Abstract
Background
One-stage direct-to-implant immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) is performed simultaneously with breast cancer resection. We explored indications, techniques, and outcomes of IBR to determine its feasibility, safety, and effectiveness.
Material and Methods
We reviewed the available literature on one-stage direct-to-implant IBR, with or without acellular dermal matrix (ADM), synthetic mesh, or autologous fat grafting. We analyzed the indications, preoperative work-up, surgical technique, postoperative care, outcomes, and complications.
Results
IBR is indicated for small-to-medium nonptotic breasts and contraindicated in patients who require or have undergone radiotherapy, due to unacceptably high complications rates. Only patients with thick, well-vascularized mastectomy flaps are IBR candidates. Expandable implants should be used for ptotic breasts, while anatomical shaped implants should be used to reconstruct small-to-medium nonptotic breasts. ADMs can be used to cover the implant during IBR and avoid muscle elevation, thereby minimizing postoperative pain. Flap necrosis, reoperation, and implant loss are more common with IBR than conventional two-staged reconstruction, but IBR has advantages such as lack of secondary surgery, faster recovery, and better quality of life.
Conclusions
IBR has good outcomes and patient-satisfaction rates. With ADM use, a shift from conventional reconstruction to IBR has occurred. Drawbacks of IBR can be overcome by careful patient selection.
1. Background
Since skin- and nipple-sparing mastectomies have proven to be oncologically safe, an increasing number of patients with invasive breast cancer undergo breast reconstruction [1, 2]. Indeed, for women who have undergone a mastectomy, breast reconstruction provides psychosocial as well as aesthetic benefits [3–5]. Breast reconstruction can be either allogeneic (implant-based), autologous (locoregional flap, free flap), or a combination of both. Reconstruction can be performed simultaneously with mastectomy as a one- or two-stage procedure, or it can be delayed and performed as a two-stage procedure.
Implant-based reconstructions account for almost 65% of all breast reconstructions in the USA [6, 7]. This type of reconstruction is considered safe, cost effective, and reliable; furthermore, it can be performed in women with a wide variety of comorbid conditions [8, 9]. One-stage immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) is a method to reconstruct a definitive breast mound at the time of oncologic resection without the need for tissue expansion or tissue expander/implant exchange. However, the likelihood of requiring secondary procedure (e.g., scar revision, autologous fat grafting, nipple-areola complex (NAC) reconstruction, and matching surgery to the contralateral breast) is not lower after one-stage IBR than after two-stage implant-based IBR [10]. Given the fewer hospital accesses required, IBR may be convenient for both patients and the healthcare system [10], and this partially explains the increasing number of IBRs performed [11, 12]. The recent introduction of acellular dermal matrices (ADMs) and synthetic meshes has also widened the indications for IBR [13–15].
Advocates of IBR highlight its advantages, which include elimination of the expander-to-implant exchange, fast recovery, better lower pole definition, and lower costs [16–18]. However, several studies have reported higher rates of complications and implant loss with direct-to-implant IBR [19–22].
Given the conflicting reports, we aimed to identify from the current literature the indications, techniques, and outcomes of IBR in order to help surgeons in choosing and performing the most suitable breast reconstruction for each patient. We reviewed the available literature on one-stage direct-to-implant IBR, with or without acellular dermal matrix (ADM), synthetic mesh, or autologous fat grafting. We analyzed the indications, preoperative work-up, surgical technique, postoperative care, outcomes, and complications, including the need for secondary procedures, of one-stage direct-to-implant IBR.
2. General Considerations
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women [23]. In 2011, it was estimated that nearly 230,000 women were diagnosed with invasive breast cancer in the USA alone [24]; 79% of the 96,277 patients who underwent breast reconstructions underwent alloplastic-based breast reconstruction [25]. Following advances in screening tests and molecular genetics, many young women (aged <45 years) with inherited predisposition genes for breast cancer are choosing to undergo bilateral prophylactic mastectomy [26]. Even women with early-stage breast cancer suitable for breast-conserving surgery may choose to undergo therapeutic mastectomy and contralateral prophylactic mastectomy [27]. These young women may obtain more pleasing cosmetic outcomes by means of autologous reconstruction but may not agree to undergo major surgery, with more scar formation at the donor site. Alloplastic breast reconstruction can ensure satisfactory cosmetic outcomes in such patients with far less-invasive surgery. Furthermore, more than 50% of breast cancer cases occur in elderly women who may opt for a less-invasive, one-stage procedure associated with early discharge, rapid recovery, and a prompt return to everyday life [28].
3. Acellular Dermal Matrix and Synthetic Mesh
Dieterich et al. [14] and Salzberg [29] first reported the use of acellular dermal matrices (ADMs) for breast reconstruction. This strategy gradually spread among reconstructive surgeons, even though early studies reported higher complication rates with ADMs than with conventional breast reconstruction [30, 31]. However, recent works have highlighted a reduction in complication rates, as a result of the increased familiarity of plastic surgeons with the use of ADMs [32–34]. Currently, members of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons use ADMs in more than 50% of their breast reconstructions [35].
ADMs are made of extracellular matrix structures and basement membrane complexes of either of fetal bovine, porcine, or human cadaver origin [36]. ADMs lack immunogenic epitopes and are therefore revascularized, recellularized, and integrated into host tissue with no evidence of encapsulation, resorption, or contracture [37–41]. In breast reconstructions with submuscular implants, ADMs can be used as pectoral expanders to cover the inferolateral pole of the implant and prevent the need for elevation of the surrounding muscle, thus reducing postoperative pain [18, 42–44]. ADMs can also be used as an internal bra to completely cover the implant during subcutaneous breast reconstruction, anchoring the implant to the chest wall and providing an additional layer of tissue supports, thereby relieving the pressure on the mastectomy flaps [45–47].
Synthetic meshes were recently introduced as an alternative to ADMs in alloplastic breast reconstruction and have shown promising results [15, 47–50]. Synthetic meshes are safe and have aesthetic benefits similar to those obtained with ADMs (improved inframammary fold definition, enhanced lower pole shape and projection) without the drawbacks of high cost and local policy restrictions.
Some authors have proposed that ADMs be substituted with autologous dermal grafts harvested at the time of mastectomy as a horizontally oriented ellipse in the lower abdomen if a preexisting scar is present or from the contralateral breast if a reductive mastoplasty is planned [51–53]. In a prospective study, Lynch et al. [51] compared the outcomes of dermal autograft- and ADM-assisted breast reconstructions. They found that the major and minor complication rates as well as total costs were higher in the ADM group, while cosmetic outcomes did not significantly differ between the ADM and autograft groups. Moreover, histological analysis showed higher integration of the autograft into the surrounding tissue, with extensive revascularization and vessel ingrowth.
4. Immediate Breast Reconstruction
4.1. Indications
Direct-to-implant IBR aims to create a naturally appearing breast mound in a single-stage surgery without harnessing the mastectomy flap blood supply. Preoperative and intraoperative evaluations commonly guide surgeons' decision to perform IBR. Young, thin, and athletic women with small-to-medium, nonptotic breasts are best suited for IBR as well as SSM [54]. However, skin-reducing mastectomy has broadened the indications of IBR to patients with a very large breast skin envelope [55]. Nevertheless, patients undergoing unilateral reconstruction must be aware that they may eventually need to undergo contralateral matching surgery [56].
