Abstract
Background
Multimorbidity and the associated use of multiple medicines (polypharmacy), is common in the older population. Despite this, there is no consensus definition for polypharmacy. A systematic review was conducted to identify and summarise polypharmacy definitions in existing literature.
Methods
The reporting of this systematic review conforms to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) checklist. MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE and Cochrane were systematically searched, as well as grey literature, to identify articles which defined the term polypharmacy (without any limits on the types of definitions) and were in English, published between 1st January 2000 and 30th May 2016. Definitions were categorised as i. numerical only (using the number of medications to define polypharmacy), ii. numerical with an associated duration of therapy or healthcare setting (such as during hospital stay) or iii. Descriptive (using a brief description to define polypharmacy).
Results
A total of 1156 articles were identified and 110 articles met the inclusion criteria. Articles not only defined polypharmacy but associated terms such as minor and major polypharmacy. As a result, a total of 138 definitions of polypharmacy and associated terms were obtained. There were 111 numerical only definitions (80.4% of all definitions), 15 numerical definitions which incorporated a duration of therapy or healthcare setting (10.9%) and 12 descriptive definitions (8.7%). The most commonly reported definition of polypharmacy was the numerical definition of five or more medications daily (n = 51, 46.4% of articles), with definitions ranging from two or more to 11 or more medicines. Only 6.4% of articles classified the distinction between appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy, using descriptive definitions to make this distinction.
Conclusions
Polypharmacy definitions were variable. Numerical definitions of polypharmacy did not account for specific comorbidities present and make it difficult to assess safety and appropriateness of therapy in the clinical setting.
Keywords: Polypharmacy, Multimorbidity, Comorbidity, Inappropriate prescribing, Aged, Systematic review
Background
Multimorbidity, commonly defined as the co-existence of two or more chronic health conditions, is common in the older population [1]. The presence of multiple chronic conditions increases the complexity of therapeutic management for both health professionals and patients, and impacts negatively on health outcomes. Multimorbidity is associated with decreased quality of life, self-rated health, mobility and functional ability as well as increases in hospitalisations, physiological distress, use of health care resources, mortality and costs [2–4]. Globally, the health burden of multimorbidity is expected to rise significantly as a result of the growing number of older people and increasing numbers of people living with multimorbidity [5].
The use of multiple medicines, commonly referred to as polypharmacy is common in the older population with multimorbidity, as one or more medicines may be used to treat each condition. Polypharmacy is associated with adverse outcomes including mortality, falls, adverse drug reactions, increased length of stay in hospital and readmission to hospital soon after discharge [6–8]. The risk of adverse effects and harm increases with increasing numbers of medications [9]. Harm can result due to a multitude of factors including drug-drug interactions and drug-disease interactions. Older patients are at even greater risk of adverse effects due to decreased renal and hepatic function, lower lean body mass, reduced hearing, vision, cognition and mobility [10].
While in many instances the use of multiple medicines or polypharmacy may be clinically appropriate, it is important to identify patients with inappropriate polypharmacy that may place patients at increased risk of adverse events and poor health outcomes. Studies have suggested a shift towards adopting the term ‘appropriate polypharmacy’ in order to differentiate between the prescribing of ‘many’ and ‘too many’ drugs instead of a simple numerical count of medications, which is of limited value in practice [11, 12]. In order to make this distinction between appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy, the term polypharmacy needs to be clearly defined. We therefore conducted a systematic review to explore the definitions of polypharmacy in existing literature. We additionally aimed to explore whether articles differentiated between appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy and how this distinction was made.
Methods
Data sources and search strategy
The reporting of this systematic review conforms to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) checklist.
MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE and Cochrane databases were searched between 1st January 2000 and 30th May 2016.
The following search terms (Medical Subject Headings or MESH and keywords) were used in EMBASE and MEDLINE (Ovid):
polypharmacy/ (MESH) OR multiple medication* OR multiple medicine* OR multiple drug* (key words) OR many medication* OR many medicine* OR many drug* (key words) (for all articles referring to polypharmacy) AND.
defin* (key word) or explan* (keyword) (for all articles defining or explaining polypharmacy).
For the review of the Cochrane database, the term “polypharmacy” was searched.
The search was limited to primary research articles which defined the term polypharmacy in any shape or form, conducted in humans and published in English between the years 2000 and 2016. Articles were considered if the abstracts were available in English and were published or in press. Reference lists of relevant articles and grey literature were screened to identify other relevant articles. The search strategy was developed in consultation with a librarian specialising in health databases, with a pre-determined protocol developed collaboratively with the authors for methods to search and select relevant articles.
Study selection and data extraction
Articles that met the inclusion criteria and provided a definition of polypharmacy were included. One author (NM) conducted the initial database search and primary screening of article titles and abstracts and articles were categorised as: relevant, irrelevant or unsure. Three reviewers (NM, SS, GC) discussed the appropriateness of inclusion of each article classed as relevant or unsure. Once all relevant articles were identified, one author (NM) reviewed full texts of all identified articles and extracted the data. A pre-defined data extraction template was developed by all authors and then applied to ensure consistent data extraction from each of the identified studies. Data items extracted included the definitions of polypharmacy and associated terms such as minor, moderate and excessive polypharmacy and whether studies distinguished between appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy and if so, how this distinction was made or defined. The definitions of polypharmacy and associated terms were categorised as: i. numerical only (using the number of medications to define polypharmacy), ii. numerical for a given duration of therapy or healthcare setting for e.g. during hospital stay or iii. Descriptive (using a brief description to define polypharmacy). Once the primary data extraction was complete all authors reviewed the content analysis for each of the extracted studies, with data further categorised and summarised in tables.
Results
A total of 1156 articles were identified and 110 articles met the full inclusion criteria for this systematic review [10–119]. Fig. 1 shows a flowchart of study selection according to the PRISMA checklist.
Fig. 1.
