Abstract
Background
The number of clinical trials including older patients, and particularly patients with cognitive impairment, is increasing. While statutory provisions exist to make sure that the capacity to consent is assessed systematically for each patient, many gray areas remain with regard to how this assessment is made or should be made in the routine practice of clinical research.
Objectives
The aim of this review was to draw up an inventory of assessment tools evaluating older patients’ capacity to consent specifically applicable to clinical research, which could be used in routine practice.
Methods
Two authors independently searched PubMed, Cochrane, and Google Scholar data-bases between November 2015 and January 2016. The search was actualized in April 2017. We used keywords (MeSH terms and text words) referring to informed consent, capacity to consent, consent for research, research ethics, cognitive impairment, vulnerable older patients, and assessment tools. Existing reviews were also considered.
Results
Among the numerous existing tools for assessing capacity to consent, 14 seemed potentially suited for clinical research and six were evaluated in older patients. The MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool for Clinical Research (MacCAT-CR) was the most frequently cited.
Conclusion
The MacCAT-CR is currently the most used and the best validated questionnaire. However, it appears difficult to use and time-consuming. A more recent tool, the University of California Brief Assessment of Capacity to Consent (UBACC), seems interesting for routine practice because of its simplicity, relevance, and applicability in older patients.
Keywords: aged, assessment tools, clinical research, decision-making capacity
Introduction
The prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and related disorders in the context of aging demographics is a major public health issue.1 Dementia leads to several functional alterations responsible for a loss of bearings in time and space and impairment of the patients’ capacity to perform activities of daily living or express their will without assistance.2,3 This progressive loss of autonomy drastically affects the life of patients (and those around them), making them vulnerable and reducing their quality of life.
One of the most important components of vulnerability in patients with cognitive decline is the loss of capacity to make decisions. This can progressively affect various domains of their everyday life and have implications in the legal or medical fields.3,4 The impairment of decisional capacity (DC) raises many questions for the patients’ relatives or professional caregivers. According to a recent literature review, the prevalence of such impairment could reach 34% of hospitalized patients and up to 45% of patients in psychiatric settings.5
In the case of alteration of their DC, the patients can easily find themselves deprived of fundamental rights. There is also a risk that they end up making decisions against their interest without realizing it. The loss of DC can, thus, affect the patients’ autonomy and make them dependent on external help. Conversely, the DC of patients with mild cognitive impairment may also be excessively underestimated.6,7 In either situation, the potential legal or ethical consequences are considerable.3,4
The field of clinical research is especially exposed to these risks. In spite of the existing bioethics laws and regulations designed to protect patients taking part in research,8,9 the means by which the inclusions to clinical trials are made can sometimes be put into question, especially regarding the evaluation of the patient’s capacity to consent for research (CR). When the CR is in doubt, it is therefore common to consult a close relative such as the patient’s support person, but there again, the means by which this person should be designated remain unclear, and the reliability of such surrogate consent is most often questionable.10–15
Various theoretical concepts have been developed for use in conceptualizing decision making specifically in informed consent contexts, merging from the fields of neuropsychiatry, psychology, sociology, or behavioral science.16 In the cognitive models, the consensus is that decision making is based on four different aptitudes.17–19 The patients need 1) to be able to understand the information and issues of the decision (comprehension), 2) to realize that the decision to be made applies to themselves and to personalize their decision in line with intimate values or beliefs (appreciation), 3) to be able to evaluate different alternatives and their consequences (reasoning), and 4) to communicate on a decision (choice). Furthermore, emotion and social factors also take a strong part in decision making.16,20,21 Short-term and semantic memory affect all four abilities but are more strongly associated with understanding and reasoning.22,23 Executive functions, which cover important domains such as attention, encoding of verbal and visual material, forward planning, organization, and cognitive flexibility, are also critical to decision making. They can be impacted even in early stages of AD- or Parkinson’s disease-related cognitive impairment and alter understanding, appreciation, and reasoning.24,25 Finally, the expression of a choice can be influenced by language or behavioral and neuropsychiatric symptoms such as apathy.26
There are two ways to assess DC in informed consent situations: assess cognitive capacities and their impairment (eg, mental status examinations and neuropsychological instruments) and assess capacities as demonstrated within the context of content that is specific to the consent situation. However, usual global screening tests such as Folstein’s mini–mental state examination (MMSE)27 are indirect and, therefore, imperfect ways of inferring what a person might do if faced with the task of understanding or reasoning about being in a clinical trial study.28,29 Consequently, an objective and direct evaluation of patients’ DC, in case of doubt as to the validity of the consent, ensures that the inclusion of subjects to clinical trials is ethical and respectful of their rights, which is the responsibility of researchers. However, it can be observed that research protocols are often vague on the means used to assess CR, suggesting that overall awareness of professionals and researchers, including those working in the field of dementia, is insufficient.
Previous reviews have essentially been focused on capacity to consent to treatment. Reviews focusing specifically on capacity to consent to research are scarce and seemed to have yielded only a few results in comparison to the numerous tools developed, especially in the psychiatric context.30,31 The aim of this review was to draw up an inventory of assessment instruments for evaluating the DC of older patients with cognitive impairment, which could be specifically applicable to the assessment of the CR.
Methods
Two authors (TG and OLS) independently consulted PubMed (Medline), Google Scholar, and the Cochrane databases in search for original articles describing tools for the assessment of DC. Existing literature reviews on the topic were also considered as additional information. The initial search was conducted between November 2015 and January 2016 and was actualized in April 2017.
The inclusion criteria were based on the tools themselves. To be included, the references had to make a description of tests specifically designed for assessing patients’ DC, with a report of the methods for assessing validity and/or reliability (either from the original report or from other studies evaluating the same test). Second, a mention of applicability to research and to older people with cognitive impairment was sought.
