Abstract
This investigation reports on the characteristics of MAPbI3 perovskite films on obliquely sputtered ITO/glass substrates that are fabricated with various sputtering times and sputtering angles. The grain size of a MAPbI3 perovskite film increases with the oblique sputtering angle of ITO thin films from 0° to 80°, indicating that the surface properties of the ITO affect the wettability of the PEDOT:PSS thin film and thereby dominates the number of perovskite nucleation sites. The optimal power conversion efficiency (Eff) is achieved 11.3% in a cell with an oblique ITO layer that was prepared using a sputtering angle of 30° for a sputtering time of 15 min.
Keywords: Oblique-angle sputtered ITO, MAPbI3 perovskite, Wettability
Background
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a transparent conductive material that comprises indium oxide (In2O3) and tin oxide (SnO2). It is widely used in liquid crystal displays, light-emitting diodes, and solar cells owing to its visible transparency of approximately 96% and conductivity of around 10 Ω/sq [1–5]. Several methods for improving the resistance and the transmittance of ITO films have been studied, including annealing and sputtering with various gas ratios and operating pressures [5–8]. The optoelectronic properties of obliquely sputtered ITO films have been reported upon [9, 10]. As an ITO film is deposited, it grows as a film with a tilted columnar structure at an angle on a substrate, owing to the shadow effect. The columnar ITO film exhibits a different morphology, anisotropic optical properties, and anisotropic resistivity [10].
Recently, solar cells with perovskite materials, such as CH3NH3PbI3, as an active layer have received much interest owing to their favorable power conversion efficiencies [11–18]. Most perovskite solar cells have transparent conductive oxide (TCO) glass, such as ITO or FTO (fluorine-doped tin oxide), as the substrate. However, the optoelectronic properties of an isotropic TCO film differ from those of an anisotropic TCO film. Therefore, this work develops planar perovskite solar cells using CH3NH3PbI3 (MAPbI3) perovskites on oblique ITO substrates that are prepared glancing angle deposition (GLAD). This investigation examines the optical, structural, and surface properties of MAPbI3 perovskite films on oblique ITO substrates that have been annealed at various temperatures and sputtered for various times. The relationships between the performance of the perovskite solar cell and the properties of the perovskite films are discussed.
Methods
In this investigation, ITO glass was cut into small pieces of size 1.5 × 1.5 cm2 be used as substrates. The ITO glass substrates were thoroughly cleaned using acetone, ethanol, and deionized (DI) water in an ultrasonic oscillator for 5 min and dried with nitrogen. An ITO film was deposited onto the ITO glass substrate by sputtering at various oblique angles using ITO targets, as presented in Fig. 1a. The working gas and pressure were pure argon and 5 mTorr, respectively. After deposition, the films were annealed at 300 °C for 30 min.
Fig. 1.
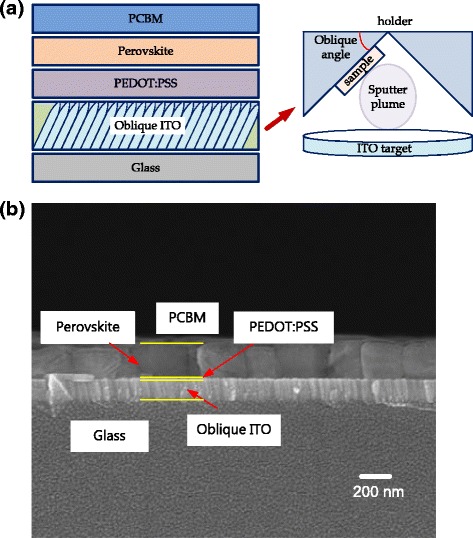
a Schematic cross section of completed structure and oblique sputtering system. b Cross-sectional FESEM image of sample with 30°-tilted sputtered oblique ITO
Glass substrates that were coated with the obliquely sputtered ITO films were used for the perovskite solar cells. PEDOT:PSS films were prepared by spin-coating the oblique ITO glass substrates at 5000 rpm for 30 s. After spin-coating, the film was annealed at 110 °C for 10 min. The perovskite layer was deposited using two-step spin-coating onto the PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO glass substrate at 1000 rpm for 10 s and 5000 rpm for 20 s. During the step at 5000 rpm for 20 s, the wet spinning film was quenched by dropping 100 μl of anhydrous toluene onto it. The perovskite precursor solutions were prepared using 1.25 mmol methylammonium bromide and 1.25 mmol PbI2 (with a purity of 99.999%) that was dissolved in 1 mL cosolvent. The volume ratio of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to γ-butyrolactone (GBL) was 1:1. After spin-coating, the film was annealed at 100 °C for 10 min. Then [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) was dissolved in chlorobenzene (20 mg/mL) and spin-coated on perovskite layers at 3000 rpm for 30 s, forming a 50-nm-thick film as an electron transport layer. Finally, an Ag electrode with a thickness of 20 nm was deposited by thermal evaporation to complete the structure of the device. The sample was covered with a shadow mask that defined an active area of 0.5 cm × 0.2 cm during the deposition. Figure 1a schematically depicts the complete structure. Figure 1b shows the cross-sectional FESEM image of the sample with the 30°-tilted obliquely sputtered ITO.
