Abstract
Copy-number changes in 16p11.2 contribute significantly to neuropsychiatric traits. Besides the 600 kb BP4-BP5 CNV found in 0.5%–1% of individuals with autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia and whose rearrangement causes reciprocal defects in head size and body weight, a second distal 220 kb BP2-BP3 CNV is likewise a potent driver of neuropsychiatric, anatomical, and metabolic pathologies. These two CNVs are engaged in complex reciprocal chromatin looping, intimating a functional relationship between genes in these regions that might be relevant to pathomechanism. We assessed the drivers of the distal 16p11.2 duplication by overexpressing each of the nine encompassed genes in zebrafish. Only overexpression of LAT induced a reduction of brain proliferating cells and concomitant microcephaly. Consistently, suppression of the zebrafish ortholog induced an increase of proliferation and macrocephaly. These phenotypes were not unique to zebrafish; Lat knockout mice show brain volumetric changes. Consistent with the hypothesis that LAT dosage is relevant to the CNV pathology, we observed similar effects upon overexpression of CD247 and ZAP70, encoding members of the LAT signalosome. We also evaluated whether LAT was interacting with KCTD13, MVP, and MAPK3, major driver and modifiers of the proximal 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 syndromes, respectively. Co-injected embryos exhibited an increased microcephaly, suggesting the presence of genetic interaction. Correspondingly, carriers of 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 rearrangements that encompass both the BP2-BP3 and BP4-BP5 loci showed more severe phenotypes. Taken together, our results suggest that LAT, besides its well-recognized function in T cell development, is a major contributor of the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 CNV-associated neurodevelopmental phenotypes.
Keywords: 16p11.2, autism, head size, zebrafish, obesity, genome architecture, epistasis
Introduction
The 16p11.2 chromosomal band experienced a rapid expansion of segmental duplications in hominoids and doubled independently in length in chimpanzees and humans.1 This pattern likely arose through selection and placed the whole region at risk for recurrent rearrangements through non-allelic homologous recombination.2 Deletions (MIM: 611913) and duplications (MIM: 614671) of the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 region are among the most frequent causes of neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders.2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 They are associated with Rolandic epilepsy8 and mirror phenotypes on body mass index (BMI), head circumference (HC), and brain volume.9, 10, 11, 12 The deletion of the distal 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 locus (MIM: 613444) is likewise enriched in individuals with early-onset obesity and is also associated with developmental delay, intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders (ASD), and schizophrenia.3, 13, 14, 15, 16 Moreover, the BP2-BP3 deletion and reciprocal duplication have mirror effects on BMI and HC, whereas the duplication of this interval, like the deletion, is associated with ASD.17 Thus, genomic rearrangements at both the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 and the 220 kb BP2-BP3, two loci 650 kb apart, present similar clinical patterns: large effect sizes on BMI and HC, as well as association with ASD and other neuropsychiatric traits.
A major challenge in the interpretation of CNVs encompassing several genes is the identification of the locus (loci) whose dosage sensitivity drives (drive) the phenotype.18 The zebrafish embryo has emerged as a powerful in vivo model to test dosage sensitivity in neurodevelopmental traits, likely due to the high evolutionary conservation of key genes and pathways between humans and this organism.19 Macrocephaly during infancy is a recurrent observation in ASD, while HC defects in general are common features of neurodevelopmental disorders.20, 21 For these phenotypes, the measurement of the head size of zebrafish embryos has served as a relevant and useful proxy to identify genes whose dosage imbalance contributes to the neuropathology. We used this approach to demonstrate that the major driver of the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 CNV head phenotype was KCTD13 (MIM: 608947), in epistasis with MVP (MIM: 605088) and MAPK3 (MIM: 601795),18, 22 while similar studies helped understand the genetic architecture of other CNVs.23, 24
Here, we have applied in vivo modeling tools to dissect genes that drive neuroanatomical defects associated with the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 CNV. This interval contains nine single-copy genes: ATXN2L (MIM: 607931), TUFM (MIM: 602389), SH2B1 (MIM: 608937), ATP2A1 (MIM: 108730), RABEP2 (MIM: 611869), CD19 (MIM: 107265), NFATC2IP (MIM: 614525), SPNS1 (MIM: 612583), and LAT (MIM: 602354). Among those, SH2B1 encodes a Src homology adaptor protein involved in leptin and insulin signaling.25, 26 Common variants near this locus are associated with BMI, serum leptin, and body fat in genome-wide association studies (GWASs),27, 28, 29, 30 while rare dominant mutations have been reported to cause obesity, social isolation, aggressive behavior, and speech and language delay.31 None of the CNV-contained genes have been associated with ASD or HC defects. As such, we considered an agnostic approach wherein we tested whether dosage perturbation in each locus, followed by genetic interaction and pathway analyses, could contribute to these phenotypes.
Material and Methods
Recruitment and Phenotyping of Individuals with 16p11.2 BP1-BP5 Rearrangements
The institutional review board of the University of Lausanne, Switzerland, approved this study. Participants were enrolled after informed consent and clinical assessment. For the data collected through questionnaires, the physicians who had ordered clinical chromosomal microarray analyses gathered information retrospectively and anonymously. Consequently, research-based informed consent was not required by the institutional review board of the University of Lausanne, which granted an exemption for this part of the data collection.
Individuals carrying 16p11.2 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 rearrangements2 were identified through routine etiological work-ups of individuals ascertained for neurodevelopmental disorders in cytogenetic centers. The coordinates of the rearrangements’ breakpoints were identified by different chromosomal microarray platforms and analyses were carried out as described9 (Table S1). We compared BMI and HC to gender-, age-, and geographical location-matched reference population as described.9 The mean age of measurement of the 16p11.2 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 individuals was 12.7 years (range 2.7–27 years, with four case subjects older than 18 years). Anthropometric measures were compared to those published for the BP2-BP317 (n = 88 and 49 unrelated deletion and duplication carriers, respectively; n = 57 females in total; age range: 0.4–78 years) and BP4-BP56 CNVs (n = 317 and 180 unrelated deletion and duplication carriers, respectively; n = 206 females in total; age range: 0.2–90 years).
In Vivo Analysis of Gene Expression and Zebrafish Embryo Manipulations
For overexpression experiments, the human wild-type mRNAs (CD19 [GenBank: NM_001178098], NFATC2IP [GenBank: NM_032815], ATXN2L [GenBank: NM_007245], TUFM [GenBank: NM_003321], ATP2A1 [GenBank: NM_004320], RABEP2 [GenBank: NM_024816], SPNS1 [GenBank: NM_032038], LAT [GenBank: NM_001014987], SH2B1 [GenBank: NM_001145795], CD247 [MIM: 186780] isoform1 [GenBank: NM_198053] and isoform2 [GenBank: NM_000734], and ZAP70 [MIM: 176947] isoform1 [GenBank: NM_001079] and isoform2 [GenBank: NM_207519]) were cloned into the pCS2 vector and transcribed using the SP6 Message Machine kit (Ambion). We injected 1 nL of diluted RNA (50, 100, or 150 ng) or diluted guide RNA (150 pg, with or without Cas9 protein, see Zebrafish Model Engineering) into wild-type zebrafish embryos at the 1- to 2-cell stage for RNAs and 1-cell stage for the CRISPR, respectively. Injected embryos were fixed at 2 to 3 dpf to perform immunostaining (see Zebrafish Whole-Mount Immunostaining) or scored at 4.5 dpf for the head size. The proxies that were used are the measurement of the distance between the eyes and the head size (distance from the anterior-most part of the forebrain until the hindbrain) on a dorsal view and brain area (from the fish mouth to the anterior part of the trunk at the first somite) on a lateral view. All the experiments were repeated three times and a t test was performed to determine the significance of the morphant phenotype.
Zebrafish Model Engineering
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) RNA guide (gRNA) was designed with ChopChop online tool. The guide RNA targets exon 2 of Danio rerio lat: 5′-GTCCCCAGCAATATGTACAA-3′. The oligo was cloned into the pT7 vector and guide RNAs was synthesized using the Mega transcript kit (Thermofisher) and purified as described.33 To assess CRISPR efficiency, the targeted region was amplified by specific primers from total DNA as described33 from 2 dpf F0 injected zebrafish embryos (F: 5′-TGCGAAATTATCCAATGCAG-3′; R: 5′-CATTTTAAATTGAGCTCACACTCTTT-3′). PCR products were denaturated and re-annealed as follows: 95°C for 2 min, cooling progressively to 85°C (−2°C per second) and then 25°C (−0.1°C per second to 25°C) and finally 16°C. The PCR products were run on Criterion precast PAGE gels (Bio-Rad) to visualize homo- and heteroduplexes, indicative of small indels. To estimate the fraction of CRISPR mosaicism, one control and six injected embryos were picked to be Sanger sequenced. From the PCR step above, DNA was purified by gel extraction (QIAquick gel extraction kit) and the fragments were cloned into TOPO4 vector (Invitrogen). Plasmid DNA was extracted from ten bacterial clones per embryo and the inserts were Sanger sequenced with M13 primers. Mosaicism percentage was determined as the number of sequences carrying an indel at the targeted guide locus sequence over the total number of sequences read.
