Abstract
Introduction
Real-world comparative effectiveness, safety, and supportive care use of nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin vs gemcitabine plus platinum were analyzed in patients with advanced or metastatic squamous cell non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Materials and methods
Patients who received ≥ 1 cycle of first-line nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin or gemcitabine plus platinum were identified from the Navigating Cancer database. Clinical effectiveness endpoints included overall survival (OS) and time to treatment discontinuation (TTD). Other endpoints included safety and utilization of supportive care. Cox proportional hazards models were used to control for potential confounding effects of baseline characteristics.
Results
In total, 193 patients were included (nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin, n = 61; gemcitabine plus platinum, n = 132). Baseline characteristics were generally similar between the cohorts. Patients receiving nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin had a significantly longer OS than those receiving gemcitabine plus carboplatin (median, 12.8 vs 9.0 months; P = 0.03). However, the adjusted difference was not statistically significant (adjusted HR 1.55; 95% CI, 0.99–2.42; P = 0.06). nab-Paclitaxel plus carboplatin-treated patients had significantly longer TTD than gemcitabine plus carboplatin-treated patients (median, 4.3 vs 3.5 months; P = 0.03; adjusted HR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.01–1.90; P = 0.04). Grade 3 or 4 anemia and neutropenia were significantly lower in patients treated with nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin vs gemcitabine plus carboplatin. Nausea and neuropathy (grade not specified) were significantly higher in the nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin than the gemcitabine plus carboplatin group. No differences in supportive care use were observed between the cohorts.
Conclusion
These real-world data support the effectiveness and safety of nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin for first-line treatment of advanced squamous cell NSCLC.
Keywords: chemotherapy, doublet treatment options, electronic medical records, NSCLC, real-world evidence, retrospective analysis
Introduction
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among men and women across the globe.1,2 Estimates suggest that in 2017 there will be ≈ 222,500 new lung cancer diagnoses.2 The majority (≈ 85%) of lung cancer cases are non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), for which the 5-year survival rate for stages IA through IIIA ranges from 49% to 14%.2,3 Patients with a diagnosis of stage IIIB or IV NSCLC have traditionally experienced 5-year survival rates ≤ 5%.3 However, a long-term follow-up analysis of a Phase I study enrolling patients with heavily pretreated advanced NSCLC demonstrated a 5-year survival rate of 16% associated with nivolumab (Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, NJ, USA) treatment.4 Survival rates have also been correlated with tumor histology in prior studies. In an analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program data, the 1-year survival rate for patients with stage IV squamous cell NSCLC was worse than that for those with stage IV adenocarcinoma.5
With respect to treatments, there remain unmet needs in patients with squamous cell NSCLC. According to the current National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines for patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC and good performance status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status [ECOG PS] 0–1), there are fewer recommended first-line treatment options for those with squamous cell vs adenocarcinoma histology.6 In terms of immunotherapy, first-line treatment with pembrolizumab (Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA) is an NCCN category 1 recommendation for patients with PD-L1-positive (≥ 50% expression) tumors that would not be amenable to genetic mutation-based targeted therapies.6 However, as reported in the KEYNOTE-001 and -010 trials, 23% to 28% of NSCLC tumors exhibit ≥ 50% PD-L1 expression.7,8 In addition, pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed (Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN, USA) and carboplatin (Hospira, Lake Forest, IL, USA) is indicated for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-squamous cell but not squamous cell NSCLC.9 Therefore, while immunotherapy agents have recently begun to reshape the treatment landscape, they are not appropriate for all patients, and first-line treatment recommendations for patients with squamous cell NSCLC remain largely focused on platinum doublets.6 nab-Paclitaxel (Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ, USA) plus carboplatin and gemcitabine (Lilly USA, LLC, Indianapolis, IN, USA) plus a platinum agent are part of the recommended first-line treatment options for patients with advanced or metastatic squamous cell NSCLC, according to the NCCN and European Society for Medical Oncology guidelines.6,10 In a pivotal trial sub-analysis of safety and efficacy by histology among patients with squamous cell NSCLC, nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin demonstrated a 68% improvement in overall response rate (primary endpoint) over paclitaxel plus carboplatin, with a trend in overall survival (OS) favoring nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin.11,12 In these patients, treatment with nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin also resulted in significantly less grade 3 or 4 neuropathy and arthralgia but more thrombocytopenia and anemia than treatment with paclitaxel plus carboplatin.11,12 The gemcitabine plus cisplatin (Bristol-Myers Squibb Company) regimen also demonstrated antitumor activity in the subset of patients with stage IIIB or IV squamous cell NSCLC in a Phase III trial.13 In the trial, gemcitabine plus cisplatin demonstrated a statistically significant survival benefit among patients with squamous cell histology compared with pemetrexed plus cisplatin. Gemcitabine plus cisplatin resulted in more grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia than pemetrexed plus cisplatin.