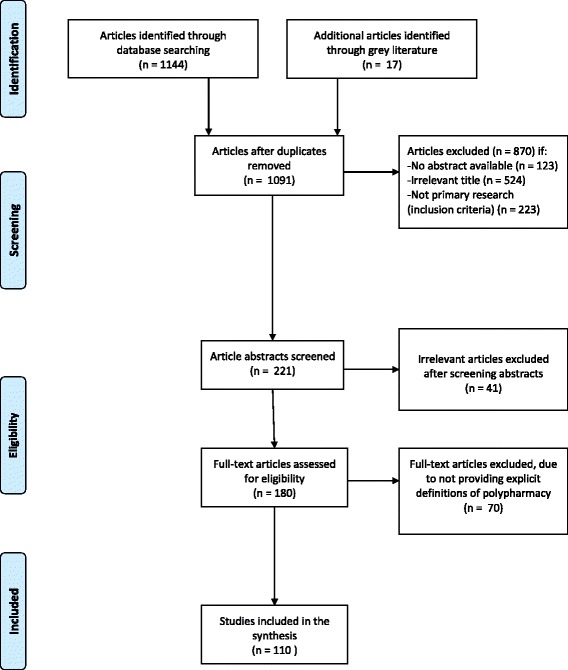
Study selection flowchart according to PRISMA checklist
Studies not only defined polypharmacy but also used associated terms to define the level of polypharmacy; including minor (8 studies, 7.3%), moderate (1 study, 0.9%), major (12 studies, 10.9%), hyper (2 studies, 1.8%), excessive (10 studies, 9.1%), severe (1 study, 0.9%), appropriate (1 study, 0.9%), rational polypharmacy and indiscriminate prescribing (1 study, 0.9%), persistent (1 study, 0.9%), chronic (1 study, 0.9%), and pseudopolypharmacy (1 study, 0.9%). As a result, a total of 138 definitions of polypharmacy and associated terms were obtained. There were 111 numerical only definitions (80.4% of all definitions), 15 numerical definitions which incorporated a duration of therapy or healthcare setting (10.9%) and 12 descriptive definitions (8.7%). Table 1 presents a breakdown of the number of definitions for each term.
Table 1.
Breakdown of polypharmacy definitions according to the category of definition
| Term | Numerical only | Numerical in a given duration of time or setting | Descriptive | Total number of definitions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypharmacy | 81 | 9 | 9 | 99 |
| Minor Polypharmacy | 8 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Moderate polypharmacy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Major polypharmacy | 11 | 1 | 0 | 12 |
| Hyperpolypharmacy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Excessive polypharmacy | 8 | 2 | 0 | 10 |
| Severe polypharmacy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Persistent polypharmacy | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Chronic polypharmacy | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Appropriate polypharmacy | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Rational polypharmacy and indiscriminate prescribing | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Pseudopolypharmacy | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Total number of definitions according to category of definition | 111 | 15 | 12 | 138 |
Out of the 110 identified articles, 81 (73.6%) included only a numerical definition of polypharmacy (i.e. did not specify duration of therapy or healthcare setting). Nine articles (8.2%) included numerical definitions of polypharmacy for a given duration of time or healthcare setting and nine articles (8.2%) included descriptive definitions of polypharmacy. Four articles included two categories of polypharmacy definitions: two articles (1.8%) included both numerical only definitions and numerical definitions of polypharmacy for a duration of time or healthcare setting and two articles (1.8%) included both numerical only and descriptive definitions of polypharmacy.
Numerical only definitions of polypharmacy in existing literature
Table 2 shows the various numerical only categorisations of polypharmacy and associated terms and the number of studies using these definitions.
Table 2.
Various numerical only definitions of polypharmacy and associated terms in existing literature
| Term | Number of medications | Number of studies | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypharmacy | ≥ 2 | 1 | [13] |
| 2 to 9 | 1 | [14] | |
| ≥ 3 | 1 | [15] | |
| 3 to 6 | 1 | [16] | |
| ≥ 4 | 6 | [17–22] | |
| ≥ 4 or ≥ 5 | 1 | [23] | |
| ≥ 5 | 51 | [11, 24–73] | |
| ≥ 6 | 10 | [10, 74–82] | |
| ≥ 7 | 2 | [83, 84] | |
| 5 to 9 | 3 | [85–87] | |
| ≥ 9 | 1 | [88] | |
| ≥ 10 | 1 | [89] | |
| ≥ 11 | 1 | [90] | |
| number of drug classes | 1 | [91] | |
| Minor Polypharmacy | 2 to 4 | 6 | [92–97] |
| 2 to 3 | 1 | [98] | |
| 0 to 4 | 1 | [99] | |
| Moderate polypharmacy | 4 to 5 | 1 | [98] |
| Major polypharmacy | ≥ 5 | 6 | [92–95, 97, 100] |
| ≥ 6 | 3 | [96, 98, 101] | |
| 5 to 9 | 1 | [99] | |
| ≥ 11 | 1 | [74] | |
| Hyperpolypharmacy | ≥ 10 | 1 | [102] |
| Excessive polypharmacy | ≥ 10 | 7 | [30, 58, 65, 70, 85–87] |
| ≥ 21 | 1 | [74] | |
| Severe polypharmacy | ≥ 10 | 1 | [99] |
There was a wide range of variability in the definitions of polypharmacy as well as associated terms such as minor, moderate and major polypharmacy. The most commonly used term was polypharmacy, but there was variation with regard to the actual definition of polypharmacy, which ranged from two or more medications to 11 or more medications [13, 90]. The most commonly used definition for polypharmacy was five or more medications daily, with 46.4% (n = 51) of studies using this definition [11, 24–73]. The second most common definition for polypharmacy was six or more medications, with ten studies using this definition [10, 74–82]. Only one study defined polypharmacy as the number of drug classes used by a patient [91].
Numerical definitions of polypharmacy incorporating a duration of therapy or healthcare setting
Eleven studies (10.0% of all studies) used numerical definitions of polypharmacy which incorporated a duration of therapy in the definition and four studies (3.6%) used definitions of polypharmacy which incorporated a healthcare setting (Table 3). The definitions of polypharmacy involving a duration of therapy, ranged from use of two or more medications for more than 240 days (‘long term use’) to five to nine medications used for 90 days or more [101, 108]. Polypharmacy definitions incorporating a healthcare setting included the use of five or more medications at hospital discharge, and the use of 10 or more medications during hospital stay [106, 110].
Table 3.