ADM-assisted IBR enables the reconstruction of breasts with varying degrees of ptosis [57]. In patients with a discrepancy between muscular coverage and native breast skin-flap coverage, ADMs can be used to lengthen the muscular tissue plane to match the overlying skin envelope. Thus, the reconstructed breast may be left with a natural pseudo-ptosis, a well-defined inframammary fold, and enhanced inferior pole projection, which better match the contralateral native breast [58]. The estimated mastectomy weight should not exceed 600 g [58]. Characteristics of the breast soft tissue, skin elasticity of the trunk and overall body habitus are commonly evaluated preoperative parameters [10].
As with expander-based breast reconstruction, direct-to-implant IBR is reported to have higher complication rates in patients who are scheduled to undergo adjuvant radiotherapy or who have a history of local irradiation; hence, the indication of IBR in such patients remains controversial [59]. Unacceptably high complication rates (i.e., capsular contracture and infection) have been reported with implant-based reconstruction followed by radiation therapy [17, 18, 60], and delayed autologous tissue reconstruction after mastectomy radiation therapy is generally regarded as the best approach [61]. Nevertheless, increased surgical expertise and improved target breast irradiation can pave the way to a safer implant-based breast reconstruction even when adjuvant radiotherapy is required [62–66]. Conflicting reports are available regarding the use of ADMs when adjuvant radiation therapy is required [67–71].
Well-vascularized mastectomy skin flaps with an at least 1 cm thick subcutaneous layer are unanimously considered to be essential to achieve successful outcomes [10, 72]. The intraoperative judgment of the surgeon is recognized as the single most important factor influencing the success of direct-to-implant IBR [17, 34, 73, 74]. Indeed, only patients with good-quality mastectomy flaps (thick and well-vascularized) should be candidates for IBR to minimize the chances of mastectomy flap necrosis [58]. The advent of intraoperative objective assessment tools such as real-time perfusion mapping assisted by SPY® (Novadaq Technologies Inc., Bonita Springs, FL, USA) has helped surgeons in this key decision-making stage [75].
4.2. Preoperative Planning
The oncologic surgeon and the plastic surgeon should perform the preoperative evaluation together. Breast cancer localization, dimensions, and nipple-areola involvement must be cautiously evaluated to decide between skin-sparing mastectomy and nipple-sparing mastectomy. Preoperative markings should favorably locate the mastectomy scar, while preserving the required skin envelope. The borders of the breast must be marked with the patient standing upright, paying particular care in the marking of the inframammary fold. The upper-pole border should match the level of the contralateral breast, which can be delineated by gently compressing the contralateral breast against the chest wall. Nipple-to-sternal notch distance, areola-to-inframammary fold distance, and breast width are measured at this stage. Skin quality, elasticity, and thickness must also be carefully assessed. When contralateral matching surgery is planned, preoperative markings are also drawn on the contralateral breast, depending on the procedure required. At this stage, surgeons should also bear in mind the type and dimensions of the implant required [13, 76].
When performing unilateral reconstruction in elderly women with ptotic breasts, permanent expandable implants provide good long-term cosmetic and oncologic outcomes [10, 77]. Becker 25 and 50 (round) and Becker 35 (shaped) implants (Mentor, Johnson & Johnson Medical Ltd., Wokingham, Berkshire, UK) as well as anatomical Style 150 implants (Allergan Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) are commonly used permanent expandable biodimensional implants. These implants differ not only in terms of the silicone elastomer used but also in terms of their capacity; the Becker series implants can be overinflated for at least 1 month and subsequently deflated. This strategy allows matching to the contralateral perimenopausal breast by creating a pseudo-ptotic effect, lowering the position of the NAC, and lessening the final projection [10, 77, 78].
Anatomic, shaped, silicone-filled implants are best suited for recreating small-to-mild nonptotic breasts or when ADM slings are required [13]. Indeed, silicone-filled implants tend to lie flat against the chest wall; hence, anatomic shapes provide appropriate volume restoration without excessive superior-pole fullness. Even round implants can achieve good results; however, there is a major risk of developing unpleasing superior border step-off. Finally, the base diameter of the implant should match that of the contralateral breast, for both round and anatomically shaped implants [13]. Given the complexity of this decision-making stage, surgical planning and virtual simulator systems have been devised to train surgeons outside of the “apprenticeship model” [79–81].
4.3. Surgical Technique
The mastectomy can be a simple skin-sparing or skin-reducing NAC-sparing mastectomy [82, 83]. The mastectomy should be conducted in the space between the subcutaneous adipose tissue and the glandular parenchyma so as not to damage the subdermal plexus of the mastectomy flaps and jeopardize their blood supply [47]. The inframammary fold is a crucial landmark of the breast and must be conserved during mastectomy [84, 85]. If damaged, it has to be restored using 4-5 braided silk or Vicryl® sutures [56].
Once the mastectomy is completed, the surgeon should assess skin-flap viability by evaluating skin-flap color, capillary refill, temperature, turgor, and dermal bleeding [86]. Fluorescein angiography and laser-assisted indocyanine green angiography can also be used to objectively assess the vitality of the mastectomy flaps [87, 88]. If the flaps are deemed viable, direct-to-implant IBR can be performed.
At this stage, the reconstructive surgeon has various options. An implant pocket can be created in either the submuscular (partial or complete) or subcutaneous plane, and ADMs, synthetic meshes, or dermal autografts can be employed. Advocates of muscular coverage of implants aim to maximize vascularity and prevent contact between the implant and the overlying mastectomy incision [56, 85]. With the patient in a supine position and the ipsilateral upper arm adducted at 60°, the pectoralis major muscle is dissected from its thoracic and sternal attachments, till the second rib [85]. A subpectoral pocket is superiorly dissected in a relatively avascular plane, following the preoperative markings. Raising either the serratus anterior muscle completely or its lower slips only (to reduce postoperative pain) can achieve complete muscular coverage of the implants [89].
A partial submuscular pocket can also be created by elevating the serratus anterior muscle in a plane within the muscle along with its overlying fascia, leaving the rib cage covered by a portion of the muscle [82]. Inferiorly, elevating the fascia of the anterior rectus muscle completes the pocket. When a skin-reducing mastectomy is performed, the dermal-adipose inferior flap is used for coverage of the lower pole [90]. The submuscular pocket can also be completed inferiorly with a rectangular 6 cm × 16 cm piece of ADM, synthetic mesh, or dermal autograft. The chosen graft is sutured to the inferior and lateral chest walls and to the inferior portion of the pectoralis muscle, acting as a hammock for the lower pole of the chosen implant. ADMs, synthetic meshes or dermal autografts should be accurately tailored so as to prevent seromas, which may result from discrepancies between muscular coverage and the native breast skin envelope, contour irregularities, or dead space [57]. The adequacy of the position of the inframammary fold and shape of the breast mound are assessed intraoperatively by placing the patient in a sitting position. The definitive implant can also be positioned in the subcutaneous pocket resulting from the mastectomy.
The implant is completely wrapped by an ADM or synthetic mesh so as to suture together the membrane. The ADM-wrapped implant can be positioned into the subcutaneous pocket and secured in place to the underlying muscles by means of apical, medial, and lateral absorbable stitches [58].
Once the pocket has been created, it must be thoroughly irrigated, and accurate hemostasis must be performed. Various irrigant solutions have been proposed to prevent subclinical pocket infection, which is regarded as a possible etiology of capsular contracture [56]. The triple antibiotic of Adams (comprising 80 mg gentamicin, 1 g cefazolin, and 50,000 U bacitracin [or equivalent vancomycin], diluted in 500 mL normal saline), single antibiotic solution, diluted povidone-iodine, and normal saline are the most frequently adopted [91–93]. However, no comparative study on the efficacy of different irrigation solutions has been carried out yet [56].