Zebrafish Whole-Mount Immunostaining
Animal maintenance and experiments were approved by the Animal Experimentation Committee of the Institutional Review Board of both the IGBMC and Duke University. Zebrafish embryos (AB strain) were raised at 28°C and were fixed in 4% PFA overnight and stored in 100% methanol at −20°C. For acetylated tubulin staining, embryos were fixed in Dent’s fixative (80% methanol, 20% dimethylsulphoxide [DMSO]) overnight at 4°C. The embryos were permeabilized with proteinase K, then postfixed with 4% PFA and washed in PBSTX (PBS+0.5%, Triton X-100). After rehydration in PBS, PFA-fixed embryos were washed in IF buffer (0.1% Tween-20, 1% BSA in PBS 1×) for 10 min at room temperature. The embryos were incubated in the blocking buffer (10% FBS, 1% BSA in PBS 1×) for 1 hr at room temperature. After two washes in IF Buffer for 10 min each, embryos were incubated in the first antibody solution, 1:750 anti-histone H3 (ser10)-R, (sc-8656-R, Santa Cruz), 1:1,000 anti-HuC/D (A21271, Invitrogen), 1:1,000 anti-acetylated tubulin (T7451, Sigma-Aldrich), in blocking solution, overnight at 4°C. After two washes in IF Buffer for 10 min each, embryos were incubated in the secondary antibody solution, 1:1,000 Alexa Fluor donkey anti-rabbit IgG and Alexa Fluor goat anti-mouse IgG (A21207, A11001, Invitrogen), in blocking solution, for 1 hr at room temperature. For the anti-H3 protocol, staining levels were analyzed by counting positive cells in defined regions of the head using the ImageJ software.
Mouse Studies
Neuroanatomical studies were performed on three 15-week-old control male mice in C57BL/6J background and three 17-week-old homozygous knock-out of Lat.34 Mouse brain samples were perfused and post fixed in 4% PFA for 48 hr. Sixty-three brain parameters (area and length measurements) were measured blind to the genotype across two coronal sections (Bregma 0.98 mm and −1.34 mm) as described35 and data were analyzed using a Student two-tailed equal variance test. Using in-house ImageJ plugins, we quantified a series of cellular parameters including cell count, cell density, total and average cell area, and ratio of the parameter area over the cell area, in 15 regions combining white and gray matter structures (cingulate cortex, genu and soma of the corpus callosum, caudate putamen, anterior commissure, primary motor cortex, secondary somatosensory cortex, retrosplenial granular cortex, dorsal hippocampal commissure, amygdaloid nucleus, mammillothalamic tract, piriform cortex, internal capsule, fimbria of the hippocampus, habenula, and hypothalamus). This resulted in an additional set of 75 cellular parameters.
Results
16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 Orthologous Genes
We first assessed whether the nine genes encompassed within the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 region, i.e., CD19, NFATC2IP, ATXN2L, TUFM, ATP2A1, RABEP2, SPNS1, LAT, and SH2B1, had orthologous genes in the zebrafish genome by performing reciprocal BLAST (basic local alignment search tool). Seven genes (NFATC2IP, ATXN2L, TUFM, SH2B1, ATP2A1, RABEP2, and SPNS1) have Ensembl-annotated orthologs in zebrafish, all mapping in a syntenic locus on Danio rerio chromosome 3 (DRE3) in single copy (tufm, sh2b1, axn2l, spns1, rabep2), with the exception of atp2a1, which has a paralog, atp2a1l (89% identity) on DRE12. No ortholog could be identified for CD19, whereas a sequence similar to LAT (27% identical and 35% similar at the amino acid level) was found on DRE3 between the genes atxn2l and spns1 by low-stringency BLAST search. LAT orthologs could be identified in mammals, amphibians, reptiles, and fish but not in birds (Figure S1B), with strong conservation of the key residues, i.e., Cys26 and 29 that are critical for its localization in lipid rafts36 and the phosphorylated residues Tyr161, 200, and 220 (numbering according to the human protein; Figure S1A).
In Vivo Testing of 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 Genes
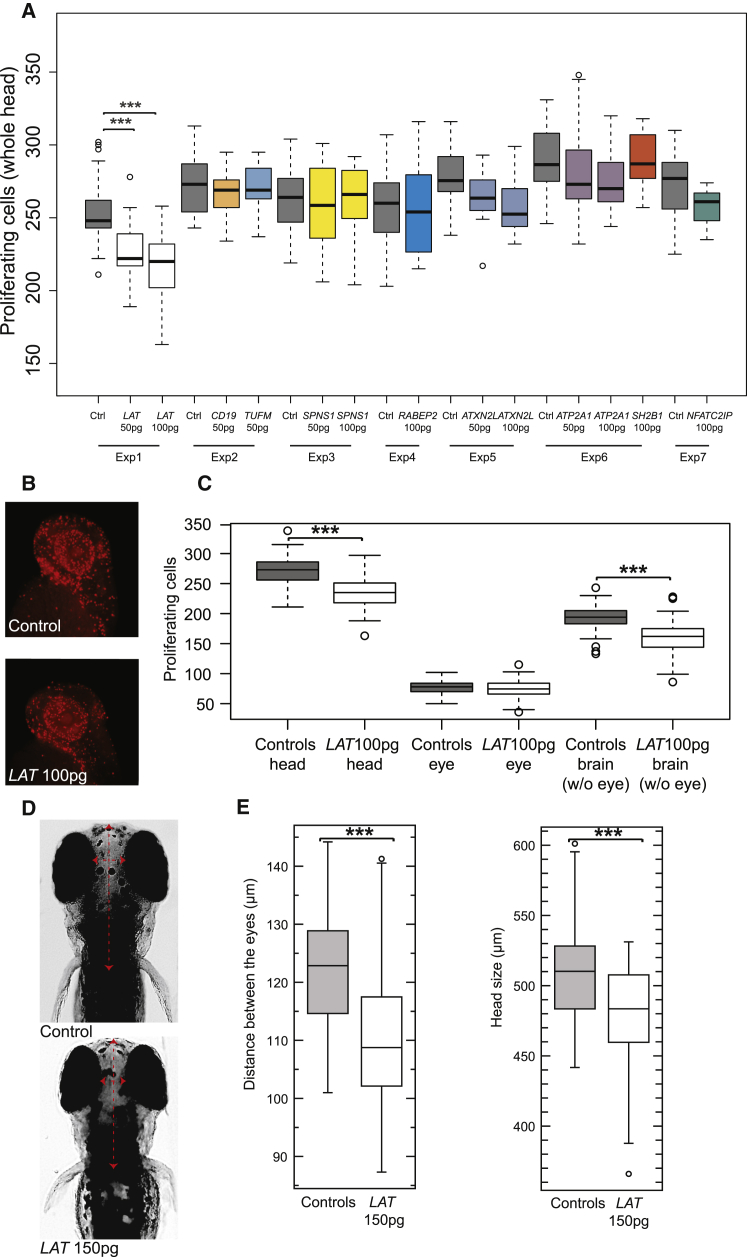
Similar to our previous studies,24, 37 we generated capped messenger RNA for the nine human genes encompassed within the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 interval and we modeled the duplication by expressing each individual human transcript in zebrafish embryos. To achieve expression above the baseline of any single transcript, we typically used an injection amount, corresponding to 0.25%–0.5% of the total poly(A) mRNA found in a zebrafish embryo.38 Previous studies confirmed the persistence of the injected human mRNAs in zebrafish up to 4.5 dpf.37 To test the effect of the expression of each transcript, we injected separately 50 or 100 pg of RNA encoding each of the nine candidate genes into the zebrafish yolk at the single- or two-cell stage. We did not observe toxicity, lethality, or gross morphological defects upon injection, except for CD19 and TUFM, for which the maximum dosage that could be tested was 50 pg. Next, we determined the level of cell proliferation in the zebrafish head at 2 dpf by immunostaining with an anti-phospho-histone H3 antibody, a M-phase marker (Figure 1A). Injection of LAT mRNA resulted in a significant decrease in the number of proliferating head cells at 2 dpf (average reduction across three replicates: −12.9%; two-tailed t test p = 2.6 × 10−17); in contrast, the proliferating cells count of the embryos injected with the eight other transcripts was not significantly different from that of control embryos (Figure 1A). Furthermore, the observed effect was dosage dependent; increasing amounts of LAT mRNA (50 to 100 pg) resulted in a stronger reduction of cell proliferation (Figure 1A). This decrease was specific to the brain (two-tailed t test p = 5.03 × 10−16) as no changes in cell counts were detected in the eye (p = 0.12) (Figures 1B and 1C). This phenotype is often associated with microcephaly in both zebrafish and humans.37, 39, 40 To assess this possibility directly, we measured the head size at 4.5 dpf in control and LAT mRNA-injected embryos. Increasing amounts of LAT mRNA injected into zebrafish embryos (100 and 150 pg) yielded a significant reduction of the head size, measured both as distance between the eyes and the anterior-most part of the forebrain until the hindbrain of the fish (two-tailed t test p = 2.96 × 10−8, and p = 3.14 × 10−5, respectively; LAT-150 pg RNA-injected embryos compared to controls) (Figures 1D and 1E).
Figure 1.