Numerical definitions of polypharmacy and associated terms by duration of therapy/ healthcare setting
| Term | Number of medications | Number of studies | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypharmacy | ≥ 2 for > 240 days (long term) | 1 | [101] |
| ≥ 5 medications in the same month | 1 | [103] | |
| > 5 medications for ≥ 90 days | 1 | [104] | |
| ≥ 5 medications in the same quarter of a year | 1 | [105] | |
| ≥ 5 medicines at hospital discharge | 1 | [106] | |
| 5 to 9 medicines on the day of maximum number of prescriptions of the study year (on the day of the study year when the number of medications prescribed was highest) | 1 | [107] | |
| 5 to 9 medications for ≥ 90 days | 1 | [108] | |
| 5 to 9 medicines during hospital stay | 1 | [109] | |
| ≥ 10 medicines during hospital stay | 1 | [110] | |
| Major polypharmacy | ≥ 10 on the day of maximum number of prescriptions of the study year (on the day of the study year when the number of medications prescribed was highest) | 1 | [107] |
| Hyperpolypharmacy | ≥ 10 medications for ≥90 days | 1 | [108] |
| Excessive polypharmacy | ≥ 10 medications in the same quarter of a year | 1 | [105] |
| ≥ 10 medications during hospital stay | 1 | [109] | |
| Persistent polypharmacy | ≥ 5 medications for 181 days | 1 | [52] |
| Chronic polypharmacy | ≥ 5 medications in 1 month for 6 months (consecutive or not) in a year | 1 | [111] |
Descriptive definitions of polypharmacy
Twelve studies used descriptive definitions of polypharmacy (Table 4). Some studies used different wording but conveyed the same definition of polypharmacy. For example, the definitions “Co-prescribing multiple medications” [113] and “Simultaneous and long term use of different drugs by the same individual” [77] describe polypharmacy as the use of multiple medications concurrently. Other studies alluded to a different issue of medications being appropriate or inappropriate for a given patient [10, 79, 114–118].
Table 4.
Descriptive definitions of polypharmacy and associated terms
| Term | Definition | Number of studies | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypharmacy | Patients visiting multiple pharmacies to obtain medications | 1 | [112] |
| Coprescribing multiple medications | 1 | [113] | |
| Simultaneous and long term use of different drugs by the same individual | 1 | [77] | |
| Polypharmacy definition ranges from the use of a large number of medications, to the use of potentially inappropriate medications, medication underuse and medication duplication | 1 | [114] | |
| Potentially inappropriate medications | 2 | [10, 79] | |
| Use of multiple medications concurrently and the use of additional medications to correct adverse effects | 1 | [115] | |
| Use of medications which are not clinically indicated | 1 | [116] | |
| More drugs being prescribed or taken than are clinically appropriate in the context of a patient’s comorbidities | 1 | [12] | |
| Appropriate polypharmacy | Optimisation of medications for patients with complex and/or multiple conditions where medicine usage agrees with best evidence | 1 | [117] |
| Rational polypharmacy and indiscriminate prescribing | Rational polypharmacy recognizes legitimate prescribing and indiscriminate prescribing suggests inappropriate prescribing (the terms “legitimate prescribing” and “inappropriate prescribing” were not explained) | 1 | [118] |
| Pseudopolypharmacy | Patients being recorded as taking more medications than they are actually taking | 1 | [119] |
Appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy
Only seven studies (6.4% of all studies) defined appropriate or rational polypharmacy, or recognised the distinction between appropriate and inappropriate medications [10, 79, 114–118]. These studies either defined polypharmacy using a brief description only (n = 3) [79, 115, 117] or used a brief description and polypharmacy tools such as the Beers criteria and the Medication Appropriateness Index (MAI) (n = 4 studies) [10, 114, 116, 118]. An example of a polypharmacy definition which recognised the use of appropriate and inappropriate medications is “polypharmacy ranges from the use of a large number of medications, to the use of potentially inappropriate medications, medication underuse and duplication” and “potentially inappropriate medications” [114]. Out of the two studies defining polypharmacy as “potentially inappropriate medications”, one study simply mentioned “potentially inappropriate medications” without further explanation [79] and the other study included examples of potentially inappropriate medications from existing literature such as duplication of medications, drug-drug interactions, medications used to treat side effects of other medications and medications which are unnecessary for a specific patient [10]. Only one study explicitly defined appropriate polypharmacy, which was defined as “the optimisation of medications for patients with complex and/or multiple conditions where medicine usage agrees with best evidence” [117].
Four studies (3.6%) used polypharmacy tools or criteria to identify potentially inappropriate medications [10, 114, 116, 118]. The Beers criteria as an indicator of potentially inappropriate medications were used in all four (three studies used Beers criteria 2003 and one used Beers criteria 1997) [10, 114, 116, 118]. One study used the Medication Appropriateness Index (MAI) and the Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS) [114]. None of the studies explicitly identified the need to distinguish between appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy based on the pharmacology of medications involved, how they interact with each other and comorbidities for a specific patient.
Of the 110 studies included in the review, only one highlighted the inconsistencies in the definitions of polypharmacy in the literature. The authors of this study suggested that polypharmacy be defined as patients visiting multiple pharmacies which may be associated with safety concerns relating to potential outcomes such as medication duplication, drug-drug interactions and adverse effects [112].
Discussion
The results of this systematic review show that there is large heterogeneity in the definition of polypharmacy; ranging from numerical counts only, numerical counts for a given duration of therapy or setting or descriptive, which included terms such as minor, moderate, major and excessive polypharmacy. The lack of a clear and universal definition of polypharmacy as well as terms such as minor, moderate major polypharmacy makes it challenging for healthcare professionals to assess and consider efficacy and safety issues within the clinical setting.
The most commonly reported category of definitions for polypharmacy and associated terms was numerical only. The most commonly used term was polypharmacy which was defined as five or more medications by 46.4% of studies (51 articles). There was a wide range of numerical only definitions of polypharmacy, ranging from two or more medications to 11 or more medications. However, the clinical basis for using a numerical count such as five or more medications to define polypharmacy and the potential of this to rationalise medication use and optimise health outcomes is not elucidated in most studies. It has been postulated that while the term polypharmacy has evolved over time, the basis for the definition is simply more drugs being prescribed or taken than are clinically appropriate in the context of a patient’s comorbidities [12]. It is commonly reported that as the number of prescribed drugs increases, so do the chances of adverse drug events and likelihood of harm [120]. However, the specific number of drugs taken is not itself indicative of appropriateness of therapy as all of the drugs may be clinically necessary and appropriate for the patient. Despite this, only one study argued that instead of using numerical counts of medications, clinicians should identify appropriateness of therapy, where potential benefits outweigh the potential harms [121]. There is a clear need towards adopting the term ‘appropriate polypharmacy’ in order to differentiate between the prescribing of ‘many’ and ‘too many’ drugs instead of a simple numerical count of medications, which is of limited value in practice [11, 12, 120–122].
