Abstract
Objective
Functional investigation of novel gene/protein targets associated with adipocyte differentiation or function heavily relies on efficient and accessible tools to manipulate gene expression in adipocytes in vitro. Recent advances in gene-editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 have not only eased gene editing but also greatly facilitated modulation of gene expression without altering the genome. Here, we aimed to develop and validate a competent in vitro adipocyte model of controllable functionality as well as multiplexed gene manipulation in adipocytes, using the CRISPRa “SAM” system and siRNAs to simultaneously overexpress and silence selected genes in the same cell populations.
Methods
We introduced a stable expression of dCas9-VP64 and MS2-P65, the core components of the CRIPSRa SAM system, in mesenchymal C3H/10T1/2 cells through viral delivery and used guide RNAs targeting Pparγ2, Prdm16, Zfp423, or Ucp1 to control the expression of key genes involved in adipocyte differentiation and function. We additionally co-transfected mature adipocytes with sgRNA plasmids and siRNA to simultaneously up-regulate and silence selected genes. Quantitative gene expression, oxygen consumption, fluorescence-activated cell sorting and immunocytochemistry served as validation proxies in pre- or mature adipocytes.
Results
CRISPRa SAM-mediated up-regulation of a key adipogenic gene, Pparγ2, was successfully achieved using selected sgRNAs targeting the Pparγ2 promoter region (i.e. up to 104 fold); this induction was long lasting and sufficient to promote adipogenesis. Furthermore, co-activation of Pparγ2 with either Prdm16 or Zfp423 transcripts drove distinct thermogenic gene expression patterns associated with increased or decreased oxygen consumption, respectively, mimicking typical characteristics of brite/beige or white cell lineages. Lastly, we demonstrated that up-regulation of endogenous genes in mature adipocytes was also easily and efficiently achieved using CRISPRa SAM, here exemplified by targeted Ucp1 overexpression (up to 4 × 103 fold), and that it was compatible with concomitant gene silencing using siRNA, allowing for bidirectional manipulation of gene expression in the same cell populations.
Conclusions
We demonstrate that the CRISPRa SAM system can be easily adopted and used to efficiently manipulate gene expression in pre- and mature adipocytes in vitro. Moreover, we describe a novel methodological approach combining the activation of endogenous genes and siRNA-mediated gene silencing, thus providing a powerful tool to functionally decipher genetic factors controlling adipogenesis and adipocyte functions.
Keywords: CRISPRa, siRNA, Adipogenesis, Adipocyte, Browning, Gene expression
Highlights
-
•
CRISPRa allows multiplex gene induction in pre- and mature adipocytes.
-
•
Adipocyte cell fate can be influenced using CRISPRa.
-
•
Bidirectional control of gene expression is achievable by combining CRISPRa with siRNA mediated knockdown.
1. Introduction
Fat tissue biology has become of significant interest over the last decades due to its central role in energy homeostasis and obesity-related metabolic pathology. In vitro models of adipogenesis have been extensively studied due to the close resemblance between in vitro adipogenesis and fat cell differentiation in vivo [1]. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) undergoing two distinct phases: commitment and terminal differentiation. Under specific environmental conditions, MSCs initiate adipogenic changes and become committed preadipocytes. In vitro, this commitment step can be induced by various hormonal stimuli such as the Bone Morphogenic Protein (BMP) and TGFβ family members, cell–cell contacts, or extra cellular matrix (ECM) composition and stiffness. The adipogenic induction step from pre- to mature adipocyte can be triggered, at least in murine cells, by insulin, glucocorticoids, and Protein Kinase A (PKA) activation [2]. Mechanistically, the terminal differentiation is characterized by the induction of a complex transcriptional program where the transcription factor Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ2 is considered a “master regulator” [3]. Thus, Pparγ2 expression is both necessary [4] and sufficient [5] to drive adipogenesis. Several other transcriptional factors are involved in the adipogenic process, including the CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP) [2], [6].
In contrast to classical white adipocytes, which primarily serve for energy storage, insulation, and adipokine secretion, brown and brite/beige adipocytes are capable of generating heat by bypassing the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation pathway through expression and activation of Uncoupling protein (UCP)-1, a process called non-shivering thermogenesis. PR domain Zink Finger Protein (PRDM)-16 has been shown not only to control the brown fat cell development [7], but also to drive the thermogenic program in white adipocytes both in vivo and in vitro [8], [9]. Conversely, Zink Finger Protein (ZFP)-423, initially found to control preadipocyte determination by regulating Pparγ2 expression [10], was recently shown to suppress the thermogenic program, including Ucp1 expression, in mature adipocytes [11]. Thus, the expression of key thermogenic genes such as Ucp1 can be controlled, at least partially, by a potent regulatory-signaling driven by Prdm16 or Zfp423. However, the complex processes involved in adipocyte commitment/maintenance, and particularly the synergistic effects of transcriptional regulators, are still poorly understood, calling for more accessible methods to manipulate gene expression in adipocytes.
