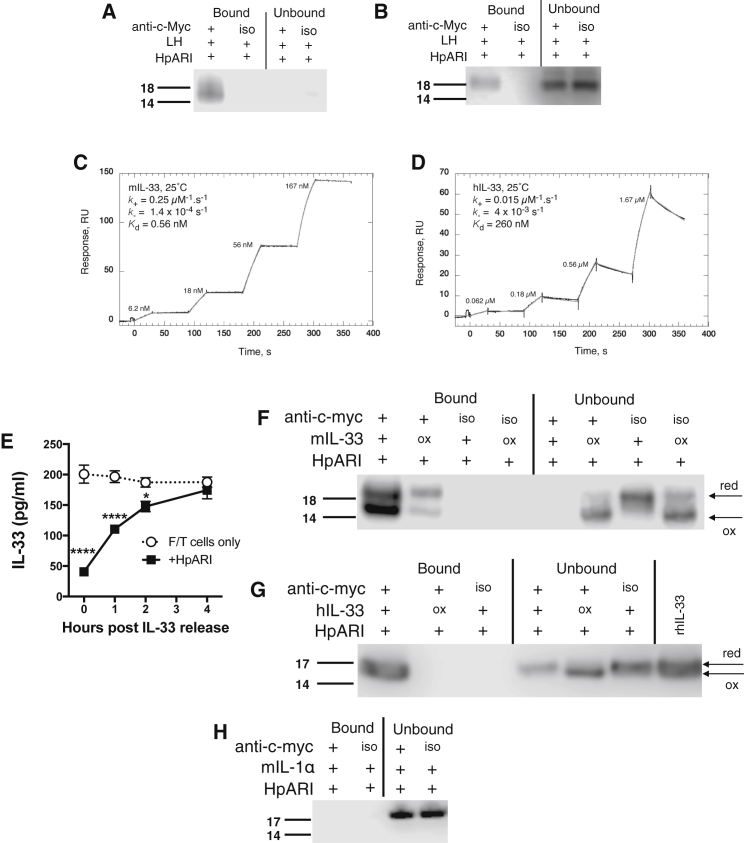
Figure 5.
HpARI Binds Active Murine and Human IL-33
(A) Murine IL-33 western blot (non-reducing) of HpARI immunoprecipitation of mouse lung homogenates, using anti-c-Myc antibody, or MOPC isotype control (iso).
(B) Human IL-33 western blot (non-reducing) of HpARI immunoprecipitation of human lung homogenates, as in (A).
(C) Characterization of the interaction of mouse IL-33 (mIL-33) with HpARI by surface plasmon resonance (SPR - BIAcore T200). Reference corrected single kinetic titration SPR binding curves (black), and a globally fitted 1:1 kinetic binding model (grey).
(D) Characterization by SPR of the interaction of human IL-33 (hIL-33) with HpARI, as in (C).
(E) IL-33 levels (ELISA) in supernatants of freeze-thawed murine lung cells, incubated at 37°C for 0, 1, 2, or 4 hr, before addition of 1 μg/ml HpARI, and a further incubation for 1 hr at 37°C.
(F) Untreated or oxidized recombinant murine IL-33 immunoprecipitated with HpARI as in (A).
(G) Untreated or oxidized recombinant human IL-33 immunoprecipitated with HpARI as in (B).
(H) Immunoprecipitation experiments repeated with recombinant murine IL-1α, and probed with anti-murine IL-1α.
Arrows indicate specific IL-33 or IL-1α bands, and IL-33 reduced (“red”) or oxidized (“ox”) bands. All data are representative of at least two independent repeats. Error bars show SEM.