To date, no clinical trial has directly compared nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin to gemcitabine plus cisplatin in advanced squamous cell NSCLC, and cross-trial comparisons are problematic due to differences in patient populations and study designs. Furthermore, randomized controlled trials may not be reflective of the real-world population. For example, despite the median age at lung cancer diagnosis being 70 years, elderly patients are often underrepresented in Phase III clinical trials.14,15 For these reasons, real-world analyses, such as those using electronic medical records (EMRs), are now being used to support clinical trial data. This analysis evaluated the real-world comparative effectiveness, safety, and supportive care use of nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin vs gemcitabine plus a platinum agent in patients with advanced or metastatic (stage IIIB or IV) squamous cell NSCLC.
Materials and methods
Data source
This analysis was performed using fully deidentified data from the Navigating Cancer database, which provides services to a variety of community-based oncologists who use various EMR platforms. At the time of this analysis, the Navigating Cancer database contained EMRs of patients treated by over 975 oncologists at 81 oncology/hematology community practices throughout the US, 47% from the South, 23% from the Northeast, 17% from the Midwest, and 13% from the West. Institutional review board or ethics committee approval was not required because all data were deidentified.
Study design and patients
Patients aged ≥ 18 years with a primary diagnosis of advanced (stage IIIB or IV) squamous cell NSCLC were included in this retrospective analysis. Key eligibility criteria included initiation of first-line therapy with nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin or gemcitabine plus a platinum agent between October 1, 2012 and December 31, 2014, completion of at least one cycle of nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin (three doses of nab-paclitaxel) or gemcitabine plus a platinum agent (≥ 2 doses of gemcitabine), and a follow-up time of ≥ 5 months or until May 31, 2015, whichever occurred later. According to the indicated schedules, one cycle of treatment was defined as three doses of nab-paclitaxel and one dose of carboplatin given during a 3-week treatment cycle, three doses of gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 and one dose of cisplatin given during a 4-week treatment cycle, or two doses of gemcitabine 1250 mg/m2 and one dose of cisplatin given during a 3-week treatment cycle.16,17 In the real-world clinical setting in this study, the platinum agent used in combination with gemcitabine was carboplatin instead of cisplatin but with the same schedule as cisplatin. Regimen line assignments were based on grouping of treatments given within 30 days of each other, and changes or addition of new agents that occurred beyond 30 days constituted an additional line of therapy. Patients who participated in any interventional clinical trial during the study period (October 1, 2012 to May 31, 2015) or received an active treatment for a second malignancy were excluded. In the final population, data for all inclusion and exclusion criteria and baseline characteristics were known, except for ECOG PS (< 50%).
Objectives and endpoints
The overall objective of this retrospective study was to evaluate relevant clinical and demographic characteristics, treatment patterns, survival, and other clinical outcomes in the management of patients receiving first-line nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin or gemcitabine plus platinum treatment for stage IIIB or IV squamous cell NSCLC. The primary objective was to evaluate OS between the treatment regimens. The secondary objectives were to evaluate time to treatment discontinuation (TTD) and association between treatment regimens and adjusted TTD, as well as to estimate the frequency and grade of adverse events.
The endpoints of this study were median OS, median TTD, incidence of common chemotherapy-related adverse events, and supportive care utilization. OS was defined as the time between the first dose of chemotherapy and the date of death, which was determined by EMR records and/or the Social Security Death Index Master File. Patients without a known date of death were censored on their last date of follow-up. TTD was defined as the time between the first and last dose of nab-paclitaxel or gemcitabine plus 7 days. Treatment discontinuation was defined as the initiation of a new regimen (different from first line) or > 60-day interruption of either nab-paclitaxel or gemcitabine. Patients were censored if the last date of administration was < 30 days before the data cutoff. Adverse events were identified by International Classification of Disease, Ninth Revision (ICD-9), codes and/or laboratory values (for hematologic adverse events [Table S1]; grade of adverse events was determined if laboratory values were available). The proportion of patients receiving supportive care and the number of supportive care doses were determined between the first and last dose of chemotherapy.
Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) was calculated by assigning points for conditions that were reported by ICD-9 codes (Table S2), these data being reflective of comorbidities as reported exclusively by the patient’s oncologist.
Statistical analyses
Baseline demographics, treatment characteristics, treatment regimens, and common chemotherapy-related adverse events in the two treatment cohorts were summarized and compared by descriptive statistics. Median OS and TTD were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and treatment differences were evaluated by log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards models were conducted to determine the association between treatment regimen and OS and TTD, adjusted for age, sex, and CCI at the start of the first-line treatment. Treatment sequences were described using frequency distributions. Adverse events and supportive care utilization were described by frequencies and proportions.