Two suction drains are usually positioned, one over the pectoralis major and under the mastectomy skin flap, and the other one at the level of the inframammary fold, coursing medially [57]. If the implant pocket is subcutaneous, only one suction drain in the inframammary fold can be positioned [58]. The skin is commonly closed in two layers [94] (Figures 1 and 2).
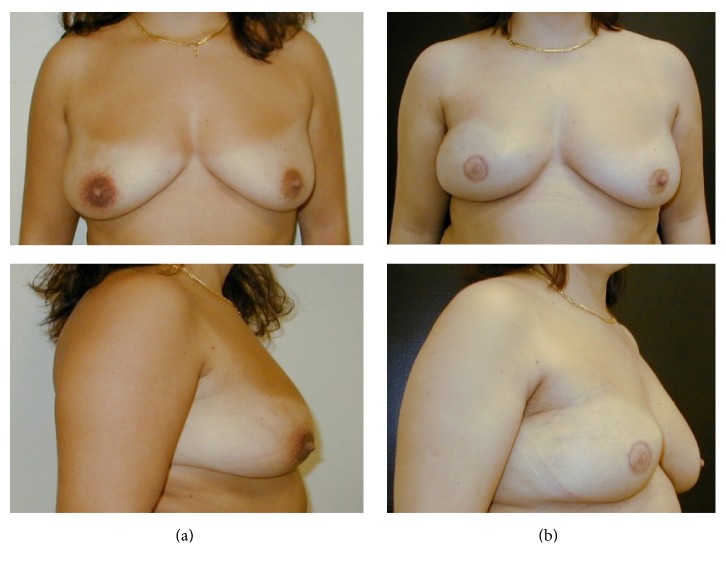
Figure 1.
Preoperative view (a) and postoperative result (b) after right breast skin-sparing mastectomy with radial lateral incision and one-stage implant-based reconstruction after. Nipple-areola complex was reconstructed with local flap and tattooing. Matching surgery of the left breast was not required.
Figure 2.
Preoperative view (a) and postoperative result (b) after right breast nipple-sparing mastectomy with radial lateral incision and one-stage implant-based reconstruction. Left breast augmentation with periareolar incision and vertical extension was also performed.
4.4. Postoperative Care
Intravenous prophylactic antibiotics are commonly given to patients undergoing direct-to-implant IBR 60 min or less prior to the time of incision [95]. Antibiotic administration should not be continued beyond the first 24 postoperative hours since there is no recommendation for prolonged postoperative antibiotics unless drainage is present [56, 96, 97]. In cases where a drain is still in place after 24 postoperative hours, the role of antibiotics is controversial, and surgeons should adhere to the hospital guidelines on antibiotic administration [98–100]. Drains should be left in place until the output is less than 20 mL/24 h, lowering the thresholds from the classic 30 mL/24 h [95]. Soft compression dressings in a nonconstricting surgical bra are used postoperatively to uniformly distribute very gentle pressure over the breast. It has been demonstrated that these measures can reduce both seroma and infection rates [95]. Postoperative pain is usually not long lasting and can be easily managed with painkillers. A supportive brassiere should be worn for the first postoperative month. Patients should avoid intense physical activity for the first 2-3 weeks.
5. Secondary Procedure
NAC reconstruction can be performed as early as the 2nd postoperative month by means of local flaps; tattooing is delayed till 6 weeks after NAC reconstruction [101]. Autologous fat grafting is a safe and effective secondary procedure after direct-to-implant IBR. Autologous fat grafting can ameliorate any residual contour deformities by correcting visible implant edges, asymmetry with the contralateral breast, and upper outer defects underneath the anterior axillary fold [102]. Furthermore, owing to the presence of a stem cell population, the so-called adipose-derived stem cells, fat grafts display regenerative potential and therapeutic effects that go beyond simple filling capability [103–107]. Adipose-derived stem cells can differentiate into multiple cell lineages and secrete paracrine factors [108–112]. Thus, angiogenesis and wound healing are strongly enhanced, leading to higher fat-graft survival as well as dermal and subcutaneous tissue regeneration [113–115]. Moreover, autologous fat grafting has been demonstrated to have positive effects on radiation-induced soft-tissue damage in reconstructed breasts [116, 117]. Fat grafts can thicken the subcutaneous tissue and improve the texture of the irradiated skin by enhancing its vascular supply [118].
6. Complications
Direct-to-implant IBR has the same postoperative complications as two-stage tissue expander/implant-based breast reconstructions [74]. However, two-stage breast reconstruction with submuscular implant pocket has traditionally been the reconstructive strategy of choice, given its demonstrated safety, reliability, and effectiveness [119–121]. Direct-to-implant IBR has recently gained popularity as a consequence of improvements in implant design and the advent of ADMs/synthetic meshes [17, 122–124].
Reports on the complication rates of direct-to-implant IBR are controversial, and these rates are supposed to be higher than those of tissue expander/implant-based reconstruction [19, 21, 22, 30]. Recently, Basta et al. [74] conducted the first head-to-head meta-analysis of the outcomes and complication rates of direct-to-implant IBR versus two-stage submuscular tissue expander/implant-based breast reconstruction. The pooled absolute incidence rates of infection (7.8% versus 7.4%), seroma (6.8% versus 7.1%), hematoma (4.3% versus 5.2%), and capsule contracture (13.5% versus 13.8%) did not significantly differ between direct-to-implant and two-stage tissue expander/implant-based reconstructions. However, the incidence rates of flap necrosis (8.6% versus 6.7%), reoperation (17.9% versus 13.8%), and implant loss (14.4% versus 8.7%) were significantly higher for direct-to-implant reconstructions. Unfortunately, there was no mention of whether the reconstructions were implant-based alone or ADM/mesh-assisted; therefore, no subgroup analysis was performed. Similarly, secondary procedure rates were not reported.
Jagsi et al. [65] retrospectively evaluated a series of 14,894 women undergoing either autologous reconstruction or direct-to-implant IBR with a mean follow-up of 2 years. Patients with autologous reconstruction reported higher wound complication rates (9.5% versus 4.4%) as well as higher infection rates (20.7% versus 20.5%) than patients who underwent implant-based reconstructions. Adjuvant radiation therapy was given to 35% of patients and was not associated with any infection in any surgical group. Among patients who received postoperative radiotherapy, the rate of implant removal was higher in the alloplastic breast reconstruction group (21.9% versus 13.1%), while the rate of fat necrosis was higher in the autologous reconstruction group (14.7% versus 8.7%).
Sbitany et al. [125] published a systematic review and meta-analysis of complications associated with ADM-assisted breast reconstruction compared with traditional implant-based musculofascial flaps. Skin-flap necrosis was the most common complication (10.9%), followed by seroma (6.9%), infection (5.7%), cellulitis (2%), and hematoma (1.3%). The rate of hematoma was 1.3% (95% CI, 0.6%–2.4%). Implant removal was necessary in 5.1% of cases. However, the rate of observed capsule contracture was very low (0.58%). ADM-assisted reconstruction was associated with a four times higher rate of seroma formation and nearly 3 times higher rates of infection and reconstruction failure than non-ADM-assisted breast reconstruction. Capsule contracture occurred in 0.58% of ADM-assisted breast reconstructions, while in the literature, the reported incidence of capsule contracture after breast reconstructions without the use of ADM ranges between 3% and 18% [126–129]. Ibrahim et al. [33] retrospectively analyzed 19,100 alloplastic breast reconstructions, of which 3301 were ADM-assisted. They reported no statistically significant difference in the overall complication rate between breast reconstruction with and without ADMs. Furthermore, they confirmed that a high body mass index, diabetes, history of smoking, radiotherapy, and steroid administration are associated with higher complication rates.