Whilst the addition of duration of therapy or healthcare setting to a count of medicines in the definition of polypharmacy provided more specific definitions, it did not provide any further clarity or consistency. Five or more medications were again used in the definitions but with a period of time attached such as 90 days or more [104]. The use of duration in the definitions appeared to be included to identify those patients with longer term or chronic use of medications, potentially identifying those patients who might be at greatest risk of medication-related problems. Definitions incorporating a healthcare setting commonly used five or more medications as the count, but using a setting such as at the time of hospital discharge [106].These definitions were largely based on the dispensing data available to assess prevalence and incidence of polypharmacy, rather than an evidence based approach of determining appropriateness of therapy; the setting provided little addition to existing definitions of polypharmacy in a clinical sense of medication rationalisation and minimisation of harm.
A recent commentary on polypharmacy stated that while a large body of literature confirms the fact that patients are increasingly taking large numbers of medications, numerical definitions of polypharmacy do not ascertain the clinical appropriateness of therapy and the process of rationalising those medications [123]. The author argued that when each of the medications can be linked to practice guidelines for chronic conditions for a given patient, using a numerical cut-off to define polypharmacy becomes irrelevant. While the number of medications can be a starting point, medications should be assessed in terms of their indication, efficacy and potential for harm with each other (not in isolation) given pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics interactions, in order to facilitate deprescribing of inappropriate medications [123, 124]. Medications should be assessed for risks and benefits and the final combination of medications should be based on benefits outweighing the risks [124, 125]. Current literature is alluding to looking beyond single disease management guidelines and considering the patient’s complete scenario by considering all comorbidities and medications being prescribed for a given patient to consider the patient as a whole and focusing on improving the overall health [11, 12, 117, 120–122, 125].
While the use of multiple medicines may be clinically appropriate for some patients, it is important to identify those patients who may be at risk of adverse health outcomes as a result of inappropriate polypharmacy. Only seven studies recognised the distinction between appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy. This is crucial to facilitate the deprescribing of inappropriate medications and optimal use of appropriate medications. Consideration of comorbid conditions and other medications is required to make definitions clinically relevant, to facilitate medication assessment and rationalisation in every day practice. While a small number of studies (3.6%) used polypharmacy tools or criteria including the Beers criteria, MAI and HEDIS to identify potentially inappropriate medications to detect potentially inappropriate medications, the limitations of the tools and criteria in the everyday clinical setting were recognised [10, 114, 116, 118].The Beers criteria which was used in all four studies identified, is a commonly used prescribing assessment tool based on a list of potentially inappropriate medications to be avoided in the older population [126, 127]. However, it has recognised limitations such as requiring regular updates to ensure clinical relevance and including a list of outdated medications which may not be used in practice at that time.
Strengths and limitations
Strengths of this systematic review include the novelty of summarising the range of polypharmacy definitions available in literature. A comprehensive search strategy of three large and reliable databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE and Cochrane) was used, meaning that it is likely that all relevant articles were identified.
A limitation of this review is the inclusion of studies in English only which can cause information bias. While EMABSE, MEDLINE (Ovid) and Cochrane databases were searched, the absence of other databases such as Scopus could have introduced selection bias. Additionally articles from the year 2000 until present have been included. There may be clinically relevant definitions for polypharmacy which were added to literature prior to 2000 which have not been included in this review. While authors discussed the inclusion criteria and data being extracted, there is still the potential for confusion bias.
Conclusions
While the most commonly used definition of polypharmacy is being on five or more medicines, definitions are variable, which can cause confusion for researchers as well as clinicians in practice. Numerical definitions of polypharmacy do not account for specific comorbidities present and make it difficult to assess safety and appropriateness of therapy in the clinical setting. There is a need for an internationally agreed definition of polypharmacy. The results indicate the need for a shift towards the term ‘appropriate polypharmacy’ using a holistic approach of assessing medication use in context of comorbidities present, according to best available evidence in order to optimise health outcomes.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
NM is supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program (RTP).
Availability of data and materials
Majority of data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article. Any other datasets during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HEDIS
Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set
- MAI
Medication Appropriateness Index
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses
Authors’ contributions
NM conducted the primary screening of article titles and abstracts and categorisation of articles as: relevant, irrelevant or unsure. Articles which were categorised as ‘unsure’ were discussed with SS and GC. The final list of relevant articles was formed by consensus amongst all authors. Once all relevant articles were identified, NM reviewed full texts of all identified articles and categorised the different polypharmacy definitions. NM, SS, LK and GC made substantive intellectual contributions to the conception and design of the study as well as interpretation of data. NM drafted the initial manuscript and all authors were involved in critically reviewing and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Nashwa Masnoon, Email: Nashwa.Masnoon@mymail.unisa.edu.au.
Sepehr Shakib, Email: Sepehr.Shakib@sa.gov.au.
Lisa Kalisch-Ellett, Email: Lisa.Kalisch@unisa.edu.au.
