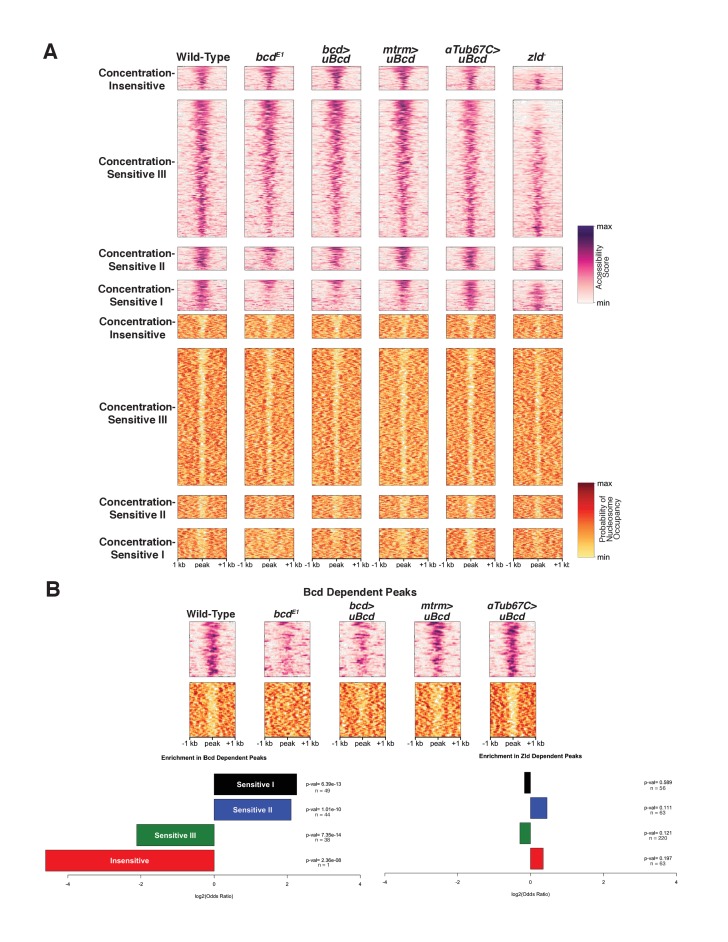
Figure 3. Bcd drives chromatin accessibility primarily at concentration-sensitive targets.
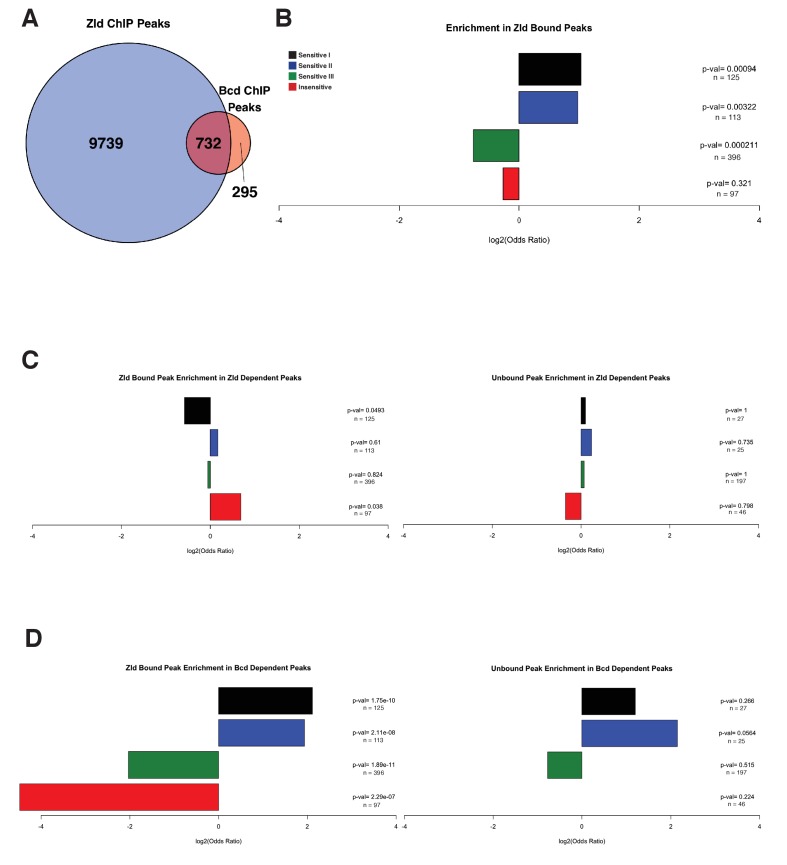
(A) Heatmaps showing chromatin accessibility (top) and probability of nucleosome occupancy (bottom) around Bcd-bound peaks from ATAC-seq experiments. Peak regions are arranged by decreasing accessibility in wild-type embryos. bcdE1 mutant embryos show a loss of accessibility and increased nucleosome occupancy most strongly at the Concentration-Sensitive I and II peaks. zld- embryos show reduced accessibility across all sensitivity classes. (B) Subset of 132 Bcd-bound peaks selected from (A) that become inaccessible in the absence of Bcd. Accessibility at these peaks increases with increasing concentrations of uniform Bcd. Odds ratios and p-values calculated from Fisher's exact test show significant overrepresentation of the Concentration-Sensitive I and II classes in the Bcd- and Zld-dependent peaks. n values indicate the number of peaks in each sensitivity class that are Bcd or Zld dependent.