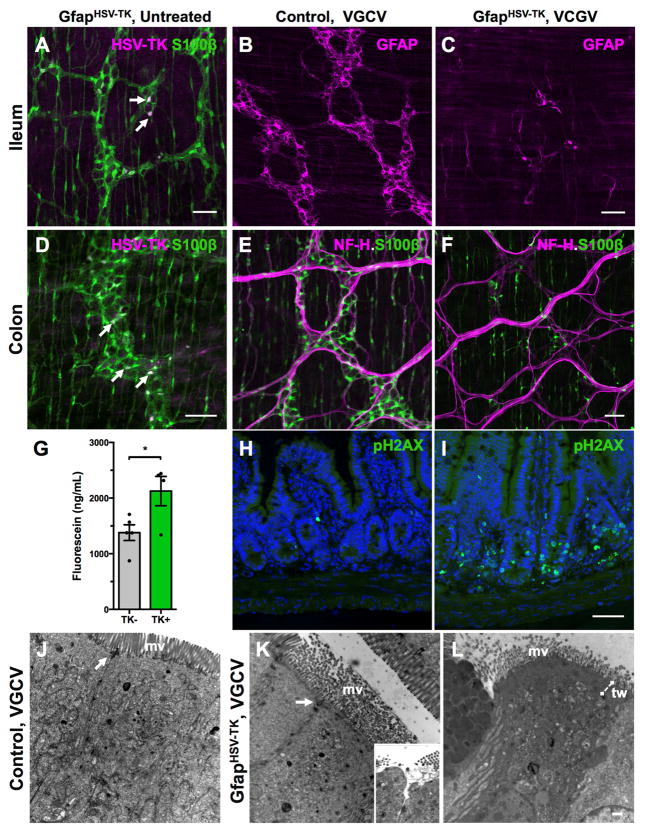
Figure 5. GfapHSV-TK mice exhibit transgene expression throughout the intestine and signs of off-target injury to the epithelium.
(A, D) Immunostaining for S100β and HSV-TK shows that only a subset of myenteric glia expresses TK (arrows) in the ileum and colon of untreated GFAPHSV-TK mice. Intramuscular glia are S100β-immunoreactive but none express TK.
(B–F) Valganciclovir (VGCV) treatment eliminates both GFAP+ (compare B and C) and S100β+ (compare E and F) enteric glia in the small and large intestine of GFAPHSV-TK mice. NF-H immunostaining highlights nerve fiber bundles in the myenteric plexus.
(G) Serum FITC levels 4 hours after oral gavage of 478Da fluorescein conjugate into TK− and TK+ mice treated with VGCV shows increased macromolecular intestinal permeability in TK+ mice.
(H–I) Immunoreactivity of the apoptotic marker, phosphorylated histone 2AX (pH2AX) in cross-sections of ilea from TK− (H) and TK+ (I) mice treated with VGCV. Nuclei counterstained with DAPI. VGCV treatment increased apoptosis primarily in crypt cells, but also in the walls of the villi and in the lamina propria of the TK+ mouse.
(J) The ultrastructure of enterocytes in the small intestine of a control TK− mouse treated with VGCV appears normal. The microvillus (mv) border was intact, and their core of actin filaments formed a terminal web and inserted into the adherens junction component of junctional complexes (arrow).
(K) The ultrastructure of some enterocytes in the small intestines of VGCV-treated TK+ mice was abnormal. The microvilli were disorganized, lacked microfilament cores, and displayed variable diameters suggesting swelling. The area of the terminal web was expanded and appeared as an amorphous electron-dense mat. Occasionally, adherens junctions were disrupted although tight junctions remained intact. In rare cells, the underlying cytoplasm appeared to push the microvillus border aside and protrude into the lumen (see inset). In these regions, tight junctions were disrupted, opening a channel to the intercellular space.
(L) In an evident later stage of abnormality in a VGCV-treated TK+ mouse, the cytoplasm of some enterocytes was electron dense, the terminal web (tw) region was expanded, and the mitochondrial matrix was vacuolated.
Scale bars A–I=50μm; J–L=500nm