LAT Overexpression Is Associated with a Decrease of Cell Proliferation in the Brain
(A) Boxplots of the number of proliferating phospho-histone H3-stained brain cells upon injection of human mRNA of CD19, NFATC2IP, ATXN2L, TUFM, ATP2A1, RABEP2, SPNS1, LAT, and SH2B1, the nine genes mapping within the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 interval, in 2 dpf zebrafish embryos. Each gene was assessed in different experiments (exp) and whenever possible using both 50 and 100 pg of mRNA (Material and Methods). All quantifications are performed with ImageJ software. Average n = 20 for each subgroup.
(B) Representative examples of uninjected and LAT-injected zebrafish embryos stained with anti-phospho-histone H3 for assessment of proliferation.
(C) Boxplots of the number of phospho-histone H3-stained cells in the whole brain (left), the eye (center), and the brain excluding the eye (right) upon injection of 100 pg of human LAT in 2 dpf zebrafish embryos. Average n = 80 for each subgroup.
(D and E) Boxplots (E) of the distance between the eye (left) and head size (i.e., anterior-most part of the forebrain until the hindbrain of the fish, right) upon injection of 150 pg of human LAT in 4.5 dpf zebrafish embryos. Representative examples of uninjected and LAT-injected animals are presented in (D). Average n = 60 per injection.
Significance was calculated by two-tailed t test comparisons between control and mRNA-injected embryos (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).
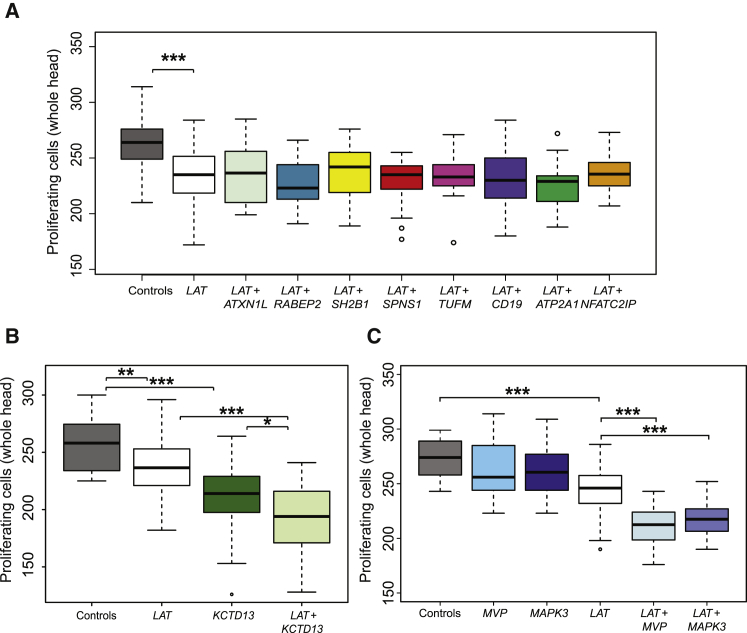
Higher LAT expression leads to smaller head size, mimicking the HC phenotype found in carriers of the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 duplication. However, as shown for other CNVs, it is unlikely that a single transcript is sufficient to drive the CNV-driven pathology.18, 24, 37 Therefore, we asked whether other genes within the CNV might contribute through additive or multiplicative interactions with LAT. We thus re-injected LAT with each of the other eight transcripts and we determined the number of proliferating cells in the brain at 2 dpf. We did not observe any significant change in the expressivity (percentile changes in mean count of stained cells) of the phenotype driven by LAT injection alone (Figure 2A), suggesting that LAT is the sole driver of the HC phenotype in the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 CNV and that none of the other genes from this interval act as modifier for the head size phenotype, at least as determined by this assay.
Figure 2.
LAT Genetically Interacts with KCTD13, MVP, and MAPK3
(A) Boxplots of the number of proliferating phospho-histone H3-stained brain cells upon pairwise injections of 100 pg LAT mRNA and 100 pg of the eight other mRNAs encoded by the 16p11.2 BP2-BP3 genes. Co-injections of CD19, NFATC2IP, ATXN2L, TUFM, ATP2A1, RABEP2, SPNS1, and SH2B1 have no effect on LAT overexpression’s induced phenotype.
(B and C) Boxplots of the number of proliferating phospho-histone H3-stained cells in the brain upon pairwise injections of 100 pg LAT mRNA and 100 pg of KCTD13, MVP, and MAPK3, the major driver and modifiers of the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 syndromes, respectively. Additive and epistatic effects are observed in the LAT/KCTD13 (B), LAT/MAPK3, and LAT/MVP cocktails (C), respectively.
Average n = 40 for each subgroup. Significance was calculated by two-tailed t test comparisons between control and mRNA-injected embryos (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).
LAT Perturbation and Neuroanatomy
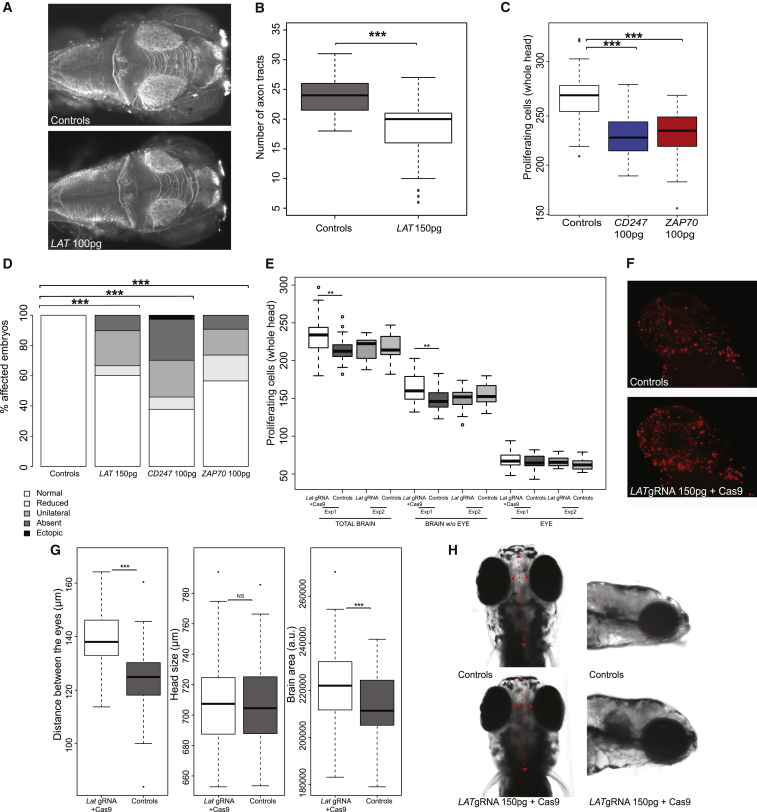
We further characterized the neuroanatomical phenotypes induced by the overexpression of LAT by looking at possible defects in neuron morphology and/or neurogenesis. Acetylated tubulin staining on 3 dpf embryos injected with 150 pg of LAT mRNA revealed a significant reduction in the number of axon tracts projecting from the optic tecta compared to controls (two-tailed t test p = 4.4 × 10−14) (Figures 3A and 3B). We hypothesized that the observed phenotypes could be driven also by changes in the number of neuronal progenitor cells in the developing brain. To test this possibility, we examined the spatial localization of HuC/D proteins (a marker for post-mitotic neurons) in the injected embryos and controls. As shown in Figure 3D, significant differences were observed in the forebrain, showing an over-representation of unilateral, reduced, and absent HuC/D protein levels in the embryos injected with 150 pg LAT compared to control ones (Fisher’s exact test p = 1.3 × 10−14). These results suggest that LAT likely causes the onset of microcephaly by affecting early neurogenesis and cell projection’s organization in the zebrafish brain.
Figure 3.
The Overexpression of LAT and Its Signalosome Partners CD247 and ZAP70 Affects Neuron Morphology and Maturation whereas Its Suppression Is Associated with Increase in Brain Cell Numbers and Size
(A) Dorsal views of control and LAT mRNA-injected embryos at 3 dpf stained with anti-acetylated tubulin (AcTub).
(B) Boxplots of inter-tecta axonal tracts’ count after acetylated Tubulin staining of 3 dpf control embryos and embryos injected with 150 pg of LAT. Average n = 80 for each subgroup.
(C) Boxplots of phospho-histone H3 staining quantification of proliferating cells in the zebrafish brain of 2 dpf control embryos, and embryos injected with CD247 isoform1 and ZAP70 isoform1. Average n = 60 for each group.
(D) Percentage of 2 dpf embryos with normal bilateral HuC/D protein levels (white) or unilateral HuC/D (gray), ectopic (black), and absent (dark gray)/reduced protein levels (light gray) in the anterior forebrain in embryo batches injected with LAT 150 pg, CD247 100 pg, and ZAP70 100 pg mRNAs. HuC/D levels in the anterior forebrain of the embryo injected with all three mRNAs are considerably decreased compared to those of the control embryo.
Significance was estimated by two-tailed t test comparisons between control and mRNA-injected embryos (B and C); enrichment of “abnormal” pattern of HuC/D staining in the injected embryos versus controls was calculated by Fisher’s exact test (D) (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).
