Abstract
Variants in CNTNAP2, a member of the neurexin family of genes that function as cell adhesion molecules, have been associated with multiple neuropsychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability; animal studies indicate a role for CNTNAP2 in axon guidance, dendritic arborization and synaptogenesis. We previously reprogrammed fibroblasts from a family trio consisting of two carriers of heterozygous intragenic CNTNAP2 deletions into human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and described decreased migration in the neural progenitor cells (NPCs) differentiated from the affected CNTNAP2 carrier in this trio. Here, we report the effect of this heterozygous intragenic deletion in CNTNAP2 on global gene expression and neuronal activity in the same cohort. Our findings suggest that heterozygous CNTNAP2 deletions affect genes involved in neuronal development and neuronal activity; however, these data reflect only one family trio and therefore more deletion carriers, with a variety of genetic backgrounds, will be needed to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying CNTNAP2 deletions.
Short Report
The shared genetic architecture underlying neuropsychiatric disorders implicates common molecular mechanisms.1 For example, while homozygous null mutations in CNTNAP2 lead to cortical dysplasia-focal epilepsy syndrome,2, 3 heterozygous intragenic deletions are associated with schizophrenia, intellectual disability, language deficits, seizures, and autism traits.4 Critically, CNTNAP2 variants are not completely penetrant.2, 5 Animal studies indicate a role for CNTNAP2 in axon guidance, dendritic arborization, and synaptogenesis.6–8
We obtained fibroblast samples from a family trio with two carriers of heterozygous intragenic CNTNAP2 deletions, one affected and one unaffected, and an unaffected non-carrier control (Table 1). The CNTNAP2 carriers display discordant clinical phenotypes; the daughter (DL7078) presented with schizo-affective disorder (depressed subtype) while the father (DL8735) was neurotypical.9 We previously used sendai viral vectors to reprogram fibroblasts from this trio into hiPSCs that were then differentiated via dual-SMAD induction into NPCs and neurons. We characterized decreased migration in NPCs and allele-biased expression of the mutant CNTNAP2 transcript by qPCR in neurons from the affected CNTNAP2 carrier in this trio.9 Here, we report the effect of this heterozygous intragenic deletion in CNTNAP2 on global gene expression and neuronal activity in this same cohort.
Table 1.
Available clinical information on hiPSC donors
| Patient ID | Source | hiPSC Line | Family | Sex | Dx | Age of Onset | IQ | Clozapine Response | Family History |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL7078 | McLeans | 7078 hiPSC#B | Proband | F | SA | 18.9 | 100 | Y | – |
| DL8735 | McLeans | 8735 hiPSC#H | Father | M | Control | n/a | 120 | n/a | SA |
| DL5535 | McLeans | 5535 hiPSC#2 | Mother | F | Control | n/a | 95 | n/a | SA |
| NSB3113 | NIH | 3113 hiPSC#1 | Non-relative | F | Control | n/a | 123 | n/a | n/a |
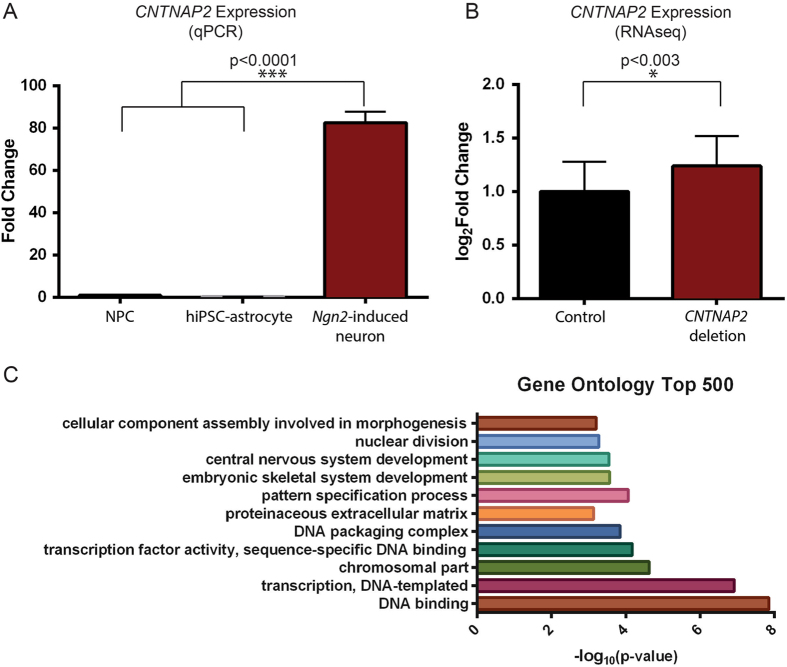
CNTNAP2 is highly expressed in Ngn2-induced neurons, a population of nearly pure excitatory neurons,10 relative to hiPSC-derived NPCs11 and hiPSC-astrocytes12 (qPCR FC = 82.5, p < 0.0001, ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-Hoc) (Fig. 1a). RNA was harvested after 21 days of Ngn2-induction. The New York Genome Center prepared RNAseq libraries using the Kapa Total 350 bp kit, followed by 2 × 125 bp Illumina RNA sequencing to a read depth of 40 M reads per sample on the HiSeq 2500.