Different search strategies were performed using in priority keywords from the MeSH thesaurus: “informed consent”, “decision making”, “neuro-cognitive disorders”, “aged”, “adult clinical protocols”, and “research subjects”. However, the following additional keywords completed the search strategy: “Alzheimer”, “dementia”, “protocol inclusion”, “ethics”, “consent for research”, “consent to research”, “inclusion in clinical trials”, “competency”, “capacity to consent”, “understanding”, and “neuro-psychological evaluation”. No language or publication date limit was set.
The article selection was based on titles, abstracts, and finally full text for relevant articles. Additional results were also retrieved from the bibliography of existing reviews. Second, the same two authors independently conducted the data extraction and the selection of suitable tests or tools for assessing patients’ CR. Finally, the results were combined, and consensus was reached through discussion between authors.
Results
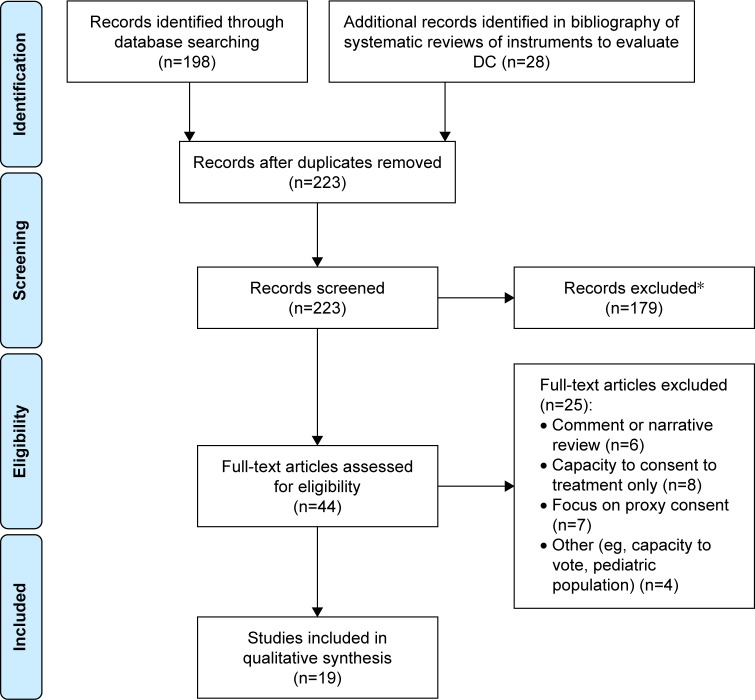
The flow diagram in Figure 1 summarizes the number of articles accepted and rejected during the selection procedure. The search of the computerized databases identified a total of 226 articles. In the end, a total of 19 publications were identified as relevant to our research on instruments assessing DC for patients with cognitive disorders (Figure 1). In addition, six literature reviews of instruments to evaluate CR were also considered as complementary information.30–35
Figure 1.
Flow chart of search results.
Note: *These were mainly comments, narrative reviews, or off-topic records.
Abbreviation: DC, decision capacity.
Thirty-eight instruments assessing DC were identified. However, the vast majority of existing tests were developed to assess the capacity of patients to consent to medical treatment and not for research purpose. For this particular context, 14 assessment tools were identified, the majority of which were initially developed or validated in psychiatric populations.30,32,34 The main characteristics of each test are summarized in Table 1. They differ by the method used (eg, self-administered questionnaire and structured interview), the abilities assessed (among the four dimensions of decision making), the population they were initially aimed for (sometimes focused on very specific populations), the administration time, and the robustness of their evaluation (validity and reliability) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Summary of included assessment tools (presented by year of publication)
| Assessment tool | Type | Abilities assessed | Administration time | Population | Validity | Internal consistency | Interrater reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-part consent form76 | Self-administered questionnaire and semistructured interview | Understanding | Not reported | Psychiatric patients | Good agreement with expert judges; correlated with age, education, occupational level, and mental status | Test–retest r=0.70–0.76; | Interrater r=0.94–0.96; Kappa =0.44–0.83 |
| CIS77 | 15-item structured interview | Understanding, appreciation, reasoning and choice (four subscale scores) | Not reported | Patients undergoing electroconvulsive therapy | Correlation with the physician’s judgment Pearson’s r=0.43–0.98 | Cronbach’s α=0.96 | Interrater reliability was 0.95 for CIS total score excellent |
| Deaconess informed consent comprehension test78 | Structured interview Requires training | Understanding | <10 minutes | Trials evaluating anti-infective agents | Correlated with Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised (r=0.44), reading (r=0.38), and education (r=0.33) | Test–retest reliability intraclass r=0.79 | Interrater r=0.84 |
| ESC38 | Five-item questionnaire delivered after information about the study, but before the formal consent process Requires training | Understanding | 5–10 minutes | Schizophrenia and HIV Also tested in 346 nursing home residents42 | Correlated with MacCAT-CR Validity measured by item mapping with fit from 0.81 to 1.0942 | Not reported | Interrater reliability (r=0.81)42 |
| ICS79 | 36-item questionnaire Requires training | Choice, understanding, appreciation, and reasoning | Not reported | Schizophrenia | Correlated with the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale r=−0.17 to −0.33 | Not reported | Not reported |
| Vignette methods described by Schmand et al (1999)36 | Vignettes, structured interview | Understanding, reasoning, and expression of a choice | 30–45 minutes | Older adults with or without dementia | Poor agreement with physician’s judgment of competency; correlated with severity of dementia Kappa =0.31 | Cronbach’s α=0.69 | Not reported |
| CAT80 | Semistructured interview Requires training | Choice, understanding, appreciation, and reasoning | Not reported | Developed in primary care setting on a small patient sample | Good agreement with independent psychiatric assessment Kappa =0.77–1.00 | Not reported | Not reported |