Salibian et al. [47] reviewed subcutaneous implant-based breast reconstructions with ADMs or meshes. The major complications (i.e., wide infection, complete NAC necrosis, complete flap necrosis, explantation, and Baker grade III/IV capsule contracture) were low in the majority of studies. Explantation (6%) was the most frequent complication, followed by seroma (4.9%), partial NAC necrosis (3.9%), wound healing problems (3.6%), and hematoma (2.4%). Direct-to-implant IBR and tissue expander/implant-based breast reconstruction had similar complication rates, even though statistical analysis could not be performed. However, interestingly, direct-to-implant IBR had higher explantation rates (6.0% versus 0%), while tissue expander/implant-based breast reconstruction had a higher rate of minor infection (16.0% versus 0%). Furthermore, subgroup analysis was performed between mesh- and ADM-assisted reconstructions. The most frequent complication of mesh-assisted reconstruction was minor infection (6.3%), followed by partial NAC necrosis (4.2%) and explantation (3.1%). ADM-assisted reconstructions were associated with higher complication rates: seroma formation, 8.9%; explantation, 6.7%; and partial NAC necrosis, 5%. The most common patient complaints after subcutaneous implant-based breast reconstruction were palpable implants (8.5%), rippling (4.7%), and visible implants (4.3%). Secondary procedures were needed in 21.4% of patients, where autologous fat grafting accounted for 11.9% of patients, and implant exchange was performed in 14.3% of patients [45, 130, 131].
7. Outcome
Direct-to-implant IBR has several potential advantages over traditional two-staged tissue expander/implant-based reconstruction such as avoidance of a second operation and no need for tissue expansion [74, 132, 133]. Indeed, final implant placement after expansion takes place in the 9th postoperative month on average. This span of time required to obtain the final result can be perceived as a significant burden to many patients. Direct-to-implant IBR implies a shorter time to reach the final reconstruction, which reduces the number of clinical visits and the sense of mutilation perceived, potentially improving patient quality of life [134, 135]. Nevertheless, direct-to-implant IBR has considerable wound issues such as mastectomy flap necrosis, which can vary from minor epidermolysis to full-thickness necrosis [74, 136]. When mastectomy flap necrosis occurs during expansion, partial deflation of the expander can allow surgical debridement and salvage reconstruction without expander removal. Conversely, direct-to-implant IBR more often requires implant exchange, which potentially compromises the final aesthetic outcome, lengthens recovery times, decreases the patient's quality of life, and delays the administration of adjuvant therapies, while increasing the economic costs to the patient and the healthcare system.
These aspects must be clearly discussed with patients in the preoperative setting, and the surgeon should highlight not only the possible shorter reconstructive course of direct-to-implant IBR but also its higher rate of reoperation and/or initial reconstructive failure. Intraoperative objective assessment tools such as real-time perfusion mapping assisted by SPY (Novadaq Technologies Inc., Bonita Springs, FL, USA) can lower the complication rate [89]. However, these devices are often expensive, time-consuming, and not readily available at all surgical centers [137].
Submuscular pockets provide additional coverage to implants [137]. However, muscle dissection can increase postoperative pain, and the submuscular location of the implant can result in action deformity and a less natural cosmetic outcome [138–141]. Furthermore, submuscular pockets can weaken even modest shoulder joint function, significantly impacting daily activities [139, 142, 143].
ADM-assisted reconstruction can reduce the operative time and speed postoperative recovery as a result of lower postoperative pain and donor-site morbidity [45]. Rapid return to work and prompt administration of adjuvant therapy when needed are further advantages. Moreover, the ADM/mesh-assisted wrapping technique is a muscle sparing-technique that can achieve good cosmetic outcome while preserving the pectoralis major muscle elevation and occurrence rate of other minor complications [144]. This approach is particularly suited for elderly patients where fast recovery and lower morbidity are mandatory for a better quality of life [58].
ADMs can cost between $2100 and $3400, depending on the size of the dermal sheet required [145]. However, it has been found that ADMs are a cost-effective therapeutic adjunct for breast reconstruction due to their better long-term aesthetic and clinical benefits [146, 147]. Furthermore, ADM-assisted reconstructions do not have significantly higher overall complication rates than non-ADM-assisted reconstructions but have lower long-term capsule contracture rates [33, 148, 149]. Given the uncertainties regarding the indications and contraindications, an algorithmic approach to aid decision-making with regard to the use of ADMs has been proposed [150, 151]. Indeed, judicious selection of candidates, careful evaluation of postmastectomy skin flaps, and consideration of possible risk factors have demonstrated the benefits of ADM-assisted breast reconstructions [57].
8. Conclusions
Direct-to-implant IBR is attractive given the good aesthetic outcomes, shared advantages with convention two-stage reconstruction, and patient-satisfaction rate achieved [152–154]. With the development of ADMs, a paradigm shift from conventional two-stage breast reconstruction to direct-to-implant one-stage IBR has been seen [135]. Nevertheless, the latter surgery has some drawbacks that we believe can be overcome by careful patient selection and strict adherence to surgical technique. However, larger comparative studies and better-defined selection criteria and outcomes reporting are needed to develop appropriate indications for performing successful direct-to-implant IBR.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- 1.Jeevan R., Cromwell D. A., Browne J. P., et al. Findings of a national comparative audit of mastectomy and breast reconstruction surgery in England. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2014;67(10):1333–1344. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2014.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Juhl A. A., Christensen S., Zachariae R., Damsgaard T. E. Unilateral breast reconstruction after mastectomy–patient satisfaction, aesthetic outcome and quality of life. Acta Oncologica. 2017;56(2):225–231. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2016.1266087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jagsi R. Patient satisfaction with postmastectomy breast reconstruction: a comparison of saline and silicone implants. Cancer. 2010;116:5584–5591. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pusic A. L., Klassen A. F., Scott A. M., Klok J. A., Cordeiro P. G., Cano S. J. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: The BREAST-Q. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2009;124(2):345–353. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181aee807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhong T., McCarthy C., Min S., et al. Patient satisfaction and health-related quality of life after autologous tissue breast reconstruction: a prospective analysis of early postoperative outcomes. Cancer. 2012;118(6):1701–1709. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cemal Y., Albornoz C. R., Disa J. J., et al. A paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction: Part 2. the influence of changing mastectomy patterns on reconstructive rate and method. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2013;131(3) doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31827cf576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Albornoz C. R., Bach P. B., Mehrara B. J., et al. A paradigm shift in U.S. Breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2013;131(1):15–23. doi: 10.1097/prs.0b013e3182729cde. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hirsch E. M., Seth A. K., Dumanian G. A., et al. Outcomes of tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction in the setting of prereconstruction radiation. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;129(2):354–361. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31823ae8b1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baschnagel A. M., Shah C., Wilkinson J. B., Dekhne N., Arthur D. W., Vicini F. A. Failure rate and cosmesis of immediate tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction after postmastectomy irradiation. Clinical Breast Cancer. 2012;12(6):428–432. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2012.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Agusti A., Ward A., Montgomery C., Mohammed K., Gui G. P. H. Aesthetic and oncologic outcomes after one-stage immediate breast reconstruction using a permanent biodimensional expandable implant. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2016;69(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2015.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang H., Li Y., Moran M. S., Haffty B. G., Yang Q. Predictive factors of nipple involvement in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2015;151(2):239–249. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Munhoz A. M., Montag E., Filassi J. R., Gemperli R. Immediate nipple-Areola-sparing mastectomy reconstruction: An update on oncological and reconstruction techniques. World Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2014;5(3):478–494. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i3.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Breuing K. H., Warren S. M. Immediate bilateral breast reconstruction with implants and inferolateral AlloDerm slings. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2005;55(3):232–239. doi: 10.1097/01.sap.0000168527.52472.3c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dieterich M., Angres J., Stubert J., Stachs A., Reimer T., Gerber B. Patient-Reported Outcomes in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction Alone or in Combination with a Titanium-Coated Polypropylene Mesh - A Detailed Analysis of the BREAST-Q and Overview of the Literature. Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde. 2015;75(7):692–701. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1546218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gschwantler-Kaulich D., Schrenk P., Bjelic-Radisic V., et al. Mesh versus acellular dermal matrix in immediate implant-based breast reconstruction - A prospective randomized trial. European Journal of Surgical Oncology. 2016;42(5):665–671. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Delgado J. F., García-Guilarte R. F., Palazuelo M. R., Mendez J. I. S., Pérez C. C. Immediate breast reconstruction with direct, anatomic, gel-cohesive, extra-projection prosthesis: 400 cases. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2010;125(6):1599–1605. doi: 10.1097/prs.0b013e3181cb63c2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Colwell A. S., Damjanovic B., Zahedi B., Medford-Davis L., Hertl C., Austen W. G. Retrospective review of 331 consecutive immediate single-stage implant reconstructions with acellular dermal matrix: Indications, complications, trends, and costs. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2011;128(6):1170–1178. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318230c2f6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Salzberg C. A., Ashikari A. Y., Koch R. M., Chabner-Thompson E. An 8-year experience of direct-to-implant immediate breast reconstruction using human acellular dermal matrix (AlloDerm) Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2011;127(2):514–524. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318200a961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hvilsom G. B., Friis S., Frederiksen K., et al. The clinical course of immediate breast implant reconstruction after breast cancer. Acta Oncologica. 2011;50(7):1045–1052. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2011.581690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bailey M. H., Smith J. W., Casas L., et al. Immediate breast reconstruction: reducing the risks. Plastic and Reconstructive surgery. 1989;83(5):845–851. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198905000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fischer J. P., Wes A. M., Tuggle C. T., III, Serletti J. M., Wu L. C. Risk analysis of early implant loss after immediate breast reconstruction: A review of 14,585 patients. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2013;217(6):983–990. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.07.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pinsolle V., Grinfeder C., Mathoulin-Pelissier S., Faucher A. Complications analysis of 266 immediate breast reconstructions. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2006;59(10):1017–1024. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2006.03.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jansen L. A., Macadam S. A. The use of AlloDerm in postmastectomy alloplastic breast reconstruction: part I. A systematic review. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2011;127(6):2232–2244. doi: 10.1097/prs.0b013e3182131c56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Siegel R., Ward E., Brawley O., Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA: Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2011;61(4):212–236. doi: 10.3322/caac.20121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. American Cancer Society. Breast cancer facts & figures 2011–2012. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures-2011-2012.pdf.
- 26.Tondu T., Thiessen F., Tjalma W. A. A. Prophylactic bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomy and a staged breast reconstruction technique: Preliminary results. Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research. 2016;10:185–189. doi: 10.4137/BCBCR.S40033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rosenberg S. M., Sepucha K., Ruddy K. J., et al. Local Therapy Decision-Making and Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy in Young Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2015;22(12):3809–3815. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4572-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Girotto J. A., Schreiber J., Nahabedian M. Y., Glat P. Breast reconstruction in the elderly: Preserving excellent quality of life. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2003;50(6):572–578. doi: 10.1097/01.SAP.0000069064.68579.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Salzberg C. A. Nonexpansive immediate breast reconstruction using human acellular tissue matrix graft (AlloDerm) Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2006;57(1):1–5. doi: 10.1097/01.sap.0000214873.13102.9f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ho G., Nguyen T. J., Shahabi A., Hwang B. H., Chan L. S., Wong A. K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of complications associated with acellular dermal matrix-assisted breast reconstruction. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2012;68(4):346–356. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31823f3cd9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Scheflan M., Colwell A. S. Tissue reinforcement in implant-based breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2014 doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Agarwal J. P., Mendenhall S. D., Anderson L. A., et al. The breast reconstruction evaluation of acellular dermal matrix as a sling trial (BREASTrial): Design and methods of a prospective randomized trial. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2015;135(1):20–28. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ibrahim A. M. S., Shuster M., Koolen P. G. L., et al. Analysis of the national surgical quality improvement program database in 19,100 patients undergoing implant-based breast reconstruction: complication rates with acellular dermal matrix. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2013;132(5):1057–1066. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182a3beec. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Colwell A. S., Tessler O., Lin A. M., et al. Breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy: Predictors of complications, reconstruction outcomes, and 5-year trends. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2014;133(3):496–506. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000438056.67375.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Plastic surgery statistics report 2012. Available at https://d2wirczt3b6wjm.cloudfront.net/News/Statistics/2012/plastic-surgery-statistics-full-report-2012.pdf.