(E and F) Boxplots (E) of the number of phospho-histone H3-stained cells in the whole brain (left), the eye (center), and the brain excluding the eye upon injection of 150 pg of lat guide RNA and Cas9 protein, lat guide RNA only and uninjected controls in 2 dpf zebrafish embryos (assessed in different experiments with respective uninjected controls). Representative examples of uninjected and lat guide RNA and Cas9-injected animals phospho-histone H3-stained for proliferation are presented in (F). Average n = 60 for each subgroup.
(G and H) Boxplots (G) of the distance between the eyes (left), head size (i.e., anterior-most part of the forebrain until the hindbrain of the fish, middle part), and head area (measured on lateral view from the fish’s mouth until the anterior part of the trunk, right) upon injection of 150 pg of lat guide RNA and Cas9 in 4.5 dpf zebrafish embryos compared to uninjected controls. Representative images of uninjected CRISPR animals in dorsal and lateral views are presented in (H), respectively. Average n = 80 per subgroup.
Significance was calculated by two-tailed t test comparisons between control and CRISPR embryos (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).
As LAT encodes a protein belonging to the T cell receptor’s signaling module, it suggests a critical role of immune molecules in the developing brain. In line with this, a previously uncharacterized role in regulating early neuronal morphogenesis was assigned to CD247 (a.k.a. CD3ζ) and ZAP70.41, 42, 43, 44 Both genes encode proteins belonging to the T cells receptor’s signaling module similar to LAT. We observed that the overexpression of the CD247 and ZAP70 in zebrafish embryos recapitulates the phenotype observed upon LAT overexpression, i.e., the decreased cell proliferation in the brain compared to control embryos (Figure 3C). Of note, the neuronal defect is driven by ZAP70 isoform 1 but not isoform 2, that differs from the canonical one, at the protein level, for missing amino acids 1–307, whereas both CD247 isoforms produce a significant decrease in phospho-H3-stained cells (Material and Methods and Figure S2). According to the GTEx portal, both pairs of isoforms display similar expression profiles. HuC/D level assessment in the forebrain of embryos injected with CD247 isoform 1 and ZAP70 isoform 1 reproduced the same reduction observed upon injection of LAT. We found an increased severity of the phenotype induced by CD247 overexpression compared to the other two transcripts, both in the HuC/D and phospho-H3-staining experiments (Figures 3C and 3D). Taken together, these data on LAT functional partners confirmed that perturbation of the signaling pathway mediated by LAT is necessary for the proliferation and differentiation of neurons in the developing brain. The manipulation of the expression of the genes encoding the three complex partners LAT, ZAP70, and CD247 in zebrafish confirms the function of this immune T cell complex in neurogenesis, a function that was hitherto unknown.
To assess further a possible role of LAT in neurogenesis and in the phenotypes exhibited by carriers of 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 rearrangements, we determined the expression pattern of lat, the zebrafish ortholog of LAT, and we engineered a CRISPR lat mutant in zebrafish. In situ hybridization with an antisense probe showed that lat is expressed strongly in the developing brain (Figure S3), in particular in mid- and hindbrain of 4 and 5 dpf embryos (Figure S3). We engineered microdeletions in lat exon 2 using CRISPR/Cas9 and validated the presence of genetic editing in 44% of injected embryos (founders, F0) by PAGE and Sanger sequencing (Figure S4). Injections of in vitro-transcribed guide RNA and purified Cas9 protein into 1-cell stage embryos, performed in duplicate by two investigators, followed by phenotyping at 2 dpf after phospho-H3 immunostaining, showed an increase in the total proliferation in the brain of the F0 zebrafish larvae injected with a cocktail of 150 pg LAT guide RNA and 150 pg Cas9 protein (average increase of +8.6% compared to uninjected embryos [two-sided t test, whole brain, p = 0.005, eye, p = 0.3; brain without the eye, p = 0.003] and compared to gRNA alone [whole brain, p = 0.007, eye, p = 0.4; brain without the eye, p = 0.004]) (Figures 3E and 3F). In addition, we saw increased total brain volume in the F0 larvae through an increase of the objective measurement of interorbital distance (two-sided t test, p = 1.5 × 10−15) and total brain area (two-sided t test, p = 0.0003), but not of the brain length from forebrain to hindbrain in CRISPR/Cas9-injected larvae compared to controls (Figures 3G and 3H).
As a further test of the specificity of the phenotypes induced by the LAT candidate and the neuroanatomical changes observed in teleosts, we studied the neuroanatomy of the established Lat knockout mouse,34 a model generated originally to study the well-known role of Lat in immunity34 but for which, to our knowledge, its role during the brain development was never assessed.
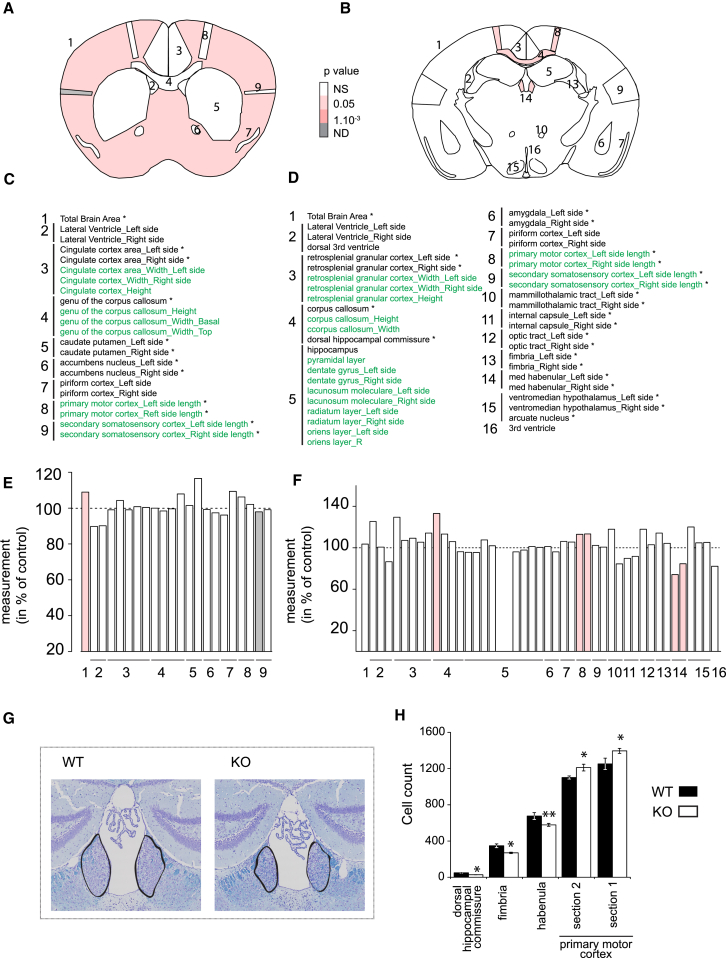
Given the volumetric changes in the zebrafish transient and stable models, we compared 63 brain histological parameters that define 16 unique brain regions between Lat−/− and control mice (Figures 4A and 4B). Consistent with our teleost findings, Lat deficiency is associated with enlargement of total brain area (+9%; p = 0.039), corpus callosum (+33%; p = 0.024), and cortex (+13%; p = 0.012) (Figures 4C–4F). In further agreement with our zebrafish results, the cell count in the cortex was increased in both sections (Bregma 0.98 mm: +11%, p = 0.04; −1.34 mm: +13%, p = 0.045) (Figures 4E and 4F). By contrast, cell size, content, and density of the habenula were decreased (−26, −23% [p < 0.01] and 9% [p = 0.006], respectively) (Figures 4G and 4H). Strikingly, both dorsal hippocampal commissure and fimbria of the hippocampus, two white-matter rich structures, were linked to major reduction of cell count (44% reduction; p = 0.008 and 15%; p = 0.03, respectively), accounting in full for reduced cell density (40.8%; p = 0.04 and 23%; p = 0.006, respectively) (Figure 4H).
Figure 4.
Lat Knockout Mice Present Morphological and Cellular Neuroanatomical Defects
(A and B) Schematic representation of brain regions modified in Lat−/− animal models plotted in coronal planes according to p values at Bregma 0.98 mm (A) and −1.34 mm (B).
(C and D) Catalog of the 63 assessed brain measured in Bregma 0.98 mm (C) and −1.34 mm (D): 1, total brain area; 2, lateral ventricles; 3, cingulate cortex (Bregma 0.98 mm) and retrosplenial cortex (−1.34 mm); 4, corpus callosum; 5, caudate putamen (0.98 mm) and hippocampus (−1.34 mm); 6 = anterior commissure (0.98 mm) and amygdala (−1.34 mm); 7, piriform cortex; 8, motor cortex; 9, somatosensory cortex; 10, mammilothalamic tract; 11, internal capsule; 12, optic tract; 13, fimbria of the hippocampus; 14, habenula; 15, ventromedial hypothalamus; and 16, third ventricle. Green refers to length and black to area measurements.
(E and F) Histograms showing the percentage increase or decrease of measured brain regions in Lat−/− mice as compared to the controls (100%) at Bregma 0.98 mm (E) and −1.34 mm (F). White coloring indicates a p value higher than 0.05 and gray to case subjects where the p value could not be computed due to missing data.
(G) Representative coronal brain images of wild-type (left) and Lat−/− mice (right), stained with Luxol and Nissl, showing a significantly smaller area of habenula in knockouts when compared to matched wild-type.