Fig. 1.
CNTNAP2 expression in excitatory neurons induced from family trio. a By qPCR, CNTNAP2 expression is significantly increased in Ngn2-induced neurons compared to neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and hiPSC-derived astrocytes. Data reflects biological triplicate samples from one hiPSC line derived from each of three healthy controls (mean +/− s.e.m). b RNA sequencing data shows total CNTNAP2 expression is increased in deletion carriers compared with non-carrier control (mean +/− s.e.m). c Genes differentially expressed in CNTNAP2 deletion carriers are enriched for genes involved in DNA binding and central nervous system development. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001
We queried the expression of CNTNAP2 in Ngn2-induced neurons from each member of this family trio, hypothesizing that heterozygous intragenic deletions may affect the expression of CNTNAP2. Surprisingly, overall CNTNAP2 expression was increased in the CNTNAP2 deletion carriers compared with the non-carrier mother (log2FC = 1.24, padj = 0.003) (Fig. 1b).
Differential expression analysis was performed using DESeq213 and the top 500 differentially expressed genes were used to perform gene ontology using DAVID14, 15 (SI Table 1). The most significant subset of genes mapped to terms relating to DNA binding and central nervous system (CNS) development (FC = 1.8, p < 0.00001 and FC = 1.9, p = 0.0003) (Fig. 1c; SI Table 2). Within the gene subset involved in CNS development, there are some interesting candidate genes such as CNTN6 and CNTN4, which are involved in regulating cell surface interactions during nervous system development and are also thought to be important in synaptogenesis (SI Table 3 ).
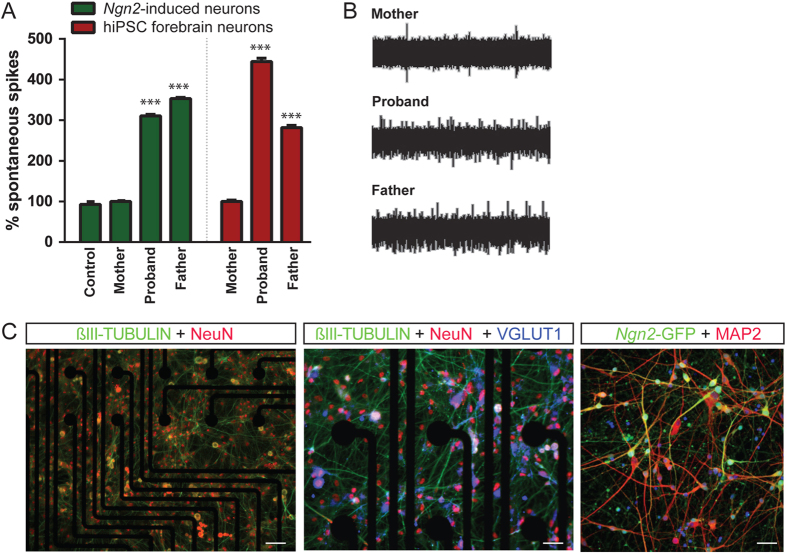
Given the differences in gene expression of critical neuronal and synaptic genes, we applied an Axion multi-electrode array (MEA) (see similar applications to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis16 and Parkinson’s disease17) to record population-wide neuronal activity under conditions similar to those used in our RNAseq analyzes. 21-day-old Ngn2-induced neurons from both the affected (daughter, DL7078) and unaffected (father, DL8735) CNTNAP2 deletion carriers showed significantly increased spontaneous network level activity (an increase of 210 and 253%, respectively) relative to the non-carrier (mother, DL5535) and an unaffected unrelated control (female, NSB3113) (N = 12 wells/condition; p < 0.001, ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-Hoc) (Fig. 2a). These results were confirmed in hiPSC-derived forebrain neuron populations, which are comprised of a mixture of mature and immature excitatory neurons, inhibitory neurons and astrocytes, with the majority of cells presumed to be excitatory neurons.18, 19 Here, NPCs were seeded (65,000 cells/mL) onto 12-well MEA plates and differentiated for 28 days; hiPSC-derived neurons from the affected and unaffected CNTNAP2 deletion carriers showed significantly increased spontaneous population wide neuronal activity relative to the non-carrier mother (increases of 344 and 182% relative to the non-carrier mother; N = 12 wells/condition; p < 0.001, ANOVA with Tukey’s Post-Hoc) (Fig. 2a, b). All measurements were performed as biological triplicates for each hiPSC line and averaged across experiments. In both populations, neurons robustly stained for neuronal markers βIII-TUBULIN, NeuN, and MAP2 (representative images in Fig. 2c).