Results and Discussion
The crystalline microstructures of the films were observed using an X-ray diffractometer. A field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) was used to observe the surface morphology of the samples. The current density–voltage (J–V) characteristics of the solar cells were measured using a Keithley 2420 programmable source meter under irradiation by a 1000 W xenon lamp. The irradiation power density on the surface of the cell was calibrated to 1000 W/m2.
Figure 2 shows the XRD patterns of the MAPbI3 perovskite films on PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO layer/glass at various oblique angles. The four mean peaks at 14.28°, 28.5°, 30.61°, and 31.93° correspond to the (110) perovskite, (220) perovskite, (110) SnO2, and (222) In2O3 planes, respectively. As the sputtering angle increases from 0° to 60°, the (110) SnO2 is formed by the incorporation of Sn atoms. The size of the crystal domain can be calculated using Scherrer’s equation [19]. The sizes of the crystal domains of the MAPbI3 perovskite films in the samples are approximately 71.8 nm. Therefore, the sizes of the crystal domains of the MAPbI3 perovskite are not affected by the oblique ITO layer.
Fig. 2.
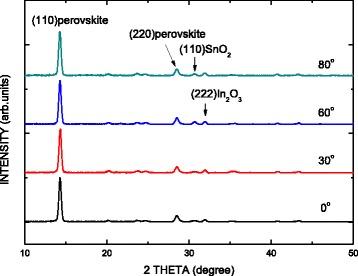
XRD patterns of MAPbI3 perovskite films on PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO layer/glass for various oblique angles
Figure 3 shows SEM images of MAPbI3 perovskite films on an oblique ITO layer/glass for various oblique angles. The grain (or particle) size of the MAPbI3 perovskite films increases with the oblique sputtering angle from 0° to 80°, revealing that the surface properties of the ITO influence the number of perovskite nucleation sites. Since the ITO is not in direct contact with the perovskite thin film and a PEDOT:PSS thin film is inserted between the ITO and the perovskite, the surface properties of the ITO should not directly influence the properties of the perovskite thin films. Hence, the wettability of the PEDOT:PSS thin films [20] is related to the surface properties of the ITO. Therefore, the different grain sizes in the MAPbI3 perovskite films may be related to the wettability of the substrate [21, 22]. Experiments on the contact angle of a water droplet were carried out to assess the wettability of the PEDOT:PSS thin films on the different ITO/glass samples, as shown in Fig. 4. The contact angle is proportional to the size of the grains in the MAPbI3 thin film, indicating that the nucleation and crystal growth of a MAPbI3 thin film can be controlled by varying the surface wettability of the PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO/glass. Contact angle images of the oblique ITO/glass samples were obtained to understand the variation of the surface wettability of the PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO/glass samples, as depicted in Fig. 5. The wettability of the PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO/glass samples is inversely proportional to the wettability of the oblique ITO/glass samples, so the vertical distributions of the hydrophilic PSS polymers and hydrophobic PEDOT polymers can be manipulated by varying the surface wettability of the oblique ITO/glass sample. PSS polymers are suggested to be distributed mostly in the upper surface of the PEDOT:PSS thin film when the substrate has a hydrophobic surface (Fig. 5a), resulting in a small water droplet contact angle on the PEDOT:PSS thin film (Fig. 4a). The experimental results (XRD and SEM) demonstrate that the MAPbI3 grains are multi-crystalline MAPbI3 particles [23].
