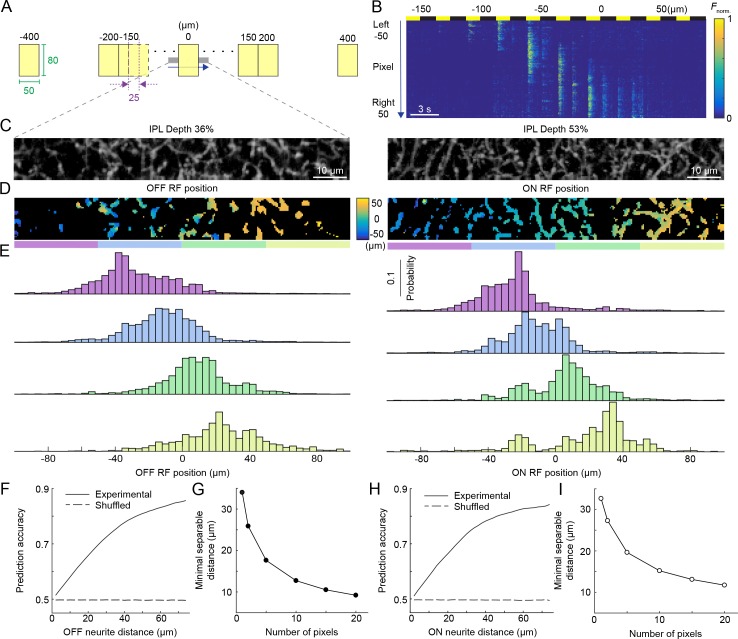
Figure 3. Population activity of the VG3-AC plexus encodes spatial information with high precision.
(A) Schematic of visual stimulus. Vertical bars (height: 60–80 μm, height: 50 μm width) were presented at 17 different positions along the horizontal axis of a rectangular imaging region (height: 13 μm, width: 100 μm). Stimulus positions were symmetric around the center of the imaging region and spaced by 25 μm center-center distances from −150 μm to 150 μm. In addition, bars were presented −400 μm, −200 μm, 200 μm, and 400 μm from the center of the imaging region. Each bar was presented three for 1.5 s with an interval of 1.5 s between stimuli. The order of stimulus positions was randomized and each stimulus repeated three times. (B) Heatmap of normalized responses in VG3-AC neurites to bars stimuli from −150 μm to 100 μm from the center of the imaging region at an IPL depth of 53%. Responses have been reordered by stimulus positions. Each row of the heatmap represents the activity a single pixel. Pixels were sorted by their distance from the center of the imaging region (−50 μm to 50 μm). (C) Representative images of the VG3-AC plexus in the scan region obtained by averaging the GCaMP6f signal over (left: IPL depth 36%, right: IPL depth 53%). (D) Maps of receptive field positions in the same regions of the VG3-AC plexus shown in (C) (left: OFF responses, right: ON responses). (E) Distributions of receptive field positions of pixels in four adjacent subsections (color-coded from left to right in: purple, sky, lime, and olive) of the scan regions shown in (C) and (D). Receptive field positions of the pixels of each image were aligned to zero their average. (F, H) The accuracy with which a naive Bayes classifier can assign the location of a VG3-AC neurite pixel based on its receptive field position to one of two image subsections increases as a function of the distance between these subsections (solid lines). Dashed lines shows the accuracy when classifiers were trained on shuffled receptive field positions. (G, I) The minimum separable distance (i.e. the point at which prediction accuracy reaches 75%) decreased when predictions were based on multiple pixels (e.g. median ROI size in VG3-AC neurites: 10 pixels).