(H) Areas in which cell counts were significantly affected. Bar graph shows total cell counts for WT (dark bars) and Lat−/− animals (open bars). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005.
Genetic Interaction of the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 and 600 kb BP4-BP5 Genes
Less than 1 Mb apart and proximal to the 220 kb locus, the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 CNVs exhibit phenotypes similar to those found in the distal 220 kb BP2-BP3 CNV carriers, i.e., mirror effect on BMI and head size, and association with ASD and schizophrenia.2, 3, 4, 5, 9, 10 The two CNVs have also been shown to interact at the chromatin level, by 4C, FISH, Hi-C, and concomitant expression changes.17, 45 To investigate whether the two regions are also conducive to genetic interactions, we co-injected LAT, the driver of the HC phenotype of the BP2-BP3 CNVs, with mRNAs encoding KCTD13, the driver of the HC phenotype of the BP4-BP5 CNVs, and MAPK3 or MVP, modifiers of the same BP4-BP5 HC phenotype, and we evaluated the number of proliferating cells. Single injections of LAT and KCTD13 led to a decreased number of proliferating cells in the brain ranging from 10% to 18%, respectively. When combined, the severity of the phenotype increased to 25% when LAT was co-injected with KCTD13, 20% with MAPK3, and 22% with MVP (Figures 2B and 2C). Of note, the two modifiers of the BP4-BP5 CNV, MAPK3 and MVP, do not drive any significant reduction in cell proliferation when overexpressed alone, as shown previously37 and reassessed in this study (Figure 2C).
16p11.2 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 Phenotype
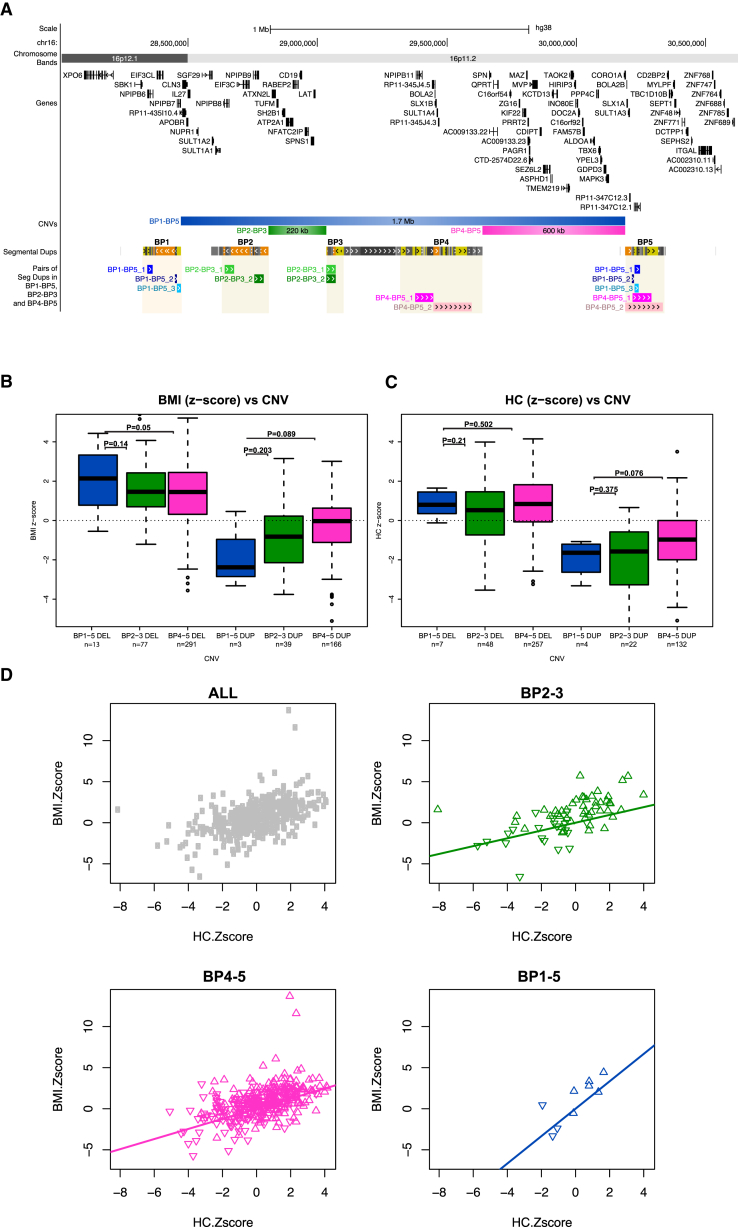
The genetic interactions between LAT, KCTD13, MAPK3, and MVP suggest that rearrangements that encompass both the BP2-BP3 and BP4-BP5 CNVs, i.e., from BP2 to BP5, would produce a more detrimental effect on growth. We are not aware of any individuals with rearrangements spanning the 1.6 Mb BP2-BP5 interval, possibly because of limited directly oriented repeat sequences that could promote non-allelic homologous recombination between these low-copy repeat regions (Figure 5A). As such, to test the severity hypothesis, we assessed the phenotypic features associated with the slightly larger 16p11.2 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 CNVs that encompass both the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 and the 600 kb BP4-BP5 intervals (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Carriers of 16p11.2 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 Rearrangements Exhibit More Severe Phenotypes than Carriers of 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 and 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 CNVs
(A) From top to bottom: UCSC Genome browser view of human chromosome 16 coordinates and cytobands; schematic representation of coding genes (GENCODE v.24)72 mapping within the distal part of 16p11.2; extent of the three recurrent and clinically relevant 16p11.2 CNVs discussed in this paper, i.e., 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 (blue), distal 220 kb BP2-BP3 (green), and proximal 600 kb BP4-BP5 (magenta); the five blocks of segmental duplications (BP1 to BP5); and pairs of directly oriented segmental duplications with >98% identity that might trigger non-allelic homologous recombination and thus changes in number of copies of the BP1-BP5 (blues), 220 kb BP2-BP3 (greens), and 600 kb BP4-BP5 intervals (magentas). Note that no such pair is present at BP2-BP5 according to the hg38 reference sequence. The breakpoint terminology was proposed in Zufferey et al.2
(B and C) Distribution of Z-score values of BMI (B) and head circumference (HC) (C) in unrelated carriers of deletion (del; left boxplots) and duplication (dup; right boxplots) of the 16p11.2 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 (blue), 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 (green), and 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 intervals (magenta), taking into account the normal effect of age and gender observed in the general population as described in Jacquemont et al.9 The general population has a mean of zero.
(D) BMI plotted against head circumference (HC) of carriers of any 16p11.2 (top left, gray), 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 (top right, green), 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 (bottom left, magenta), and 16p11.2 1.7 Mb BP1-BP5 (bottom right, blue) rearrangements. Deletion and duplication carriers are depicted with triangles pointing up and down, respectively.
We recruited and phenotyped 17 carriers of the BP1-BP5 deletion (14 probands) and five (four) of the reciprocal duplication (Table S1), as well as four familial control subjects, and we compared their BMI and HC Z-score to those published previously for the BP2-BP317 and BP4-BP56 CNVs (Figures 5B and 5C). The BMI and HC mean Z-score of the large 16p11.2 BP1-BP5 deletion and duplication carriers deviated from that of the general population (one-sided Wilcoxon test with mean equals zero, BMI p = 0.001 and p = 0.25; HC p = 0.039 and p = 0.062 for deletion and duplication, respectively; all p values are nominal; Figure S5). Observing this trend, we performed permutation analyses that confirmed significant effects: p < 0.0001, p < 0.005, p < 0.05, p < 0.003 for BMI and HC in deletion and duplications carriers, respectively; all p values are adjusted for multiple testing). The reported correlation between BMI and HC appears to have a greater slope for the 1.7 Mb rearrangements compared to each of the shorter CNVs (Figure 5D). Our results indicate that the 16p11.2 1.7 Mb deletion and reciprocal duplication oppositely affect growth parameters (t test, BMI p = 0.0005; HC p = 0.003). Although we were able to collect only a few familial control subjects, the normal range of these individuals’ anthropometric data suggest that the effects are not familial in origin (Figure S5). Despite power limitations due to cohort size, the observed BMI of carriers of 1.7 Mb rearrangements is nonetheless more severely altered than that of corresponding carriers of deletion and duplication of the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 and 600 kb BP4-BP5 regions, respectively (Wilcoxon test, BMI of the 1.7 Mb deletion carriers compared to the 220 kb BP2-BP3, p = 0.14; compared to the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5, p = 0.05, and BP2-3 and BP4-5 effects together, p = 0.062; similarly for their duplications, p = 0.203, p = 0.089, p = 0.104, respectively). A possibly additive effect could also be identified for the 1.7 Mb duplications on HC, particularly compared to the 600 kb CNV carriers (p = 0.375, p = 0.076, p = 0.099), in agreement with the hypothesis that aneuploidy of the genes of the entire region could be more detrimental (Figure 5).
