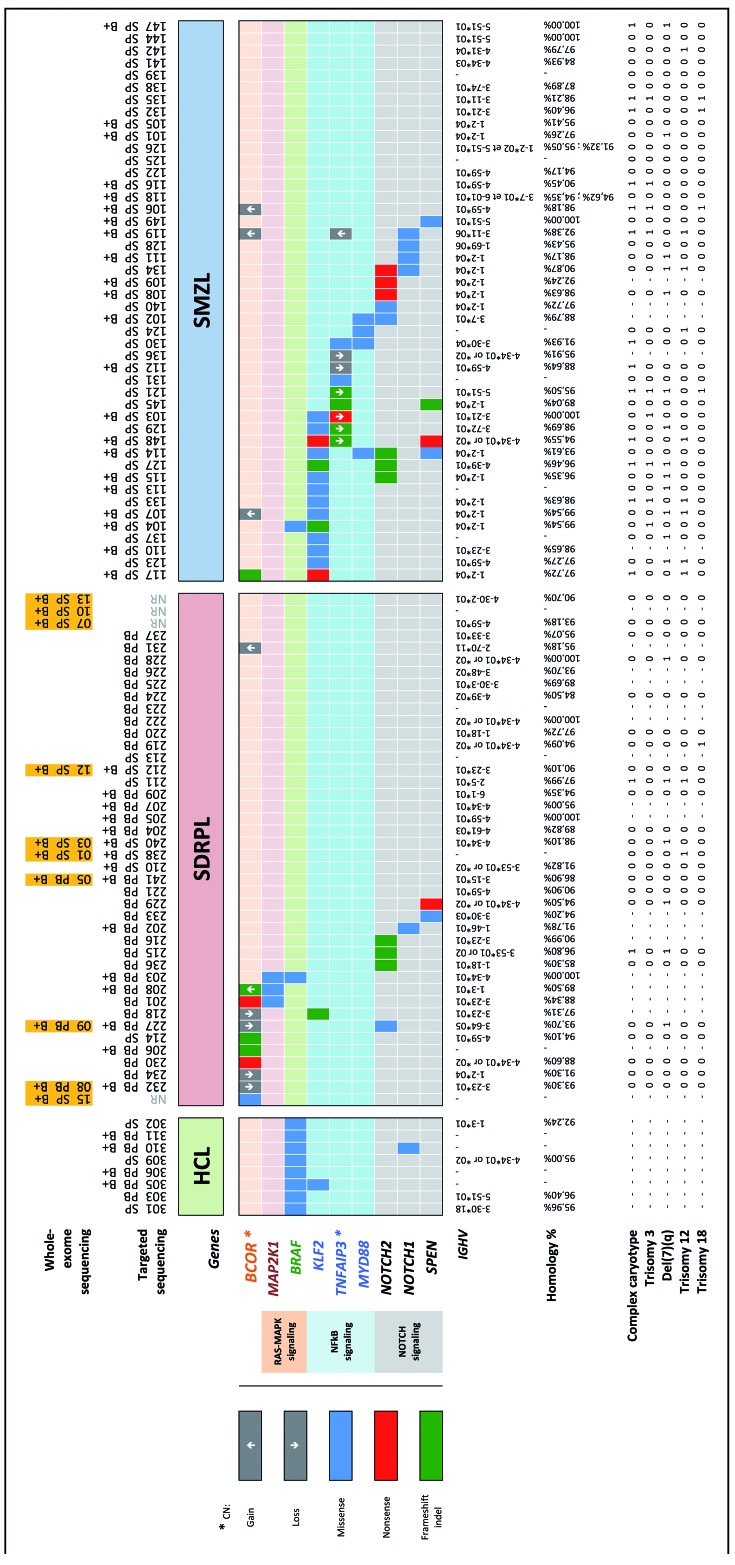
Figure 1.
Distribution of mutations in hairy-cell leukemia, splenic diffuse red pulp lymphoma and splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Each column represents a type of lymphoma and corresponding tissue (HCL: hairy cell lymphoma; SDRPL: splenic diffuse red pulp lymphoma; SMZL: splenic marginal zone lymphoma; PB: peripheral blood; SP: spleen; B+: CD19+ immunoselected sample). The orange colored boxes indicate the ten cases investigated by whole-exome sequencing. Six of them were also reanalyzed by targeted sequencing as internal controls, whereas the four remaining were not (NR: not resequenced). Each row (top) represents a gene linked to the corresponding RAS/MAPK, NF-κB or NOTCH signaling pathway. Three types of mutations (missense, nonsense, frameshift indel) are highlighted in different colors. Details of the mutations are available in Online Supplementary Table S3. Gene copy number (CN) was only reported as a gain (↑) or loss (↓) for relevant genes (❋), namely BCOR and TNFAIP3. The last row (bottom) represents the IGHV gene status, homology with germline sequence percentage, and cytogenetic findings (complex karyotype, trisomy 3, 12, 18 and deletion 7q) for each case when available.