Fig. 2.
hiPSC-derived neurons from CNTNAP2 carriers show increased neuronal activity compared to control. a Summary data of population-wide MEA spike frequency of individuals in the family trio in both the Ngn2-induced neurons (green) and hiPSC-derived forebrain mixed neuronal populations (red) reveal significantly increased synaptic activity in the CNTNAP2 deletion carriers. *** p < 0.001 b Representative traces of population-wide neuronal activity measured by MEA. c Representative staining of directed differentiation neurons (left and center) at Day28 for general neuronal markers on MEA plates demonstrate normal expression of TUJ1 (green), NEUN (red); (left, 100X), as well as VGLUT1 (blue); (center, 200X)) (s.b. left = 100 μM; right = 50 μM). Representative staining of Ngn2-induced neurons (right) for MAP2 and, as well as expression of hNgn2-eGFP-PuroR (addgene #79823) at Day21 (right, 200X) (s.b. = 40 μM)
Our genetic analyzes and functional assays together show that heterozygous deletion of CNTNAP2 may impact neuronal activity. The significant increase in spontaneous spiking activity in the unaffected carrier father and carrier daughter may underlie aspects of the aberrant behavior displayed by the proband. Additionally, this alteration in spike activity may in part explain observations of disrupted neuronal synchrony in CNTNAP2-null mice.6
Here we demonstrated that hiPSC-derived neurons from individuals with heterozygous intragenic deletions in CNTNAP2 display differential expression of genes involved in synaptic transmission and altered neuronal activity, consistent with reports of disrupted cortical neuronal activity in CNTNAP2-null mice,6 and potentially independent of clinical outcome. Our report reflects results from just one family trio; a greater variety of disease-associated CNTNAP2 mutations, on an array of genetic backgrounds, will be needed to understand the full breath of genotype-phenotype relationships with respect to CNTNAP2.18, 20–22
Ethical approval
The methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations and approved by the McLean Hospital Institutional Review Board. Participants were subject to informed and written consent.
Data availability
All case and control hiPSCs, which have been mycoplasma tested, will be deposited with the NIMH Center For Collaborative Studies Of Mental Disorders At RUCDR. RNAseq data for CNTNAP2 carrier and non-carrier neurons (GEO GSE102838) have been deposited at the GeneExpression Omnibus (GEO) repository. Antibodies used in this study are: βIII-TUBULIN (1:500; Chicken; Biolegend; 801201), NeuN(1:100; Rabbit; Abcam; ab104225), MAP2 (1:500; Chicken; Abcam; ab5392).
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
Kristen Brennand is a New York Stem Cell Foundation—Robertson Investigator. This work was supported in part by National Institute of Health (NIH) grants R01 MH101454 (KJB), R01 MH106056 (KJB), NIH grant R21 MH097470 (DLL), the New York Stem Cell Foundation (KJB), Brain and Behavior Young Independent Investigator Award (KJB), and the Ellison Foundation (DLL, KJB). Michael Nestor is an Investigator at The Hussman Institute for Autism. This work was supported in part by a Hussman Foundation Pilot Grant (HIAS15004). Shane McCarthy, Dheeraj Malhotra, and Jonathan Sebat originally identified the CNTNAP2 deletion. Claudia M.B. Carvalho, Luciana W. Zuccherato, and James R. Lupski fully characterized the CNTNAP2 deletion.