Manipulating gene expression in pre- and mature adipocytes is fundamental to the loss- and gain-of-function studies investigating the role of a given gene in regulating adipogenesis or adipocyte function. While gene silencing is generally easily achievable, several obstacles become obvious in the conventional overexpression approaches; these include the limiting size of the DNA construct and uncontrollable expression levels, which often result in non-physiological concentrations of the protein and thus affecting its physical properties. Additionally, manipulating gene expression in the mature adipocyte is challenging due to inefficient adenovirus-mediated gene expression [12] associated with cytopathogenicity [13] or poor gene silencing efficacy using transfection-based siRNA delivery as observed in e.g. 3T3-L1 cells [14]. Furthermore, since retroviral-based approaches depend on integration of the virus into the host genome, the likelihood of perturbing endogenous genes, and thus inducing protein signaling artifacts, must be taken into account. Although preadipocytes are more susceptible to gene manipulations compared to mature lipid-containing adipocytes, strategies targeting the preadipocyte to elucidate gene functions in the mature state should be avoided due to possible interference with the differentiation process per se. Several modern technical improvements indeed eased the manipulation of gene expression in adipocytes, including electroporation [14], reverse transfection [15], various viral-based vector delivery systems [16] and a stable expression of the Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) [17], however, efficient and easily adaptable tools allowing for sustainable overexpression and bi-directional gene manipulation in mature fat cells are still largely limited.
The versatile gene-editing system CRISPR-Cas9, first used to edit the mammalian genome [18], [19], has several derived applications including repressing (CRISPRi) or activating (CRISPRa) endogenous genes [20]. Subtypes of the activator system rely on the enzymatically dead Cas9 enzyme coupled to a transactional activator – often the VP64 domain. An introduction of a single guide (sg) RNA targeting a specific promoter allows for manifold induction of an endogenous gene and, importantly, co-expression of multiple sgRNAs allows multiplex gene expression [21]. Recently, more advanced and potent versions of the CRISPRa systems have been engineered such as the Synergistic Activation Mediator (SAM) system, in which a third component consisting of the P65 subunit of the transcription factor NF-κB and the activator domain found on heat-shock factor 1 form a complex with the dCAS9-sgRNA to synergistically boost the transcription [21], making it one of the most powerful CRISPRa types developed thus far [22].
We hypothesized that the CRISPRa SAM system can be adopted as a tool for (co-)activation of key functional genes in preadipocytes, as well as for manipulation of gene expression in mature adipocytes.
We showed that endogenous Pparγ2-expression can be induced to varying levels, depending on sgRNA-promoter region binding position; importantly this expression was sufficient to promote adipogenesis and thus functionally affect cell morphology. Furthermore, we demonstrated that co-delivery of sgRNAs controlling the expression of either Prdm16 or Zfp423, in combination with a Pparγ2-targeting sgRNA, influenced the differentiation towards either a more brite/beige or white phenotype, respectively. Lastly, we showed that CRIPSRa SAM permitted the manifold induction of endogenous genes, here Ucp1, in mature adipocytes. This overexpression was successfully combined with siRNA-mediated gene silencing for other targets, thereby demonstrating efficient bidirectional manipulation of gene expression in mature fat cells after bypassing the differentiation period.
Thus, we report here a detailed in vitro protocol using easily accessible tools to manipulate gene expression in adipocytes. The major advantage of this model is that once the core components of the CRISPRa SAM system are established, it is easy to use and allows concurrent expression and silencing of virtually any gene of interest – either alone or in combination – in both pre- and mature adipocytes.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Reagents
C3H/10T1/2 clone 8 cells were obtained from ATCC (Wesel, Germany). Lenti dCas9-VP64 vector (#61425), lenti MS2-P65-HSF vector (#61426) and sgRNA cloning backbone (#61424) were from Addgene (Cambridge, MA, USA). Glutamine, Hygromycin, Blasticidin, 3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), human insulin, Rosiglitazone, Dexamethasone, CL 316,243, and siRNA (Mission®; SASI_Mm01_00036294) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Brøndby, Denmark); BODIPY, DMEM-high glucose, Penicillin-streptomycin, Sodium Pyruvate, Non-essential amino acids, Lipofectamine 3000 reagent, Lipofectamine RNAiMAX, DAPI (4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dihydrochloride) AlexaFluor 594 antibody, and ProLong Gold Antifade reagent were from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Slangerup, Denmark); BMP2 was from R&D Systems (Abingdon, UK); Mirus TransIT-X2 was from Kem-En-Tec (Taastrup, Denmark); anti-mouse UCP1 antibody Cat#UCP11-A (AH Diagnostics, Aarhus, Denmark); FCCP, Rotenone, Antimycin A, and XF assay medium modified DMEM were from Agilent Technologies (Copenhagen, Denmark); oligo DNAs from TagCopenhagen (Copenhagen, Denmark); Superfect was from Qiagen (Copenhagen, Denmark), and Lenti-X concentrator was from Clontech (Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France). iScript was from BIO-RAD (Copenhagen, Denmark); RNeasy was from Qiagen (Copenhagen, Denmark); Brilliant III SYBR green Master Mix was from AH Diagnostics.
2.2. Generation of the C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM stable cell line
Lentiviruses expressing dCas9-VP64 and MS2-P65-HSF1 were generated in 293 cells by co-transfection of the packaging plasmids psPAX.2 and psMD2.g using Superfect transfection reagent. Virus-containing supernatant was harvested 72 h post transfection and concentrated using Lenti-X concentrator. Sub-confluent C3H/10T1/2 cells were subsequently exposed to virus (with polybrene; 8 ug/ml) and selected with blasticidin (2.5 ug/ml) and hygromycin (200 ug/ml). Expression of the two components was verified using RT-qPCR. The resulting cell-line stably expressing the SAM components was termed “C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM”.
2.3. Single guide (sg)RNA design and cloning
sgRNAs were designed using the online tool: http://sam.genome-engineering.org/database/ and cloned into the backbone vector according to Konermann et al. [21]. Correct insertion was verified by sequencing. sgRNA sequences: Prdm16; GCGGCGGCGGCGCGACGAAG, Zfp423; GAGGAGGGTGAGGGTGGCGG, Ucp1; GGGAGTGACGCGCGGCTGGG. Pparγ2 sgRNAs are listed in Figure 1A.
