcement,29 and minimize the risk of suture cutout. After the repair, complete dynamic evaluation is then performed to ensure adequate stability and security of the repair.
Type B Tears
Chronic Medial Cuff Tears with Adequate Muscle Quality and Insufficient Tendon Length
In contrast to more acute cases, chronic medial cuff tears often exhibit insufficient tissue quality not suitable for primary repair. There may be lateral tendon that remains, but in type B cases, the medial torn rotator cuff tendon is deficient (too short) whereas the muscle remains healthy. Patch augmentation can be performed in these cases (Fig 5), especially when the quality of muscle tissue is adequate for suture holding but the quality of the remnant tendon stump is insufficient to maintain postoperative knot security.30, 31 This technique can also be used when lateral excursion of medial cuff tissue remains inadequate for primary repair to the lateral tendon stump even after extensive releases. Augmentation of such tear patterns can be useful in cases such as this.30, 31
Fig 5.
Augmentation with a human acellular dermal extracellular matrix patch in a right shoulder for a type B tear at the musculotendinous junction, which can be performed in an arthroscopic or open procedure. (A) Illustration with a view from the anterior aspect, showing a tear of supraspinatus (SSP) at the musculotendinous junction. The muscle has retracted away from the tendon stump. (B) Illustration with the same view. The tendon is debrided and the SSP has been pulled laterally. The insufficient length of the SSP has been augmented with a patch. The patch and lateral edge of the remaining host tissue is compressed down to the anatomic footprint with a SpeedBridge technique using medial and lateral row anchors. (C) Illustration with a view from the superolateral aspect, showing the linked double-row construct. Horizontal mattress stitches are used for additional stability, attaching the patch to native host cuff tissue.
When using tissue augmentation, most studies suggest that allografts work better than xenografts.32 We believe that active patients who present with chronic medial cuff tears with insufficient lateral excursion (type B MTJ tears) are particularly suited for this procedure, particularly when the tendon can reach to the medial aspect of the footprint on the greater tuberosity. Although the operation is now typically performed arthroscopically, for many years we did open repair with patch augmentation through a deltoid split for larger tears or when an extended double-row repair is anticipated and good results were obtained.31 It should be noted that current commercially available allograft materials are not approved by the Food and Drug Administration to span across a tissue defect more than 1 cm in distance and, thus, using these materials to span larger gaps is considered off-label use.
Technique: Double-Row Repair with Patch Augmentation
Following diagnostic arthroscopy (as described above), subacromial bursectomy, decompression, and acromioplasty are performed as necessary. Acromioplasty is often done in this setting to prevent graft abrasion beneath the acromion. The lateral tendon stump is resected, previous suture anchors are removed where applicable, and the greater tuberosity footprint is debrided to a bleeding surface. An arthroscopic ruler is used to measure the area of tendon loss that corresponds to the required dimensions of the allograft patch (ArthroFlex; Arthrex). On the back table, the patch is then trimmed to match the planned area of augmentation. The planned sites for medial suture anchors are prepared using the techniques described above, each anchor is double-loaded with no. 2 nonabsorbable suture (FiberWire; Arthrex) and no. 2 suture tape (FiberTape; Arthrex), and each medial anchor is inserted while maintaining an adequate bone bridge. One strand each of the nonabsorbable suture and the suture tape are passed through the medial cuff remnant approximately 5 mm medial to the tear edge using a standard shuttling device. Each limb of suture and suture tape is retrieved and pulled through the anterolateral portal. The suture tapes are then passed through the medial and lateral regions of the patch allograft ex vivo according to its planned in vivo positioning while maintaining a distance of at least 5 mm from its cut edges.
With the arthroscope in the posterior portal, the patch is introduced into the subacromial space through the anterolateral portal following the path of the suture tapes, which guides the patch allograft into the correct position on the medial cuff remnant. Using the previously loaded no. 2 nonabsorbable sutures tied over the allograft in a horizontal mattress configuration, the remnant medial cuff tissue is reduced and secured to the greater tuberosity together with the patch allograft. The planned sites for lateral row anchor placements are then marked using a radiofrequency ablator as described above. An arthroscopic punch is again used to prepare the bone sockets laterally. One limb of suture tape from each medial anchor is retrieved and loaded into another knotless suture anchor that is subsequently driven into the first lateral bone socket. The suture tapes are then pulled to achieved adequate tension, thus reducing the patch allograft laterally and completely covering the greater tuberosity footprint. The suture tails are then cut and the procedure is repeated as necessary using the remaining limbs of suture tape from each medial anchor. In this way, the graft acts to reinforce the repair and as an augment for new tissue growth (bioscaffold).
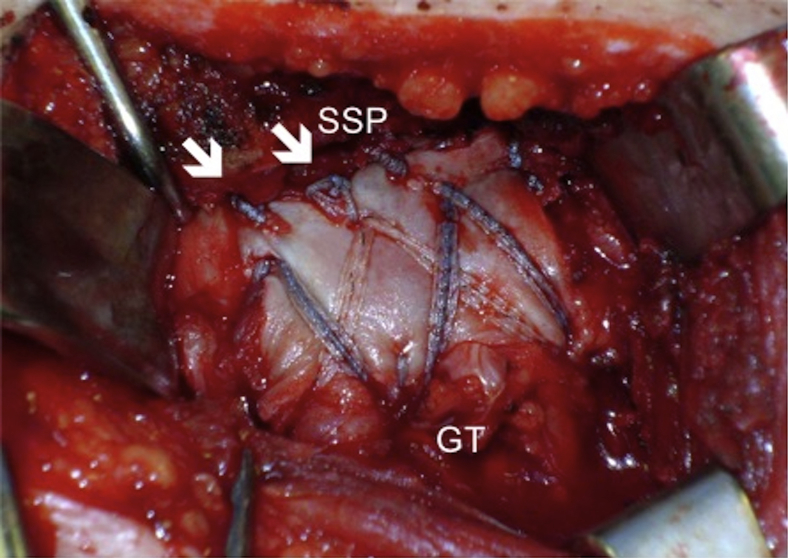
An open technique can also be used for these types of tears, which is shown in Video 1, and the final construct can be seen in Fig 6.