Fig. 3.
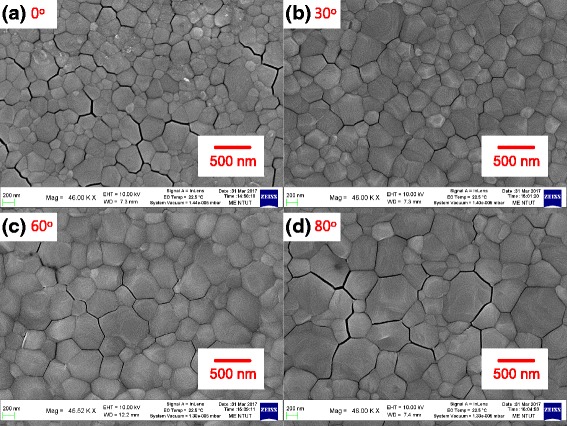
a–d SEM images of MAPbI3 perovskite films on PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO layer/glass for various oblique angles
Fig. 4.
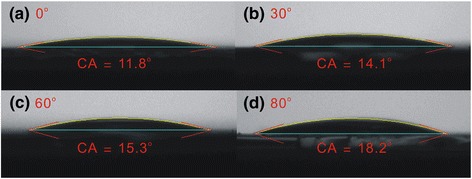
a–d Images that show contact angle of water on PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO layer/glass for various oblique angles. CA contact angle
Fig. 5.
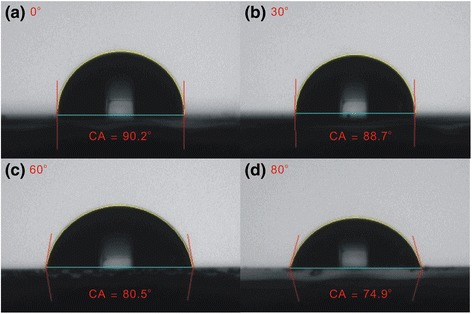
a–d Images that show contact angle of water on oblique ITO layer/glass for various oblique angles
Figure 6 presents the photoluminescence (PL) spectra of the MAPbI3 perovskite films on PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO/glass for various oblique angles. One main peak is observed at 768 nm, corresponding to emission by MAPbI3. The finding is supported by the XRD results. The PL emission energy of the MAPbI3 perovskite is not affected from beneath the oblique ITO layer. Additionally, the different PL intensities of the MAPbI3 films on ITOs sputtered with various oblique angles were obtained as a result of the separation of the light-induced exciton. A better interface between PEDOT:PSS and perovskite provided better exciton separation, inducing a stronger PL quenching effect. Therefore, ITO at an oblique angle of 80° exhibited the best exciton separation from the perovskite layer to PEDOT:PSS, owing to the favorable surface wettability of the PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO, as shown in Fig. 4.
Fig. 6.
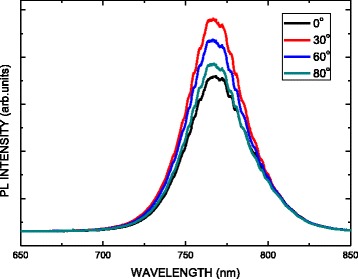
PL spectra of MAPbI3 perovskite films on PEDOT:PSS/oblique ITO layer/glass for various oblique angles
Figure 7 plots the current density–voltage (J–V) curve of the solar cells that are based on MAPbI3 perovskite with an oblique ITO layer that is sputtered at various oblique angles and undergoes heat treatment at an annealing temperature of 300 °C. The sputtering time is 15 min. Table 1 presents the resulting power conversion efficiency (Eff), short-circuit current density (J sc), open-circuit voltage (V oc), and fill factor (FF) of the MAPbI3 solar cells. The performance of the device degrades as the sputtering angle of the oblique ITO layer increases, because the oxygen content in the oblique ITO layers and their resistance increase with the sputtering angle [10]. Maximum efficiency can be achieved following deposition at an oblique angle of 30° owing to the favorable conductivity.
Fig. 7.

Current density–voltage (J–V) of solar cells based on MAPbI3 perovskite with oblique ITO layer sputtered at various oblique angles
Table 1.