Results
Cohort determination and baseline characteristics
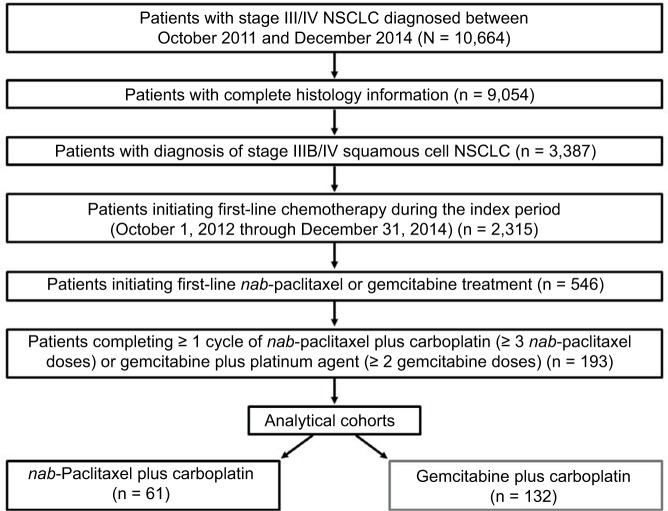
Overall, 10,664 patients who had received a diagnosis of stage III or IV NSCLC between October 2011 and December 2014 were identified in the database. Of the 9,054 patients with complete histology information, 3,387 had a diagnosis of stage IIIB or IV squamous cell NSCLC, based on information from both structured fields, which physicians were not required to complete, and natural language processing algorithms. During the index period (October 1, 2012 through December 31, 2014), 2,315 patients initiated first-line chemotherapy. Of these, 546 patients were treated with nab-paclitaxel- or gemcitabine-based regimens. A total of 193 patients with squamous cell histology initiated and completed ≥ 1 cycle of first-line therapy with nab-paclitaxel- or gemcitabine-based regimens (nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin, n = 61; gemcitabine plus platinum, n = 132 [all patients in the gemcitabine plus platinum cohort received carboplatin as the platinum agent]) between October 1, 2012 and December 31, 2014 (Figure 1). Because stage (specifically IIIB) and histology were captured by a combination of non-mandatory structured fields and natural language processing, missing information led to attrition. The majority of patients were male (62%), aged ≥ 60 years (81%), and had a diagnosis of stage IV disease (95%; Table 1). Baseline characteristics were generally similar between patients in the two cohorts; however, performance status was unknown for ≈ 54% of patients at initiation of first-line treatment.
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram: patients with squamous cell non-small cell lung cancer who received first-line nab-paclitaxel- or gemcitabine-based treatment.
Abbreviation: NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics
| Baseline characteristics |
nab-Paclitaxel plus carboplatin (n = 61) |
Gemcitabine plus carboplatin (n = 132) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean, years | 68.7 | 67.9 | 0.57 |
| ≥ 60 years, n (%) | 51 (84) | 105 (80) | |
| ≥ 70 years, n (%) | 33 (54) | 59 (45) | |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 40 (66) | 80 (61) | 0.51 |
| Female | 21 (34) | 52 (39) | 0.51 |
| Stage at index date, n (%) | |||
| IIIB | 3 (5) | 6 (5) | 0.91 |
| IV | 58 (95) | 126 (95) | |
| Treatments prior to first line, n (%) | |||
| Radiation | 19 (31) | 35 (27) | 0.61 |
| Surgery | 2 (3) | 2 (2) | |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy, n (%) | |||
| Did not receive | 58 (95) | 128 (97) | 0.54 |
| Received | 3 (5) | 4 (3) | |
| ECOG PS at first line, n (%)a | |||
| 0–1 | 17 (28) | 51 (39) | 0.15 |
| ≥2 | 4 (7) | 16 (12) | 0.24 |
| Unknown | 40 (66) | 65 (49) | 0.04 |
| Location of metastasis, n (%)a | |||
| Bone | 15 (25) | 28 (21) | 0.60 |
| Brain | 4 (7) | 6 (5) | 0.56 |
| Liver | 2 (3) | 14 (11) | 0.09 |
| CCI, meanb | 2.7 | 4.1 | 0.10 |
| Serum creatinine at first line, mean, mg/dL | 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.05 |
Notes:
Descriptive only due to missing values;
CCI comorbidities included cardiovascular disease, cancers, human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS, diabetes, renal disease, and others.
Abbreviations: CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status.