Gillian E. Caughey, Email: Gillian.Caughey@unisa.edu.au
References
- 1.Salive ME. Multimorbidity in older adults. Epidemiol Rev. 2013:1–9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Roughead EE, Vitry AI, Caughey GE, Gilbert AL. Multimorbidity, care complexity and prescribing for the elderly. Aging Health. 2011;7(5):695–705. doi: 10.2217/ahe.11.64. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Caughey GE, Ramsay EN, Vitry AI, Gilbert AL, Luszcz MA, Ryan P, et al. Comorbid chronic diseases, discordant impact on mortality in older people: a 14-year longitudinal population study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2010;64(12):1036–1042. doi: 10.1136/jech.2009.088260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Marengoni A, Angleman S, Melis R, Mangialasche F, Karp A, Garmen A, et al. Aging with multimorbidity: a systematic review of the literature. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10(4):430–439. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2011.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.World Health Organization . Global age-friendly cities project. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Milton JC, Hill-Smith I, Jackson SHD. Prescribing for older people. BMJ. 2008;336(7644):606–609. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39503.424653.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Caughey GE, Roughead EE, Pratt N, Shakib S, Vitry AI, Gilbert AL. Increased risk of hip fracture in the elderly associated with prochlorperazine: is a prescribing cascade contributing? Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010;19(9):977–982. doi: 10.1002/pds.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Caughey GE, Roughead EE, Vitry AI, McDermott RA, Shakib S, Gilbert AL. Comorbidity in the elderly with diabetes: identification of areas of potential treatment conflicts. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87(3):385–393. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2009.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Maher RL, Hanlon J, Hajjar ER. Clinical consequences of polypharmacy in elderly. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(1):57–65. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2013.827660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bushardt RL, Massey EB, Simpson TW, Ariail JC, Simpson KN. Polypharmacy: misleading, but manageable. Clin Interv Aging. 2008;3(2):383–389. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S2468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Viktil KK, Blix HS, Moger TA, Reikvam A. Polypharmacy as commonly defined is an indicator of limited value in the assessment of drug-related problems. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63(2):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zarowitz BJ, Stebelsky LA, Muma BK, Romain TM, Peterson EL. Reduction of high-risk Polypharmacy drug combinations in patients in a managed care setting. Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy. 2005;25(11):1636–1645. doi: 10.1592/phco.2005.25.11.1636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Veehof LJG, Meyboom-De Jong B, Haaijer-Ruskamp FM. Polypharmacy in the elderly - a literature review. Eur J Gen Pract. 2000;6(3):98–106. doi: 10.3109/13814780009069956. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zia A, Kamaruzzaman SB, Tan MP. Polypharmacy and falls in older people: balancing evidence-based medicine against falls risk. Postgrad Med. 2015;127(3):330–337. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2014.996112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Alic A, Pranjic N, Ramic E. Polypharmacy and decreased cognitive abilities in elderly patients. Med Arh. 2011;65(2):102–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Frazier SC. Health outcomes and polypharmacy in elderly individuals: an integrated literature review. J Gerontol Nurs. 2005;31(9):4–11. doi: 10.3928/0098-9134-20050901-04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Garcia J, Vaz M, Poggi M. Estimated prevalence of contraindicated, severe and moderate interactions in ambulatory patients with polypharmacy in a healthcare provider in Uruguay. Clin Ther. 2015;1:145.
- 18.Patton D, Hughes C, Cadogan CA, Francis J, Gormley GJ, Kerse N, et al. Using the theoretical domains framework (TDF) to explore barriers and facilitators to adherence to prescribed medicines in community-based older adults. Int J Pharm Pract. 2015;23:11–12. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Trumic E, Pranjic N, Begic L, Becic F, Asceric M. Idiosyncratic adverse reactions of most frequent drug combinations longterm use among hospitalized patients with polypharmacy. Med Arh. 2012;66(4):243–248. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2012.66.243-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ziere G, Dieleman JP, Hofman A, Pols HAP, Van Der Cammen TJM, Stricker BHC. Polypharmacy and falls in the middle age and elderly population. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;61(2):218–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pasina L, Brucato AL, Falcone C, Cucchi E, Bresciani A, Sottocorno M, et al. Medication non-adherence among elderly patients newly discharged and receiving polypharmacy. Drugs Aging. 2014;31(4):283–289. doi: 10.1007/s40266-014-0163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.McMahon CG, Cahir CA, Kenny RA, Bennett K. Inappropriate prescribing in older fallers presenting to an Irish emergency department. Age Ageing. 2014;43(1):44–50. doi: 10.1093/ageing/aft114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bahat G, Tufan F, Bahat Z, Tufan A, Aydin Y, Akpinar TS, et al. Comorbidities, polypharmacy, functionality and nutritional status in Turkish community-dwelling female elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2014;26(3):255–259. doi: 10.1007/s40520-014-0229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Blyth FM, Naganathan V, Waite L, Seibel MJ, et al. Polypharmacy cutoff and outcomes: five or more medicines were used to identify community-dwelling older men at risk of different adverse outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2012;65(9):989–995. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.02.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Prithviraj GK, Koroukian S, Margevicius S, Berger NA, Bagai R, Owusu C. Patient characteristics associated with polypharmacy and inappropriate prescribing of medications among older adults with cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. 2012;3(3):228–237. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2012.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rasu RS, Iqbal M, Hanifi SMA, Moula A, Hoque S, Rasheed S, et al. Level, pattern, and determinants of polypharmacy and inappropriate use of medications by village doctors in a rural area of Bangladesh. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2014;6:515–521. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S67424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ahmed B, Nanji K, Mujeeb R, Patel MJ. Effects of polypharmacy on adverse drug reactions among geriatric outpatients at a tertiary care Hospital in Karachi: a prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):1–7. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Launay CP, De Decker L, Kabeshova A, Annweiler C, Beauchet O. Screening for older emergency department inpatients at risk of prolonged hospital stay: the brief geriatric assessment tool. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):1–10. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Haider SI, Ansari Z, Vaughan L, Matters H, Emerson E. Prevalence and factors associated with polypharmacy in Victorian adults with intellectual disability. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35(11):3071–3080. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2014.07.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Diez-Manglano J, Gimenez-Lopez M, Garces-Horna V, Sevil-Puras M, Castellar-Otin E, Gonzalez-Garcia P, et al. Excessive polypharmacy and survival in polypathological patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;71(6):733–739. doi: 10.1007/s00228-015-1837-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jiron M, Tapia M, Sandoval T, Palma D, Orellana S, Escobar L, et al. Potentially inappropriate medication among Chilean older inpatients: comparison between a 2012 beers criteria and STOPP. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2015;24:102–103. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jiron M, Herrada L, Rojas A, Lueiza A, Vega E, Buckel E, et al. Prevalence of potentially inappropriate medication prescribing among older adults in emergency Department in Chile. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2015;24:102. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fustinoni S, Renard D, Santos-Eggimann B, Seematter-Bagnoud L. Polypharmacy and associated factors among community-dwelling older persons in a Swiss canton. Clin Ther. 2015;37:39–40.
