Abstract
Background
Orthostatic tremor (OT) was first described in 1977. It is characterized by rapid tremor of 13–18 Hz and can be recorded in the lower limbs and trunk muscles. OT remains difficult to treat, although some success has been reported with deep brain stimulation (DBS).
Case Report
We report a 68‐year‐old male with OT who did not improve significantly after bilateral thalamic stimulation.
Discussion
Although some patients were described who improved after DBS surgery, more information is needed about the effect of these treatment modalities on OT, ideally in the form of randomized trial data.
Keywords: DBS, orthostatic tremor
Introduction
Orthostatic tremor (OT) was first described by Pazzaglia et al. in 1977; they described three patients with lower body tremor during standing.1 Rapid movements of 13–18 Hz can be recorded in the lower limbs and trunk muscles and are unique to OT.2 Medical therapy may be helpful in patients with OT, but many don’t improve. OT remains difficult to treat, although some success has been reported with deep brain stimulation (DBS).3 The nature of case reports is a tendency to only publish successful interventions, leading to a bias that likely doesn’t reflect average outcomes. In this article we present a patient with OT with limited response to bilateral thalamic stimulation.
Case report
We report a 68‐year‐old male who presented with a 15‐year history of progressive unsteadiness when standing. The patient reported he could not stand for more than a few minutes, but his symptoms resolved by walking, sitting, and leaning. This had a major impact on his quality of life, as he was not able to stand in queues or do other activities that required standing.
Physical examination demonstrated visible bilateral leg tremor involving most muscle groups with a latency of approximately 14 seconds after standing. He was able to stand independently for a maximum of 3 minutes. No other abnormal movements were detected; there was no upper limb tremor and gait was normal.
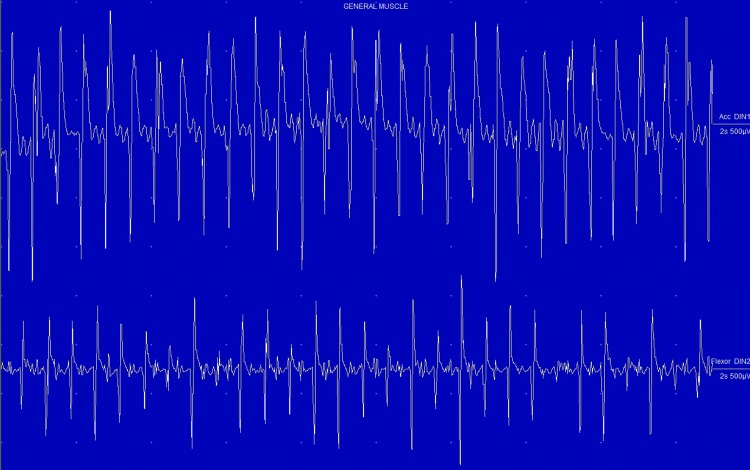
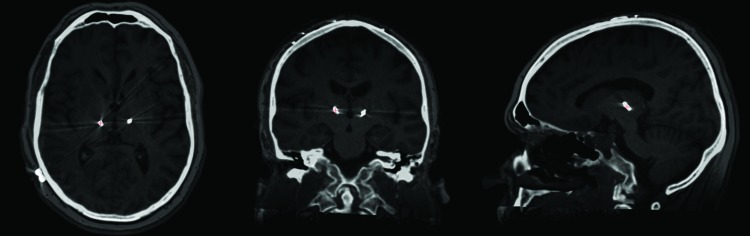
Surface electromyography (EMG) of the medial gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior muscles demonstrated 16 Hz regular alternating tremor bursts (Figure 1), which appeared immediately after standing (Video 1). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and cervical spine were unremarkable. Trials of pregabalin 150 mg twice a day, pramipexole 0.5 mg twice a day, and clonazepam 0.5 three times a day (the patient was unable to tolerate higher doses because of drowsiness) were ineffective. Stereotactic surgery was performed without sedation and bilateral DBS electrodes (model 6146, St. Jude Medical, Plano, TX, USA) were implanted targeting the ventral intermediate nucleus (Vim) thalamus. After preoperative planning (Waypoint Navigator Software, FHC, Bowdoin, ME, USA) the final target was determined with intraoperative microelectrode recording and test stimulation (looking for the occurrence of side effects such as paresthesia) at several positions. No intraoperative testing of the actual effect of DBS was performed due to the tremor not being present in the supine position. The electrodes were connected to an implantable pulse generator (Brio rechargeable IPG, model 6788, St. Jude Medical). Postoperative localization of the active electrodes (computed tomography–MRI fusion) showed the active electrode (contact 3 cathodal; contact 1 anodal) to be 12 mm lateral, 6 mm posterior, and 3.5 mm superior to the mid‐commissure point (MC) on the left and 12.6 mm lateral, 6 mm posterior, and 3.5 mm superior to the MC on the right (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Surface electromyography recording from left medial gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior when standing: regular alternating bursts of motor unit potentials at a rate of 15 Hz.
