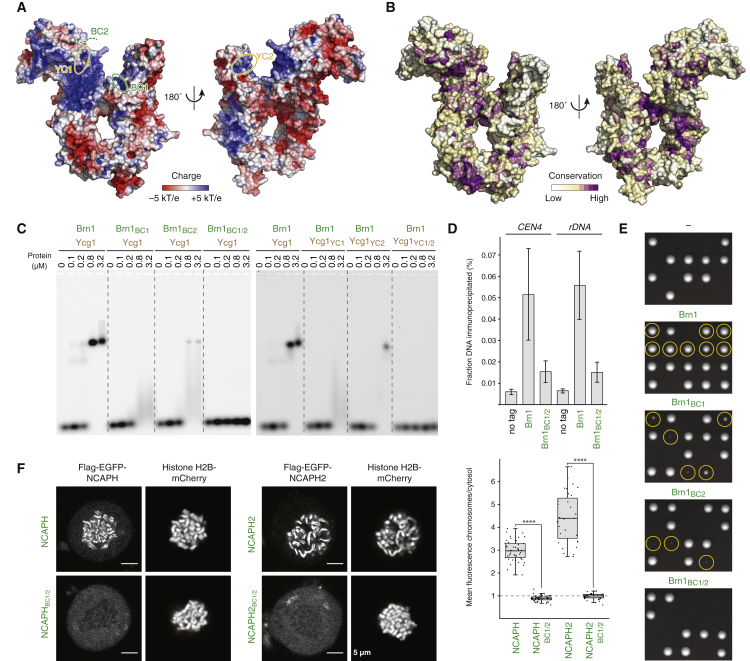
Figure 3.
A Conserved Positively Charged Ycg1–Brn1 Groove Is Essential for Condensin’s Association with Chromosomes
(A) Electrostatic surface potential representation of the Sc Ycg1–Brn1 subcomplex. Regions of positively charged Brn1 (BC1, BC2) or Ycg1 (YC1, YC2) residue patches are indicated.
(B) Conservation surface representation of the Sc Ycg1–Brn1 subcomplex. Conservation scores were calculated based on an alignment of sequences from 35 evolutionary distant eukaryotic species.
(C) EMSA of a 6-FAM-labeled 35-bp dsDNA substrate (0.2 μM) with copurified Ct Ycg124–1006–His6-TEV-Brn1515–634 subcomplexes containing wild-type or charged-patch mutant versions of Ct Brn1 (BC1: Ct Brn1R539D, R541D, K542D, K544D, BC2: Bc Brn1R554D, R556D, K557D, K559D, BC1/2: Bc Brn1R539D, R541D, K542D, K544D, R554D, R556D, K557D, K559D) or Ct Ycg1 (YC1: Ct Ycg1K100D, K101D, YC2: Ct Ycg1K916D, K917D, YC1/2: Ct Ycg1K100D, K101D, K916D, K917D).
(D) ChIP-qPCR of condensin complexes containing wild-type Sc Brn1-PK6 (strain C4239) or mutant Sc Brn1BC1/2-PK6 (Sc Brn1K409D, R411D, K414D, K451D, K452D, K454D, K456D, K457D) in asynchronous cells at centromeric (CEN4) and rDNA genomic loci. Error bars indicate mean ± SD of two independent experiments with two qPCR repeats each.
(E) Tetrad dissection of BRN1/brn1Δ diploid budding yeast cells expressing no (–, strain C4237), wild-type (Brn1, strain C4239), or mutant (BC1: Sc Brn1K409D, R411D, K414D, strain C4257, BC2: Sc Brn1K451D, K452D, K454D, K456D, K457D, strain C4259, BC1/2: Sc Brn1K409D, R411D, K414D, K451D, K452D, K454D, K456D, K457D, strain C4261) versions of Brn1-PK6 from an ectopic locus under control of the endogenous promoter. Images were recorded after three days at 25°C. Genetic marker analysis identifies BRN1x, brn1Δ cells (circles).
(F) Representative example images of nocodazole-arrested HeLa cells expressing mCherry-tagged histone H2B and transiently transfected Flag-EGFP-tagged NCAPH or NCAPH2 as wild-type or charged-patch mutant (BC1/2: Hs NCAPHR446D, R448D, R450D, R451D, K452D, K462D, K463D, K464D, K467D, K468D, Hs NCAPH2K329D, K332D, K333D, R335D, K350D, R351D, K352D, R353D, K354D) versions. Scale bars: 5 μm. The graph plots ratios of chromosomal to cytosolic EGFP intensities. Horizontal lines indicate median, hinges indicate first and third quartiles, and whiskers extend to the highest or lowest point from the hinges within 1.5 times interquartile range, calculated from two independent experiments with a total of n = 45 (NCAPH), n = 45 (NCAPHBC1/2), n = 31 (NCAPH2), and n = 35 (NCAPH2BC1/2) cells (p < 0.0001 by Student’s t test with Welch’s correction).
See also Figures S3, S4, and S5 and Table S2.