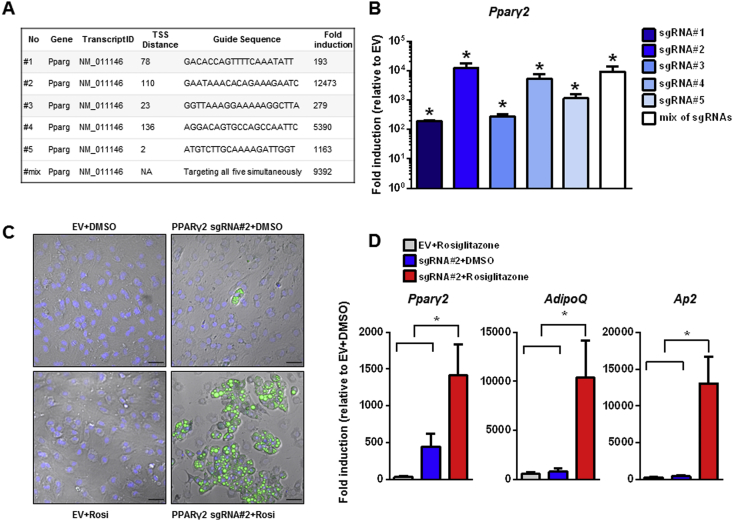
Figure 1.
Regulating endogenous Pparγ2 expression and adipogenesis. (A) Pparγ2 sgRNA sequences, distance to transcription start site (TSS) and fold induction. (B) Fold induction of Pparγ2 expression two days post transfection in the C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells using different sgRNAs binding distinct places on the Pparγ2 promoter. Differentiation of C3H/101/2-CRISPR-SAM cells using Pparγ2 sgRNA or empty vector (EV) stimulated with 5 μM Rosiglitazone or vehicle (DMSO) for 8 days assessed by (C) BODIPY (green) and DAPI (blue) staining or (D) RT-qPCR of the adipogenic markers Ap2 and Adiponectin and Pparγ2. Data are presented as means + SEM, n = 3, One-way ANOVA with Dunnett's test, *p < 0.05 versus EV transfected cells (B) or versus the Pparγ2 sgRNA transfected cells treated with Rosiglitazone (D).
2.4. Transfection of pre- and mature adipocytes
45,000 C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were seeded in 12-wells and transfected with 250 ng of sgRNA per well using TransIT-X2 reagent. Evaluation of sgRNA efficacy was done 48 h post transfection. 2,000–4,000 C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were seeded in the seahorse-wells and transfected with 40 ng of sgRNA per well using TransIT-X2 reagent. For transfection of mature adipocytes, 500,000 cells were reverse transfected with 2 ug of sgRNA using TransIT-X2, Lipofectamine- 3000 or RNAiMAX reagent. For bidirectional expression studies, a final concentration of 50 nM siRNA targeting the pyruvate kinase M [23] was added. Supplemental Figure 1 summarizes optimal details for transfection of pre- and mature adipocytes with sgRNA and siRNA allowing bidirectional manipulation of gene expression.
2.5. Cell culture and differentiation
C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were cultured in DMEM high glucose with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% Penicillin and Streptomycin, Blasticidin, and Hygromycin. For differentiation of C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells with Pparγ2 sgRNA, cells were given Rosiglitazone (5 μM) every other day starting 2 days after transfection. For co-expression studies Rosiglitazone (5 μM) was only added for 48 h following transfection. For transfection of mature adipocytes, C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were pre-treated with BMP2 (100 ng/ml) for four days, and differentiation was induced at confluence by Dexamethasone (5 μM), IBMX (500 μM), insulin (0.85 μM), and Rosiglitazone (1 μM) for two days followed by insulin (0.85 μM) and Rosiglitazone (1 μM) for another two days; at this point, the differentiated cells were ready for reverse transfection. Differentiated cells were kept in complete media (DMEM, 12% FBS, 1% Penicillin and Streptomycin, 1% extra Glutamine, 1% non-essential amino acids, 1% Sodium Pyruvate). For BODIPY/DAPI staining of pre- and mature adipocytes, BODIPY (0.1 ug/ml) and DAPI (0.5 ug/ml) were diluted in DMEM without serum and incubated for 30 min.
2.6. Quantitative PCR
RNA was extracted using RNeasy and cDNA synthesized using the iScript kit according to the manufacturer's instructions. Real-time PCR was performed using the CFX384 Real-Time System according to the supplier's manual (Bio-Rad). Each cDNA sample was run in duplicates and raw data were normalized to house keeping genes (18S or Tbp). Primer sequences are described in Supplemental Table 1.
2.7. Oxygen consumption
Real-time measurements of oxygen consumption rates (OCR) were performed using a Seahorse XF96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer (Agilent Technologies). The cell culture medium was changed 1 h before the first measurement to XF assay medium modified DMEM (Agilent Technologies) supplemented with 5 mM glucose and 2 mM l-glutamine and adjusted to pH 7.4. OCR was measured under basal conditions and after injection of 5 μM CL 316,243, 1 μM FCCP and 1 μM Rotenone combined with 1 μM Antimycin A. Area under the curve (AUC) was calculated from the time of the CL 316,243 injection (uncoupling) or the FCCP injection (maximal respiratory capacity).
2.8. Flow cytometry
Adipocytes were stained with BODIPY and DAPI for 30 min before trypsinization and resuspended in PBS + 1% BSA. Cells were forced through a cell-strainer and gated according to BODIPY intensity on a BD FACS Aria III sorter.