Fig 6.
A photograph of an extended, linked double-row construct showing the integration of a human acellular dermal patch into the rotator cuff repair in a left shoulder. The rotator cuff was repaired medially onto the native tendon footprint of the tuberosity, the graft was placed on top of the native tendon, and the graft was secured by sutures and suture tapes, thus completing the double-row construct. (GT, greater tuberosity; SSP, supraspinatus; white arrows are additional sutures.)
Type C MTJ Tears
Chronic Medial Cuff Tears with Poor Muscle Quality or Tear Extension
Chronic medial cuff tears (Fig 7) with inferior extension or fatty infiltration (i.e., Goutallier grade 3 or 4) are particularly challenging to repair because of the high rates of clinical and structural failure even when patch augmentation techniques are used.33, 34, 35 Historically, techniques that involved bridging across a rotator cuff tendon defect with a graft have not been favorable; however, new evidence suggests that bridging grafts may provide significant clinical benefit for selected patients with chronic tendon loss who are not ideal candidates for other salvage procedures (e.g., partial repair, tendon transfer, or RTSA, among others).36, 37, 38
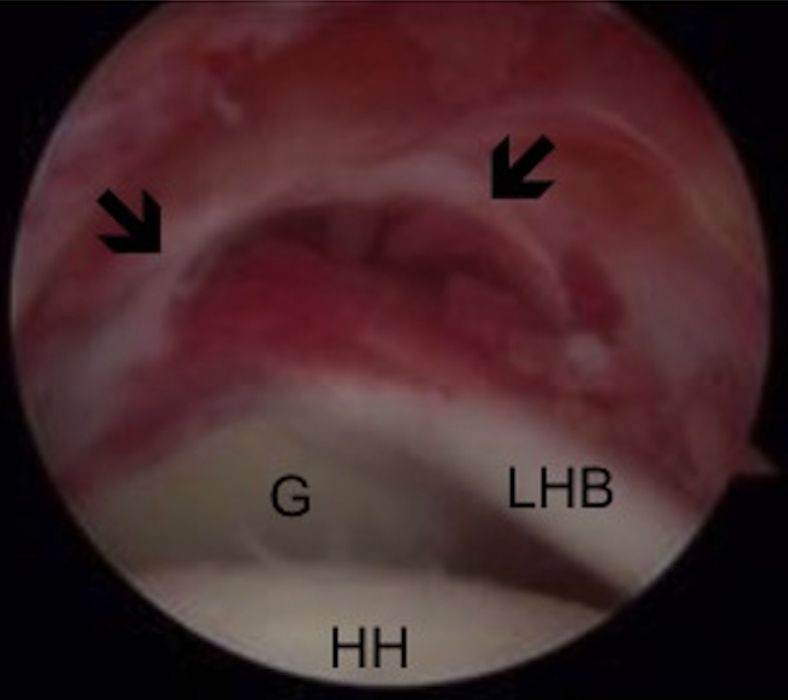
Fig 7.
Arthroscopic image of right shoulder through the posterolateral portal showing a massive type C tear at the musculotendinous junction. The rotator cuff is retracted (black arrows), making successful reattachment directly to the footprint unachievable. (G, glenoid; HH, humeral head; LHB, long head of biceps.)
Because patients with type C tears are often young and therefore not ideal candidates for RTSA, Mihata et al.39 developed the SCR, a procedure in which a fascia lata autograft is anchored to both the superior glenoid and the greater tuberosity, thereby reconstituting the superior capsule, which is normally confluent with the undersurface of the rotator cuff. The SCR functions as a superior stabilizer that prevents proximal humeral migration in the setting of a chronic, massive rotator cuff tear. Preliminary clinical data have been favorable thus far39; however, given its recent development, longer-term follow-up will be needed to evaluate the effectiveness of the procedure relative to other salvage options.