Discussion
Several groups have reported associations between the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 and 220 kb BP2-BP3 rearrangements and loss of IQ points, ASD, schizophrenia, and dosage-dependent mirror phenotypes of HC and BMI.2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 15, 17 As shown by 4C-seq, FISH, and Hi-C, the two 16p11.2 CNV-prone regions are reciprocally engaged in evolutionary-conserved complex chromatin looping, as well as coordinated expression of encompassed genes.17, 45 Here we assessed whether these findings were paralleled by genetic interactions between the 28 and 9 single-copy genes within the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 and 220 kb BP2-BP3 intervals, respectively. Our zebrafish and mouse data indicate that LAT (linker for activation of T cells) is a major driver of the 16p11.2 220 kb BP2-BP3 CNV head size phenotype, a pathology seen consistently in CNV carriers, where the duplication is associated with microcephaly and the deletion is associated with macrocephaly. Further, we found that LAT interacts genetically with three genes of the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 interval. The effects on head size appear additive with KCTD13 and epistatic with MVP and MAPK3. Of note, chromatin conformation capture showed that the promoter of LAT 4C-seq viewpoint contacts genes in the 600 kb interval, in particular MAPK3, TAOK2 (MIM: 613199), ALDOA (MIM: 103850), INO80E (GenBank: NM_173618), KCTD13, and MVP.17 Notably, LAT was, after MVP, the viewpoint whose contacted genes had the highest enrichment in ASD-associated genes.17
Growing evidence points to intimate connections between the immune and nervous systems. Disrupting the fine regulation between circulating immune cells, macrophages, microglia, and neurons or the imbalance in immune molecules can cause a pro-inflammatory skew and produce changes in neuronal function.46, 47 Several immune-related molecules have been shown to have pleiotropic functions in the brain that can directly influence synaptic function.48, 49 LAT encodes a transmembrane adaptor protein with a role in the development, activation, and maintenance of T cells.34 It is modulated by CD247 and ZAP70 tyrosine phosphorylation upon TCR activation and controls signal diversification and amplification.50 Consistent with this observation, overexpression of these two genes phenocopies the overexpression of LAT, i.e., decreases cell proliferation in the zebrafish developing brain. These phenotypes are not restricted to zebrafish: Lat−/− mice also show alterations in several brain regions including cortex and habenula, a structure that plays a central role in the positive and negative reinforcements of the reward process.51, 52, 53 Cd247−/− mice show brain morphological defects, in particular reduced glutamatergic synaptic activity in the retina54 and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus,41 as well as impaired learning and memory, a T cell-independent mechanism.44 In zebrafish, ZAP70 is expressed ubiquitously in early development, and highly and specifically in the head from the 16-somite stage, with low expression level throughout the rest of the embryo.55
Three related individuals with homozygote loss of function of LAT presented with combined immunodeficiency and autoimmune diseases.56 Consistent with our findings of a genetic interaction effect of co-overexpression of LAT and MAPK3, residual T cells of these individuals lacked MAPK/ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) signaling.56 The product of MVP that also genetically interacts with LAT has been postulated to act as a scaffold that modulates MAPK/ERK signaling.57, 58 Evidence is accumulating that it might be involved in the regulation of important cell signaling pathways, including PI3K/AKT, based on the finding that MVP binds several phosphatases and kinases such as PTEN,59 PTPN11 (tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2),58 as well as MAPK358 itself. The activity of the PI3K was shown to be essential to the signaling capacity of LAT-mediated complexes.60 In support of the possible interplay between LAT and the BP4-BP5 mapping loci, copy number variants of the BP4-BP5 interval was associated with LAT differential expression in human lymphoblastoid cell lines.45
Our findings suggest that LAT, like CD247 and ZAP70,41, 42, 43, 44 plays a role in neurogenesis and that perturbation of this pathway may lead to neurodevelopmental phenotypes. They also provide an interesting example of the non-random organization of the genome61 as gene dosage modification of (at least) one and five of the 9 and 28 genes mapping within the 220 kb BP2-BP3 and 600 kb BP4-BP5 intervals can influence the PTEN-antagonized (phosphatase and tensin homolog) PI3K/AKT and Ras/MAPK pathways: LAT, TAOK2, that encodes a PTEN-binding MAP kinase kinase kinase essential for dendrite morphogenesis,62, 63 MVP, the product of which interacts with PTEN and regulates its intracellular localization,59, 64, 65 MAPK3, KCTD13,37 and CDIPT (MIM: 605893) encoding an enzyme of the phosphatidylinositol synthesis pathway. Consistent with this view, the genes differentially expressed in cell lines of 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 carriers were enriched not only in pathways relevant to neurodevelopmental defects and ciliopathy but also in genes involved in phosphoinositide signaling.22 Of note, germline variants in PTEN present the ASD, obesity, and macrocephaly triad of phenotypes,66, 67, 68, 69, 70 whereas those in the Ras/MAPK signaling pathway are associated with social impairment.71
The interactions observed at this cluster of genes, both at the chromatin and genetic level, suggest that the CNV-prone non-overlapping loci at 16p11.2 should be approached and studied as “connected regions” rather than completely independent entities.
Consortia
Members of the 16p11.2 Consortium are Maria Nicla Loviglio, Aia Elise Jønch, Konstantin Popadin, Giuliana Giannuzzi, Anne M. Maillard, Christina Fagerberg, Charlotte Brasch Andersen, Martine Doco-Fenzy, Marie-Ange Delrue, Laurence Faivre, Benoit Arveiler, David Geneviève, Anouck Schneider, Marion Gerard, Joris Andrieux, Salima El Chehadeh, Elise Schaefer, Christel Depienne, Mieke Van Haelst, Eva H. Brilstra, Ellen Van Binsbergen, Jeske van Harssel, Lars T. van der Veken, James F. Gusella, Yiping Shen, Elyse Mitchell, Usha Kini, Lara Hawkes, Carolyn Campbell, Florence Niel Butschi, Marie-Claude Addor, Jacques S. Beckmann, Sébastien Jacquemont, and Alexandre Reymond. The affiliations and email addresses of the members of the 16p11.2 Consortium are listed in Table S2.
Acknowledgments
We thank the affected individuals and their families for their contribution to this study. We are grateful to Weiguo Zhang (Duke University) for kindly providing Lat knockout mouse model. M.N.L. is recipient of an EMBO ASTF 153-2015 short-term fellowship award and a Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) postdoctoral fellowship, G.G. of a Pro-Women Scholarship from the Faculty of Biology and Medicine, University of Lausanne, and A.M.M. of a Mary Heim-Vögtlin SNSF fellowship. C.G. is a grantee of a NARSAD Young Investigator Grant from the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation. K.P. was supported by the 5 Top 100 Russian Academic Excellence Project at the Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University. S.J. is recipient of a Bursary Professor fellowship of the SNSF P2LAP3_171809, a Canada Research Chair, and the Jeanne et Jean-Louis Levesque Chair. This work was supported by grants from the Simons Foundation (SFARI274424), the National Institute of Mental Health, NIH (P50 MH094268 to N.K.), the French National Research Agency (ANR) as part of the “Investments d’Avenir” Programme LabEx-INRT (C.G.) and the Swiss National Science Foundation (31003A_160203 to A.R.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Published: September 28, 2017
Footnotes
Supplemental Data include five figures and two tables and can be found with this article online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.08.016.
Contributor Information
Christelle Golzio, Email: christelle.golzio@igbmc.fr.
Alexandre Reymond, Email: alexandre.reymond@unil.ch.