OS and TTD
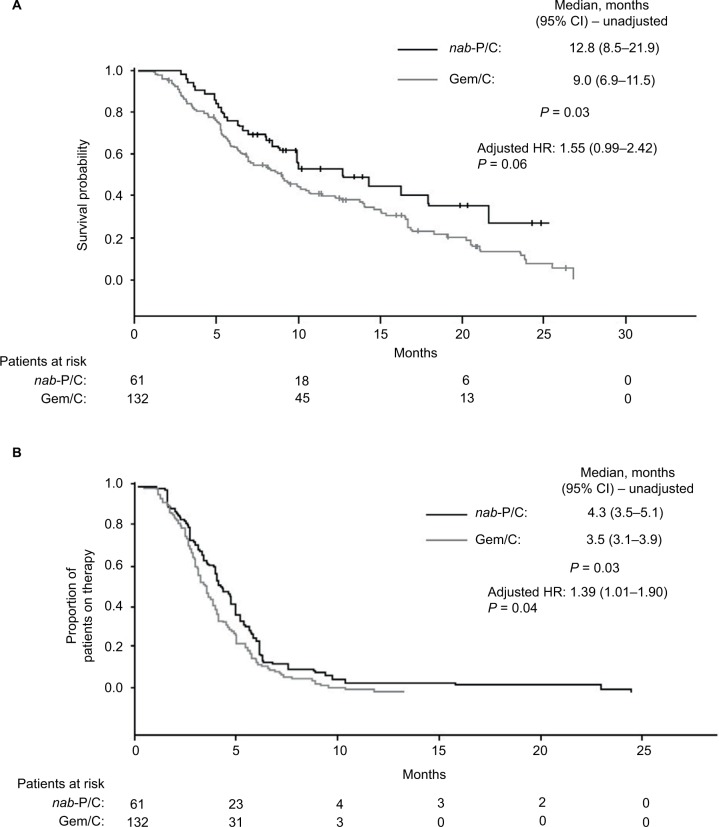
OS was significantly longer for patients who received nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin compared with those who received gemcitabine plus carboplatin (Figure 2A; median, 12.8 vs 9.0 months; P = 0.03); however, after adjusting for covariates (age, sex, and CCI), the OS difference was no longer statistically significant between the two groups (adjusted HR 1.55; 95% CI, 0.99–2.42; P = 0.06). The TTD was significantly longer for patients who received nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin compared with gemcitabine plus carboplatin (Figure 2B; median, 4.3 vs 3.5 months; P = 0.03). The difference in TTD between the two cohorts remained statistically significant after adjusting for covariates (age, sex, and CCI; adjusted HR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.01–1.90; P = 0.04).
Figure 2.
(A) Overall survival (initiation of first-line therapy until death) and (B) time to treatment discontinuation (initiation of first-line therapy until treatment discontinuation) among patients who received nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin or gemcitabine plus carboplatin.
Abbreviations: nab-P/C, nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin; Gem/C, gemcitabine plus carboplatin.
Safety and use of supportive care
While receiving first-line treatment, 92% of all patients had an adverse event reported. In patients who received nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin and those who received gemcitabine plus carboplatin, the rates of all-grade anemia (62% vs 66%; P = 0.63), neutropenia (51% vs 56%; P = 0.54), and thrombocytopenia (16% vs 23%; P = 0.34) were similar (Table 2). However, rates of grade 3 or 4 anemia (10% vs 26%; P = 0.01) and neutropenia (2% vs 11%; P = 0.04) were significantly lower among patients who received nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin compared with gemcitabine plus carboplatin. Grade information for non-hematologic adverse events was not reported. Rates of nausea were significantly higher in patients treated with nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin than in those who received gemcitabine plus carboplatin (89% vs 73%; P = 0.01), and similar findings were observed for rates of neuropathy (30% vs 12%; P < 0.01). Rates of other non-hematologic adverse events were not significantly different between the two groups.
Table 2.
Incidence of adverse events
| Adverse events, % |
nab-Paclitaxel plus carboplatin (n = 61) |
Gemcitabine plus carboplatin (n = 132) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hematologic | |||
| Anemia | 62 | 66 | 0.63 |
| Grade 3/4 | 10 | 26 | 0.01 |
| Neutropenia | 51 | 56 | 0.54 |
| Grade 3/4 | 2 | 11 | 0.04 |
| Thrombocytopeniaa | 16 | 23 | 0.34 |
| Non-hematologic (grade not specified) | |||
| Nausea | 89 | 73 | 0.01 |
| Pain | 79 | 79 | 0.99 |
| Vomiting | 61 | 58 | 0.69 |
| Fatigue | 62 | 63 | 0.94 |
| Diarrhea | 59 | 48 | 0.15 |
| Mucositis | 25 | 31 | 0.36 |
| Neuropathy | 30 | 12 | < 0.01 |
| Dehydration | 25 | 17 | 0.20 |
Note:
Not able to calculate grade 3 and 4 thrombocytopenia due to low incidence and/or missing lab values.
In both groups, all patients received premedication and 87% of patients used supportive care agents. No difference was observed between the two cohorts in the doses of erythropoiesis-stimulating agent, G-CSF, antiemetics, or steroids received during first-line treatment (Table 3).
Table 3.
Use of supportive care
| Supportive care use |
nab-Paclitaxel plus carboplatin (n = 61) |
Gemcitabine plus carboplatin (n = 132) |
P-valuea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Received supportive care, % | 87 | 87 | 0.43 |
| Received growth factor (ESA or G-CSF), % | 57 | 46 | 0.15 |
| Individual agents (doses/patient/100 days) | |||
| ESA agents | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.86 |
| G-CSF agents | 1.6 | 1.4 | 0.58 |
| Antiemetics | 9.9 | 9.0 | 0.26 |
| Steroids | 10.2 | 9.2 | 0.16 |
Note:
P-value for categorical variables was calculated by χ2; P-value for continuous variables was calculated by independent samples t-test.
Abbreviation: ESA, erythropoiesis-stimulating agent.
Treatments received
Patients in the nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin cohort received an average of 12.8 doses of nab-paclitaxel (median, 11.0 doses) and 7.3 doses of carboplatin (median, 6.0 doses). Patients in the gemcitabine plus carboplatin cohort received an average of 9.0 doses of gemcitabine (median, 8.0 doses) and 5.0 doses of carboplatin (median, 4.0 doses).