2.9. Immunocytochemistry
After trypsinization, cells were reseeded during the reverse transfection on gelatin-coated coverslips. Two days post-transfection, cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized (0.1% Triton-X in PBS), and blocked (1% FBS in PBS) prior to primary antibody (1:400) incubation overnight in a humidified chamber at 4 °C. UCP1 protein was visualized using a secondary AlexaFluor 594 antibody (1:1000) for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were counter-stained with BODIPY for 30 min at room temperature and DAPI (300 nM in PBS) for 10 min at room temperature for lipid and nuclear detection, respectively. Coverslips were mounted on glass slides with ProLong Gold Antifade. Imaging was performed using a confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM 780) with ×20 water-immersion or ×63 oil-immersion lenses; images were captured in Z-stacks (16–24 stacks per image; ZEN Black software) using identical exposure settings throughout conditions for qualitative comparisons.
2.10. Statistical analyses
All data are presented as means + SEM. Comparisons between groups were carried out by ANOVA followed by Dunnett-corrected or Sidak-corrected multiple comparisons or Bonferroni-corrected Student's t-test using Prism (GraphPad). P-values below 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
To increase the expression of endogenous genes in pre- and mature adipocytes, we first established a C3H/10T1/2 MSC line stably expressing the two core components of the SAM system (Supplemental Figure 2); the cell-line is here after referred to as “C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM”.
3.1. CRISPRa-mediated overexpression of the endogenous Pparγ2 gene promotes adipocyte differentiation
In an attempt to create a model of in vitro adipogenesis without the use of any differentiation cocktail, we assessed the ability of the CRISPRa SAM system to induce adipocyte differentiation by targeted transcription of endogenous Pparγ2 alone. Indeed PPARγ2 is considered a master transcription factor driving adipogenesis. In fact, ectopic overexpression and stimulation of PPARγ2 alone promotes adipogenesis [5]. We thus designed 5 different sgRNAs targeting different regions of the Pparγ2 promoter and tested their efficacy in inducing Pparγ2 expression (Figure 1A and B). We observed varying degrees of induction ranging from ∼200 fold (sgRNA#1) to more than 12,000 fold (sgRNA#2). A pool of all 5 sgRNAs simultaneously targeting the Pparg2 promoter did not exceed the over-expression level reached with sgRNA#2 alone, indicating no additive effect. Substantial differentiation was achieved in C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells transfected with sgRNA#2 and treated with the PPARγ2 agonist Rosiglitazone, as measured by BODIPY-staining (Figure 1C) and expression levels of classic adipogenic markers such as Adipocyte protein (Ap)-2 and AdipoQ (Figure 1D). These data show that CRISPRa SAM is effective in controlling the expression level of endogenous genes in preadipocytes, consequently affecting cell fate – here adipogenesis.
3.2. Multiplex gene induction influences the characteristics of mature adipocytes
Next, we investigated whether the CRISPRa SAM system could be used to promote or repress “brite/beige-like” characteristics by simultaneously targeting specific endogenous genes. As a proof of principle, we chose the brown-promoting factor Prdm16 [9] and the white-maintaining factor Zfp423 [11], which were previously shown to either increase or suppress the expression of thermogenic genes in adipocytes, respectively. We tested the efficacy of 5 sgRNAs for both Prdm16 and Zfp423 and selected the most potent guides for further studies (data not shown). We transfected cells with sgRNAs for these two factors either alone or in combination with the Pparγ2 sgRNA#2. In contrast to the “standard” differentiation cocktail containing Dexamethasone, IBMX and insulin (DMI), we induced adipogenesis by Rosiglitazone alone specifically targeting successfully transfected cells to differentiate. Thus, this system allows direct interrogation of the effects of gene multiplexing within the same cell.
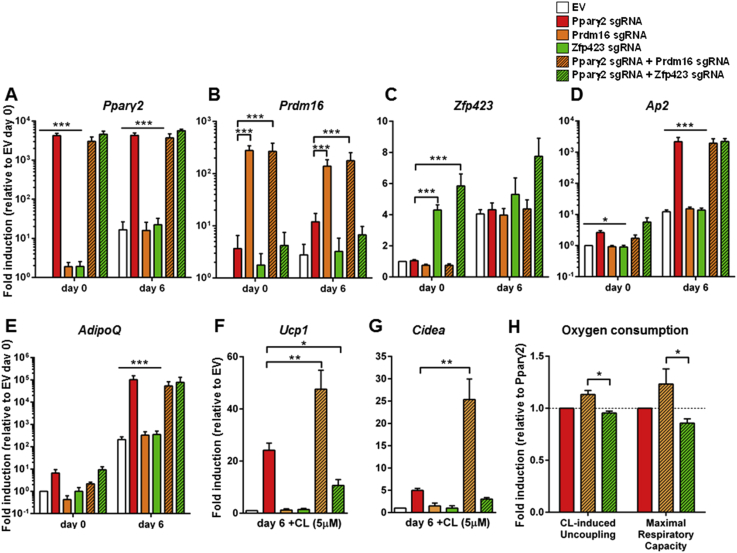
As shown in Figure 2A–C, the sgRNAs produced a robust induction of Pparγ2 (∼4000 fold), Prdm16 (∼275 fold) and a mild but significant up-regulation of Zfp423 (∼4 fold) compared to empty vector (EV) controls in preadipocytes 2 days post transfection. Interestingly, we observed that the basal expression levels of both Pparγ2 and Prdm16 were manifold lower than that of Zfp423 in the C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells, suggesting an inverse correlation between basal expression level and sgRNA efficacy. Activation of Prdm16 or Zfp423 did not affect overall differentiation levels in Pparγ2-transfected cells, as assessed by Ap2 and AdipoQ expression (Figure 2D and E). However, when differentiated cells were stimulated with the β3 adrenergic receptor agonist CL 316,243 (CL), induction of Ucp1 was significantly potentiated by co-activation of Prdm16 compared to Pparγ2 alone, and in contrast to Zfp423 co-expression, which blocked Ucp1 up-regulation (Figure 2F). A similar trend was observed for Cidea (Figure 2G). In line with these data, co-activation of Prdm16 with Pparγ2 showed increased CL-induced uncoupling and maximal respiratory capacity compared to co-activation of Zfp423 and Pparγ2 (Figure 2H). Thus, we demonstrated that CRISPRa SAM is suitable to be used for multiplex gene expression, and thereby for the control of thermogenic gene expression and mitochondrial respiration in adipocytes, independently of differentiation.