Author contributions
E.F. and K.J.B. designed and conducted the RNAseq experiments. E.A., R.M.D., and M.W.N. designed and conducted the functional assays. E.F., K.J.B., and M.W.N wrote the manuscript. D.L. initiated the study, identified and clinically characterized the patient trio, and made critical revisions to the manuscript; A.J.S. performed the skin biopsy on the family trio; K.J.B. reprogrammed the hiPSCs; I.G.L. differentiated NPCs from unrelated control hiPSCs.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies the paper on the npj Schizophrenia website (doi:10.1038/s41537-017-0033-5).
Contributor Information
Michael W. Nestor, Phone: +(443) 860-2580, Email: mnestor@hussmanautism.org
Kristen J. Brennand, Phone: +(212) 659-8259, Email: kristen.brennand@mssm.edu
References
- 1.Doherty JL, Owen MJ. Genomic insights into the overlap between psychiatric disorders: implications for research and clinical practice. Genome Med. 2014;6:29. doi: 10.1186/gm546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Strauss KA, et al. Recessive symptomatic focal epilepsy and mutant contactin-associated protein-like 2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:1370–1377. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jackman C, Horn ND, Molleston JP, Sokol DK. Gene associated with seizures, autism, and hepatomegaly in an Amish Girl. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009;40:310–313. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2008.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rodenas-Cuadrado P, Ho J, Vernes SC. Shining a light on CNTNAP2: complex functions to complex disorders. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014;22:171–178. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bakkaloglu B, et al. Molecular cytogenetic analysis and resequencing of contactin associated protein-like 2 in autism spectrum disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;82:165–173. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Peñagarikano O, et al. Absence of CNTNAP2 leads to epilepsy, neuronal migration abnormalities, and core autism-related deficits. Cell. 2011;147:235–246. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Anderson GR, et al. Candidate autism gene screen identifies critical role for cell-adhesion molecule CASPR2 in dendritic arborization and spine development. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 2012;109:18120–18125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216398109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Girault JA, Oguievetskaia K, Carnaud M, Denisenko-Nehrbass N, Goutebroze L. Transmembrane scaffolding proteins in the formation and stability of nodes of Ranvier. Biol. Cell. 2003;95:447–452. doi: 10.1016/S0248-4900(03)00073-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee IS, et al. Characterization of molecular and cellular phenotypes associated with a heterozygous CNTNAP2 deletion using patient-derived hiPSC neural cells. npj Schizophr. 2015;1:15019. doi: 10.1038/npjschz.2015.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ho SM, et al. Rapid Ngn2-induction of excitatory neurons from hiPSC-derived neural progenitor cells. Methods. 2016;101:113–124. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.11.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Topol, A., Tran, N. N. & Brennand, K. J. A guide to generating and using hiPSC derived NPCs for the study of neurological diseases. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE96, e52495 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.TCW, J. et al. An efficient platform for astrocyte differentiation from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rep.10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.06.018. (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huang DW, Lempicki Ra, Sherman BT. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009;4:44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:1–13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wainger BJ, et al. Intrinsic membrane hyperexcitability of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient-derived motor neurons. Cell Rep. 2014;7:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Woodard CM, et al. iPSC-derived dopamine neurons reveal differences between monozygotic twins discordant for parkinson’s disease. Cell Rep. 2014;9:1173–1182. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.10.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brennand KJ, et al. Modelling schizophrenia using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2011;473:221–225. doi: 10.1038/nature09915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brennand K, et al. Phenotypic differences in hiPSC NPCs derived from patients with schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry. 2014;20:1–8. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Brennand KJ, Landek-Salgado MA, Sawa A. Modeling heterogeneous patients with a clinical diagnosis of Schizophrenia with induced pluripotent stem cells. Biol. Psychiatry. 2014;75:936–944. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.10.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shi Y, Kirwan P, Smith J, Robinson HPC, Livesey FJ. Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2012;15:477–486. doi: 10.1038/nn.3041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Prè, D. et al. A time course analysis of the electrophysiological properties of neurons differentiated from human induced Pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). PLoS ONE9, e103418 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All case and control hiPSCs, which have been mycoplasma tested, will be deposited with the NIMH Center For Collaborative Studies Of Mental Disorders At RUCDR. RNAseq data for CNTNAP2 carrier and non-carrier neurons (GEO GSE102838) have been deposited at the GeneExpression Omnibus (GEO) repository. Antibodies used in this study are: βIII-TUBULIN (1:500; Chicken; Biolegend; 801201), NeuN(1:100; Rabbit; Abcam; ab104225), MAP2 (1:500; Chicken; Abcam; ab5392).