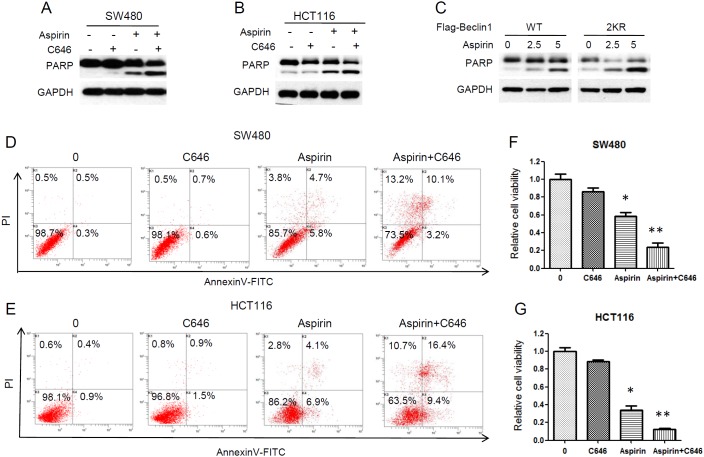
Figure 5. Inhibition of Beclin 1 acetylation by C646 promoted aspirin-induced cell death.
(A-B) HCT116 and SW480 cells were treated with or without 30μM C646 in the presence or absence of 5mM aspirin for 24 h, and western blot analyse of PARP was performed. (C) Flag-tagged Beclin 1 (WT, 2KR) was transfected into HCT116 cells, then the transfected cells were treated with different concentration of aspirin for 24 h. Western blot analyse of PARP was performed. (D-E) Flow cytometric assay with Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining. HCT116 and SW480 cells were treated with or without 30μM C646 in the presence of 5mM aspirin for 24 h, stained with AnnexinV-FITC and PI, then measured by flow cytometer. (F-G) HCT116 and SW480 cells were treated with 5mM aspirin with or without 30μM C646 for 72 h. Cell viability was then determined using CCK-8 assays. Bars represent mean ± SEM. Three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student’s t-test).