Technique: Superior Capsule Reconstruction
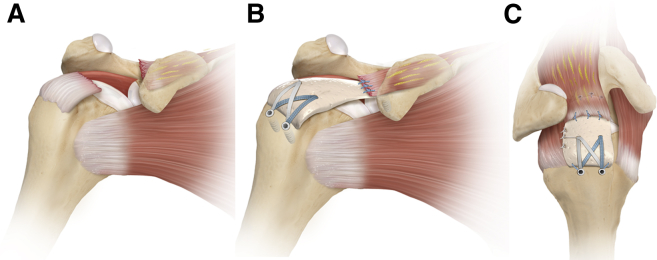
Our preferred technique for SCR is similar to that described by Mihata et al.,39 but we have modified the technique to use an off-the-shelf allograft to obviate donor site morbidity. We typically use the thickest graft available as Mihata et al.40 recently published a biomechanical study showing that thicker grafts, especially when placed between 15° and 45° of scaption, can reduce proximal humeral migration. As such, with our modified technique24, 25 (Figs 8 and 9) we use a commercially available allograft with greater mechanical strength (3.5 mm thickness) (ArthroFlex; Arthrex). In general, we typically perform an acromioplasty in these cases to reduce the possibility of graft-cuff abrasion beneath the acromion but prefer to preserve the coracoacromial ligament to minimize the risk of anterosuperior escape. We also use marrow stimulation techniques in these cases, typically using a motorized drill to release blood and marrow components into the greater tuberosity footprint as a method to enhance graft-bone-tendon integration (PowerPick; Arthrex). A number of reports (including our own) have been published in Arthroscopy Techniques that describe the technical nuances and individual surgeon preferences involved with SCR.24, 41, 42 Therefore, readers are directed to evaluate these reports for further details and considerations regarding the procedure itself. Our preferred technique is also shown in Video 1. When there is reasonable rotator cuff tissue remaining, as may be the case in many type C tears, the remaining medial cuff tissue can be sewn in to the top of the allograft (Fig 8 B and C) to bring in additional blood supply and to enhance the repopulation of the allograft collagen scaffold. Pearls and pitfalls of the complete procedure are outlined in Table 2.
Fig 8.
Superior capsule reconstruction (SCR) in a right shoulder, for a type C tear at the musculotendinous junction. (A) Illustration with a view from the anterior aspect, showing a tear of supraspinatus (SSP) at the musculotendinous junction. The muscle has significantly retracted away from the tendon stump. The muscle quality is poor, and cannot be pulled laterally to the footprint. (B) Illustration with the same view. The tendon is debrided and SSP is not manipulated because of deficient length. A large human acellular dermal patch is used to reconstruct the superior capsule. Glenoid anchors fix the patch medially, and the lateral edge is compressed down to the anatomic footprint with a SpeedBridge technique using medial and lateral row anchors. (C) Illustration with a view from the superolateral aspect showing the linked double-row construct laterally and glenoid anchors medially.
Fig 9.
Arthroscopic image of right shoulder through the lateral portal showing a completed superior capsule reconstruction (SCR), using an extended SpeedBridge technique to fix the graft at the greater tuberosity (red arrow). Once the medial and lateral rows are secured, margin convergence sutures are placed using a side-to-side technique (white arrow), securing the posterior edge of the graft to the free edge of the remaining posterior rotator cuff.
Table 2.
Pearls and Pitfalls
| Surgical Steps | Pitfalls | Pearls |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic arthroscopy | Missing concomitant lesions | Performing a thorough and standardized examination allows for identification of concomitant lesions. |
| Mobilization of the rotator cuff | Insufficient release and poor debridement of tendon lateral to the tear may lead to poor healing. | If complete footprint coverage with native rotator cuff after debridement cannot be achieved, consider patch augmentation or superior capsule reconstruction. |
| Overly aggressive release can lead to traction damage to the suprascapular nerve and compromise blood supply. | ||
| Medial-row anchor insertions | Dog-ear formation | The surgeon should start with the anterior and posterior anchors and work from outside in |
| If a human acellular dermal patch is required: Preparation of ArthroFlex patch according to defect size and suture passage with SutureLasso | Incorrect size measurement, resulting in a graft that is too large or too small | Use of an arthroscopic ruler beforehand (arthroscopic measurement probe, 220 mm, 60°) |
| Introduction of patch | Suture derangement | Arthroscopic visualization from the posterior portal and patch introduction through the anterolateral portal with an arthroscopic knot pusher |
| Lateral-row anchor insertions and fixation | Insufficient room | A radiofrequency device can be used to mark the location for the anchors to be inserted. |
| Soft bone | Assess bone quality with a punch. If the bone is soft, a 5.5-mm BioComposite SwiveLock should be used. | |
| Dog-ear formation | The surgeon should start with the anterior and posterior anchors and work from outside in. | |
| Postoperative rehabilitation | Postoperative stiffness | Early passive range of motion for 4 weeks Progression to full passive motion and start of active and active-assisted motion at 6 weeks postoperatively. |
Postoperative Rehabilitation
Our routine postoperative rehabilitation protocol after rotator cuff repair consists of early passive range of motion for 4 weeks limited to 30° of external rotation, 90° of abduction, and 120° of forward flexion, after which full passive and active-assisted range of motion exercises are permitted. For type B and C MTJ tears where a graft is used, we immobilize in a sling for 6 weeks with an abduction pillow to allow for the graft to incorporate. At 6 weeks, passive motion is started, and active motion is allowed at 8 weeks. When tenodesis of the long head of the biceps tendon is performed, resisted elbow flexion is restricted up to 4 weeks postoperatively. For type A tears, active shoulder motion exercises are commenced at 6 weeks. Full return to daily activities (including sports) is typically achieved after 4 to 6 months of structured rehabilitation.
Discussion
Rotator cuff tears that occur medially near the MTJ are relatively uncommon, but they can have devastating effects on shoulder function and the quality of life of affected patients when appropriate surgical management is not performed. Because of the number of rotator cuff repairs that are being performed, secondary MTJ retears (type 2 tears) are being seen more frequently. Medial cuff tears are difficult to repair and have few reported treatment methods. In addition, the lack of clinical outcomes data following surgical repair of medial cuff tears provides little guidance toward surgical decision making in either the primary or revision setting.