Figure 2.
Co-expression of either Prdm16 or Zfp423 with Pparγ2 regulates thermogenic characteristics in adipocytes. C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were transfected with EV, Pparγ2 and/or Prdm16/Zfp423 sgRNAs. Expression of (A) Pparγ2, (B) Prdm16, (C) Zfp423, (D) Ap2, and (E) AdipoQ were assessed by RT-qPCR. To stimulate the expression of thermogenic genes, C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were treated with 5 μM CL 316,243 for 6 h and (F) Ucp1 and (G) Cidea expression assessed by RT-qPCR. Oxygen consumption was assessed using Seahorse (H). Data are presented as means + SEM, n = 4 (n = 3 for Seahorse data), ANOVA with Dunnett's (A–E) or Sidak-corrected test (H) or Bonferroni-corrected Student's t-tests (F + G), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus the Pparγ2 sgRNA transfected cells.
3.3. Regulating endogenous gene expression in mature adipocytes
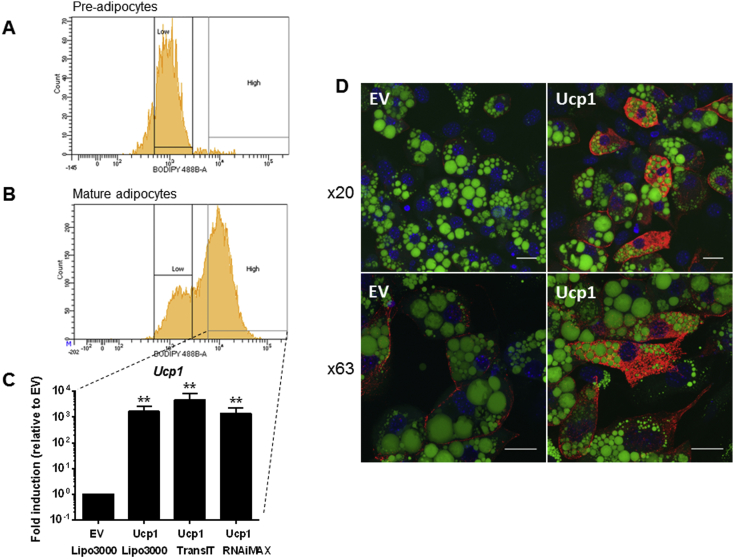
Next, we aimed at utilizing CRISPRa SAM to increase gene expression in mature adipocytes. To bypass the differentiation state, we modified previous siRNA-based transfection protocols for mature adipocytes [15], [23]. Briefly, this method utilizes reverse transfection (transfection of cells in suspension) with siRNAs in adipocyte cell-lines 6–9 days after induction and has proven highly efficient for gene silencing. We substituted the siRNAs with sgRNAs and employed a sgRNA-expressing plasmid targeting the Ucp1 promoter. Additionally, we tested three different transfection reagents (Lipofectamine3000, TransIT and RNAiMAX) for their efficiency to deliver the sgRNAs. Adipocytes were reverse transfected 8 days after differentiation start, followed by gene expression and immunocytochemical analyses two days post-transfection. Importantly, to demonstrate that the Ucp1 induction indeed occurred in mature cell population, we stained cells with BODIPY to collect low BODIPY-fluorescence cells (non-adipocytes) and high BODIPY-fluorescence cells (adipocytes) by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Preadipocytes were almost exclusively found in the group of cells with “low” BODIPY-fluorescence intensity (Figure 3A), whereas the majority of the differentiated cells appeared in the “high” BODIPY-fluorescence intensity group (Figure 3B). Importantly, reverse transfection of the Ucp1 sgRNA led to a robust induction of Ucp1 (more than 4 × 103 fold for TransIT reagent), regardless of transfection reagent in the mature adipocytes population (Figure 3C). Lastly, using immunofluorescence against UCP1 protein, we confirmed that reverse transfection of the Ucp1-sgRNA indeed leads to up-regulation of UCP1 protein levels in mature adipocytes, with UCP1 immunoreactivity predominantly detected in lipid-laden BODIPY-positive cells transfected with Ucp1 sgRNA (Figure 3D, Supplemental Videos 1A+B). Hence, CRISPRa SAM is appropriate for endogenous RNA and protein overexpression in mature adipocytes. Of note, delivering sgRNAs as U6-expression cassettes [24], thereby reducing the size from ∼3 kb to just ∼430 bp, resulted in the induction of Ucp1 expression, although the efficacy was lower compared to the plasmid-based delivery (Supplemental Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Induction of Ucp1 mRNA and protein in mature adipocytes. C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were differentiated to mature adipocytes and reverse transfected with Ucp1 sgRNA or EV. Cell sorting was used to select mature adipocytes. (A) Preadipocytes stained with BODIPY elicited a “low” BODIPY-fluorescence intensity compared to (B) mature adipocytes. (C) After reverse transfection the mature adipocyte fraction was collected and endogenous Ucp1 expression examined by RT-qPCR. (D) Mature adipocytes, reverse-transfected with either EV or Ucp1 sgRNA, were fixed and stained for UCP1 protein expression (red), nuclei (blue) and lipids (green) using immunofluorescence and BODIPY/DAPI staining. 20× and 63× magnifications are shown. n = 3–4, Bonferroni-corrected Student's t-test, **p < 0.01 versus EV transfected cells.