| MacCAT-CR37 | 21-item structured interview | Appreciation, understanding, reasoning, and choice (four subscale scores) | 15–20 minutes | Developed initially on patients with mental illnesses (depression, schizophrenia) but also evaluated in dementia (Alzheimer’s disease),44,47 cancer,81 HIV disease, diabetes, and control subjects | Correlations with Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale and MMSE; distinguishes between patients and control subjects Kappa >0.97 for each subscale81 | Poor test–retest correlations: Kendall’s Tau =−0.15 for reasoning, 0.26 for understanding, and 0.36 for appreciation82 | High interrater reliability (ICC: 0.78–0.98)44,47,83 Kappa =0.53–0.7984 |
| Quality of informed consent questionnaire85 | Self-administered 34-item questionnaire | Understanding (objective and subjective) | Mean completion time: 7.2 minutes (2.5–12.8) | Cancer patients | Consensus among independent experts: accuracy and comprehensiveness No correlation or agreement measure with expert panel conducted |
Test–retest ICC: 0.66 for objective understanding and 0.77 for subjective understanding | Not reported |
| CSA86 | 18-item structured interview (13 close-ended questions and five open-ended questions) Requires training | Appreciation | 10–20 minutes | Schizophrenia or related psychotic disorder and controls | Correlated with psychopathology and cognitive impairment | Cronbach’s α: 0.83–0.88 | Interrater percent agreement: 0.82–100 |
| Brief informed consent test, Buckles et al39 | 11-item questionnaire (yes/no questions) Requires training | Understanding | 5–10 minutes | Older patients with dementia | Correlated with Clinical Dementia Rating (Spearman r=−0.48) and MMSE (Pearson r=0.58) Not compared with other tests such as MacCAT-CR |
Internal consistency: Cronbach’s α=0.63 or 0.70 (with one item removed) | Not reported |
| Capacity-to-consent screen52 | 10-item questionnaire | Choice, understanding, appreciation, and reasoning | 20 minutes | Psychiatric populations | Tested on 68 patients and correlated to psychiatric evaluation but psychometric properties not given | Not reported | Not reported |
| UBACC questionnaire40 | 10-item questionnaire | Understanding, appreciation and reasoning | <5 minutes | Middle-aged and older outpatients with schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects40 | Correlation with the MacCAT-CR scores Sensitivity 89% Specificity 100% |
Internal consistency: Cronbach’s α=0.77 | Interrater reliability: ICC 0.84–0.98 |
| OACCR41 | Four-item scale | Choice, understanding, appreciation, and reasoning | Brief, no time reported | Older patients in community and institutional settings | Validity evaluated in reference to the capacity to Consent Screen Score52 Pearson’s coefficient r=0.939 Sensitivity 99.2% Specificity 72.9% |
Cronbach’s α=0.85 | Item-total correlation: 0.59–0.76 |
Abbreviations: CAT, capacity assessment tool; CIS, Competency Interview Schedule; CSA, California Scale of Appreciation; ESC, evaluation to sign consent; ICC, intraclass correlation coefficient; ICS, Informed Consent Survey; MacCAT-CR, MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool for Clinical Research; MMSE, mini–mental state examination; OACCR, older adults’ capacity to consent to research; UBACC, University of California Brief Assessment of Capacity to Consent.
In older patients with cognitive disorders, the following six tests have been evaluated, with variable consistency: the vignette method by Schmand et al,36 the MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool for Clinical Research (MacCAT-CR),37 the evaluation to sign consent (ESC),38 the brief informed consent test,39 the University of California Brief Assessment of Capacity to Consent (UBACC) questionnaire,40 and the older adults’ capacity to consent to research (OACCR).41 These tools are described briefly hereafter in chronological order.
ESC
The ESC is a short questionnaire tailored to the research protocol.38 The ESC presents the advantage of being short and simple to use. The patient reflects his understanding of the protocol by answering five questions, four of which require the assessor to make subjective judgments of the patient’s capacity. However, the three other dimensions of DC assessment are not covered by this test. Furthermore, the evaluation may be at risk of examiner bias, as the scoring mainly relies on the subjective judgment of the examiner, without any explicit cutoff. The ESC was initially tested in schizophrenia and HIV patients but has also been evaluated in 346 older nursing home residents.42
Vignettes method developed by Schmand et al
This method was developed in the 1990s and evaluated in aged Dutch people (70–90 years), who were cognitively intact (n=176) or had dementia (n=64; mostly AD).36 Two vignettes were used as competency assessment instruments. A vignette is a description of an imaginary situation in which the subject is asked to decide on a proposed treatment or on participation in research. His/her understanding of the situation and the quality of the reasoning underlying that choice are tested by a short series of questions. The answers to the vignette questions were summed to form a competency score. The reliability (internal consistency) of this score was 0.82 for both vignettes combined. However, when assessing agreement between Schmand’s vignette method and a physician’s judgment in the group of patients with dementia, Cohen’s kappa was only of 0.36 (fair agreement) and dropped to 0.04 (no agreement) when patients with “minimal dementia” were left out of the analysis.