Figure 2. Merge of planning magnetic resonance imaging with postoperative high‐resolution brain computed tomography was done to confirm the ventral intermediate nucleus lead position.
Video 1. Regular sound immediately after standing (helicopter sign) and disappearing with sitting down is a unique feature of orthostatic tremor.
An interrogation of the DBS system was performed 2 weeks after surgery, mainly looking for a threshold until side effects occurred. This guided subsequent DBS programming. At 10 months after DBS implantation, his stimulator settings were as follows: amplitude 2.05 mA; pulse width, 75 µs; frequency, 130 Hz bilaterally. At this point, the tremor latency on standing had increased to 29 seconds, and the patient could remain standing for 5 minutes. However, this benefit was not clinically meaningful as the patient reported no improved ability to stand in queues or perform other standing activities.
Discussion
So far there have been eleven cases reported of DBS to the Vim for OT (Table 1). Surgery was effective in all but one case (who had undergone unilateral procedure).3
Table 1. Published cases of Vim DBS for OT.
| Author | Target | Outcome | Follow‐up in Months | Active Contact (a), Target (t), or Lead Tip Location (l) in Planes x, y, z | Stimulator Settings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Espay et al.4 | Vim bilateral | Improved standing time from 30 s to >3 min | >18 | L: –14.2, 7.2, 2.3 (a); R: 12.0, 4.9, 0.3 (a) | L: 0+2–, 4.0 V, 90 µs, 185 Hz; R: C+1–, 4.0 V, 60 µs, 185 Hz |
| Espay et al.4 | Vim unilateral (right) | Near resolution of symptoms for 3 months, then return to presurgical level of function | 18 | R: 13.5, 7.8, 1.7 (a) | R: 3+1–, 1.5 V, 90 µs, 160 Hz |
| Guridi et al.5 | Vim bilateral | “marked cessation of tremor” | 48 | L: –15, 4–5, 1 (t); R: 15, 4–5, 1 (t) | L: C+0–, 2.0 V, 60 µs, 130 Hz; R: C+4–, 2.0 V, 60 µs, 130 Hz |
| Magarinos‐Ascone et al.6 | Vim bilateral | “The patient could stand up normally without any help or leg tremor” | 12 | – | L: bipolar?, V, 90 µs, 185 Hz; R: bipolar?, V, 90 µs, 185 Hz |
| Yaltho et al.7 | Vim bilateral | Improved standing time from 30 s to >4 min | 6 | – | L: C+0–3–, 2.1 V, 90 µs, 135 Hz; R: C+0–1–3–, 2.6 V, 90 µs, 170 Hz |
| Lyons et al.8 | Vim bilateral | Improved standing time from 20 s to >7 min | 30 | 11.5 mm lateral to 3rd ventricle (t) | L: 6+4–5–, 2.2 V, 90 µs, 185 Hz; R: 1+0–, 2.7 V, 90 µs, 185 Hz |
| Contarino et al.9 | Vim bilateral | Initially marked symptomatic improvement, although benefit lessened to no “optimal clinical improvement” | 60 | L: –15.2, 7.2, 0.8 (l); R: 12.8, 8.3, 1.8 (l) | – |
| Hassan et al.2 | Vim bilateral | “improved standing ability and reduction of OT severity” | 36 | – | – |
| Hassan et al.2 | Vim bilateral | “improved standing ability and reduction of OT severity” | 36 | – | – |
| Coleman et al.3 | Vim bilateral | Improved standing time from 50 s to 15 min | 16 | L: –14.8, 8.6, 1.5 (a); R: 12.8, 7.9, 3.8 (a) | L: 1+2–, 3.0 V, 60 µs, 140 Hz; R: 9+10–, 2.6 V, 60 µs, 140 Hz |
| Coleman et al.3 | Vim bilateral | Improved standing time from <30 s to >4 min | 7 | L:–15.4, 9.7, 7.8 (a); R: 10.8, 5.4, –1.2 (a) | L: 2–3+, 1.9 V, 60 µs, 170 Hz; R: C+8–, 2.1 V, 60 µs, 170 Hz |
| Current case | Vim bilateral | Improved standing time from 3 min to 5 min | 12 | L: –12, 6, 3.5 (a) 10.5 mm lateral to 3rd ventricle (t); R: 12.6, 6, 3.5 (a) 11.5 mm lateral to 3rd ventricle (t) | L: –1+3, 2.05 mA, 75 µs, 130 Hz; R: –1+3, 2.05 mA, 75 µs, 130 Hz |
Abbrevitation: DBS, Deep Brain Stimulation; OT, Orthostatic Tremor; Vim, Ventral Intermediate Nucleus.