- 36.Butler C. E., Langstein H. N., Kronowitz S. J. Pelvic, abdominal, and chest wall reconstruction with AlloDerm in patients at increased risk for mesh-related complications. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2005;116(5):1263–1275. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000181692.71901.bd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Terino E. O. Alloderm acellular dermal graft: Applications in aesthetic soft-tissue augmentation. Clinics in Plastic Surgery. 2001;28(1):83–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Connor J., McQuillan D., Sandor M., et al. Retention of structural and biochemical integrity in a biological mesh supports tissue remodeling in a primate abdominal wall model. Regenerative Medicine. 2009;4(2):185–195. doi: 10.2217/17460751.4.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wainwright D. J. Use of an acellular allograft dermal matrix (AlloDerm) in the management of full-thickness burns. Burns. 1995;21(4):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0305-4179(95)93866-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chaplin J. M., Costantino P. D., Wolpoe M. E., Bederson J. B., Griffey E. S., Zhang W. X. Use of an acellular dermal allograft for dural replacement: An experimental study. Neurosurgery. 1999;45(2):320–327. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199908000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Preminger B. A., McCarthy C. M., Hu Q. Y., Mehrara B. J., Disa J. J. The influence of AlloDerm on expander dynamics and complications in the setting of immediate tissue expander/implant reconstruction: A matched-cohort study. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2008;60(5):510–513. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31816f2836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Davila A. A., Seth A. K., Wang E., et al. Human acellular dermis versus submuscular tissue expander breast reconstruction: A multivariate analysis of short-term complications. Archives of Plastic Surgery. 2013;40(1):19–27. doi: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Spear S. L., Parikh P. M., Reisin E., Menon N. G. Acellular dermis-assisted breast reconstruction. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2008;32(3):418–425. doi: 10.1007/s00266-008-9128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Endress R., Choi M. S. S., Lee G. K. Use of fetal bovine acellular dermal xenograft with tissue expansion for staged breast reconstruction. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2012;68(4):338–341. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31823b68d0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bernini M., Calabrese C., Cecconi L., et al. Subcutaneous direct-to-implant breast reconstruction: surgical, functional, and aesthetic results after long-term follow-up. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open. 2015;3(12):p. e574. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Novitsky Y. W., Rosen M. J. The Biology of Biologics. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;130:9S–17S. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31825f395b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Salibian A. A., Frey J. D., Choi M., Karp N. S. Subcutaneous implant-based breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix/mesh: a systematic review. Plastic and reconstructive surgery—global open. 2016;4(11):p. e1139. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Van Deventer P. V., Graewe F. R., Würinger E. Improving the longevity and results of mastopexy and breast reduction procedures: Reconstructing an internal breast support system with biocompatible mesh to replace the supporting function of the ligamentous suspension. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2012;36(3):578–589. doi: 10.1007/s00266-011-9845-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.De Bruijn H. P., Johannes S. Mastopexy with 3D preshaped mesh for long-term results: Development of the internal bra system. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2008;32(5):757–765. doi: 10.1007/s00266-008-9186-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dieterich M., Reimer T., Dieterich H., Stubert J., Gerber B. A short-term follow-up of implant based breast reconstruction using a titanium-coated polypropylene mesh (TiLoop® Bra) European Journal of Surgical Oncology. 2012;38(12):1225–1230. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2012.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lynch M. P., Chung M. T., Rinker B. D. Dermal autografts as a substitute for acellular dermal matrices (ADM) in tissue expander breast reconstruction: A prospective comparative study. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2013;66(11):1534–1542. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Maguina P., Hoffman R., Szczerba S. Autologous dermal graft in breast reconstruction and treatment of breast implant malposition. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2010;125(4) doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181d45ac7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hudson D. A., Adams K. G., Adams S. Autologous dermal graft in breast reconstruction. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2012;68(3):253–256. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e318216b52d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Scuderi N., Alfano C., Campus G. V., et al. Multicenter study on breast reconstruction outcome using becker implants. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2011;35(1):66–72. doi: 10.1007/s00266-010-9559-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nava M. B., Cortinovis U., Ottolenghi J., et al. Skin-reducing mastectomy. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2006;118(3):603–610. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000233024.08392.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.McCue J. D., Migliori M., Cunningham B. L. Expanders and breast reconstruction with gel and saline implants. Aesthetic and Reconstructive Surgery of the Breast. 2010:29–50. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chun Y., Ganske I., Verma K., Rosen H., Eriksson E. Minimizing complications with the use of acellular dermal matrix for immediate implant- based breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2013;71:464–470. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182a7cc9b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Maruccia M, Mazzocchi M, Dessy LA, Onesti MG. One-stage breast reconstruction techniques in elderly patients to preserve quality of life. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2016; 20: 5058-5066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Ribuffo D, Monfrecola A, Guerra M, et al. Does postoperative radiation therapy represent a contraindication to expander-implant based immediate breast reconstruction? An update 2012- 2014. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2015; 19: 2202-2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Spear S. L., Seruya M., Rao S. S., et al. Two-stage prosthetic breast reconstruction using AlloDerm including outcomes of different timings of radiotherapy. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;130(1):1–9. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182547a45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kronowitz S. J., Robb G. L. Radiation therapy and breast reconstruction: A critical review of the literature. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2009;124(2):395–408. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181aee987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Speers C., Zhao S., Liu M., Bartelink H., Pierce L. J., Feng F. Y. Development and validation of a novel radiosensitivity signature in human breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research. 2015;21(16):3667–3677. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Jagsi R. Progress and controversies: Radiation therapy for invasive breast cancer. CA Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2014;64(2):135–152. doi: 10.3322/caac.21209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Anderson P. R., Hanlon A. L., McNeeley S. W., Freedman G. M. Low complication rates are achievable after postmastectomy breast reconstruction and radiation therapy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2004;59(4):1080–1087. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.12.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Jagsi R., Jiang J., Momoh A. O., et al. Complications after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for breast cancer a claims-bas ed analysis. Annals of Surgery. 2016;263(2):219–227. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Rietjens M., De Lorenzi F., Veronesi P., et al. Breast conservative treatment in association with implant augmentation and intraoperative radiotherapy. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2006;59(5):532–535. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2005.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Vandeweyer E., Deraemaecker R. Radiation therapy after immediate breast reconstruction with implants. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 2000;106(1):56–58. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200007000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Spear S. L., Onyewu C. Staged breast reconstruction with saline-filled implants in the irradiated breast: Recent trends and therapeutic implications. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2000;105(3):930–942. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200003000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Contant C. M. E., Van Geel A. N., Van Der Holt B., Griep C., Tjong Joe Wai R., Wiggers T. Morbidity of immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) after mastectomy by a subpectorally placed silicone prosthesis: The adverse effect of radiotherapy. European Journal of Surgical Oncology. 2000;26(4):344–350. doi: 10.1053/ejso.1999.0896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Benediktsson K., Perbeck L. Capsular contracture around saline-filled and textured subcutaneously-placed implants in irradiated and non-irradiated breast cancer patients: Five years of monitoring of a prospective trial. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2006;59(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2005.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Persichetti P., Cagli B., Simone P., et al. Implant breast reconstruction after salvage mastectomy in previously irradiated patients. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2009;62(4):350–354. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e318184aac8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Clemens M. W., Kronowitz S. J. Acellular dermal matrix in irradiated tissue expander/implant- based breast reconstruction: evidence-based review. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;130:27S–34S. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318265f690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Fischer J. P., Nelson J. A., Serletti J. M., Wu L. C. Peri-operative risk factors associated with early tissue expander (TE) loss following immediate breast reconstruction (IBR): A review of 9305 patients from the 2005-2010 ACS-NSQIP datasets. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2013;66(11):1504–1512. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Basta M. N., Gerety P. A., Serletti J. M., Kovach S. J., Fischer J. P. A Systematic Review and Head-to-Head Meta-Analysis of Outcomes following Direct-to-Implant versus Conventional Two-Stage Implant Reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2015;136(6):1135–1144. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Munabi N. C. O., Olorunnipa O. B., Goltsman D., Rohde C. H., Ascherman J. A. The ability of intra-operative perfusion mapping with laser-assisted indocyanine green angiography to predict mastectomy flap necrosis in breast reconstruction: A prospective trial. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2014;67(4):449–455. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.12.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Raposio E., Belgrano V., Santi P. L., Chiorri C. Which is the ideal breast size? some social clues for plastic surgeons. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2016;76(3):340–345. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Camilleri I. G., Malata C. M., Stavrianos S., McLean N. R. A review of 120 Becker permanent tissue expanders in reconstruction of the breast. British Journal of Plastic Surgery. 1996;49(6):346–351. doi: 10.1016/S0007-1226(96)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Gui G. P. H., Tan S.-M., Faliakou E. C., Choy C., A'Hern R., Ward A. Immediate breast reconstruction using biodimensional anatomical permanent expander implants: A prospective analysis of outcome and patient satisfaction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2003;111(1):125–138. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200301000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Raposio E., Caregnato P., Barabino P., et al. A computer-based preoperative planning for the surgical treatment of unilateral breast hypoplasia. Minerva Chirurgica. 2002;57(5):711–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Raposio E., Cicchetti S., Adami M., Ciliberti R. G., Santi P. L. Computer planning for breast reconstruction by tissue expansion: An update. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2004;113(7):2095–2097. doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000121189.51406.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Porro I., Schenone A., Fato M., Raposio E., Molinari E., Beltrame F. An integrated environment for plastic surgery support: Building virtual patients, simulating interventions, and supporting intraoperative decisions. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics. 2005;29(5):385–394. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2005.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Cordeiro P. G., Jazayeri L. Two-stage implant-based breast reconstruction: An evolution of the conceptual and technical approach over a two-decade period. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2016;138(1):1–11. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Folli S., Mingozzi M., Curcio A., Buggi F., Rossi C. Nipple areola complex sparing mastectomy. Gland Surgery. 2015;4:528–540. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.04.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Fan J., Raposio E., Wang J., Nordström R. E. A. Development of the inframammary fold and ptosis in breast reconstruction with textured tissue expanders. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2002;26(3):219–222. doi: 10.1007/s00266-002-1477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Nava MB, Catanuto G, Pennati A, Cividin VV, Spano A. Expander-implants breast reconstruction. In: Neligan PC, ed. Plastic Surgery, 3rd ed. New York: Elsevier Ltd.; 2013, pp. 336–369. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Phillips B. T., Lanier S. T., Conkling N., et al. Intraoperative perfusion techniques can accurately predict mastectomy skin flap necrosis in breast reconstruction: Results of a prospective trial. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;129(5) doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31824a2ae8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Singer R., Lewis C. M., Franklin J. D., Lynch J. B. Fluorescein test for prediction of flap viability during breast reconstructions. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 1978;61(3):371–375. doi: 10.1097/00006534-197803000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Losken A., Styblo T. M., Schaefer T. G., Carlson G. W. The use of fluorescein dye as a predictor of mastectomy skin flap viability following autologous tissue reconstruction. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2008;61(1):24–29. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e318156621d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Disa J. J., Ad-El D. D., Cohen S. M., Cordeiro P. G., Hidalgo D. A. The premature removal of tissue expanders in breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 1999;104(6):1662–1665. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199911000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Folli S., Mingozzi M., Curcio A., Buggi F., Rossi C. Nipple-sparing mastectomy: An alternative technique for large ptotic breasts. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2015;220(5):e65–e69. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Adams W. P., Jr., Rios J. L., Smith S. J. Enhancing patient outcomes in aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery using triple antibiotic breast irrigation: Six-year prospective clinical study. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2006;117(1):30–36. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000185671.51993.7e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wiener T. C. The role of betadine irrigation in breast augmentation. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2007;119(1):12–15. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000251088.51675.a8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Burkhardt B., Eades E. The effect of biocell texturing and povidone- iodine irrigation on capsular contracture around saline-inflatable breast implants. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 1995;96(6):1317–1325. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199511000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.A Macadam S., A Lennox P. Acellular dermal matrices: use in reconstructive and aesthetic breast surgery. Canadian Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2012;20:75–89. doi: 10.4172/plastic-surgery.1000739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Alderman A., Gutowski K., Ahuja A., Gray D. ASPS clinical practice guideline summary on breast reconstruction with expanders and implants. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2014;134(4):648e–655e. doi: 10.1097/prs.0000000000000541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Phillips B., Bishawi M., Dagum A., Bui D., Khan S. A systematic review of infection rates and associated antibiotic duration in acellular dermal matrix breast reconstruction. Eplasty. 2014;14:e42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Townley W. A., Baluch N., Bagher S., et al. A single pre-operative antibiotic dose is as effective as continued antibiotic prophylaxis in implant-based breast reconstruction: A matched cohort study. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2015;68(5):673–678. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2014.12.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Classen D. C., Evans R. S., Pestotnik S. L., Horn S. D., Menlove R. L., Burke J. P. The timing of prophylactic administration of antibiotics and the risk of surgical-wound infection. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1992;326(5):281–286. doi: 10.1056/nejm199201303260501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Bunn F., Jones D. J., Bell-Syer S. Prophylactic antibiotics to prevent surgical site infection after breast cancer surgery. Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) 2012;1:p. CD005360. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005360.pub3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Gyssens I. C. Preventing postoperative infections. Current treatment recommendations. Drugs. 1999;57(2):175–185. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199957020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Farhadi J., Maksvytyte G. K., Schaefer D. J., Pierer G., Scheufler O. Reconstruction of the nipple-areola complex: An update. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2006;59(1):40–53. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2005.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Delay E. Fat injections to the breast: The lipomodeling technique. Aesthetic and Reconstructive Surgery of the Breast. 2010:171–192. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Simonacci F., Bertozzi N., Grieco M. P., Grignaffini E., Raposio E. Autologous fat transplantation for breast reconstruction: A literature review. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2016;12:94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2016.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Raposio E., Caruana G., Petrella M., Bonomini S., Grieco M. P. A standardized method of isolating adipose-derived stem cells for clinical applications. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2016;76(1):124–126. doi: 10.1097/sap.0000000000000609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Raposio E., Caruana G., Bonomini S., Libondi G. A novel and effective strategy for the isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: minimally manipulated adipose-derived stem cells for more rapid and safe stem cell therapy. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2014;133(6):1406–1409. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Bhatia M., Elefanty A. G., Fisher S. J., Patient R., Schlaeger T., Snyder E. Y. Current Protocols in Stem Cell Biology. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Raposio E., Simonacci F., Perrotta R. E. Adipose-derived stem cells: comparison between two methods of isolation for clinical applications. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2017;20:87–91. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.07.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Scanarotti C., Bassi A. M., Catalano M., et al. Neurogenic-committed human pre-adipocytes express CYP1A isoforms. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 2010;184(3):474–483. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Coradeghini R., Guida C., Scanarotti C., et al. A comparative study of proliferation and hepatic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010;191(6):466–477. doi: 10.1159/000273266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Aluigi M. G., Coradeghini R., Guida C., et al. Pre-adipocytes commitment to neurogenesis 1: Preliminary localisation of cholinergic molecules. Cell Biology International. 2009;33(5):594–601. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2009.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Raposio E., Guida C., Baldelli I., et al. Characterization and induction of human pre-adipocytes. Toxicology in Vitro. 2007;21(2):330–334. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2006.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Raposio E., Guida C., Coradeghini R., et al. In vitro polydeoxyribonucleotide effects on human pre-adipocytes. Cell Proliferation. 2008;41(5):739–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2008.00547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Caruana G., Bertozzi N., Boschi E., Grieco M. P., Grignaffini E., Raposio E. Role of adipose-derived stem cells in chronic cutaneous wound healing. Annali Italiani di Chirurgia. 2015;86(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Raposio E., Bertozzi N., Bonomini S., et al. Adipose-derived stem cells added to platelet-rich plasma for chronic skin ulcer therapy. Wounds. 2016;28(4):126–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Bertozzi N., Simonacci F., Grieco M. P., Grignaffini E., Raposio E. The biological and clinical basis for the use of adipose-derived stem cells in the field of wound healing. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2017;20:41–48. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.06.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Rigotti G., Marchi A., Galiè M., et al. Clinical treatment of radiotherapy tissue damage by lipoaspirate transplant: a healing process mediated by adipose-derived adult stem cells. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2007;119(5):1409–1424. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000256047.47909.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Serra-Renom J. M., Muñoz-Olmo J. L., Serra-Mestre J. M. Fat grafting in postmastectomy breast reconstruction with expanders and prostheses in patients who have received radiotherapy: Formation of new subcutaneous tissue. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2010;125(1):12–18. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181c49458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Simonacci F., Bertozzi N., Grieco M. P., Grignaffini E., Raposio E. Procedure, applications, and outcomes of autologous fat grafting. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2017;20:49–60. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.06.059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Cordeiro P. G., McCarthy C. M. A single surgeon's 12-year experience with tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction: Part I. A prospective analysis of early complications. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2006;118(4):825–831. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000232362.82402.e8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Cordeiro P. G., McCarthy C. M. A single surgeon's 12-year experience with tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction: Part II. An analysis of long-term complications, aesthetic outcomes, and patient satisfaction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2006;118(4):832–839. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000232397.14818.0e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Lennox P. A., Bovill E. S., Macadam S. A. Evidence-based medicine: alloplastic breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2017;140(1):94e–108e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Glasberg S. B., Light D. AlloDerm and strattice in breast reconstruction: a comparison and techniques for optimizing outcomes. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;129(6):1223–1233. doi: 10.1097/prs.0b013e31824ec429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Salzberg C. A. Focus on technique: one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;130:95S–103S. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318262e1a1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Jahkola T., Asko-Seljavaara S., Van Smitten K. Immediate breast reconstruction. Scandinavian Journal of Surgery. 2003;92(4):249–256. doi: 10.1177/145749690309200403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Sbitany H., Sandeen S. N., Amalfi A. N., Davenport M. S., Langstein H. N. Acellular dermis-assisted prosthetic breast reconstruction versus complete submuscular coverage: A head-to-head comparison of outcomes. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2009;124(6):1735–1740. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181bf803d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Spear S. L., Seruya M., Clemens M. W., Teitelbaum S., Nahabedian M. Y. Acellular dermal matrix for the treatment and prevention of implant-associated breast deformities. Plastic Surgical Nursing. 2017;37(2):76–87. doi: 10.1097/PSN.0000000000000189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Mowlds D. S., Salibian A. A., Scholz T., Paydar K. Z., Wirth G. A. Capsular contracture in implant-based breast reconstruction: Examining the role of acellular dermal matrix fenestrations. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2015;136(4):629–635. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Stump A., Holton L. H., Connor J., Harper J. R., Slezak S., Silverman R. P. The use of acellular dermal matrix to prevent capsule formation around implants in a primate model. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2009;124(1):82–91. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181ab112d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Casella D., Calabrese C., Bianchi S., Meattini I., Bernini M. Subcutaneous tissue expander placement with synthetic titanium-coated mesh in breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—Global Open. 2015;3(12):p. e577. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Becker H., Lind J. G., Hopkins E. G. Immediate implant-based prepectoral breast reconstruction using a vertical incision. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open. 2015;3(6):p. e412. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Roostaeian J., Sanchez I., Vardanian A., et al. Comparison of immediate implant placement versus the staged tissue expander technique in breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;129(6) doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31824ec411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Raposio E, Bertozzi N. Quantitative difference of acute intraoperative expansion in various body regions. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2017; 21: 454–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Raposio E., Bertozzi N. Ultrastructural effects of topical dimethyl sulfoxide on collage fibers during acute skin expansion in a human ex-vivo model. European Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2017:1–6. doi: 10.1007/s00238-017-1301-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Abedi N., Ho A. L., Knox A., et al. Predictors of mastectomy flap necrosis in patients undergoing immediate breast reconstruction a review of 718 patients. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2016;76(6):629–634. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Grieco M. P., Grignaffini E., Simonacci F., Di Mascio D., Raposio E. Post-bariatric body contouring: our experience. Acta Biomedica. 2016;87(1):70–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Gruber R. P., Kahn R. A., Lash H., Maser M. R., Apfelberg D. B., Laub D. R. Breast reconstruction following mastectomy: A comparison of submuscular and subcutaneous techniques. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 1981;67(3):312–317. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198103000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Bindingnavele V., Gaon M., Ota K. S., Kulber D. A., Lee D.-J. Use of acellular cadaveric dermis and tissue expansion in postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2007;60(11):1214–1218. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2007.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Wallace M. S., Wallace A. M., Lee J., Dobke M. K. Pain after breast surgery: a survey of 282 women. Pain. 1996;66(2-3):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(96)03064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Spear S. L., Schwartz J., Dayan J. H., Clemens M. W. Outcome assessment of breast distortion following submuscular breast augmentation. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2009;33(1):44–48. doi: 10.1007/s00266-008-9275-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Hammond D. C., Schmitt W. P., O'Connor E. A. Treatment of Breast Animation Deformity in Implant-Based Reconstruction with Pocket Change to the Subcutaneous Position. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2015;135(6):1540–1544. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Kiernan t., Martin l. Surgery Curr Res. Vol. 3. 3: 2013. Use of acellular dermal matrix is comparable to expander based breast reconstructions for postoperative physiotherapy requirements; pp. 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Scuderi N., Mazzocchi M., Fioramonti P., et al. Treatment of the capsular contracture around mammary implants: our experience. Il Giornale di chirurgia. 2008;29:369–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Apte A., Walsh M., Chandrasekharan S., Chakravorty A. Immediate breast reconstruction using ADM and implant: 5-year experience. European Journal of Surgical Oncology (EJSO) 2017;43(5):S59–S60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.01.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Berna G., Cawthorn S. J., Papaccio G., Balestrieri N. Evaluation of a novel breast reconstruction technique using the Braxon® acellular dermal matrix: A new muscle-sparing breast reconstruction. ANZ Journal of Surgery. 2014 doi: 10.1111/ans.12849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Chen W. F., Barounis D., Kalimuthu R. A novel cost-saving approach to the use of acellular dermal matrix (AlloDerm) in postmastectomy breast and nipple reconstructions. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2010;125(2):479–481. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181c82da6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Krishnan N. M., Chatterjee A., Rosenkranz K. M., Powell S. G., Nigriny J. F., Vidal D. C. The cost effectiveness of acellular dermal matrix in expander-implant immediate breast reconstruction. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2014;67(4):468–476. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.12.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Kim J. Y. S., Davila A. A., Persing S., et al. A meta-analysis of human acellular dermis and submuscular tissue expander breast reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2012;129(1):28–41. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182361fd6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Bertozzi N., Pesce M., Santi P., Raposio E. Oncoplastic breast surgery: comprehensive review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:2572–2585. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.07.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Bertozzi N., Pesce M., Santi P., Raposio E. Tissue expansion for breast reconstruction: Methods and techniques. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2017;21:34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.07.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.MM V. u., Kim J. Y. Current opinions on indications and algorithms for acellular dermal matrix use in primary prosthetic breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2015;4:195–203. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.05.07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Jordan S. W., Khavanin N., Fine N. A., Kim J. Y. S. An algorithmic approach for selective acellular dermal matrix use in immediate two-stage breast reconstruction: Indications and outcomes. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2014;134(2):178–188. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Libondi G., Solinas M., Martella E. M., Cattelani L. Nipple sparing mastectomy with immediate silicone implant reconstruction for malignant phyllodes tumor in a 19-year-old girl. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2015;19(23):4498–4500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Gardani M., Bertozzi N., Grieco M. P., et al. Breast reconstruction with anatomical implants: A review of indications and techniques based on current literature. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2017;21:96–104. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.07.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Veronesi U., Stafyla V., Petit J.-Y., Veronesi P. Conservative mastectomy: Extending the idea of breast conservation. The Lancet Oncology. 2012;13(7):e311–e317. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70133-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]