- 34.Jodar-Sanchez F, Malet-Larrea A, Martin JJ, Garcia-Mochon L. Lopez del Amo MP, Martinez-Martinez F, et al. cost-utility analysis of a medication review with follow-up Service for Older Adults with Polypharmacy in community pharmacies in Spain: the conSIGUE program. PharmacoEconomics. 2015;33(6):599–610. doi: 10.1007/s40273-015-0270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang M, Lu J, Hao Q, Luo L, Dong B. Does residing in urban or rural areas affect the incidence of polypharmacy among older adults in western China? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2015;60(2):328–333. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2014.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nguyen OK, Makam AN, Halm E. Use of safety net clinics for primary care among insured individuals in the United States: NAMCS 2006-2010. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30:295. doi: 10.1007/s11606-014-2969-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jensen LD, Andersen O, Hallin M, Petersen J. Potentially inappropriate medication related to weakness in older acute medical patients. Int J Clin Pharm. 2014;36(3):570–580. doi: 10.1007/s11096-014-9940-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mastromarino V, Casenghi M, Testa M, Gabriele E, Coluccia R, Rubattu S, et al. Polypharmacy in heart failure patients. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2014;11(2):212–219. doi: 10.1007/s11897-014-0186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lau DT, Mercaldo ND, Shega JW, Rademaker A, Weintraub S. Functional decline associated with polypharmacy and potentially inappropriate medications in community-dwelling older adults with dementia. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2011;26(8):606–615. doi: 10.1177/1533317511432734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lai SW, Su LT, Lin CH, Tsai CH, Sung FC, Hsieh DP. Polypharmacy increases the risk of Parkinson's disease in older people in Taiwan: a population-based study. Psychogeriatrics. 2011;11(3):150–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-8301.2011.00369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Richardson K, Ananou A, Lafortune L, Brayne C, Matthews FE. Variation over time in the association between polypharmacy and mortality in the older population. Drugs Aging. 2011;28(7):547–560. doi: 10.2165/11592000-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nobili A, Licata G, Salerno F, Pasina L, Tettamanti M, Franchi C, et al. Polypharmacy, length of hospital stay, and in-hospital mortality among elderly patients in internal medicine wards. The REPOSI study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67(5):507–519. doi: 10.1007/s00228-010-0977-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ariza G, Blanco E, Leon M, Gonzalez-Correa JA. Polipharmacy in primary care. Eur Geriatr Med. 2011;2:172. doi: 10.1016/j.eurger.2011.04.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cronin H, O'Regan C, Savva G, Richardson K, Donoghue O, Kenny RA. Polypharmacy and falls in older Irish adults. Ir J Med Sci. 2011;180:S355. doi: 10.1007/s11845-011-0689-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nomura K, Mendelsohn AB, Kusama M, Igarashi A, Akazawa M. Drug use patterns and predictors of polypharmacy among elderly, community-residing persons in hiroshima. Japan Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:301–302. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Blanco-Reina E, Ariza-Zafra G, Gonzalez-Correa JA, Leon-Ortiz M. Polypharmacy and pattern of medication use among the elderly. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;109:67. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00774.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Heuberger R. Polypharmacy and food-drug interactions among older persons: a review. J Nutr Gerontol Geriatr. 2012;31(4):325–403. doi: 10.1080/21551197.2012.729902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Slabaugh SL, Maio V, Templin M, Abouzaid S. Prevalence and risk of polypharmacy among the elderly in an outpatient setting: a retrospective cohort study in the Emilia-Romagna region. Italy. Drugs Aging. 2010;27(12):1019–1028. doi: 10.2165/11584990-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Slabaugh SL, Maio V, Abouzaid S, Templin M. Prevalence and predictors of polypharmacy amongst elderly patients: a population-based cohort study. Value Health. 2010;13(3):181. doi: 10.1016/S1098-3015(10)72883-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Grimmsmann T, Himmel W. Polypharmacy in primary care practices: an analysis using a large health insurance database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2009;18(12):1206–1213. doi: 10.1002/pds.1841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lapi F, Pozzi C, Mazzaglia G, Ungar A, Fumagalli S, Marchionni N, et al. Epidemiology of suboptimal prescribing in older, community dwellers: a two-wave, population-based survey in dicomano. Italy Drugs Aging. 2009;26(12):1029–1038. doi: 10.2165/11319390-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chan DC, Hao YT, Wu SC. Characteristics of outpatient prescriptions for frail Taiwanese elders with long-term care needs. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2009;18(4):327–334. doi: 10.1002/pds.1712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Haider SI, Johnell K, Thorslund M, Fastbom J. Analysis of the association between polypharmacy and socioeconomic position among elderly aged >77 years in Sweden. Clin Ther. 2008;30(2):419–427. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kuijpers MA, van Marum RJ, Egberts AC, Jansen PA, Group OS Relationship between polypharmacy and underprescribing. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;65(1):130–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Turner JP, Shakib S, Singhal N, Hogan-Doran J, Prowse R, Johns S, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with polypharmacy in older people with cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2014;22(7):1727–1734. doi: 10.1007/s00520-014-2171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Dhikav V, Sethi M, Singhal AK, Anand KS. Polypharmacy and use of potentially inappropriate medications in patients with dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2014;7(2):218–220. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Van Daalen AM, Van Leeuwen JA, Spruit-Van Eijk M, Achterberg WP. Polypharmacy as predictive factor for successful discharge in geriatric rehabilitation of stroke patients admitted to skilled nursing facilities. Eur Geriatr Med. 2014;5:242–243. doi: 10.1016/S1878-7649(14)70670-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nightingale G, Hajjar E, Swartz K, Andrel-Sendecki J, Hersh L, Chapman A. The prevalence of polypharmacy (PP) and potentially inappropriate medication (PIM) use in senior adult oncology (SAO) patients at an urban academic medical center. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2014;1:5.
- 59.Sheehan K, O'Shea D, Crowe M, Hughes G, Browne J. Potentially inappropriate medications in older hospitalised patients. Ir J Med Sci. 2014;1:328.
- 60.Shimizu K, Ishii S, Tanaka T, Shibasaki K, Akishita M, Iijima K. Use of potentially inappropriate medication and polypharmacy in community-dwelling japanese elderly population from the kashiwa study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:249–250. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sato I, Akazawa M. Polypharmacy and adverse drug reactions in Japanese elderly taking antihypertensives: a retrospective database study. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2013;5(1):143–150. doi: 10.2147/DHPS.S45347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Koper D, Kamenski G, Flamm M, Bohmdorfer B, Sonnichsen A. Frequency of medication errors in primary care patients with polypharmacy. Fam Pract. 2013;30(3):313–319. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cms070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lin HF, Lai SW, Liao KF, Muo CH, Hsientang Hsieh DP. Synergistic interaction between alcoholism and polypharmacy on the risk of falls in the elderly. Int J Gerontol. 2013;7(2):122–123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijge.2012.07.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pal A, Babbott S, Wilkinson ST. Can the targeted use of a discharge pharmacist significantly decrease 30-day readmissions? Hosp Pharm. 2013;48(5):380–388. doi: 10.1310/hpj4805-380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hovstadius B, Petersson G. The impact of increasing polypharmacy on prescribed drug expenditure-a register-based study in Sweden 2005-2009. Health Policy. 2013;109(2):166–174. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2012.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Blanco E, Ariza G, Ocana R, Leon M. Potential prescribing omissions vs. Polipharmacy among elderly patients Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;113:10. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Costa JO, Moura CS, Acurcio FA, Guimaraes MDC. Prevalence and correlates of polypharmacy among men and women with mental illness in Brazil: Pessoas project. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2013;22:461. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gonzalez-Muniz V, Soler-Rodenas A, Gil Manez E, Gea Rodriguez E. Spreading results of a previous start/stop study in older institutionalized residents: Impact on the prevalence of polypharmacy. Int J Clin Pharm. 2013;2:961.