Parameters of perovskite MAPbI3 film on oblique ITO layer with various oblique angles
| Oblique angle (°) | V oc (V) | J sc (mA/cm2) | FF (%) | Eff (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.92 | 20.46 | 60.00 | 11.30 |
| 60 | 0.922 | 19.68 | 49.11 | 8.91 |
| 80 | 0.80 | 8.75 | 31.06 | 2.19 |
Figure 8 plots the current density–voltage (J–V) curves of the solar cells that are based on MAPbI3 perovskite with the oblique ITO layer sputtered for various sputtering times, before undergoing heat treatment at an annealing temperature of 300 °C. Table 2 presents the corresponding power conversion efficiency (Eff), short-circuit current density (J sc), open-circuit voltage (V oc), and fill factor (FF) of the MAPbI3 solar cells. Optimum efficiency is reached when the sputtering time of the oblique ITO layer is 15 min because of the thickness of the layer and its good conductivity. The best device is obtained using this deposition angle, with J SC = 20.46 mA/cm2, V OC = 0.92 V, FF = 60.00%, and Eff = 11.30%.
Fig. 8.
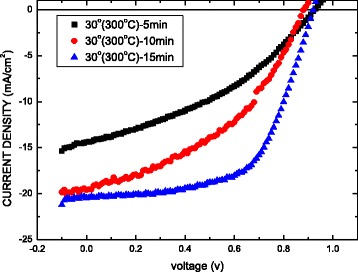
Current density–voltage (J–V) of solar cells based on MAPbI3 perovskite with oblique ITO layer sputtered for various sputtering times
Table 2.
Parameters of perovskite MAPbI3 film on oblique ITO with various sputtering times
| Sputtering time (min) | V oc (V) | J sc (mA/cm2) | FF (%) | Eff (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.92 | 14.40 | 37.78 | 5.042 |
| 10 | 0.88 | 19.60 | 42.59 | 7.359 |
| 15 | 0.92 | 20.46 | 60.00 | 11.30 |
Conclusions
In summary, this work demonstrated the characteristics of MAPbI3 perovskite films on the PEDOT:PSS/oblique-sputtered ITO/glass substrates that were fabricated using various sputtering times and sputtering angles. The device performance was optimized using an oblique ITO layer that was prepared by sputtering at 30° for 15 min, with a short-circuit current density (J SC) = 20.46 mA/cm2, open-circuit voltage (V OC) = 0.92 V, fill factor (FF) = 66.0%, and power conversion efficiency (Eff) = 11.3%. The performance of the device degrades as the sputtering angle of the oblique ITO layer increases from 30° to 80° because the resistance of the device increases with the sputtering angle. Although oblique ITO layers improve the scattering of incident light, the high resistivity degrades the performance of the device. Therefore, optimum efficiency can be achieved by deposition at an oblique angle of 30° owing to the conductivity.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China under Contract No. NSC 106-2221-E-027-091.
Funding
This work was supported by the financial plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China.
Abbreviations
- FESEM
Field-emission scanning electron microscope
- GLAD
Glancing angle deposition
- ITO
Indium tin oxide
- J–V
Current density–voltage
- MAPbI3
CH3NH3PbI3
- PEDOT:PSS
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate
- TCO
Transparent conductive oxide
- XRD
X-ray diffractometer
Authors’ Contributions
KYL and LCC prepared the figures. LCC wrote the paper, designed the experiments, and analyzed the data. YJW prepared the samples and did all the measurements. LCC and KYL made the discussion and suggested the parameter. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Kun-Yi Lee, Email: kelvin119@gmail.com.
Lung-Chien Chen, Email: ocean@ntut.edu.tw.