This article highlights that MTJ tears do occur primarily, and it is important for the surgeon to recognize this type of tear pattern preoperatively and intraoperatively because the repair technique should be modified to deal with the pathoanatomy. Secondary MTJ tears are also being seen more commonly.12 The mechanisms of secondary medial repair failures are often attributed to stress concentration at the medial row, subacromial knot impingement, decreased vascular inflow, use of braided suture materials, and overtensioning of repair constructs.12, 19 Primary prevention is one way to address secondary type 2 retears, and techniques that utilize knotless, linked, bridging constructs have been developed to prevent tissue strangulation medially and better force distribution.10, 43 The use of wider suture tapes with these knotless repairs as described in this report is also thought to not only improve the biological healing environment by decreasing the compressive stress per unit area of tendon8, 28 but also decrease the risk of a type 2 retear. Another prevention strategy with this construct is that it more closely restores the native length-tension relation of the posterosuperior rotator cuff without compromising overall construct stability.44, 45 Furthermore, the lack of medial knots avoids the possibility of acute or chronic postoperative knot impingement within the subacromial space26 while also decreasing operative time46 and improving technical efficiency.29, 47 We have also observed new tissue growth on the suture tapes in second look arthroscopy and in postoperative magnetic resonance images, and believe this acts as a scaffold for tissue regeneration.
In our recently published results of knotless double-row repair in 44 patients older than 70 years, median satisfaction was 10/10, outcomes scores improved significantly, and no patients required revision surgery after a minimum 2-year follow-up period.48 Similar findings have been reported by multiple studies.13, 17, 49, 50 Therefore, where possible, we prefer to perform bridging double-row repair for type A MTJ tears that occur either primarily or after previous double-row repair. When there is healthy muscle but a short, deficient medial tendon (type B MTJ tears) the repair can be augmented with a collagen graft. For those who present with type C MTJ tears with large tears and poor tissue quality, SCR is currently our preferred surgical approach for young and active patients, whereas RTSA is reserved for elderly and more sedentary patients with type C tears.
Footnotes
This research was performed at the Steadman Philippon Research Institute, Vail, Colorado, U.S.A.
The authors report the following potential conflicts of interest or sources of funding: P.J.M. receives consultant's fees and royalties from Arthrex, Medbridge, and Springer; is a partner of the Steadman Clinic; owns stock and stock options in GameReady and VuMedi; and receives financial support for a part of his research from Arthrex; the Steadman Philippon Research Institute receives funding from Smith & Nephew, Arthrex, Siemens, and Össur. Z.B.H. is employed by the Steadman Philippon Research Institute where this article was written. E.M.F. is employed by the Steadman Philippon Research Institute where this article was written. R.J.W. is employed by the Steadman Philippon Research Institute where this article was written. Arthrex supports J.C.K.'s position in the Steadman Philippon Research Institute. Arthrex supports J.P.'s position in the Steadman Philippon Research Institute.
Supplementary Data
In this video, we introduce a classification and present typical cases illustrating the surgical options for supraspinatus tendon tears at the musculotendinous junction. A musculotendinous junction tear is classified as a type 1 tear if it is a primary tear, or a type 2 retear if it is secondary, occurring after prior rotator cuff repair. These tears are simultaneously classified by their tear pattern, into A, B or C, as follows. This figure illustrates a type A tear, which shows a medial tendon/muscle stump without significant retraction, while the lateral part of the tendon remains attached to the lateral footprint. This type of tear requires a bridging repair, which is shown here from anterior and superior views. The next figure illustrates a type B tear, which is characterized by a deficient medial tendon/muscle body with the lateral part of the tendon also attached to the lateral footprint. Because of the advanced retraction and insufficient tissue quality of the tendon, this type of tear requires a bridging repair with graft augmentation, which is shown here from anterior and superior views. The final figure illustrates a type C tear, which shows a tendon stump attached to the lateral footprint and at the same time a deficient medial tendon with retracted, atrophied muscle with fatty infiltration. This type of tear requires a superior capsule reconstruction to replace the irreparable muscle and to restore normal shoulder biomechanics. The final construct is shown here from anterior and superior views. In general, it is crucial to gain an accurate diagnosis of the tear pattern as this determines the optimal management strategy. We will now present clinical examples for several types of musculotendinous junction tears. This is a case example of a musculotendinous junction tear, classified as type 1A. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirms a supraspinatus tear at the musculotendinous junction, with adequate tissue remaining at the lateral footprint. This is unique in that it is a primary musculotendinous junction tear, therefore classified as type 1, and is not iatrogenic or postsurgical. The pattern is classified as A, which means that it can be repaired primarily. Intraoperative findings confirmed the diagnosis of a type 1A tear of the supraspinatus tendon, displaying a medially retracted muscle and a tendon stump. The remaining tear margins are assessed for mobility with a grasper and, if necessary, intra- and extra-articular releases are performed. A primary repair is performed as the remaining length is sufficient. The tuberosity is prepared and medialized to improve healing. A medial row of anchors is placed and each limb of the suture tape and fiber wire is passed through the tendon. A primary repair of the tendon is performed medial to lateral with the eyelet fiber wire sutures creating a margin-convergence-to-bone construct using the medial anchors. Permanent high-strength sutures are used in a tendon-to-tendon repair technique of the supraspinatus tendon. A lateral row of anchors is inserted. The limbs of the suture tapes are tensioned, and the rotator cuff is compressed down onto the footprint by a knotless double-row repair with suture tapes and tendon-to-tendon sutures from the medial anchors. The next case will illustrate a musculotendinous junction retear, classified as type 2B. MRI revealed a type 2 rotator cuff retear of the supraspinatus tendon with the failure located at the medial row. This is classified as type 2 because it is a retear, and the tear pattern is classified as B because of the insufficient tissue quality. Intraoperative findings confirmed the diagnosis of a type 2B tear with poor-quality tendon tissue at the footprint and a coronal split of the supraspinatus tendon. The coronal split is fixed with multiple side-to-side sutures in a margin convergence technique. As the remaining tendon was of poor quality but the muscle relatively healthy, an allograft patch was externally trimmed and inserted into the joint to augment the remaining rotator cuff. Medial-row anchors are inserted and the patch is tied using simple stitches, and finally laterally fixed with a SpeedBridge construct. If the tendon cannot be mobilized sufficiently in an arthroscopic procedure, an open technique is performed. After thorough arthroscopic mobilization, resection of the lateral stump, and removal of retained hardware, an open deltoid-splitting approach is used. The greater tuberosity footprint is debrided to a bleeding surface using a motorized shaver. A first medial row anchor is placed at the anteromedial footprint. Strands of suture and suture tape are passed through the native rotator cuff and shuttled out through the arthroscopic anterior standard portal. Because of the size of the tear, 2 more anchors of the medial row are placed with the same technique, and the sutures are shuttled out posteriorly. The native tendon is first extensively mobilized and fixed to the medial row of anchors using the eyelet fiber wire sutures. The 6 strands of fiber tape are also passed through the native tendon stump. Next, the defect size is measured using a foil template. The patch is then externally trimmed to the required size. After the tapes and sutures have been previously shuttled through the native rotator cuff, they are now shuttled through the medial aspect of the patch. Additional suture loops are passed through the anterolateral and posterolateral aspects of the patch, to tension it. The graft is then pressed down onto the footprint. Once the graft is correctly placed, multiple single nonabsorbable sutures are used to fix the allograft to the medial cuff remnant. These sutures prevent the graft from bunching up or sliding. The lateral sockets are prepared with a punch. Limbs of suture tape from 2 medial anchors are retrieved and crossed, and then loaded with the FiberLink sutures into the first lateral row anchor. The suture tapes are pulled to achieve adequate tension, thus securing the allograft patch laterally and completely covering the greater tuberosity footprint. This method is repeated for the remaining 2 lateral anchors in the extended SpeedBridge construct. The final construct shows an extended double row repair compressing the patch onto the footprint. The next case will illustrate a musculotendinous junction tear, classified as type 2C. MRI revealed a type 2 supraspinatus tendon retear at the musculotendinous junction. This is classified as type 2 because it is a retear, and the tear pattern is classified as C because there is deficient remaining tendon. This requires a tendon transfer, a bridging rotator cuff graft or a superior capsule reconstruction. Intraoperative findings showed that the tendon was torn and the remaining muscle was retracted, atrophied, and nonmobile. This is classified as a type 2C tear. After removal of the old anchors from the prior repair, the retracted supraspinatus tendon is extensively mobilized and debrided. The tear margins are assessed for mobility with a grasper. As a persistent muscle tendon defect remained, a superior capsule reconstruction is performed. The glenoid rim is prepared and glenoid anchors are inserted for medial fixation. An arthroscopic ruler is used to determine the size of the human acellular dermal patch needed. On the humeral side, medial row anchors are inserted. The patch is externally trimmed and then introduced into the shoulder, and the tapes and sutures are shuttled through the graft. After medial fixation on the glenoid, the graft is then fixed laterally onto the footprint. To complete this fixation, the lateral anchors are inserted, completing an extended SpeedBridge construct. The graft is then sutured posteriorly to the remaining infraspinatus, using a side-to-side technique, for further stability. In this case, the residual tendon is repaired over the top to enhance the biology and the biomechanics of the construct. With superior capsule reconstruction, we always close the posterior interval between the residual infraspinatus and the graft with simple sutures. The graft is also secured to the subscapularis anterolaterally at the greater tuberosity using the anteromedial suture anchor, but the rotator interval is not typically closed medially. In summary, rotator cuff tears at the musculotendinous junction are rare and difficult to treat. We have presented a system to classify these tears—firstly into type 1 or type 2 depending on if there had been prior surgery or not, and then into type A, B, or C, mainly depending on the tear pattern, retraction of the tendon, and remaining tissue quality. Prevention of medial cuff failures is paramount, but when it does occur, this video highlights some options for surgical repair.