- 69.Davila Barboza YR, Azana Fernandez EH. Polypharmacy in elderly patients: influence of hospitalization. Eur Geriatr Med. 2013;4:S189–SS90. doi: 10.1016/j.eurger.2013.07.633. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.O'Dwyer M, Peklar J, McCarron M, McCallion P, Henman M. Prevalence, patterns and factors associated with polypharmacy and excessive polypharmacy in an ageing population with intellectual disability in Ireland. Ir J Med Sci. 2013;182:210. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Carvalho MF, Romano-Lieber NS, Bergsten-Mendes G, Secoli SR, Ribeiro E, Lebrao ML, et al. Polypharmacy among the elderly in the city of Sao Paulo, Brazil - SABE study. Rev Bras Epidemiol. 2012;15(4):817–827. doi: 10.1590/S1415-790X2012000400013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Skov J, Bladbjerg EM, Sidelmann J, Vamosi M, Jespersen J. Plenty of pills: polypharmacy prevails in patients of a Danish anticoagulant clinic. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67(11):1169–1174. doi: 10.1007/s00228-011-1045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pugh MJ, Palmer RF, Parchman ML, Mortensen E, Markides K, Espino DV. Association of suboptimal prescribing and change in lower extremity physical function over time. Gerontology. 2007;53(6):445–453. doi: 10.1159/000119460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kim HA, Shin JY, Kim MH, Park BJ. Prevalence and predictors of polypharmacy among Korean elderly. PLoS One. 2014;9 (6) (e98043):1–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 75.Puvanendran R, Mamun K, Lim KH. Polypharmacy and unneccessary medication use in elderly patients discharged from acute hospitals to community hospital. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare. 2011;20:167. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Golchin N, Frank S, Isham L, Vince A, Meropol SB. Polypharmacy in the elderly. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:S296–S2S7. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Joaquim JJ, Campos MC. Drug use and knowledge in a elderly polimedicated Portuguese population. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;109:143. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chang YP, Huang SK, Tao P, Chien CW. A population-based study on the association between acute renal failure (ARF) and the duration of polypharmacy. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13(1):1–7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Chong J, Ang S. Polypharmacy in hospitalized older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:162. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mohammed S, Arabi A, El-Menyar A, Abdulkarim S, Awaisu A, Alqahtani A, et al. Impact of polypharmacy on adherence to evidence-based medications in patients who underwent percutenous coronary intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;2:3.
- 81.Best O, Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Naganathan V, McLachlan AJ. Investigating polypharmacy and drug burden index in hospitalised older people. Intern Med J. 2013;43(8):912–918. doi: 10.1111/imj.12203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kuzuya M, Masuda Y, Hirakawa Y, Iwata M, Enoki H, Hasegawa J, et al. Underuse of medications for chronic diseases in the oldest of community-dwelling older frail Japanese. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(4):598–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Schuler J, Duckelmann C, Beindl W, Prinz E, Michalski T, Pichler M. Polypharmacy and inappropriate prescribing in elderly internal-medicine patients in Austria. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(23–24):733–741. doi: 10.1007/s00508-008-1089-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hoffman J, Gleiberman S, Stern D, Osterweil D. Impact of a pharmacist in a specialized ambulatory care geriatric setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:139. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Dorks M, Herget-Rosenthal S, Schmiemann G, Hoffmann F. Polypharmacy and renal failure in nursing home residents: results of the inappropriate medication in patients with renal insufficiency in nursing homes (IMREN) study. Drugs Aging. 2016;33(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/s40266-015-0333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Herr M, Robine JM, Pinot J, Arvieu JJ, Ankri J. Polypharmacy and frailty: prevalence, relationship, and impact on mortality in a French sample of 2350 old people. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2015;24(6):637–646. doi: 10.1002/pds.3772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Nightingale G, Hajjar E, Swartz K, Andrel-Sendecki J, Chapman A. Evaluation of a pharmacist-led medication assessment used to identify prevalence of and associations with polypharmacy and potentially inappropriate medication use among ambulatory senior adults with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(13):1453–1459. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.7550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Dwyer LL, Han B, Woodwell DA, Rechtsteiner EA. Polypharmacy in nursing home residents in the United States: results of the 2004 national nursing home survey. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2010;8(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2010.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Onder G, Liperoti R, Foebel A, Fialova D, Topinkova E, Van der Roest HG, et al. Polypharmacy and mortality among nursing home residents with advanced cognitive impairment: results from the shelter study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013;14(6):450.7–45012. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Teymoorian SS, Pal A, Hayley D. Risk factors for 30-day hospital readmissions in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59:S188. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Barnett K, McCowan C, Evans JM, Gillespie ND, Davey PG, Fahey T. Prevalence and outcomes of use of potentially inappropriate medicines in older people: cohort study stratified by residence in nursing home or in the community. BMJ Qual Saf. 2011;20(3):275–281. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs.2009.039818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Jorgensen TL, Herrstedt J, Friis S, Hallas J. Polypharmacy and drug use in elderly Danish cancer patients during 1996 to 2006. J Geriatr Oncol. 2012;3(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2011.09.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Nagaraju B, Padmavathi GV, Dattathreya G. Prevalence and assessment of polypharmacy in Sri Devraj URS medical college & hospital. Kolar Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2012;4(1):488–493. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Borja-Oliveira CR, Lotti L. Polypharmacy and inappropriate prescribing in institutionalized elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:228. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Lu J, Yang M, Luo L, Hao Q, Dong B. Polypharmacy among nonagenarians/centenarians in rural China. Intern Med J. 2014;Part A. 44(12):1193-1199. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 96.Yu H, Foley SE, Crocker JA, Tuskey AG, Behm BW. Polypharmacy in patients with crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:445–6.