Yu-June Wu, Email: y1999026@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Cui HN, Teixeira V, Meng LJ, Martins R, Fortunato E. Influence of oxygen/argon pressure ratio on the morphology, optical and electrical properties of ITO thin films deposited at room temperature. Vacuum. 2008;82:1507–1511. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2008.03.061. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lewis BG, Paine DC. Applications and processing of transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 2000;25:22–27. doi: 10.1557/mrs2000.147. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Limmer SJ, Cruz SV, Cao GZ. Films and nanorods of transparent conducting oxide ITO by a citric acid sol route. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. 2004;79:421–424. doi: 10.1007/s00339-004-2738-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cui HN, Xi SQ. The fabrication of dipped CdS and sputtered ITO thin films for photovoltaic solar cells. Thin Solid Films. 1996;288:325–329. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(96)08825-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gorjanc TC, Leong D, Py C, Roth D. Room temperature deposition of ITO using r.f. magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films. 2002;413:181–185. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(02)00425-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim SM, Rim YS, Keum MJ, Kim KH. Study on the electrical and optical properties of ITO and AZO thin film by oxygen gas flow rate. J Electroceram. 2009;23:341–345. doi: 10.1007/s10832-008-9452-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Minami T, Sonohara H, Kakumu T, Takata S. Physics of very thin ITO conducting films with high transparency prepared by DC magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films. 1995;270:37–42. doi: 10.1016/0040-6090(95)06889-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Danson N, Safi I, Hall GW, Howson RP. Techniques for the sputtering of optimum indium-tin oxide films on to room-temperature substrates. Surf Coat Technol. 1998;99:147–160. doi: 10.1016/S0257-8972(97)00436-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Barranco A, Borras A, Gonzalez-Elipe AR, Palmero A. Perspectives on oblique angle deposition of thin films: from fundamentals to devices. Prog Mater Sci. 2016;76:59–153. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.06.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen LC, Chen CC, Sung YT, Hsu YY. Oblique-angle sputtering effects on characteristics of nanocolumnar structure anisotropic indium tin oxide films. J Electrochem Soc. 2009;156:H471. doi: 10.1149/1.3116248. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hodes G. Perovskite-based solar cells. Science. 2013;342:317–318. doi: 10.1126/science.1245473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen LC, Tseng ZL, Chen CC, Chang SH, Ho CH. Fabrication and characteristics of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells with molybdenum-selenide hole-transport layer. Appl Phys Express. 2016;9:122301. doi: 10.7567/APEX.9.122301. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yang WS, Noh JH, Jeon NJ, Kim YC, Ryu S, Seo J, Seok SI. High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science. 2015;348:1234–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa9272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu M, Johnston MB, Snaith HJ. Efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells by vapour deposition. Nature. 2013;501:395–398. doi: 10.1038/nature12509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Im JH, Jang IH, Pellet N, Grätzel M, Park NG. Growth of CH3NH3PbI3 cuboids with controlled size for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. Nat Nano. 2014;9:927–932. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jeon NJ, Noh JH, Yang WS, Kim YC, Ryu S, Seo J, Seok S., II Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells. Nature. 2015;517:476–480. doi: 10.1038/nature14133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen LC, Tseng ZL, Huang JK. A study of inverted-type perovskite solar cells with various composition ratios of (FAPbI3)1 − x(MAPbBr3)x. Nano. 2016;6:183. doi: 10.3390/nano6100183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tong X, Lin F, Wu J, Wang ZM. High performance perovskite solar cells. Adv Sci. 2016;3:5. doi: 10.1002/advs.201500201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang Z, Wang CC, Zakaria R, Ying JY. Role of particle size in nanocrystalline TiO2-based photocatalysts. J Phys Chem B. 1998;102:10871–10878. doi: 10.1021/jp982948+. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chang SH, Chen W-N, Chen C-C, Yeh S-C, Cheng H-M, Tseng Z-L, Chen L-C, Chiu KY, Wu W-T, Chen C-T, Chen S-H, Wu C-G. Manipulating the molecular structure of PEDOT chains through controlling the viscosity of PEDOT:PSS solutions to improve the photovoltaic performance of CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2017;161:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2016.11.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bi C, Wang Q, Shao Y, Yuan Y, Xiao Z, Huang J. Non-wetting surface-driven high-aspect-ratio crystalline grain growth for efficient hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7747. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee K-M, Chen C-C, Chen L-C, Chang SH, Chen K-S, Yeh S-C, Chen C-T, Wu C-G. Thickness effects of thermally evaporated C60 thin films on regular-type CH3NH3PbI3 based solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2017;164:13–18. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2017.02.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen CC, Chang SH, Chen LC, Cheng HM, Tseng ZL, Wu CG. Manipulating multicrystalline grain size in CH3NH3PbI3 thin films for application in photovoltaics. Sol Energy. 2016;139:518–523. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.10.025. [DOI] [Google Scholar]