References
- 1.Guerini H., Pluot E., Pessis E. Tears at the myotendinous junction of the infraspinatus: Ultrasound findings. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015;96:349–356. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2014.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tavernier T., Walch G., Barthelemy R., Nove-Josserand L., Liotard J.P. Isolated lesion of the infraspinatus at the myotendinous junction: A new lesion. J Radiol. 2006;87:1875–1882. doi: 10.1016/s0221-0363(06)74168-3. [in French] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Walch G., Nové-Josserand L., Liotard J.P., Noël E. Musculotendinous infraspinatus ruptures: An overview. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009;95:463–470. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2009.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Benazzo F., Marullo M., Pietrobono L. Supraspinatus rupture at the musculotendinous junction in a young woman. J Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15:231–234. doi: 10.1007/s10195-013-0271-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hertel R., Lambert S.M. Supraspinatus rupture at the musculotendinous junction. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7:432–435. doi: 10.1016/s1058-2746(98)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lädermann A., Christophe F.K., Denard P.J., Walch G. Supraspinatus rupture at the musclotendinous junction: An uncommonly recognized phenomenon. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21:72–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2011.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Apreleva M., Ozbaydar M., Fitzgibbons P.G., Warner J.J. Rotator cuff tears: The effect of the reconstruction method on three-dimensional repair site area. Arthroscopy. 2002;18:519–526. doi: 10.1053/jars.2002.32930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park J.Y., Lee S.Y., Chung S.W., Zulkifli H., Cho J.H., Oh K.S. Clinical comparison between double-row and transosseous-equivalent repairs for medium to large size rotator cuff tears. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133:1727–1734. doi: 10.1007/s00402-013-1872-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Killian M.L., Cavinatto L., Shah S.A. The effects of chronic unloading and gap formation on tendon-to-bone healing in a rat model of massive rotator cuff tears. J Orthop Res. 2014;32:439–447. doi: 10.1002/jor.22519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mazzocca A.D., Millett P.J., Guanche C.A., Santangelo S.A., Arciero R.A. Arthroscopic single-row versus double-row suture anchor rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33:1861–1868. doi: 10.1177/0363546505279575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Millett P.J., Warth R.J., Dornan G.J., Lee J.T., Spiegl U.J. Clinical and structural outcomes after arthroscopic single-row versus double-row rotator cuff repair: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Level I randomized clinical trials. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23:586–597. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2013.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cho N.S., Lee B.G., Rhee Y.G. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair using a suture bridge technique: Is the repair integrity actually maintained? Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:2108–2116. doi: 10.1177/0363546510397171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hug K., Gerhardt C., Haneveld H., Scheibel M. Arthroscopic knotless-anchor rotator cuff repair: A clinical and radiological evaluation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:2628–2634. doi: 10.1007/s00167-014-3026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim J.R., Cho Y.S., Ryu K.J., Kim J.H. Clinical and radiographic outcomes after arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears using a suture bridge technique: Assessment of repair integrity on magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:786–793. doi: 10.1177/0363546511434546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim K.C., Shin H.D., Cha S.M., Lee W.Y. Comparison of repair integrity and functional outcomes for 3 arthroscopic suture bridge rotator cuff repair techniques. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:271–277. doi: 10.1177/0363546512468278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee K.W., Seo D.W., Bae K.W., Choy W.S. Clinical and radiological evaluation after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair using suture bridge technique. Clin Orthop Surg. 2013;5:306–313. doi: 10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rhee Y.G., Cho N.S., Parke C.S. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair using modified Mason-Allen medial row stitch: Knotless versus knot-tying suture bridge technique. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:2440–2447. doi: 10.1177/0363546512459170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Voigt C., Bosse C., Vosshenrich R., Schulz A.P., Lill H. Arthroscopic supraspinatus tendon repair with suture-bridging technique: Functional outcome and magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38:983–991. doi: 10.1177/0363546509359063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Christoforetti J.J., Krupp R.J., Singleton S.B., Kissenberth M.J., Cook C., Hawkins R.J. Arthroscopic suture bridge transosseus equivalent fixation of rotator cuff tendon preserves intratendinous blood flow at the time of initial fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21:523–530. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2011.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim S.H., Kim J., Choi Y.E., Lee H.R. Healing disturbance with suture bridge configuration repair in rabbit rotator cuff tear. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25:478–486. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.08.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kullar R.S., Reagan J.M., Kolz C.W., Burks R.T., Henninger H.B. Suture placement near the musculotendinous junction in the supraspinatus: Implications for rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43:57–62. doi: 10.1177/0363546514553091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Virk M.S., Bruce B., Hussey K.E. Biomechanical performance of medial row suture placement relative to the musculotendinous junction in transosseous equivalent suture bridge double-row rotator cuff repair. Arthroscopy. 2017;33:242–250. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2016.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Greenspoon J.A., Petri M., Millett P.J. Arthroscopic knotless, double-row, extended linked repair for massive rotator cuff tears. Arthrosc Tech. 2016;5:e127–e132. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2015.10.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Petri M., Greenspoon J.A., Millett P.J. Arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction for irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthrosc Tech. 2015;4:e751–e755. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2015.07.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Katthagen JC, Tahal D, Millett PJ. Arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction for irreparable rotator cuff tears. Orthop Today March, 2016. [Epub ahead of print.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Yamakado K., Katsuo S., Mizuno K., Arakawa H., Hayashi S. Medial-row failure after arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:430–435. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2009.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Katthagen J.C., Marchetti D.C., Tahal D.S., Turnbull T.L., Millett P.J. The effects of arthroscopic lateral acromioplasty on the critical shoulder angle and the anterolateral deltoid origin: An anatomic cadaveric study. Arthroscopy. 2016;32:569–575. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2015.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vaishnav S., Millett P.J. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: Scientific rationale, surgical technique, and early clinical and functional results of a knotless self-reinforcing double-row rotator cuff repair system. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19:83–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2009.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Park M.C. Biomechanical validation of rotator cuff repair techniques and considerations for a “technical efficiency ratio”. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:1230–1234. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2013.03.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Petri M., Greenspoon J.A., Bhatia S., Millett P.J. Patch-augmented latissimus dorsi transfer and open reduction-internal fixation of unstable os acromiale for irreparable massive posterosuperior rotator cuff tear. Arthrosc Tech. 2015;4:e487–e492. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2015.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Petri M., Warth R.J., Horan M.P., Greenspoon J.A., Millett P.J. Outcomes after open revision repair of massive rotator cuff tears with biologic patch augmentation. Arthroscopy. 2016;32:1752–1760. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2016.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Steinhaus M.E., Makhni E.C., Cole B.J., Romeo A.A., Verma N.N. Outcomes after patch use in rotator cuff repair. Arthroscopy. 2016;32:1676–1690. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2016.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Audenaert E., Van Nuffel J., Schepens A., Verhelst M., Verdonk R. Reconstruction of massive rotator cuff lesions with a synthetic interposition graft: A prospective study of 41 patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:360–364. doi: 10.1007/s00167-005-0689-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Moore D.R., Cain E.L., Schwartz M.L., Clancy W.G., Jr. Allograft reconstruction for massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34:392–396. doi: 10.1177/0363546505281237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Soler J.A., Gidwani S., Curtis M.J. Early complications from the use of porcine dermal collagen implants (Permacol) as bridging constructs in the repair of massive rotator cuff tears. A report of 4 cases. Acta Orthop Belg. 2007;73:432–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Greenspoon J.A., Petri M., Warth R.J., Millett P.J. Massive rotator cuff tears: Pathomechanics, current treatment options, and clinical outcomes. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24:1493–1505. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gupta A.K., Hug K., Berkoff D.J. Dermal tissue allograft for the repair of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:141–147. doi: 10.1177/0363546511422795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gupta A.K., Hug K., Boggess B., Gavigan M., Toth A.P. Massive or 2-tendon rotator cuff tears in active patients with minimal glenohumeral arthritis: Clinical and radiographic outcomes of reconstruction using dermal tissue matrix xenograft. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:872–879. doi: 10.1177/0363546512475204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mihata T., Lee T.Q., Watanabe C. Clinical results of arthroscopic superior capsule reconstruction for irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:459–470. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2012.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mihata T., McGarry M.H., Kahn T., Goldberg I., Neo M., Lee T.Q. Biomechanical effect of thickness and tension of fascia lata graft on glenohumeral stability for superior capsule reconstruction in irreparable supraspinatus tears. Arthroscopy. 2016;32:418–426. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2015.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hirahara A.M., Adams C.R. Arthroscopic superior capsular reconstruction for treatment of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthrosc Tech. 2015;4:e637–e641. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2015.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tokish J.M., Beicker C. Superior capsule reconstruction technique using an acellular dermal allograft. Arthrosc Tech. 2015;4:e833–e839. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2015.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Denard P.J., Jiwani A.Z., Lädermann A., Burkhart S.S. Long-term outcome of arthroscopic massive rotator cuff repair: The importance of double-row fixation. Arthroscopy. 2012;28:909–915. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2011.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bisson L.J., Manohar L.M. A biomechanical comparison of the pullout strength of no. 2 FiberWire suture and 2-mm FiberWire tape in bovine rotator cuff tendons. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:1463–1468. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2010.04.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Spang J.T., Buchmann S., Brucker P.U. A biomechanical comparison of 2 transosseous-equivalent double-row rotator cuff repair techniques using bioabsorbable anchors: Cyclic loading and failure behavior. Arthroscopy. 2009;25:872–879. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2009.02.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Burkhart S.S., Adams C.R., Burkhart S.S., Schoolfield J.D. A biomechanical comparison of 2 techniques of footprint reconstruction for rotator cuff repair: The SwiveLock-FiberChain construct versus standard double-row repair. Arthroscopy. 2009;25:274–281. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2008.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Park M.C., Peterson A., Patton J., McGarry M.H., Park C.J., Lee T.Q. Biomechanical effects of a 2 suture-pass medial inter-implant mattress on transosseous-equivalent rotator cuff repair and considerations for a “technical efficiency ratio”. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23:361–368. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2013.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bhatia S., Greenspoon J.A., Horan M.P., Warth R.J., Millett P.J. Two-year outcomes after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair in recreational athletes older than 70 years. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43:1737–1742. doi: 10.1177/0363546515577623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Boyer P., Bouthors C., Delcourt T. Arthroscopic double-row cuff repair with suture-bridging: A structural and functional comparison of two techniques. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:478–486. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Werthel J.D., Pelissier A., Massin P., Boyer P., Valenti P. Arthroscopic double row cuff repair with suture-bridging and autologous conditioned plasma injection: Functional and structural results. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2014;8:101–106. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.145232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