Sequencing outcomes
Overall, 43% and 46% of patients in the nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin and gemcitabine plus carboplatin cohorts, respectively, received a second-line treatment (Table 4). The most frequent second-line therapy (only considering instances where the second-line agent was reported) among patients who received first-line nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin was gemcitabine (35%); for those who received first-line gemcitabine plus carboplatin, it was docetaxel (39%). Among patients in the gemcitabine plus carboplatin cohort who received subsequent therapy, 13% were treated with second-line nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin.
Table 4.
Sequential therapy
| Second-line treatment, n (%) |
nab-Paclitaxel plus carboplatin (n = 26) |
Gemcitabine plus carboplatin (n = 61) |
|---|---|---|
| Docetaxel | 1 (4) | 24 (39) |
| Gemcitabine | 9 (35) | 1 (2) |
| Paclitaxel plus carboplatin | 3 (12) | 7 (11) |
| Paclitaxel | 2 (8) | 7 (11) |
| nab-Paclitaxel plus carboplatin | – | 8 (13) |
| Other | 11 (42) | 14 (23) |
Discussion
This retrospective analysis assessed effectiveness and safety outcomes in patients treated with two recommended regimens for advanced or metastatic squamous cell NSCLC in a real-world setting, and supported the clinical benefit of nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin for treating advanced squamous cell NSCLC. In the overall analysis, patients receiving nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin had a significantly longer OS compared with those receiving gemcitabine plus carboplatin. However, this difference was not statistically significant after adjusting for covariates, likely due to the small sample size. The nature of design of a retrospective cohort analysis is such that the analysis is not powered to detect statistically significant differences between treatment groups in the same way a randomized clinical trial is. The TTD was significantly longer in patients receiving nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin than in those receiving gemcitabine plus carboplatin, and the difference remained statistically significant after adjusting for covariates. Furthermore, nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin treatment was associated with a lower incidence of grade 3 or 4 anemia and neutropenia than gemcitabine plus carboplatin. However, nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin treatment was associated with a greater incidence of nausea and neuropathy (grade not specified) than gemcitabine plus carboplatin. There was no difference in supportive care use between the two cohorts.
Treatment duration and intensity may correlate with positive outcomes in patients with advanced NSCLC, but intensive chemotherapy has also been associated with more frequent adverse events in some clinical studies.18,19 In this real-world analysis of patients with advanced squamous cell NSCLC, nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin was associated with improved outcomes and lower rates of grade 3 or 4 anemia and neutropenia than gemcitabine plus carboplatin. The difference in the toxicities observed between these treatments does not appear to be associated with an increase in supportive care utilization because the proportion of patients using supportive care was similar in the treatment groups. Rates of non-hematologic adverse events were similar between the two groups, except for nausea and neuropathy, which occurred more often with nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin than gemcitabine plus carboplatin. In the nab-paclitaxel Phase III study, the rate of grade 3 or 4 neuropathy in the subset of patients with squamous cell NSCLC receiving nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin was 3% and the median time to improvement from grade 3 or 4 to grade 1 neuropathy was 38 days.12 Taken together with the results of the Phase III trial vs paclitaxel plus carboplatin,12 the more efficacious outcomes and lower rates of grade 3 or 4 anemia and neutropenia observed with nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin vs gemcitabine plus carboplatin in this analysis support the appropriateness and manageable safety profile of this option for the treatment of this patient population.
Traditionally, many patients with stage IIIB or IV NSCLC do not go on to receive therapy after first-line treatment.20 There are several reasons for this, but the ability to receive subsequent therapy in NSCLC may be influenced by the efficacy and safety of the regimen used for first-line treatment – second-line therapy for patients with NSCLC is typically reserved for those with a good performance status.21 However, because of recent advances, such as the approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors,22–24 more patients may receive second-line treatments. Data from randomized clinical trials demonstrated that, in patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC, approved immune checkpoint inhibitors were associated with fewer grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events and a significantly longer OS compared with docetaxel.8,25–28 In this study, 43% and 46% of patients in the nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin and gemcitabine plus carboplatin treatment groups, respectively, received a subsequent therapy consisting of chemotherapeutic agents. Currently, according to the NCCN guidelines, the preferred subsequent therapy for patients with advanced squamous cell NSCLC and a performance status of 0–2 is a systemic immune checkpoint inhibitor, whereas it is recommended that those with a performance status of 3–4 receive best supportive care.6 The evaluation of immune checkpoint inhibitors as second-line therapies could not be determined in this study because the US Food and Drug Administration approved nivolumab (approved in 2015), pembrolizumab (approved in 2015), and atezolizumab (Genentech, Inc, South San Francisco, CA, USA) (approved in 2016) for these patients after our index period.29–31
In the US, the median age at diagnosis of lung cancer is 70 years.14 In this study, 48% of the patients were at least 70 years of age. There was a higher proportion of patients ≥ 70 years of age in the nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin cohort than in the gemcitabine plus carboplatin cohort (54% vs 45%). In this patient population, the decision to use a systemic chemotherapeutic agent must be diligently weighed in terms of the potential toxicities. Whether practicing physicians chose the nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin regimen more frequently in this population due to its manageable toxicity profile is unknown.