16p11.2 Consortium:
Maria Nicla Loviglio, Aia Elise Jønch, Konstantin Popadin, Giuliana Giannuzzi, Anne M. Maillard, Christina Fagerberg, Charlotte Brasch Andersen, Martine Doco-Fenzy, Marie-Ange Delrue, Laurence Faivre, Benoit Arveiler, David Geneviève, Anouck Schneider, Marion Gerard, Joris Andrieux, Salima El Chehadeh, Elise Schaefer, Christel Depienne, Mieke Van Haelst, Eva H. Brilstra, Ellen Van Binsbergen, Jeske van Harssel, Lars T. van der Veken, James F. Gusella, Yiping Shen, Elyse Mitchell, Usha Kini, Lara Hawkes, Carolyn Campbell, Florence Niel Butschi, Marie-Claude Addor, Jacques S. Beckmann, Sébastien Jacquemont, and Alexandre Reymond
Web Resources
CHOPCHOP, http://chopchop.cbu.uib.no/
ClustalX, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2
Gencode, http://www.gencodegenes.org
GTEx Portal, http://www.gtexportal.org/home/
ImageJ, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/
MGI-Mouse Vertebrate Homology, http://www.informatics.jax.org/marker/MGI:88334R
OMIM, http://www.omim.org/
UCSC Genome Browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu
Supplemental Data
References
- 1.Nuttle X., Giannuzzi G., Duyzend M.H., Schraiber J.G., Narvaiza I., Sudmant P.H., Penn O., Chiatante G., Malig M., Huddleston J. Emergence of a Homo sapiens-specific gene family and chromosome 16p11.2 CNV susceptibility. Nature. 2016;536:205–209. doi: 10.1038/nature19075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zufferey F., Sherr E.H., Beckmann N.D., Hanson E., Maillard A.M., Hippolyte L., Macé A., Ferrari C., Kutalik Z., Andrieux J., Simons VIP Consortium. 16p11.2 European Consortium A 600 kb deletion syndrome at 16p11.2 leads to energy imbalance and neuropsychiatric disorders. J. Med. Genet. 2012;49:660–668. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cooper G.M., Coe B.P., Girirajan S., Rosenfeld J.A., Vu T.H., Baker C., Williams C., Stalker H., Hamid R., Hannig V. A copy number variation morbidity map of developmental delay. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:838–846. doi: 10.1038/ng.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McCarthy S.E., Makarov V., Kirov G., Addington A.M., McClellan J., Yoon S., Perkins D.O., Dickel D.E., Kusenda M., Krastoshevsky O., Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium Microduplications of 16p11.2 are associated with schizophrenia. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:1223–1227. doi: 10.1038/ng.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Green E.K., Rees E., Walters J.T., Smith K.G., Forty L., Grozeva D., Moran J.L., Sklar P., Ripke S., Chambert K.D. Copy number variation in bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry. 2016;21:89–93. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.D’Angelo D., Lebon S., Chen Q., Martin-Brevet S., Snyder L.G., Hippolyte L., Hanson E., Maillard A.M., Faucett W.A., Macé A., Cardiff University Experiences of Children With Copy Number Variants (ECHO) Study. 16p11.2 European Consortium. Simons Variation in Individuals Project (VIP) Consortium Defining the effect of the 16p11.2 duplication on cognition, behavior, and medical comorbidities. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:20–30. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Weiss L.A., Shen Y., Korn J.M., Arking D.E., Miller D.T., Fossdal R., Saemundsen E., Stefansson H., Ferreira M.A., Green T., Autism Consortium Association between microdeletion and microduplication at 16p11.2 and autism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;358:667–675. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa075974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reinthaler E.M., Lal D., Lebon S., Hildebrand M.S., Dahl H.H., Regan B.M., Feucht M., Steinböck H., Neophytou B., Ronen G.M., 16p11.2 European Consortium. EPICURE Consortium. EuroEPINOMICS Consortium 16p11.2 600 kb duplications confer risk for typical and atypical Rolandic epilepsy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014;23:6069–6080. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jacquemont S., Reymond A., Zufferey F., Harewood L., Walters R.G., Kutalik Z., Martinet D., Shen Y., Valsesia A., Beckmann N.D. Mirror extreme BMI phenotypes associated with gene dosage at the chromosome 16p11.2 locus. Nature. 2011;478:97–102. doi: 10.1038/nature10406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maillard A.M., Ruef A., Pizzagalli F., Migliavacca E., Hippolyte L., Adaszewski S., Dukart J., Ferrari C., Conus P., Männik K., 16p11.2 European Consortium The 16p11.2 locus modulates brain structures common to autism, schizophrenia and obesity. Mol. Psychiatry. 2015;20:140–147. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Qureshi A.Y., Mueller S., Snyder A.Z., Mukherjee P., Berman J.I., Roberts T.P., Nagarajan S.S., Spiro J.E., Chung W.K., Sherr E.H., Buckner R.L., Simons VIP Consortium Opposing brain differences in 16p11.2 deletion and duplication carriers. J. Neurosci. 2014;34:11199–11211. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1366-14.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Walters R.G., Jacquemont S., Valsesia A., de Smith A.J., Martinet D., Andersson J., Falchi M., Chen F., Andrieux J., Lobbens S. A new highly penetrant form of obesity due to deletions on chromosome 16p11.2. Nature. 2010;463:671–675. doi: 10.1038/nature08727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Barge-Schaapveld D.Q., Maas S.M., Polstra A., Knegt L.C., Hennekam R.C. The atypical 16p11.2 deletion: a not so atypical microdeletion syndrome? Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2011;155A:1066–1072. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guha S., Rees E., Darvasi A., Ivanov D., Ikeda M., Bergen S.E., Magnusson P.K., Cormican P., Morris D., Gill M., Molecular Genetics of Schizophrenia Consortium. Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 Implication of a rare deletion at distal 16p11.2 in schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:253–260. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamapsychiatry.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bochukova E.G., Huang N., Keogh J., Henning E., Purmann C., Blaszczyk K., Saeed S., Hamilton-Shield J., Clayton-Smith J., O’Rahilly S. Large, rare chromosomal deletions associated with severe early-onset obesity. Nature. 2010;463:666–670. doi: 10.1038/nature08689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bachmann-Gagescu R., Mefford H.C., Cowan C., Glew G.M., Hing A.V., Wallace S., Bader P.I., Hamati A., Reitnauer P.J., Smith R. Recurrent 200-kb deletions of 16p11.2 that include the SH2B1 gene are associated with developmental delay and obesity. Genet. Med. 2010;12:641–647. doi: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181ef4286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Loviglio M.N., Leleu M., Mannik K., Passeggeri M., Giannuzzi G., van der Werf I., Waszak S.M., Zazhytska M., Roberts-Caldeira I., Gheldof N. Chromosomal contacts connect loci associated with autism, BMI and head circumference phenotypes. Mol. Psychiatry. 2016 doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Golzio C., Katsanis N. Genetic architecture of reciprocal CNVs. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2013;23:240–248. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stewart A.M., Braubach O., Spitsbergen J., Gerlai R., Kalueff A.V. Zebrafish models for translational neuroscience research: from tank to bedside. Trends Neurosci. 2014;37:264–278. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2014.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Courchesne E., Mouton P.R., Calhoun M.E., Semendeferi K., Ahrens-Barbeau C., Hallet M.J., Barnes C.C., Pierce K. Neuron number and size in prefrontal cortex of children with autism. JAMA. 2011;306:2001–2010. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.1638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ceol C.J., Houvras Y., Jane-Valbuena J., Bilodeau S., Orlando D.A., Battisti V., Fritsch L., Lin W.M., Hollmann T.J., Ferré F. The histone methyltransferase SETDB1 is recurrently amplified in melanoma and accelerates its onset. Nature. 2011;471:513–517. doi: 10.1038/nature09806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Migliavacca E., Golzio C., Männik K., Blumenthal I., Oh E.C., Harewood L., Kosmicki J.A., Loviglio M.N., Giannuzzi G., Hippolyte L., 16p11.2 European Consortium A potential contributory role for ciliary dysfunction in the 16p11.2 600 kb BP4-BP5 pathology. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015;96:784–796. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Carvalho C.M., Vasanth S., Shinawi M., Russell C., Ramocki M.B., Brown C.W., Graakjaer J., Skytte A.B., Vianna-Morgante A.M., Krepischi A.C. Dosage changes of a segment at 17p13.1 lead to intellectual disability and microcephaly as a result of complex genetic interaction of multiple genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014;95:565–578. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dauber A., Golzio C., Guenot C., Jodelka F.M., Kibaek M., Kjaergaard S., Leheup B., Martinet D., Nowaczyk M.J., Rosenfeld J.A. SCRIB and PUF60 are primary drivers of the multisystemic phenotypes of the 8q24.3 copy-number variant. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013;93:798–811. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Duan C., Li M., Rui L. SH2-B promotes insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1)- and IRS2-mediated activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in response to leptin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:43684–43691. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408495200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ren D., Zhou Y., Morris D., Li M., Li Z., Rui L. Neuronal SH2B1 is essential for controlling energy and glucose homeostasis. J. Clin. Invest. 2007;117:397–406. doi: 10.1172/JCI29417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Willer C.J., Speliotes E.K., Loos R.J., Li S., Lindgren C.M., Heid I.M., Berndt S.I., Elliott A.L., Jackson A.U., Lamina C., Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genetic Investigation of ANthropometric Traits Consortium Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:25–34. doi: 10.1038/ng.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Thorleifsson G., Walters G.B., Gudbjartsson D.F., Steinthorsdottir V., Sulem P., Helgadottir A., Styrkarsdottir U., Gretarsdottir S., Thorlacius S., Jonsdottir I. Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:18–24. doi: 10.1038/ng.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Speliotes E.K., Willer C.J., Berndt S.I., Monda K.L., Thorleifsson G., Jackson A.U., Lango Allen H., Lindgren C.M., Luan J., Mägi R., MAGIC. Procardis Consortium Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:937–948. doi: 10.1038/ng.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jamshidi Y., Snieder H., Ge D., Spector T.D., O’Dell S.D. The SH2B gene is associated with serum leptin and body fat in normal female twins. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007;15:5–9. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Doche M.E., Bochukova E.G., Su H.W., Pearce L.R., Keogh J.M., Henning E., Cline J.M., Saeed S., Dale A., Cheetham T. Human SH2B1 mutations are associated with maladaptive behaviors and obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122:4732–4736. doi: 10.1172/JCI62696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bernier R., Golzio C., Xiong B., Stessman H.A., Coe B.P., Penn O., Witherspoon K., Gerdts J., Baker C., Vulto-van Silfhout A.T. Disruptive CHD8 mutations define a subtype of autism early in development. Cell. 2014;158:263–276. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang W., Sommers C.L., Burshtyn D.N., Stebbins C.C., DeJarnette J.B., Trible R.P., Grinberg A., Tsay H.C., Jacobs H.M., Kessler C.M. Essential role of LAT in T cell development. Immunity. 1999;10:323–332. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mikhaleva A., Kannan M., Wagner C., Yalcin B. Histomorphological phenotyping of the adult mouse brain. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2016;6:307–332. doi: 10.1002/cpmo.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gringhuis S.I., Papendrecht-van der Voort E.A., Leow A., Nivine Levarht E.W., Breedveld F.C., Verweij C.L. Effect of redox balance alterations on cellular localization of LAT and downstream T-cell receptor signaling pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002;22:400–411. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.400-411.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Golzio C., Willer J., Talkowski M.E., Oh E.C., Taniguchi Y., Jacquemont S., Reymond A., Sun M., Sawa A., Gusella J.F. KCTD13 is a major driver of mirrored neuroanatomical phenotypes of the 16p11.2 copy number variant. Nature. 2012;485:363–367. doi: 10.1038/nature11091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takeda H., Matsuzaki T., Oki T., Miyagawa T., Amanuma H. A novel POU domain gene, zebrafish pou2: expression and roles of two alternatively spliced twin products in early development. Genes Dev. 1994;8:45–59. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Beunders G., Voorhoeve E., Golzio C., Pardo L.M., Rosenfeld J.A., Talkowski M.E., Simonic I., Lionel A.C., Vergult S., Pyatt R.E. Exonic deletions in AUTS2 cause a syndromic form of intellectual disability and suggest a critical role for the C terminus. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013;92:210–220. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jordan D.M., Frangakis S.G., Golzio C., Cassa C.A., Kurtzberg J., Davis E.E., Sunyaev S.R., Katsanis N., Task Force for Neonatal Genomics Identification of cis-suppression of human disease mutations by comparative genomics. Nature. 2015;524:225–229. doi: 10.1038/nature14497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Baudouin S.J., Angibaud J., Loussouarn G., Bonnamain V., Matsuura A., Kinebuchi M., Naveilhan P., Boudin H. The signaling adaptor protein CD3zeta is a negative regulator of dendrite development in young neurons. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2008;19:2444–2456. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-09-0947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Angibaud J., Baudouin S.J., Louveau A., Nerrière-Daguin V., Bonnamain V., Csaba Z., Dournaud P., Naveilhan P., Noraz N., Pellier-Monnin V., Boudin H. Ectopic expression of the immune adaptor protein CD3zeta in neural stem/progenitor cells disrupts cell-fate specification. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012;46:431–441. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9607-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hatterer E., Benon A., Chounlamountri N., Watrin C., Angibaud J., Jouanneau E., Boudin H., Honnorat J., Pellier-Monnin V., Noraz N. Syk kinase is phosphorylated in specific areas of the developing nervous system. Neurosci. Res. 2011;70:172–182. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2011.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Louveau A., Angibaud J., Haspot F., Opazo M.C., Thinard R., Thepenier V., Baudouin S.J., Lescaudron L., Hulin P., Riedel C.A., Boudin H. Impaired spatial memory in mice lacking CD3ζ is associated with altered NMDA and AMPA receptors signaling independent of T-cell deficiency. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:18672–18685. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3028-13.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Blumenthal I., Ragavendran A., Erdin S., Klei L., Sugathan A., Guide J.R., Manavalan P., Zhou J.Q., Wheeler V.C., Levin J.Z. Transcriptional consequences of 16p11.2 deletion and duplication in mouse cortex and multiplex autism families. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014;94:870–883. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhan Y., Paolicelli R.C., Sforazzini F., Weinhard L., Bolasco G., Pagani F., Vyssotski A.L., Bifone A., Gozzi A., Ragozzino D., Gross C.T. Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2014;17:400–406. doi: 10.1038/nn.3641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hsiao E.Y., Patterson P.H. Placental regulation of maternal-fetal interactions and brain development. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012;72:1317–1326. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Boulanger L.M. Immune proteins in brain development and synaptic plasticity. Neuron. 2009;64:93–109. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Garay P.A., McAllister A.K. Novel roles for immune molecules in neural development: implications for neurodevelopmental disorders. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2010;2:136. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2010.00136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Salek M., McGowan S., Trudgian D.C., Dushek O., de Wet B., Efstathiou G., Acuto O. Quantitative phosphoproteome analysis unveils LAT as a modulator of CD3ζ and ZAP-70 tyrosine phosphorylation. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e77423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Proulx C.D., Hikosaka O., Malinow R. Reward processing by the lateral habenula in normal and depressive behaviors. Nat. Neurosci. 2014;17:1146–1152. doi: 10.1038/nn.3779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lawson R.P., Seymour B., Loh E., Lutti A., Dolan R.J., Dayan P., Weiskopf N., Roiser J.P. The habenula encodes negative motivational value associated with primary punishment in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:11858–11863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323586111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hennigan K., D’Ardenne K., McClure S.M. Distinct midbrain and habenula pathways are involved in processing aversive events in humans. J. Neurosci. 2015;35:198–208. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0927-14.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Xu H.P., Chen H., Ding Q., Xie Z.H., Chen L., Diao L., Wang P., Gan L., Crair M.C., Tian N. The immune protein CD3zeta is required for normal development of neural circuits in the retina. Neuron. 2010;65:503–515. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.01.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Christie T.L., Carter A., Rollins E.L., Childs S.J. Syk and Zap-70 function redundantly to promote angioblast migration. Dev. Biol. 2010;340:22–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Keller B., Zaidman I., Yousefi O.S., Hershkovitz D., Stein J., Unger S., Schachtrup K., Sigvardsson M., Kuperman A.A., Shaag A. Early onset combined immunodeficiency and autoimmunity in patients with loss-of-function mutation in LAT. J. Exp. Med. 2016;213:1185–1199. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Liang P., Wan Y., Yan Y., Wang Y., Luo N., Deng Y., Fan X., Zhou J., Li Y., Wang Z. MVP interacts with YPEL4 and inhibits YPEL4-mediated activities of the ERK signal pathway. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010;88:445–450. doi: 10.1139/o09-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kolli S., Zito C.I., Mossink M.H., Wiemer E.A., Bennett A.M. The major vault protein is a novel substrate for the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 and scaffold protein in epidermal growth factor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:29374–29385. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313955200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yu Z., Fotouhi-Ardakani N., Wu L., Maoui M., Wang S., Banville D., Shen S.H. PTEN associates with the vault particles in HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:40247–40252. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207608200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Cruz-Orcutt N., Houtman J.C. PI3 kinase function is vital for the function but not formation of LAT-mediated signaling complexes. Mol. Immunol. 2009;46:2274–2283. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Warnecke T., Hurst L.D. Error prevention and mitigation as forces in the evolution of genes and genomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011;12:875–881. doi: 10.1038/nrg3092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.de Anda F.C., Rosario A.L., Durak O., Tran T., Gräff J., Meletis K., Rei D., Soda T., Madabhushi R., Ginty D.D. Autism spectrum disorder susceptibility gene TAOK2 affects basal dendrite formation in the neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2012;15:1022–1031. doi: 10.1038/nn.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Yadav S., Oses-Prieto J.A., Peters C.J., Zhou J., Pleasure S.J., Burlingame A.L., Jan L.Y., Jan Y.N. TAOK2 kinase mediates PSD95 stability and dendritic spine maturation through septin7 phosphorylation. Neuron. 2017;93:379–393. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chung J.H., Ginn-Pease M.E., Eng C. Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) has nuclear localization signal-like sequences for nuclear import mediated by major vault protein. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4108–4116. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang W., Neo S.P., Gunaratne J., Poulsen A., Boping L., Ong E.H., Sangthongpitag K., Pendharkar V., Hill J., Cohen S.M. Feedback regulation on PTEN/AKT pathway by the ER stress kinase PERK mediated by interaction with the Vault complex. Cell. Signal. 2015;27:436–442. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.O’Roak B.J., Vives L., Girirajan S., Karakoc E., Krumm N., Coe B.P., Levy R., Ko A., Lee C., Smith J.D. Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature. 2012;485:246–250. doi: 10.1038/nature10989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Butler M.G., Dasouki M.J., Zhou X.P., Talebizadeh Z., Brown M., Takahashi T.N., Miles J.H., Wang C.H., Stratton R., Pilarski R., Eng C. Subset of individuals with autism spectrum disorders and extreme macrocephaly associated with germline PTEN tumour suppressor gene mutations. J. Med. Genet. 2005;42:318–321. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2004.024646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Herman G.E., Butter E., Enrile B., Pastore M., Prior T.W., Sommer A. Increasing knowledge of PTEN germline mutations: Two additional patients with autism and macrocephaly. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2007;143A:589–593. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pal A., Barber T.M., Van de Bunt M., Rudge S.A., Zhang Q., Lachlan K.L., Cooper N.S., Linden H., Levy J.C., Wakelam M.J. PTEN mutations as a cause of constitutive insulin sensitivity and obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:1002–1011. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Huang W.C., Chen Y., Page D.T. Hyperconnectivity of prefrontal cortex to amygdala projections in a mouse model of macrocephaly/autism syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:13421. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Adviento B., Corbin I.L., Widjaja F., Desachy G., Enrique N., Rosser T., Risi S., Marco E.J., Hendren R.L., Bearden C.E. Autism traits in the RASopathies. J. Med. Genet. 2014;51:10–20. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Harrow J., Frankish A., Gonzalez J.M., Tapanari E., Diekhans M., Kokocinski F., Aken B.L., Barrell D., Zadissa A., Searle S. GENCODE: the reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res. 2012;22:1760–1774. doi: 10.1101/gr.135350.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.