MacCAT-CR
The MacCAT-CR was the most frequently cited existing tool, often referred to and used as a reference to assess capacity to consent to research and test the validity of other tools37 as it is the most widespread and the most validated of all.3,30,32,43–45 It is a modified version of the MacCAT-T used to assess the capacity to consent to treatment.46 This is a 21-item structured interview with four subscales assessing the following four main dimensions of decision making: understanding, appreciation, reasoning, and expressing a choice. Each subscore is predictive of decision-making capacity. Thirteen questions are dedicated to understanding, three questions are dedicated to appreciation, four questions are dedicated to reasoning, and one question is dedicated to expressing a choice. Each item is scored 0 (inadequate), 1 (partially adequate), or 2 (adequate). Questions are tailored to the specific research context in which the patient is asked to participate. This test was developed in a wide variety of clinical situations and for different populations. Yet, the reliability and validation of derived versions are less established.30 In particular, two groups of researchers adapted this test for use in patients with AD, in which they suggested dummy clinical trial protocols.44,47 The test comes with a user’s guide and a precise rating manual. However, there is no threshold or limit score that would directly discriminate patients able to decide from those who are not. Rather, this tool was conceived as an aid to be used by the assessor for the appreciation of DC.30 The other downsides of this test are its relative complexity, the need for specific training, the absence of specific cutoff scores, and the duration of the test of ~20 minutes, which could also be a barrier in the process of patient inclusions to clinical trials.30,48
Brief informed consent test
This test was constructed to address the following eight elements of informed consent as stated in the Code of Federal Regulations:9 1) explanation of the purposes of the research and the requirements of participation; 2) description of any reasonably foreseeable risks or discomforts to the participant; 3) description of any benefits to the participant or to others; 4) disclosure of appropriate alternative procedures or courses of treatment; 5) statement describing the extent, if any, to which confidentiality of records identifying the participant will be maintained; 6) for research involving more than minimal risk, an explanation/information as to whether any medical treatments are available if injury occurs; 7) contact information for the study investigator in the event of a research related injury to the participant and for questions; and 8) a statement that participation is voluntary and that refusal to participate will involve no penalty or loss of benefits. After a review process by ethical and research committees, 11 items were selected and closed-ended questions were used. This test shows only moderate correlation with the Clinical Dementia Rating scale (Table 1) and was not evaluated against psychiatric expertise or other specific DC tools such as the MacCAT-CR.39
UBACC
UBACC is a 10-item questionnaire.40 This test uses a pragmatic approach using a teach-back process of the protocol and the potential risks and benefits of participating. The total score is determined by the accuracy of answers depending on expected answers for each question. It has the advantage of being short and does not require specific training. It can be tailored specifically to the clinical trial proposed to the patient. Yet, this tool does not evaluate the capacity to express a choice.43 A validation study showed good performances of the UBACC in terms of external and internal validity, reliability, sensitivity, and specificity.40 Although initially developed for all vulnerable patients, including those with schizophrenia, it has also shown promise in AD patients and showed good correlation with cognitive features such as verbal fluency and global cognition.49 However, expression of a choice is not evaluated by this test. It has been translated and validated in different languages and should soon be recommended by European regulatory authorities.48,50,51
OACCR
The OACCR was developed in nursing home residents and community dwelling older adults in South Korea.41 It was designed to cover the four dimensions of decision making with a short questionnaire of only four open questions. The strength of this questionnaire relies in its simplicity, which could make it interesting for use in routine practice. However, one could think such a simple test might not be enough to evaluate the complexity of the assessment of DC, and the validation procedure seems still insufficient, especially with regard to the gold standard chosen as reference. Rather than testing the correlation to psychiatric expertise or the MacCAT-CR (despite limitations enounced earlier), the authors have preferred to use the capacity-to-consent screen by Zayas et al,52 a test which is a less validated test.31 Finally, it is not clear whether an English version has been evaluated.
Discussion
In this study, we searched existing tools for assessing older patients’ DC in the context of clinical research. Five reviews were identified.30,32–34,43 During our search, we listed 13 assessment tests specifically designed to evaluate the patients’ capacity to consent to be included in a research protocol. Two of these appeared particularly relevant to us: the MacCAT-CR37 and the UBACC.40 No new instruments were identified as having been developed in the past 6 years, and only two of the 14 were developed in the past 10 years.
While physiological aging does not normally affect communication and DC,34,48 many incident pathologies in aging, such as a decrease in sensory acuity, depression, stroke (especially in the case of aphasia), and of course dementia, can have a serious impact on DC.
There is no debate over the strong impairment of DC in severe stages of AD.28,53,54 Moreover, in the case of mild-to-moderate disease, many studies suggest that DC can be affected even at the early stages of cognitive decline.33,53,55–59 Understanding capacities would be affected the earliest, followed by reasoning and appreciation, while the capacity of choice would be preserved the longest.58,60 Indeed, understanding is mainly affected by an impairment of episodic and semantic memory, whereas reasoning and appreciation depend on both memory and executive functions.23–25,55,57
Another particularity is that AD is often accompanied by anosognosia. Lack of awareness could alter the patient’s capacity to anticipate and weigh the possible consequences of a decision or action (reasoning and appreciation). Patients may also paradoxically be able to reason situations for others but not as well for themselves. Lack of awareness is correlated with disease severity but can affect patients at an early stage. Some authors suggest using specific tests for anosognosia (such as the Anosognosia Questionnaire for Dementia61) when judging on a patient’s competence, as awareness and DC could be affected differently in patients with cognitive impairment.62
Many clinicians or researchers use their clinical impression or Folstein’s MMSE27 to give an opinion on the patients’ DC. This attitude seems appealing, as it means there is no need for complementary investigations. In comparison with psychiatric expertise, this approach appears however imprecise.29,63 The interpretation of the results and the norms depend on the level of education of the patient and can thus vary from one patient to the an other.64 Additionally, besides extreme values, the MMSE score is not sufficiently reliable to evaluate the patients’ comprehension and judgment ability.28,29 Moreover, there can be differences between individuals for a given MMSE score, and discrepancies can exist between the global assessment of cognitive functions and the DC of the patients as assessed by more specific evaluations.7,30 To a certain extent, this implies that the DC of patients can be affected, although the cognitive impairment remains mild, or oppositely, that the DC can sometimes be underestimated when the cognitive tests show greater impairment. Kim and Caine28 have studied the reliability of Folstein’s MMSE to assess DC, in comparison to the MacCAT-CR, used as a reference. They concluded that MMSE was not a good predictor of incompetence. However, this test could still be useful if using two different thresholds: a score of >26 had a high sensitivity of 96%–100% to detect competent patients while a score of <19 had a specificity of 85%–94%.28 The authors suggested that a score of >26 on the MMSE would allow to safely identify competent subjects with no need for further investigation.65 In another study, Pucci et al66 found that an MMSE score of ≤17 had a positive predictive value of incompetence of 95%, while only ~63% of patients above this threshold were rated sufficiently competent. Therefore, for patients with mild cognitive impairment (with MMSE values between 17 and 26), a gray area remains, with the need for more precise and specific assessment tools.