Supplementary videos related to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2017.07.001.
The following are the Supplementary data related to this article:
EV transfected adipocytes.
Ucp1 sgRNA transfected adipocytes.
3.4. Bidirectional gene regulation in mature adipocytes
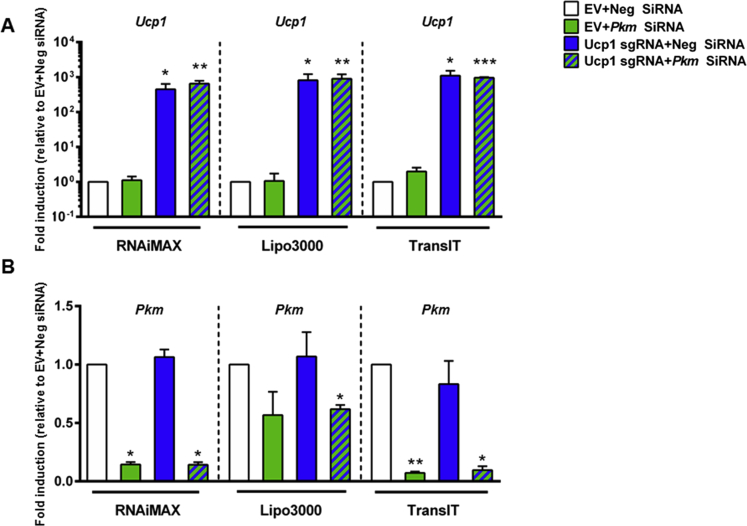
Almost any change in cell homeostasis is a net result of changes in numerous genes being either induced or repressed. Therefore, we tested whether the CRISPRa SAM system could be used in combination with gene silencing using siRNA in mature adipocytes. As an example, we used the Ucp1 sgRNA in combination with siRNAs targeting pyruvate kinase M (Pkm), which we have previously shown to be efficient in mature adipocytes [23]. We also tested the efficacy of the three transfection reagents described in Figure 3 to efficiently deliver both sgRNAs and siRNAs in mature cells. As shown in Figure 4A, Ucp1 expression was robustly and equally induced following transfection of its sgRNA using any of the transfection reagents. However, the level of Pkm knockdown was dependent on the transfection reagent. Indeed, 89% and 83% knockdown of Pkm were obtained with TransIT and RNAiMAX, respectively, when combined with Ucp1 overexpression, whereas Lipofectamine 3000 produced a 49% reduction. These data demonstrate that bidirectional gene expression can be achieved by combining the CRISPRa SAM system with siRNAs in the same transfection when a compatible transfection reagent is used.
Figure 4.
Bidirectional gene regulation in mature adipocytes. C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells were differentiated to mature adipocytes and reverse transfected with a combination of Ucp1 sgRNA, EV sgRNA, Pkm siRNA, or a negative control siRNA. Expression of (A) Ucp1 and (B) Pkm were measured by RT-qPCR. Data are presented as means + SEM, n = 3, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus EV transfected cells with same transfection reagent.
4. Discussion
Genetic loss- and gain-of-function studies are invaluable to elucidate the function of genes and proteins. Gene silencing using RNAi revolutionized loss-of-function studies and has been extensively used to study adipocyte biology [14], [25]. However, gene overexpression has remained a challenge, especially in mature adipocytes, due to poor plasmid delivery and time-consuming experimental procedures such as subcloning and virus production. Other pitfalls such as gene size limitations and lack of control over the ectopic expression level further complicate the feasibility of overexpression studies.
While CRISPRa has some drawbacks including limited activation of genes with high baseline expression [21], [22], and possible sgRNAs off-targets similar to RNAi-based strategies relying on complementary nucleotides should not be ignored, a number of advantages greatly favor this technique. Indeed, we show here that CRISPRa SAM allows for overexpression of endogenous genes for which the level of overexpression can be controlled by selecting appropriate sgRNAs of various efficacies. Importantly, we also demonstrated that CRISPRa SAM can be applied in mature adipocytes, thus overcoming many caveats of the existing conventional overexpression tools. It is of interest that different levels of expression can be achieved by selecting different sgRNAs (e.g. Pparγ2 from ∼200-fold to ∼12,000-fold compared to EV controls); as this allows to adjust the induction of a given gene of interest to mirror a physiological or pathological situation. Furthermore, endogenous promoters frequently control several isoforms of the same gene, including intronic microRNAs [26]. Thus, the CRISPRa should allow the induction of all promoter-based products, mimicking the activation of a biological pathway to a largely better extent compared to ectopic overexpression of an isoform of interest.