Limitations
This was a retrospective cohort analysis of data from a large, diverse database – not a randomized study – and some baseline characteristics differed among the cohorts. However, where possible, imbalances were adjusted for in the OS and TTD analyses. No data on response rate or progression were available in the database. Performance status was unavailable for ≈ 54% of the patients in this study and could not be adjusted for as a covariate, which may have had a confounding effect. The current analysis was restricted to those patients with complete histology information available; this information was missing in 15% of those identified in the database as having received a diagnosis of stage III or IV NSCLC between October 2011 and December 2014. Adverse events were assessed using ICD-9 codes and laboratory values only, meaning that subjective adverse events such as neuropathy may be underreported. Furthermore, hematologic adverse events were identified by ICD-9 codes and adverse event grade could only be determined if laboratory values were available. Therefore, it is possible that hematologic adverse events by grade were underreported in the EMR database. Non-hematologic adverse events were also identified through ICD-9 codes and grade information for these adverse events was not available. The index date of the current analysis preceded the approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors; therefore, the effectiveness of these agents could not be assessed. Finally, use of specific regimens and data availability in the EMR limited the sample size, which ideally would have been larger. The relatively small sample size may detract from the ability to draw generalizable conclusions from the data, and any conclusions should take into consideration the sample size.
Conclusion
There is a paucity of data reflecting real-world outcomes in patients with advanced squamous cell NSCLC treated with first-line standard chemotherapy regimens. This study demonstrated the effectiveness and safety of nab-paclitaxel plus carboplatin in patients with advanced squamous cell NSCLC in a real-world setting, supporting the use of this regimen as a first-line treatment option.
Supplementary materials
Table S1.
Adverse event ICD-9-CM codes
| Adverse event | ICD-9 code |
|---|---|
| Neutropenia | 288.03 |
| Leukocytopenia, unspecified | 288.50 |
| Chemotherapy-induced anemia | 285.3 |
| Iron deficiency anemia secondary to blood loss | 280.0 |
| Other specified iron deficiency anemia | 280.8 |
| Iron deficiency anemia, unspecified | 280.9 |
| Constitutional red blood cell aplasia | 284.01 |
| Other constitutional aplastic anemia | 284.09 |
| Pancytopenia | 241.1 |
| Antineoplastic chemotherapy-induced pancytopenia | 284.11 |
| Other pancytopenia | 284.19 |
| Other specified aplastic anemia | 284.89 |
| Aplastic anemia, unspecified | 284.9 |
| Acute posthemorrhagic anemia | 285.1 |
| Anemia of chronic illness | 285.2 |
| Anemia in neoplastic disease | 285.22 |
| Anemia of chronic disease | 285.29 |
| Other specified anemia | 285.8 |
| Anemia, unspecified | 285.9 |
| Other abnormal blood chemistry | 790.6 |
| Nonspecific elevation of levels of transaminase or lactic acid | 790.4 |
| Other nonspecific findings on examination of blood | 790.99 |
| Acute kidney failure, unspecified | 584.9 |
| Renal failure, unspecified | 586 |
| Other emphysema | 492.8 |
| Bronchiectasis without acute exacerbation | 494.0 |
| Bronchiectasis with acute exacerbation | 494.1 |
| Pneumonia, organism unspecified | 486 |
| Pneumonia, due to other virus not classified elsewhere | 480.8 |
| Viral pneumonia, unspecified | 480.9 |
| Hypersomnia, unspecified | 780.54 |
| Nonspecific abnormal results of function study of kidney | 794.4 |
| Nonspecific abnormal electrocardiogram | 794.31 |
| Nonspecific abnormal results of function study of liver | 794.8 |
| Secondary thrombocytopenia | 287.4 |
| Other secondary thrombocytopenia | 287.49 |
| Malaise and fatigue NEC | 780.79 |
| Anorexia | 783.0 |
| Nausea with vomiting | 787.01 |
| Nausea alone | 787.02 |
| Vomiting alone | 787.03 |
| Acute bronchospasm | 519.11 |
| Acute interstitial pneumonitis | 516.33 |
| Idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonitis | 516.32 |
| Leukocytosis unspecified | 288.60 |
| Acute and sub-acute bacterial endocarditis | 421.0 |
| Endocarditis NEC | 424.99 |
| Secondary cardiomyopathy, unspecified | 425.9 |
| Angina pectoris NEC/NOS | 413.9 |
| Hypotension NEC | 458.8 |
| Hypotension NOS | 458.9 |
| Congestive heart failure NOS | 428.0 |
| Acute upper respiratory infection | 465.9 |
| Urinary tract infection NOS | 599.0 |
| Hypertension NOS (unspecified essential hypertension) | 401.9 |
| Pruritus ani | 698.0 |
| Alopecia NEC | 704.09 |
| Alopecia NOS | 704.00 |
| Non-specific skin eruption NEC (rash and other nonspecific skin eruption) | 782.1 |
| Diarrhea | 787.91 |
| Constipation NOS | 564.00 |
| Constipation NEC | 564.09 |
| Electrolyte and fluid disorders | 276.9 |
| Stomatitis/mucositis NOS | 528.00 |
| Other stomatitis/mucositis (ulcerative) | 528.09 |
| Dehydration | 276.51 |
| Proteinuria | 791.0 |
| Neuropathy due to drugs | 357.6 |
| Hemorrhage NOS | 459.0 |
| Acute pain NEC | 338.19 |
| Neoplasm related pain (acute) (chronic) | 338.3 |
| Myalgia and myositis NOS | 729.1 |
| Other anaphylactic reaction | 995.0 |
| Sepsis | 995.91 |
| Cough | 786.2 |
| Shortness of breath | 786.05 |
| Hyperosmolality (hyperosmolality and/or hypernatremia) | 276.0 |
| Hypocalcemia | 275.41 |
Abbreviations: ICD-9, International Classification of Disease, Ninth Revision; NEC, not elsewhere classified; NOS, not otherwise specified.
