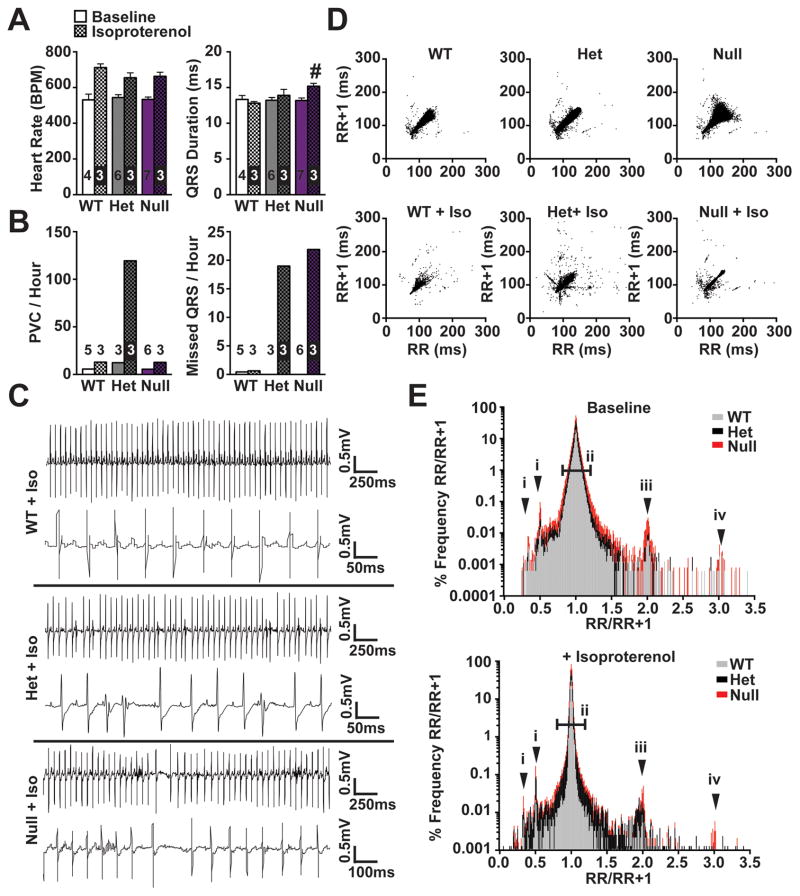
Figure 7. Increased frequency of arrhythmic events in Mybphl mutant mice.
A. Conscious ambulatory ECG analysis shows significantly prolonged QRS duration in Mybphl null mice following isoproterenol administration. B. Following isoproterenol, PVCs and nonconducted beats per hour were increased in heterozygous mice. Nonconducted beats were increased in both heterozygous and homozygous mice following isoproterenol. C. Representative ECG traces from each group following isoproterenol administration show an interval with a high rate of PVCs from heterozygous mice and a period with non-conducted beats and sinus arrest in the homozygous traces. D. Poincaré plots showing increased R-R variability in Mybphl heterozygous and null mice that is exacerbated with isoproterenol treatment. E. Histogram of the RR/RR+1 ratio illustrating peaks representing PVCs or early beats (i), single and double skipped beats in sinus rhythm (iii, iv), and overall RR variability illustrated by increased deviation around the 1.0 ratio point (ii) (n=3–5). # = p<0.05 vs. WT + Isoproterenol by two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni multiple comparison test.