Standardized tools for assessing DC started to be developed in the 1990s.67 We observed that the large majority of tests were developed to evaluate the patients’ capacity to consent to a medical treatment or other everyday life situations, especially in the field of psychiatry.20 However, there are some heterogeneities between schizophrenia and dementia with regard to DC68 and clinical research is also a very specific domain. The distinction between consent to treatment and consent to research needs to be underlined. In the context of clinical trials, the patients need to be able to understand the aims of the research and other particularities such as randomization, the use of placebos, and the fact that they might not benefit from the treatment.69 Patients with mild cognitive impairment may present with low understanding of the design, potential benefits, and risks of the study.70 In fact, depending on the criteria considered, very few patients would be considered actually capable of giving consent with regard to the thresholds of the specific tests.55,60,68 However, patients with mild cognitive impairment remain able to participate in decisions affecting themselves.12,71 Among the numerous existing tests, only some36,40,51,72,74,75 enable simultaneous evaluation of the four dimensions of decision making (comprehension, choice, reasoning, and appreciation). Most of the tests only evaluate comprehension, while others are designed to evaluate other dimensions more specifically. Also, some tests explore certain components of understanding that are not studied by others. The notion of double blind is, for example, evaluated by the MacCAT-CR but not by the UBACC.
Another difficulty is that, during the evaluation of each tool, discrepancies in the evaluation of DC were found between the results of the tests and the point of view of experts.30 Such differences could cause important interpretation problems and complicate the development of assessment tools. For example, Schmand et al36 have described a very low agreement between there vignette method and physicians’ assessment (kappa =0.04–0.36) of capacity. While this initially appears like a flaw in the test’s reliability, the authors attributed this to a lack of consistency of the subjective clinical evaluation and used this argument to warrant the use of their method.36 Both psychiatric expertise and the large majority of assessment tools rely on subjective interpretation. This highlights the major difficulties of developing a reliable tool in the absence of an indisputable gold-standard evaluation. Many tools have been developed using the MacCAT-CR as a reference. Indeed, it is the most widely employed instrument and recognized as the most validated and reliable in this population.45 However, it has limitations as a gold standard because it does not have a specific objective cut-point (clinical decision making is still required for interpretation) and was developed with reference to psychiatric expertise, which also lacks consistency. As there is currently no clear diagnostic reference to compare the reviewed diagnostic tests to, it becomes impossible to assess sensitivity and specificity of measures; this is also the main reason why the Cochrane systematic project was withdrawn from publication.35 Furthermore, DC is ultimately a legal construct, which depends mainly on the external evaluation and also remains subjective, despite efforts toward standardization of procedures.
In this difficult context, the evaluation of interrater reliability appears very important, but this information was unfortunately lacking for six out of the 14 tests presented in Table 1. Among the six tools evaluated in the cognitively impaired geriatric population, interrater reliability was reported for only four and could be as low as 0.59 as for the OACCR.41
Following validation works from Kim et al47 and Karlawish et al,44 the MacCAT-CR can be applicable to the particular context of AD. However, in both of these studies, the MacCAT-CR tended to underestimate the patients’ competency to decide, as compared to the judgment of experts.32,44,47 This could suggest that the MacCAT-CR is too “severe” for this type of population. However, this finding needs to be put into perspective, as it could also be argued conversely that the experts have overestimated the patients’ competency, illustrating there again the interpretation problems due to the lack of a clear gold standard. In a study aiming to compare the DC of patients with schizophrenia and dementia, the same authors have developed a short three-item questionnaire derived from the understanding subscale of the MacCAT-CR, focused on understanding the purpose, risks, and benefits of the protocol.68 For a cut-point of 2.5, this simplified tool achieved a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 77.3% for detecting impaired understanding using the understanding subscale of the MacCAT-CR.68 Such an approach could potentially help to rapidly discriminate patients with need for further assessment and make use of the MacCAT-CR more practical. However, this three-item questionnaire was only developed for the purpose of this study and would need further evaluation to be considered as a potential tool to be used independently.
