Figure 7.
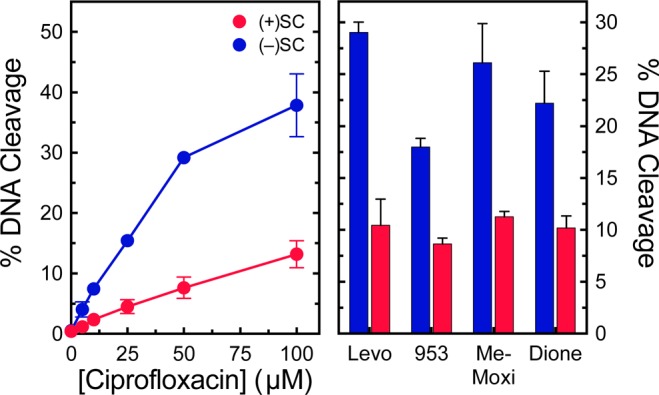
Gyrase maintains lower levels of cleavage complexes on positively supercoiled DNA in the presence of ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, and other quinolone-derived compounds. Left: Levels of cleavage complexes generated by gyrase on positively supercoiled [(+)SC DNA, red] or negatively supercoiled [(−)SC DNA, blue] in the presence of ciprofloxacin. Right: Levels of cleavage complexes generated by gyrase on positively supercoiled [(+)SC DNA, red] or negatively supercoiled [(−)SC DNA, blue] in the presence of levofloxacin (Levo, 100 μM), CP-115,953 (953, 100 μM), 8-methyl-moxifloxacin (Me-Moxi, 20 μM), and 3′-(AM)P-dione (dione, 20 μM). Error bars represent the standard deviations for at least three independent experiments.