Here, not only did we prove that CRIPSRa SAM is a useful tool to overexpress genes in adipocyte cell-lines, we also provided a model of controlling brite/beige-like characteristics such as induction of Ucp1 expression and increased mitochondrial respiration. To study key adipogenic genes, we chose the C3H/10T1/2 cells, which were established in 1972 from clone 8 derived from mouse embryo cells [27]. This is an MSC cell line with the potential to differentiate into both myofibers [28] and adipocytes with either white or brown characteristics e.g. through treatment with the BMP cytokines such as BMP2,-4 or -7 [29], [30], [31]; however, any adipocyte cell-line may be engineered to express the two CRISPRa SAM components. Based on the work by Tontonoz, Hu, and Spiegelman [5], in which they elegantly demonstrated that retroviral delivery of Pparγ2 was sufficient to drive adipogenesis in NIH 3T3 cells, we reproduced this finding through overexpression of the endogenous Pparγ2 gene. Furthermore, by manipulating the endogenous expression of either Prdm16 [9] or Zfp423 [10], we provide an accessible, easy, and quick system for manipulating brite/beige-like characteristics without exogenous gene delivery, hence yielding higher physiological relevance. Indeed, the robust induction of Prdm16 potentiated the effect of CL-treatment on both Ucp1 and Cidea expression, whereas Zfp423 overexpression repressed it.
Interestingly, PRDM16 was recently shown to drive Ucp1 expression through binding to the subunit MED-1 of the Mediator complex at the 2.5 kb upstream enhancer [32]. Whether a similar mechanism lies behind the induction of Cidea is currently not known. Gupta et al. [10] also showed that similarly to Prdm16 [7], ectopic expression of Zfp423 drives Pparγ2 expression. We observed a similar trend (Figure 2A); however, this was not sufficient to induce differentiation in this cell line as measured by Ap2 and AdipoQ expression.
Of note, ectopic expression of MyoD1 in C3H/10T1/2 cells has been shown to drive myogenesis [33]. Thus, similarly to this Ppargγ2-driven adipogenic commitment model, overexpression of MyoD1, and/or (co-)expression of novel myogenic players in C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cells may provide a suitable model to assess whether a given target affects myogenic processes in this cell line.
The multiplex feature of CRISPRa allows better interrogation of novel gene/protein targets and high throughput-based data, including commonly used OMICs-based discoveries to predict key pathways regulated in a given physiological or pathological condition of interest. The majority of validation/follow-up studies seek causation by addressing the action of one selected target, either through overexpression and/or knockdown; however, this may be too simplistic – as illustrated by the necessity of co-ectopic expression of PPARγ/RXRα with PRDM16 to uncover the full transcriptional capacity of PRDM16 [7]. In stark contrast to the standard single gene-targeted approach, our method grants synergistic and bidirectional gene expression in both pre- and mature adipocytes allowing for more sophisticated experimental designs to study complex multi-player signaling pathways such as adipogenesis, in which a multitude of genes is regulated for the process to occur [34]. Complementing a modified CRISPRa approach to allow gene activation and gene knockout simultaneously [35], our method is the first to combine CRISPRa with siRNA, thereby allowing easy to use, efficient, and reversible gene manipulation without altering the genome. Employing the simultaneous and bi-directional gene expression manipulation tool we described here, therefore, can serve as a powerful resource for assessing the role of key target genes involved in the regulation of adipocyte cell fate and function.
5. Conclusion
We report a methodological advancement using a combination of simple and robust tools to selectively increase the expression of endogenous genes in both pre- and mature adipocytes. We propose it to be used not only as an alternative method to current gain-of-function studies in vitro, but also as a new method for studying bidirectional gene expression. From a therapeutic standpoint, the CRISPRa system also yields a high potential for clinical applications since it does not require changes in the host genome.
Funding sources
ML was a recipient of a research grant from the Danish Council for Independent Research and Sapere Aude Research Talent: DFF – 5053-00112. KP, MSI, PSSP and BE were supported by Novo Nordisk Foundation. The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research is an independent research center at the University of Copenhagen partially funded by an unrestricted donation from the Novo Nordisk Foundation (http://www.metabol.ku.dk).
Author contributions
ML and BE conceived and designed the study; ML wrote the manuscript with input from KP and BE. ML, KP, and MSI carried out the main experimental work and interpreted the results. PSSP provided technical assistance throughout the study. BE supervised the work. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Resource sharing
The C3H/10T1/2-CRISPRa-SAM cell line and sgRNA-containing plasmids are available upon request.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Zach Gerhart-Hines for his scientific input. We acknowledge the Flow Cytometry Core Facility, University of Copenhagen, for cell sorting and the Core Facility for Integrated Microscopy, University of Copenhagen, for assisting with confocal imaging.