- 97.Cross RK, Wilson KT, Binion DG. Polypharmacy and Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;21(10):1211–1216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Fano V, Chini F, Pezzotti P, Bontempi K, Rossi A. Estimating prevalence of polypharmacy using data from a health administrative database: A comparison of results obtained with different algorithms. Eur J Epidemiol. 2013;1:1–7.
- 99.Housley BC, Stawicki SP, Evans DC, Jones C. Comorbidity-polypharmacy score predicts readmission in older trauma patients. J Surg Res. 2015;199(1):237–243. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Ferreira AR, Passos J, Martins S, Fernandes L. Comorbidity and polypharmacy in residential care and community-dwelling elderly in Portugal. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;25:S595. doi: 10.1016/S0924-977X(15)30837-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Veehof L, Stewart R, Haaijer-Ruskamp F, Jong BM. The development of polypharmacy. A longitudinal study. Fam Pract. 2000;17(3):261–267. doi: 10.1093/fampra/17.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Blyth FM, Naganathan V, Cumming RG, Handelsman DJ, et al. High-risk prescribing and incidence of frailty among older community-dwelling men. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91(3):521–528. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2011.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Jiron M, Pate V, Hanson LC, Funk MJ, Sturmer T. Prevalence and determinants of potentially inappropriate medication prescribing among older US adults according to STOPP criteria. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2015;24:105.
- 104.Narayan SW, Nishtala PS. Associations of potentially inappropriate medicine use with fall-related Hospitalisations and primary care visits in older new Zealanders: a population-level study using the updated 2012 beers criteria. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2015;2(2):137–141. doi: 10.1007/s40801-015-0020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kann IC, Lundqvist C, Luras H. Polypharmacy among the elderly in a list-patient system. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2015;2(3):193–198. doi: 10.1007/s40801-015-0036-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Nobili A, Marengoni A, Tettamanti M, Salerno F, Pasina L, Franchi C, et al. Association between clusters of diseases and polypharmacy in hospitalized elderly patients: results from the REPOSI study. Eur J Intern Med. 2011;22(6):597–602. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2011.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Chan DC, Hao YT, Wu SC. Polypharmacy among disabled taiwanese elderly: a longitudinal observational study. Drugs Aging. 2009;26(4):345–354. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200926040-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Nishtala PS, Salahudeen MS. Temporal trends in polypharmacy and hyperpolypharmacy in older new zealanders over a 9-year period: 2005-2013. Gerontology. 2015;61(3):195–202. doi: 10.1159/000368191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Vetrano DL, Landi F, De Buyser SL, Carfi A, Zuccala G, Petrovic M, et al. Predictors of length of hospital stay among older adults admitted to acute care wards: a multicentre observational study. Eur J Intern Med. 2014;25(1):56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2013.08.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Sganga F, Vetrano DL, Volpato S, Cherubini A, Ruggiero C, Corsonello A, et al. Physical performance measures and polypharmacy among hospitalized older adults: results from the crime study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18(6):616–621. doi: 10.1007/s12603-014-0029-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Franchi C, Cartabia M, Risso P, Mari D, Tettamanti M, Parabiaghi A, et al. Geographical differences in the prevalence of chronic polypharmacy in older people: eleven years of the EPIFARM-elderly project. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;69(7):1477–1483. doi: 10.1007/s00228-013-1495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Gillette C, Prunty L, Wolcott J, Broedel-Zaugg K. A new lexicon for polypharmacy: implications for research, practice, and education. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2015;11(3):468–471. doi: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2014.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Filkova M, Carvalho J, Norton S, Scott DL, Mant T, Cope AP, et al. Polypharmacy is a predictor of hospitalisation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. American College of Rheumatology and Association of Rheumatology Health Professionals Annual Scientific Meeting; San Francisco, CA 2015.
- 114.Maggiore RJ, Gross CP, Hurria A. Polypharmacy in older adults with cancer. Oncologist. 2010;15(5):507–522. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Medeiros-Souza P, dos Santos-Neto LL, Kusano LTE, Pereira MG. Diagnosis and control of polypharmacy in the elderly. Rev Saude Publica. 2007;41(6):1049–1053. doi: 10.1590/S0034-89102006005000050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Fulton MM, Allen ER. Polypharmacy in the elderly: a literature review. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2005;17(4):123–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1041-2972.2005.0020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Cadogan C, Ryan C, Gormley G, Passmore P, Francis J, Kerse N, et al. Dispensing appropriate polypharmacy to older people in primary care: a qualitative, theory-based study of community pharmacists' perceptions and experiences. Int J Pharm Pract. 2015;23:32. doi: 10.1111/ijpp.12182. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ballentine NH. Polypharmacy in the elderly: maximizing benefit, minimizing harm. Crit Care Nurs Q. 2008;31(1):40–45. doi: 10.1097/01.CNQ.0000306395.86905.8b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Rollason V, Vogt N. Reduction of polypharmacy in the elderly: a systematic review of the role of the pharmacist. Drugs Aging. 2003;20(11):817–832. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200320110-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Rambhade S, Chakarborty A, Shrivastava A, Patil UK, Rambhade A. A survey on Polypharmacy and use of inappropriate medications. Toxicol Int. 2012;19(1):68–73. doi: 10.4103/0971-6580.94506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Hanger C. Polypharmacy in primary care: managing a clinical conundrum. Best Practice Journal. 2014;64
- 122.Cadogan CA, Ryan C, Hughes CM. Appropriate Polypharmacy and medicine safety: when many is not too many. Drug Saf. 2016;39(2):109–116. doi: 10.1007/s40264-015-0378-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Steinman MA. Polypharmacy-time to get beyond numbers. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(4):482–483. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.8597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Scott IA, Hilmer SN, Reeve E, Potter K, Le Couteur D, Rigby D, et al. Reducing inappropriate polypharmacy: the process of deprescribing. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(5):827–834. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Gorard DA. Escalating polypharmacy. QJM. 2006;99(11):797–800. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcl109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Beers MH. Explicit criteria for determining potentially inappropriate medication use by the elderly. An update Arch Intern Med. 1997;157(14):1531–1536. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1997.00440350031003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Fick DM, Cooper JW, Wade WE, Waller JL, Maclean J, Beers MH. Updating the beers criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults: results of a us consensus panel of experts. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(22):2716–2724. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.22.2716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Majority of data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article. Any other datasets during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