Due to the prevalence of cognitive decline and multiple comorbidities in this population, older patients have, until recently, rarely been included in clinical trials – even though this age group accounts for a majority of overall medication consumption.72 Currently, clinical trials specifically oriented to aged patients are multiplying, especially in the field of dementia research. However, these studies are often forced to limit the inclusions to patients at very early and mild stages of the disease.73 Scientific progress requires that clinical trials can be carried out and that potentially vulnerable patients can take part in the research in the most ethical and considerate way. Moreover, it appears important that patients recruited in clinical trials are representative of the target population. In order to improve the ethics of patient inclusion without altering participation rates to clinical trials, valid consent procedures are needed. In the event of incompetence, the means by which surrogate consent is used and the way the proxy is designated remain unclear.14,15,74,75 Finally, the awareness among professionals and researchers on this issue needs to be raised. Project reviewers and ethical boards should give particular focus to the procedures for patient inclusion when reviewing study protocols.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Lobo A, Launer LJ, Fratiglioni L, et al. Prevalence of dementia and major subtypes in Europe: a collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology. 2000;54(11 suppl 5):S4–S9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Traykov L, Rigaud A-S, Cesaro P, Boller F. Le déficit neuropsychologique dans la maladie d’Alzheimer débutante. [Neuropsychological impairment in the early Alzheimer’s disease] L’Encéphale. 2007;33(3 pt 1):310–316. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(07)92044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Karlawish J. Measuring decision-making capacity in cognitively impaired individuals. Neurosignals. 2008;16(1):91–98. doi: 10.1159/000109763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Welie SP. Criteria for patient decision making (in)competence: a review of and commentary on some empirical approaches. Med Health Care Philos. 2001;4(2):139–151. doi: 10.1023/a:1011493817051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lepping P, Stanly T, Turner J. Systematic review on the prevalence of lack of capacity in medical and psychiatric settings. Clin Med Lond Engl. 2015;15(4):337–343. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.15-4-337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ganzini L, Volicer L, Nelson W, Derse A. Pitfalls in assessment of decision-making capacity. Psychosomatics. 2003;44(3):237–243. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.44.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Palmer BW, Harmell AL, Pinto LL, et al. Determinants of capacity to consent to research on Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Gerontol. 2017;40(1):24–34. doi: 10.1080/07317115.2016.1197352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.WMA [webpage on the Internet] The Helsinki Statement. 1964. [Accessed July 27, 2017]. Available from: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/
- 9.Code of Federal Regulations [webpage on the Internet] Title 21. Section 50.25. Informed consent of Human Subjects. 2016. [Accessed July 27, 2017]. Available from: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?SID=aef4d60308e79aaacf3283747dc38c59&mc=true&tpl=/ecfrbrowse/Title21/21cfr50_main_02.tpl.
- 10.Kim SYH, Kim HM, Langa KM, Karlawish JHT, Knopman DS, Appelbaum PS. Surrogate consent for dementia research: a national survey of older Americans. Neurology. 2009;72(2):149–155. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000339039.18931.a2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moye J, Sabatino CP, Weintraub Brendel R. Evaluation of the capacity to appoint a healthcare proxy. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(4):326–336. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2012.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Black BS, Wechsler M, Fogarty L. Decision making for participation in dementia research. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(4):355–363. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2012.11.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kim SYH, Karlawish JH, Kim HM, Wall IF, Bozoki AC, Appelbaum PS. Preservation of the capacity to appoint a proxy decision maker: implications for dementia research. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68(2):214–220. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim SYH, Kim HM, Ryan KA, et al. How important is “accuracy” of surrogate decision-making for research participation? PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54790. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.De Vries R, Ryan KA, Stanczyk A, et al. Public’s approach to surrogate consent for dementia research: cautious pragmatism. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013;21(4):364–372. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2012.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee D. Neural basis of quasi-rational decision making. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16(2):191–198. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2006.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Appelbaum PS, Roth LH. Competency to consent to research: a psychiatric overview. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982;39(8):951–958. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290080061009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Berg JW, Appelbaum PS, Grisso T. Constructing competence: formulating standards of legal competence to make medical decisions. Rutgers Law Rev. 1996;48(2):345–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Saks ER, Jeste DV. Capacity to consent to or refuse treatment and/or research: theoretical considerations. Behav Sci Law. 2006;24(4):411–429. doi: 10.1002/bsl.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.ABA/APA. American Bar Association/American Psychologists Association . Assessment of Older Adults with Diminished Capacity: A Handbook for Psychologists. Washington, DC: ABA, APA; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR. Emotion, decision making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2000;10(3):295–307. doi: 10.1093/cercor/10.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Moye J, Karel MJ, Gurrera RJ, Azar AR. Neuropsychological predictors of decision-making capacity over 9 months in mild-to-moderate dementia. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(1):78–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2005.00288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stormoen S, Almkvist O, Eriksdotter M, Sundström E, Tallberg I-M. Cognitive predictors of medical decision-making capacity in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2014;29(12):1304–1311. doi: 10.1002/gps.4114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Moelter ST, Weintraub D, Mace L, et al. Research consent capacity varies with executive function and memory in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2016;31(3):414–417. doi: 10.1002/mds.26469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schillerstrom JE, Rickenbacker D, Joshi KG, Royall DR. Executive function and capacity to consent to a noninvasive research protocol. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15(2):159–162. doi: 10.1097/01.JGP.0000249392.10426.c6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bertrand E, van Duinkerken E, Landeira-Fernandez J, et al. Behavioral and psychological symptoms impact clinical competence in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:182. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim SYH, Caine ED. Utility and limits of the mini mental state examination in evaluating consent capacity in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(10):1322–1324. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.53.10.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Warner J, McCarney R, Griffin M, Hill K, Fisher P. Participation in dementia research: rates and correlates of capacity to give informed consent. J Med Ethics. 2008;34(3):167–170. doi: 10.1136/jme.2006.019786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dunn LB, Nowrangi MA, Palmer BW, Jeste DV, Saks ER. Assessing decisional capacity for clinical research or treatment: a review of instruments. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(8):1323–1334. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2006.163.8.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Simpson C. Decision-making capacity and informed consent to participate in research by cognitively impaired individuals. Appl Nurs Res. 2010;23(4):221–226. doi: 10.1016/j.apnr.2008.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sturman ED. The capacity to consent to treatment and research: a review of standardized assessment tools. Clin Psychol Rev. 2005;25(7):954–974. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2005.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Moye J, Gurrera RJ, Karel MJ, Edelstein B, O’Connell C. Empirical advances in the assessment of the capacity to consent to medical treatment: Clinical implications and research needs. Clin Psychol Rev. 2006;26(8):1054–1077. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2005.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sessums LL, Zembrzuska H, Jackson JL. Does this patient have medical decision-making capacity? JAMA. 2011;306(4):420–427. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hein IM, Daams J, Troost P, Lindeboom R, Lindauer RJ. Accuracy of assessment instruments for patients’ competence to consent to medical treatment or research. In: The Cochrane Collaboration, editor. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2015. [Accessed January 3, 2016]. webpage on the Internet. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/14651858.CD011099.pub2. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schmand B, Gouwenberg B, Smit JH, Jonker C. Assessment of mental competency in community-dwelling elderly. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1999;13(2):80–87. doi: 10.1097/00002093-199904000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Appelbaum PS, Grisso T. MacCAT-CR: MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool for Clinical Research. 2001. [Accessed January 9, 2016]. Available from: http://shpac.doctorsonly.co.il/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/MacCAT-CR-complete-Hebrew-3-2-13-1.pdf.