Footnotes
Supplementary data related to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2017.07.001.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following are the supplementary data related to this article:
References
- 1.Rosen E.D., Spiegelman B.M. Molecular regulation of adipogenesis. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 2000;16:145–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cristancho A.G., Lazar M.A. Forming functional fat: a growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2011;12:722–734. doi: 10.1038/nrm3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tontonoz P., Spiegelman B.M. Fat and beyond: the diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2008;77:289–312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.061307.091829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kubota N., Terauchi Y., Miki H., Tamemoto H., Yamauchi T., Komeda K. PPAR gamma mediates high-fat diet-induced adipocyte hypertrophy and insulin resistance. Molecular Cell. 1999;4:597–609. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tontonoz P., Hu E., Spiegelman B.M. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell. 1994;79:1147–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lefterova M.I., Haakonsson A.K., Lazar M.A., Mandrup S. PPARgamma and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2014;25:293–302. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Seale P., Bjork B., Yang W., Kajimura S., Chin S., Kuang S. PRDM16 controls a brown fat/skeletal muscle switch. Nature. 2008;454:961–967. doi: 10.1038/nature07182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Seale P., Conroe H.M., Estall J., Kajimura S., Frontini A., Ishibashi J. Prdm16 determines the thermogenic program of subcutaneous white adipose tissue in mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2011;121:96–105. doi: 10.1172/JCI44271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Seale P., Kajimura S., Yang W., Chin S., Rohas L.M., Uldry M. Transcriptional control of brown fat determination by PRDM16. Cell Metabolism. 2007;6:38–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gupta R.K., Arany Z., Seale P., Mepani R.J., Ye L., Conroe H.M. Transcriptional control of preadipocyte determination by Zfp423. Nature. 2010;464:619–623. doi: 10.1038/nature08816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shao M., Ishibashi J., Kusminski C.M., Wang Q.A., Hepler C., Vishvanath L. Zfp423 maintains white adipocyte identity through suppression of the beige cell thermogenic gene program. Cell Metabolism. 2016;23:1167–1184. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Orlicky D.J., Schaack J. Adenovirus transduction of 3T3-L1 cells. The Journal of Lipid Research. 2001;42:460–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Carlotti F., Bazuine M., Kekarainen T., Seppen J., Pognonec P., Maassen J.A. Lentiviral vectors efficiently transduce quiescent mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Molecular Therapy. 2004;9:209–217. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2003.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jiang Z.Y., Zhou Q.L., Coleman K.A., Chouinard M., Boese Q., Czech M.P. Insulin signaling through Akt/protein kinase B analyzed by small interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100:7569–7574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1332633100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kilroy G., Burk D.H., Floyd Z.E. High efficiency lipid-based siRNA transfection of adipocytes in suspension. PLoS One. 2009;4 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gomez-Banoy N., Lo J.C. Genetic manipulation with viral vectors to assess metabolism and adipose tissue function. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2017;1566:109–124. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6820-6_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ross S.A., Song X., Burney M.W., Kasai Y., Orlicky D.J. Efficient adenovirus transduction of 3T3-L1 adipocytes stably expressing coxsackie-adenovirus receptor. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2003;302:354–358. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cong L., Ran F.A., Cox D., Lin S., Barretto R., Habib N. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science. 2013;339:819–823. doi: 10.1126/science.1231143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mali P., Yang L., Esvelt K.M., Aach J., Guell M., DiCarlo J.E. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science. 2013;339:823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.1232033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gilbert L.A., Horlbeck M.A., Adamson B., Villalta J.E., Chen Y., Whitehead E.H. Genome-scale CRISPR-mediated control of gene repression and activation. Cell. 2014;159:647–661. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Konermann S., Brigham M.D., Trevino A.E., Joung J., Abudayyeh O.O., Barcena C. Genome-scale transcriptional activation by an engineered CRISPR-Cas9 complex. Nature. 2015;517:583–588. doi: 10.1038/nature14136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chavez A., Tuttle M., Pruitt B.W., Ewen-Campen B., Chari R., Ter-Ovanesyan D. Comparison of Cas9 activators in multiple species. Nature Methods. 2016;13:563–567. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Isidor M.S., Winther S., Basse A.L., Petersen M.C., Cannon B., Nedergaard J. An siRNA-based method for efficient silencing of gene expression in mature brown adipocytes. Adipocyte. 2016;5:175–185. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2015.1111972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ran F.A., Hsu P.D., Wright J., Agarwala V., Scott D.A., Zhang F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nature Protocols. 2013;8:2281–2308. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhou Q.L., Park J.G., Jiang Z.Y., Holik J.J., Mitra P., Semiz S. Analysis of insulin signalling by RNAi-based gene silencing. Biochemical Society Transactions. 2004;32:817–821. doi: 10.1042/BST0320817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ruby J.G., Jan C.H., Bartel D.P. Intronic microRNA precursors that bypass Drosha processing. Nature. 2007;448:83–86. doi: 10.1038/nature05983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Reznikoff C.A., Brankow D.W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Research. 1973;33:3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pinney D.F., Emerson C.P., Jr. 10T1/2 cells: an in vitro model for molecular genetic analysis of mesodermal determination and differentiation. Environmental Health Perspectives. 1989;80:221–227. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8980221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Huang H., Song T.J., Li X., Hu L., He Q., Liu M. BMP signaling pathway is required for commitment of C3H10T1/2 pluripotent stem cells to the adipocyte lineage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106:12670–12675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906266106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tseng Y.H., Kokkotou E., Schulz T.J., Huang T.L., Winnay J.N., Taniguchi C.M. New role of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in brown adipogenesis and energy expenditure. Nature. 2008;454:1000–1004. doi: 10.1038/nature07221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xue R., Wan Y., Zhang S., Zhang Q., Ye H., Li Y. Role of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in the differentiation of brown fat-like adipocytes. American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2014;306:E363–E372. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00119.2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Iida S., Chen W., Nakadai T., Ohkuma Y., Roeder R.G. PRDM16 enhances nuclear receptor-dependent transcription of the brown fat-specific Ucp1 gene through interactions with Mediator subunit MED1. Genes & Development. 2015;29:308–321. doi: 10.1101/gad.252809.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tapscott S.J., Davis R.L., Thayer M.J., Cheng P.F., Weintraub H., Lassar A.B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988;242:405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jang M.K., Lee S., Jung M.H. RNA-seq analysis reveals a negative role of KLF16 in adipogenesis. PLoS One. 2016;11 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dahlman J.E., Abudayyeh O.O., Joung J., Gootenberg J.S., Zhang F., Konermann S. Orthogonal gene knockout and activation with a catalytically active Cas9 nuclease. Nature Biotechnology. 2015;33:1159–1161. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
EV transfected adipocytes.
Ucp1 sgRNA transfected adipocytes.