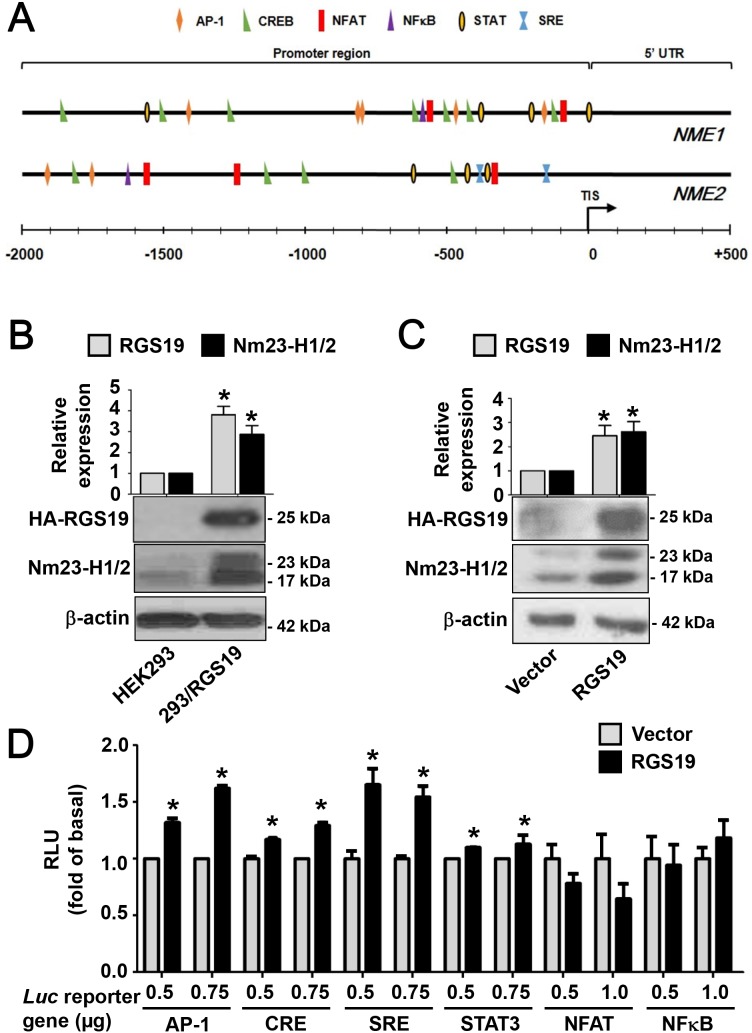
Figure 1. RGS19 upregulates the protein level of Nm23-H1/2 and activates the transcription factors AP-1, CRE, SRE and STAT3.
(A) Locations of G protein signaling-associated transcription factor binding sites on NME1/2 promoter regions were predicted by the MatInspector program. TIS, translational initiation site; 5’-UTR, 5’-untranslated region. (B) Lysates of HEK293 and 293/RGS19 cells were subjected to Western blot for detecting Nm23-H1/2 and HA-RGS19 with anti-Nm23H1/2 and anti-HA antibodies, respectively. Representative immunoblots are shown. β-actin was used as an internal control; quantification of mean band intensities by Image J is shown on top with the values normalized against the control (parental cell). *RGS19 and Nm23-H1/2 expressions in 293/RGS19 cells are significantly higher than those of HEK293 cells (P < 0.05). (C) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with cDNAs encoding HA-RGS19 or vector (pcDNA3.0) and lysates were assayed as in B. (D) Activation of transcriptional factors by transient expression of RGS19 in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transiently co-transfected with either HA-RGS19 or vector in combination with different luciferase reporter genes (at 0.5, 0.75, or 1.0 μg) as indicated. Transfected cells were cultured for 24 h and lysates were subjected to luciferase assay. Data shown are relative values of luciferase normalized to the respective vector controls. Each bar represents the average of triplicate determinations ± S.E. RLU, relative luciferase unit. *Significantly higher than the vector control (P < 0.05).