- 38.DeRenzo EG, Conley RR, Love R. Assessment of capacity to give consent to research participation: state-of-the-art and beyond. J Health Care Law Policy. 1998;1(1):66–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Buckles VD, Powlishta KK, Palmer JL, et al. Understanding of informed consent by demented individuals. Neurology. 2003;61(12):1662–1666. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000098933.34804.fc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Appelbaum PS, et al. A new brief instrument for assessing decisional capacity for clinical research. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64(8):966–974. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.64.8.966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee M. The capacity to consent to research among older adults. Educ Gerontol. 2010;36(7):592–603. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Resnick B, Gruber-Baldini AL, Pretzer-Aboff I, et al. Reliability and validity of the evaluation to sign consent measure. Gerontologist. 2007;47(1):69–77. doi: 10.1093/geront/47.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hein IM, Daams J, Troost P, Lindeboom R, Lindauer RJ. Accuracy of assessment instruments for patients’ competence to consent to medical treatment or research. In: The Cochrane Collaboration, editor. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2014. [Accessed January 3, 2016]. webpage on the Internet. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/14651858.CD011099.pub2. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Karlawish JHT, Casarett DJ, James BD. Alzheimer’s disease patients’ and caregivers’ capacity, competency, and reasons to enroll in an early-phase Alzheimer’s disease clinical trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(12):2019–2024. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rubright J, Sankar P, Casarett DJ, Gur R, Xie SX, Karlawish J. A memory and organizational aid improves Alzheimer disease research consent capacity: results of a randomized, controlled trial. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010;18(12):1124–1132. doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181dd1c3b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Grisso T, Appelbaum PS, Hill-Fotouhi C. The MacCAT-T: a clinical tool to assess patients’ capacities to make treatment decisions. Psychiatr Serv. 1997;48(11):1415–1419. doi: 10.1176/ps.48.11.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kim SY, Caine ED, Currier GW, Leibovici A, Ryan JM. Assessing the competence of persons with Alzheimer’s disease in providing informed consent for participation in research. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158(5):712–717. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.158.5.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gzil F, Rigaud AS, Latour F. Démence, autonomie et compétence. Éthique publique. 2008;10(2) doi: 10.4000/ethiquepublique.1453. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Seaman JB, Terhorst L, Gentry A, Hunsaker A, Parker LS, Lingler JH. Psychometric properties of a decisional capacity screening tool for individuals contemplating participation in Alzheimer’s disease research. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;46(1):1–9. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Duron E, Boulay M, Vidal JS, et al. Capacity to consent to biomedical research’s evaluation among older cognitively impaired patients. A study to validate the University of California Brief Assessment of Capacity to Consent questionnaire in French among older cognitively impaired patients. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17(4):385–389. doi: 10.1007/s12603-013-0036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Diener L, Hugonot-Diener L, Alvino S, et al. European Forum for Good Clinical Practice Geriatric Medicine Working Party Guidance synthesis. Medical research for and with older people in Europe: proposed ethical guidance for good clinical practice: ethical considerations. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17(7):625–627. doi: 10.1007/s12603-013-0340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zayas LH, Cabassa LJ, Perez MC. Capacity-to-consent in psychiatric research: development and preliminary testing of a screening tool. Res Soc Work Pract. 2005;15(6):545–556. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Karlawish JHT, Casarett DJ, James BD, Xie SX, Kim SYH. The ability of persons with Alzheimer disease (AD) to make a decision about taking an AD treatment. Neurology. 2005;64(9):1514–1519. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000160000.01742.9D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Appelbaum PS. Clinical practice. Assessment of patients’ competence to consent to treatment. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(18):1834–1840. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp074045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Marson DC, Chatterjee A, Ingram KK, Harrell LE. Toward a neurologic model of competency: cognitive predictors of capacity to consent in Alzheimer’s disease using three different legal standards. Neurology. 1996;46(3):666–672. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.3.666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gurrera RJ, Moye J, Karel MJ, Azar AR, Armesto JC. Cognitive performance predicts treatment decisional abilities in mild to moderate dementia. Neurology. 2006;66(9):1367–1372. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000210527.13661.d1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Moye J, Karel MJ, Azar AR, Gurrera RJ. Capacity to consent to treatment: empirical comparison of three instruments in older adults with and without dementia. Gerontologist. 2004;44(2):166–175. doi: 10.1093/geront/44.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Okonkwo O, Griffith HR, Belue K, et al. Medical decision-making capacity in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2007;69(15):1528–1535. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000277639.90611.d9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bouyer C, Teulon M, Toullat G, Gil R. Conscience et compréhension du consentement dans la maladie d’Alzheimer. [Awareness and understanding of consent in Alzheimer’s disease] Rev Neurol (Paris) 2015;171(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2014.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Okonkwo OC, Griffith HR, Copeland JN, et al. Medical decision-making capacity in mild cognitive impairment: a 3-year longitudinal study. Neurology. 2008;71(19):1474–1480. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000334301.32358.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Starkstein SE, Jorge R, Mizrahi R, Robinson RG. A diagnostic formulation for anosognosia in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77(6):719–725. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2005.085373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gambina G, Bonazzi A, Valbusa V, et al. Awareness of cognitive deficits and clinical competence in mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: their relevance in clinical practice. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(3):385–390. doi: 10.1007/s10072-013-1523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Etchells E, Darzins P, Silberfeld M, et al. Assessment of patient capacity to consent to treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 1999;14(1):27–34. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1999.00277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Crum RM, Anthony JC, Bassett SS, Folstein MF. Population-based norms for the mini-mental state examination by age and educational level. JAMA. 1993;269(18):2386–2391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kim SYH, Karlawish JHT, Caine ED. Current state of research on decision-making competence of cognitively impaired elderly persons. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002;10(2):151–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pucci E, Belardinelli N, Borsetti G, Rodriguez D, Signorino M. Information and competency for consent to pharmacologic clinical trials in Alzheimer disease: an empirical analysis in patients and family caregivers. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2001;15(3):146–154. doi: 10.1097/00002093-200107000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Marson DC, Ingram KK, Cody HA, Harrell LE. Assessing the competency of patients with Alzheimer’s disease under different legal standards. A prototype instrument. Arch Neurol. 1995;52(10):949–954. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1995.00540340029010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Palmer BW, Dunn LB, Appelbaum PS, et al. Assessment of capacity to consent to research among older persons with schizophrenia, Alzheimer disease, or diabetes mellitus: comparison of a 3-item questionnaire with a comprehensive standardized capacity instrument. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(7):726–733. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.7.726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tam NT, Huy NT, Thoa LTB, et al. Participants’ understanding of informed consent in clinical trials over three decades: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ. 2015;93(3):186H–198H. doi: 10.2471/BLT.14.141390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Porteri C, Andreatta C, Anglani L, Pucci E, Frisoni GB. Understanding information on clinical trials by persons with Alzheimer’s dementia. A pilot study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2009;21(2):158–166. doi: 10.1007/BF03325224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Feinberg LF, Whitlatch CJ. Are persons with cognitive impairment able to state consistent choices? Gerontologist. 2001;41(3):374–382. doi: 10.1093/geront/41.3.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.NCHS – National Center for Health Statistics Centers for Disease Control and prevention. FastStats. Therapeutic drug use, United States. 2015. [Accessed July 27, 2017]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus15.pdf#079.
- 73.Galeotti F, Vanacore N, Gainotti S, et al. AdCare Study Group How legislation on decisional capacity can negatively affect the feasibility of clinical trials in patients with dementia. Drugs Aging. 2012;29(8):607–614. doi: 10.1007/BF03262277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Livingston G, Leavey G, Manela M, et al. Making decisions for people with dementia who lack capacity: qualitative study of family carers in UK. BMJ. 2010;341:c4184. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c4184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kraft SA, Cho MK, Constantine M, et al. A comparison of institutional review board professionals’ and patients’ views on consent for research on medical practices. Clin Trials Lond Engl. 2016;13(5):555–565. doi: 10.1177/1740774516648907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Roth LH, Lidz CW, Meisel A, et al. Competency to decide about treatment or research: an overview of some empirical data. Int J Law Psychiatry. 1982;5(1):29–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bean G, Nishisato S, Rector NA, Glancy G. The assessment of competence to make a treatment decision: an empirical approach. Can J Psychiatry Rev Can Psychiatr. 1996;41(2):85–92. doi: 10.1177/070674379604100205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Miller CK, O’Donnell DC, Searight HR, Barbarash RA. The Deaconess Informed Consent Comprehension Test: an assessment tool for clinical research subjects. Pharmacotherapy. 1996;16(5):872–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Wirshing DA, Wirshing WC, Marder SR, Liberman RP, Mintz J. Informed consent: assessment of comprehension. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(11):1508–1511. doi: 10.1176/ajp.155.11.1508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Carney MT, Neugroschl J, Morrison RS, Marin D, Siu AL. The development and piloting of a capacity assessment tool. J Clin Ethics. 2001;12(1):17–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Casarett DJ, Karlawish JHT, Hirschman KB. Identifying ambulatory cancer patients at risk of impaired capacity to consent to research. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2003;26(1):615–624. doi: 10.1016/s0885-3924(03)00221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Appelbaum PS, Grisso T, Frank E, O’Donnell S, Kupfer DJ. Competence of depressed patients for consent to research. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156(9):1380–1384. doi: 10.1176/ajp.156.9.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Carpenter WT, Gold JM, Lahti AC, et al. Decisional capacity for informed consent in schizophrenia research. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57(6):533–538. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.57.6.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kovnick JA, Appelbaum PS, Hoge SK, Leadbetter RA. Competence to consent to research among long-stay inpatients with chronic schizophrenia. Psychiatr Serv. 2003;54(9):1247–1252. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.54.9.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Joffe S, Cook EF, Cleary PD, Clark JW, Weeks JC. Quality of informed consent: a new measure of understanding among research subjects. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93(2):139–147. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Saks ER, Dunn LB, Marshall BJ, Nayak GV, Golshan S, Jeste DV. The California Scale of Appreciation: a new instrument to measure the appreciation component of capacity to consent to research. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002;10(2):166–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]