In this video, we introduce a classification and present typical cases illustrating the surgical options for supraspinatus tendon tears at the musculotendinous junction. A musculotendinous junction tear is classified as a type 1 tear if it is a primary tear, or a type 2 retear if it is secondary, occurring after prior rotator cuff repair. These tears are simultaneously classified by their tear pattern, into A, B or C, as follows. This figure illustrates a type A tear, which shows a medial tendon/muscle stump without significant retraction, while the lateral part of the tendon remains attached to the lateral footprint. This type of tear requires a bridging repair, which is shown here from anterior and superior views. The next figure illustrates a type B tear, which is characterized by a deficient medial tendon/muscle body with the lateral part of the tendon also attached to the lateral footprint. Because of the advanced retraction and insufficient tissue quality of the tendon, this type of tear requires a bridging repair with graft augmentation, which is shown here from anterior and superior views. The final figure illustrates a type C tear, which shows a tendon stump attached to the lateral footprint and at the same time a deficient medial tendon with retracted, atrophied muscle with fatty infiltration. This type of tear requires a superior capsule reconstruction to replace the irreparable muscle and to restore normal shoulder biomechanics. The final construct is shown here from anterior and superior views. In general, it is crucial to gain an accurate diagnosis of the tear pattern as this determines the optimal management strategy. We will now present clinical examples for several types of musculotendinous junction tears. This is a case example of a musculotendinous junction tear, classified as type 1A. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirms a supraspinatus tear at the musculotendinous junction, with adequate tissue remaining at the lateral footprint. This is unique in that it is a primary musculotendinous junction tear, therefore classified as type 1, and is not iatrogenic or postsurgical. The pattern is classified as A, which means that it can be repaired primarily. Intraoperative findings confirmed the diagnosis of a type 1A tear of the supraspinatus tendon, displaying a medially retracted muscle and a tendon stump. The remaining tear margins are assessed for mobility with a grasper and, if necessary, intra- and extra-articular releases are performed. A primary repair is performed as the remaining length is sufficient. The tuberosity is prepared and medialized to improve healing. A medial row of anchors is placed and each limb of the suture tape and fiber wire is passed through the tendon. A primary repair of the tendon is performed medial to lateral with the eyelet fiber wire sutures creating a margin-convergence-to-bone construct using the medial anchors. Permanent high-strength sutures are used in a tendon-to-tendon repair technique of the supraspinatus tendon. A lateral row of anchors is inserted. The limbs of the suture tapes are tensioned, and the rotator cuff is compressed down onto the footprint by a knotless double-row repair with suture tapes and tendon-to-tendon sutures from the medial anchors. The next case will illustrate a musculotendinous junction retear, classified as type 2B. MRI revealed a type 2 rotator cuff retear of the supraspinatus tendon with the failure located at the medial row. This is classified as type 2 because it is a retear, and the tear pattern is classified as B because of the insufficient tissue quality. Intraoperative findings confirmed the diagnosis of a type 2B tear with poor-quality tendon tissue at the footprint and a coronal split of the supraspinatus tendon. The coronal split is fixed with multiple side-to-side sutures in a margin convergence technique. As the remaining tendon was of poor quality but the muscle relatively healthy, an allograft patch was externally trimmed and inserted into the joint to augment the remaining rotator cuff. Medial-row anchors are inserted and the patch is tied using simple stitches, and finally laterally fixed with a SpeedBridge construct. If the tendon cannot be mobilized sufficiently in an arthroscopic procedure, an open technique is performed. After thorough arthroscopic mobilization, resection of the lateral stump, and removal of retained hardware, an open deltoid-splitting approach is used. The greater tuberosity footprint is debrided to a bleeding surface using a motorized shaver. A first medial row anchor is placed at the anteromedial footprint. Strands of suture and suture tape are passed through the native rotator cuff and shuttled out through the arthroscopic anterior standard portal. Because of the size of the tear, 2 more anchors of the medial row are placed with the same technique, and the sutures are shuttled out posteriorly. The native tendon is first extensively mobilized and fixed to the medial row of anchors using the eyelet fiber wire sutures. The 6 strands of fiber tape are also passed through the native tendon stump. Next, the defect size is measured using a foil template. The patch is then externally trimmed to the required size. After the tapes and sutures have been previously shuttled through the native rotator cuff, they are now shuttled through the medial aspect of the patch. Additional suture loops are passed through the anterolateral and posterolateral aspects of the patch, to tension it. The graft is then pressed down onto the footprint. Once the graft is correctly placed, multiple single nonabsorbable sutures are used to fix the allograft to the medial cuff remnant. These sutures prevent the graft from bunching up or sliding. The lateral sockets are prepared with a punch. Limbs of suture tape from 2 medial anchors are retrieved and crossed, and then loaded with the FiberLink sutures into the first lateral row anchor. The suture tapes are pulled to achieve adequate tension, thus securing the allograft patch laterally and completely covering the greater tuberosity footprint. This method is repeated for the remaining 2 lateral anchors in the extended SpeedBridge construct. The final construct shows an extended double row repair compressing the patch onto the footprint. The next case will illustrate a musculotendinous junction tear, classified as type 2C. MRI revealed a type 2 supraspinatus tendon retear at the musculotendinous junction. This is classified as type 2 because it is a retear, and the tear pattern is classified as C because there is deficient remaining tendon. This requires a tendon transfer, a bridging rotator cuff graft or a superior capsule reconstruction. Intraoperative findings showed that the tendon was torn and the remaining muscle was retracted, atrophied, and nonmobile. This is classified as a type 2C tear. After removal of the old anchors from the prior repair, the retracted supraspinatus tendon is extensively mobilized and debrided. The tear margins are assessed for mobility with a grasper. As a persistent muscle tendon defect remained, a superior capsule reconstruction is performed. The glenoid rim is prepared and glenoid anchors are inserted for medial fixation. An arthroscopic ruler is used to determine the size of the human acellular dermal patch needed. On the humeral side, medial row anchors are inserted. The patch is externally trimmed and then introduced into the shoulder, and the tapes and sutures are shuttled through the graft. After medial fixation on the glenoid, the graft is then fixed laterally onto the footprint. To complete this fixation, the lateral anchors are inserted, completing an extended SpeedBridge construct. The graft is then sutured posteriorly to the remaining infraspinatus, using a side-to-side technique, for further stability. In this case, the residual tendon is repaired over the top to enhance the biology and the biomechanics of the construct. With superior capsule reconstruction, we always close the posterior interval between the residual infraspinatus and the graft with simple sutures. The graft is also secured to the subscapularis anterolaterally at the greater tuberosity using the anteromedial suture anchor, but the rotator interval is not typically closed medially. In summary, rotator cuff tears at the musculotendinous junction are rare and difficult to treat. We have presented a system to classify these tears—firstly into type 1 or type 2 depending on if there had been prior surgery or not, and then into type A, B, or C, mainly depending on the tear pattern, retraction of the tendon, and remaining tissue quality. Prevention of medial cuff failures is paramount, but when it does occur, this video highlights some options for surgical repair.