Recently, Merola et al.10 reported on long‐term follow‐up of a patient who had undergone Vim DBS surgery 8 years previously. Although there had been benefit with increased gait velocity and stride length, non‐optimized DBS settings led to gait imbalance.
Orthostatic tremor is a rare disorder and evidence for treatment is lacking. There is a paucity of outcome data especially regarding treatment with DBS. DBS or spinal cord stimulation11 could be possible therapies for refractory OT, but clearly more information is needed about the effect of these treatment modalities on OT, ideally in the form of randomized trial data.
Our patient showed improvement to his latency of tremor onset and standing time, but this was not enough to be clinically meaningful. Several factors could have played a role in this: one is lead placement; perhaps more lateral placement (aiming for proximity to the leg‐related part of Vim) could have yielded more of a benefit. Another factor is stimulation parameters. Although little is known about the optimal stimulation parameters in OT, for tremor control often high frequencies of 185 Hz are used. In our patient, this did not lead to an additional benefit. A further factor could be target choice: several units now use the posterior subthalamic area as a target for the treatment of proximal/axial tremors. While there are no comparative studies done to the Vim and to our knowledge there are no published case reports, this is a target of interest for the treatment of OT. Lastly, new DBS developments like directional leads could provide better outcomes because of improved tailoring of stimulation.
Functional connectivity changes in the Vim–motor cortex–cerebellum circuit are associated with the occurrence of essential tremor (ET) and stimulation of this target reduces ET.12 The same target is also presumed to be involved in the development of OT.4
There are several limitations of this report. One is that only a preoperative EMG was performed without a follow‐up study. Also, we did not use intraoperative EMG to guide lead position (as done by Lyons et al.8). Another limitation is the relatively short period of follow‐up.
Footnotes
Funding: None.
Financial Disclosures: None.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethics Statement: All patients that appear on video have provided written informed consent; authorization for the videotaping and for publication of the videotape was provided.
References
- 1.Pazzaglia P, Sabattini L, Lugaresi E. [On an unusual disorder of erect standing position (observation of 3 cases)] Riv Sper Freniatr Med Leg Alien Ment. 1970;94:450–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hassan A, Ahlskog JE, Matsumoto JY. Orthostatic tremor: clinical, electrophysiologic, and treatment findings in 184 patients. Neurology. 2016;86:458–464. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002328. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Coleman RR, Starr PA, Katz M. Intermediate nucleus thalamic deep brain stimulation in orthostatictremor. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2016;94:69–74. doi: 10.1159/000444127. doi: 10.1159/000444127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Espay AJ, Duker AP, Chen R, Okun MS, Barrett ET, Devoto J, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral intermediate nucleus of the thalamus in medically refractory orthostatic tremor: preliminary observations. Mov Disord. 2008;23:2357–2362. doi: 10.1002/mds.22271. doi: 10.1002/mds.22271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Guridi J, Rodriguez‐Oroz MC, Arbizu J, Alegre M, Prieto E, Landecho I, et al. Successful thalamic deep brain stimulation for orthostatic tremor. Mov Disord. 2008;23:1808–1811. doi: 10.1002/mds.22001. doi: 10.1002/mds.22001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Magariños‐Ascone C, Ruiz FM, Millán AS, Montes E, Regidor I, del Alamo de Pedro M, et al. Electrophysiological evaluation of thalamic DBS for orthostatic tremor. Mov Disord. 2010;25:2476–2477. doi: 10.1002/mds.23333. doi: 10.1002/mds.23333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yaltho TC, Ondo WG. Thalamic deep brain stimulation for orthostatic tremor. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov. 2011:1. doi: 10.7916/D8NZ86C1. doi: 10.7916/D8NZ86C1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lyons MK, Behbahani M, Boucher OK, Caviness JN, Evidente VG. Orthostatic tremor responds to bilateral thalamic deep brain stimulation. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov. 2012:2. doi: 10.7916/D8TQ608K. doi: 10.7916/D8TQ608K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Contarino MF, Bour LJ, Schuurman PR, Blok ER, Odekerken VJ, van den Munckhof P, et al. Thalamic deep brain stimulation for orthostatic tremor: clinical and neurophysiological correlates. Parkinsonism. Relat Disord. 2015;21:1005–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.06.008. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Merola A, Duker AP, Mandybur G. Thalamic deep brain stimulation and gait in orthostatic tremor. Mov Disord. 2017;32:937–938. doi: 10.1002/mds.26958. doi: 10.1002/mds.26958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Blahak C, Sauer T, Baezner H. Long-term follow-up of chronic spinal cord stimulation for medically intractable orthostatic tremor. J Neurol. 2016;263:2224–2228. doi: 10.1007/s00415-016-8239-4. doi: 10.1007/s00415‐016‐8239‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fang W, Chen H, Wang H. Essential tremor is associated with disruption of functional connectivity in the ventral intermediate nucleus—motor cortex—cerebellum circuit. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016;37:165–7. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23024. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]