Table S2.
Charlson Comorbidity Index
| Comorbidity | ICD-9 | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Myocardial infarctiona | 410.x, 412.x | 1 |
| Congestive heart failurea | 428.x | 1 |
| Peripheral vascular diseasea | 440.x, 441.2, 441.4, 441.7, 441.9, 443.1 – 443.9, 447.1, 557.1, 557.9, V43.4 | 1 |
| Cerebrovascular diseasea | 430.x – 438.x | 1 |
| Dementiaa | 290.x | 1 |
| Chronic pulmonary diseasea | 490.x – 505.x, 506.4 | 1 |
| Rheumatologic diseasea | 710.0, 710.1, 710.4, 714.0 – 714.2, 714.81, 725.x | 1 |
| Peptic ulcer diseasea | 531.x – 534.x | 1 |
| Hemiplegia or paraplegiaa | 344.1, 342.x | 2 |
| Renal diseasea | 582.x, 583 – 583.7, 585.x, 586.x, 588.x | 2 |
| AIDS/HIVa | 042.x – 044.x | 6 |
| Age 40–49 years | 1 | |
| Age 50–59 years | 2 | |
| Age 60–69 years | 3 | |
| Age ≥70 years | 4 | |
| Diabetesb | ||
| With chronic complication | 250.4 – 250.6 | 2 |
| Without chronic complication | 250.0 – 250.3, 250.7 | 1 |
| Liver diseaseb | ||
| Moderate or severe | 456.0 – 456.21, 572.2 – 572.8 | 3 |
| Mild | 571.2, 571.4 – 571.6 | 1 |
| Cancersb | ||
| Metastatic solid tumor | 196.x – 199.1 or 140.x – 172.x, 174.x – 195.8c | 6 |
| Any malignancy, including leukemia and lymphoma | 140.x – 172.x, 174.x – 195.8, 200.x – 208.x | 2 |
Notes:
For these conditions, sum points for each row.
For these conditions, assign points for the first condition, if met, but not for the second. If the second condition is met but the first is not, assign the points for the second condition.
With Met 1 or higher for breast cancer, or second line or beyond for other solid cancers.
Abbreviations: HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ICD-9, International Classification of Disease, Ninth Revision.
Acknowledgments
Writing assistance was provided by Aaron Runkle, PhD, MediTech Media, through funding by Celgene Corporation. The authors were fully responsible for all content and editorial decisions for this manuscript. This work was supported by the Celgene Corporation. Presented previously as a poster at the 2016 NCCN Annual Conference (April 1, 2016; Hollywood, FL).
Footnotes
Disclosure
RM is a consultant for Celgene Corporation; MBP and SMD are employees of Celgene; DG and LSL were employees of Cardinal Health, which received research funding from Celgene Corporation. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1. globocan.iarc.fr [homepage on the Internet] GLOBOCAN 2012: estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. World Health Organization; 2012. [Accessed August 29, 2017]. [updated 2017; cited July 13, 2016]. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx. [Google Scholar]
- 2. cancer.org [homepage on the Internet] Cancer Facts & Figures 2017. American Cancer Society; 2017. [Accessed August 29, 2017]. [updated 2017; cited February 8, 2017]. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2017.html. [Google Scholar]
- 3. cancer.org [homepage on the Internet] Non-small cell lung cancer. American Cancer Society; 2017. [Accessed August 29, 2017]. [updated 2017; cited February 10, 2017]. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/non-small-cell-lung-cancer.html. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brahmer J, Horn L, Jackman D, et al. Five-year follow-up from the CA209-003 study of nivolumab in previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): clinical characteristics of long-term survivors [abstract] Cancer Res. 2017;77(13 Suppl):CT077. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cetin K, Ettinger DS, Hei YJ, O’Malley CD. Survival by histologic subtype in stage IV nonsmall cell lung cancer based on data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program. Clin Epidemiol. 2011;3:139–148. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S17191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.National Comprehensive Cancer Network . NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. V8.2017. National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2017. [Accessed August 29, 2017]. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(21):2018–2028. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10027):1540–1550. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Keytruda® (pembrolizumab) [package insert] Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co Inc; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Novello S, Barlesi F, Califano R, et al. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(Suppl 5):v1–v27. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Socinski MA, Bondarenko I, Karaseva NA, et al. Weekly nab-paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin versus solvent-based paclitaxel plus carboplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: final results of a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(17):2055–2062. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.39.5848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Socinski MA, Okamoto I, Hon JK, et al. Safety and efficacy analysis by histology of weekly nab-paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(9):2390–2396. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, et al. Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(21):3543–3551. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.0375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. seer.cancer.gov [homepage on the Internet] SEER Cancer Stat Facts: lung and bronchus cancer Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute; 2014. [Accessed August 29, 2017]. [updated June 28, 2017; cited Jul 25, 2017]. Available from: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gajra A. Defining the issues in the treatment of elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer Management. 2015;4(1):17–30. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Abraxane® for Injectable Suspension (paclitaxel protein-bound particles for injectable suspension) (albumin-bound) [package insert] Summit, NJ: Celgene Corporation; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gemzar (gemcitabine) [package insert] Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang XS, Lu C, Shi Q, et al. Symptom burden and survival outcome: 3 cycles versus 6 cycles of chemotherapy in advanced NSCLC [abstract] J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(18 Suppl):17054. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Soon YY, Stockler MR, Askie LM, Boyer MJ. Duration of chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(20):3277–3283. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.4522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sculier JP, Moro-Sibilot D. First- and second-line therapy for advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 2009;33(4):915–930. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00132008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.De Marinis F, De Santis S, De Petris L. Second-line chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2006;(17Suppl 5):v68–v71. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdj954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Keytruda® (pembrolizumab) [package insert] Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co Inc; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Opdivo® (nivolumab) [package insert] Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tecentriq® (atezolizumab) [package insert] South San Francisco, CA: Genentech, Inc; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(17):1627–1639. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1507643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(2):123–135. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Barlesi F, Park K, Ciardiello F, et al. Primary analysis from OAK, a randomized phase III study comparing atezolizumab with docetaxel in 2L/3L NSCLC [abstract] Ann Oncol. 2016;27(Suppl 6):LBA44_PR. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387(10030):1837–1846. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00587-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.US Food and Drug Administration . FDA expands approved use of Opdivo to treat lung cancer [press release] Silver Spring, MD: US Food and Drug Administration; 2015. [Accessed August 29, 2017]. [March 5]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm436534.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 30.US Food and Drug Administration . FDA approves Keytruda for advanced non-small cell lung cancer [press release] Silver Spring, MD: US Food and Drug Administration; 2015. Oct 5, [Accessed August 29, 2017]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm465444.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 31. fda.gov [homepage on the Internet] Atezolizumab (TECENTRIQ) US Food and Drug Administration; 2016. 2016. [Accessed August 29, 2017]. [updated October 19, 2016; cited November 30, 2016]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm525780.htm. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1.
Adverse event ICD-9-CM codes
| Adverse event | ICD-9 code |
|---|---|
| Neutropenia | 288.03 |
| Leukocytopenia, unspecified | 288.50 |
| Chemotherapy-induced anemia | 285.3 |
| Iron deficiency anemia secondary to blood loss | 280.0 |
| Other specified iron deficiency anemia | 280.8 |
| Iron deficiency anemia, unspecified | 280.9 |
| Constitutional red blood cell aplasia | 284.01 |
| Other constitutional aplastic anemia | 284.09 |
| Pancytopenia | 241.1 |
| Antineoplastic chemotherapy-induced pancytopenia | 284.11 |
| Other pancytopenia | 284.19 |
| Other specified aplastic anemia | 284.89 |
| Aplastic anemia, unspecified | 284.9 |
| Acute posthemorrhagic anemia | 285.1 |
| Anemia of chronic illness | 285.2 |
| Anemia in neoplastic disease | 285.22 |
| Anemia of chronic disease | 285.29 |
| Other specified anemia | 285.8 |
| Anemia, unspecified | 285.9 |
| Other abnormal blood chemistry | 790.6 |
| Nonspecific elevation of levels of transaminase or lactic acid | 790.4 |
| Other nonspecific findings on examination of blood | 790.99 |
| Acute kidney failure, unspecified | 584.9 |
| Renal failure, unspecified | 586 |
| Other emphysema | 492.8 |
| Bronchiectasis without acute exacerbation | 494.0 |
| Bronchiectasis with acute exacerbation | 494.1 |
| Pneumonia, organism unspecified | 486 |
| Pneumonia, due to other virus not classified elsewhere | 480.8 |
| Viral pneumonia, unspecified | 480.9 |
| Hypersomnia, unspecified | 780.54 |
| Nonspecific abnormal results of function study of kidney | 794.4 |
| Nonspecific abnormal electrocardiogram | 794.31 |
| Nonspecific abnormal results of function study of liver | 794.8 |
| Secondary thrombocytopenia | 287.4 |
| Other secondary thrombocytopenia | 287.49 |
| Malaise and fatigue NEC | 780.79 |
| Anorexia | 783.0 |
| Nausea with vomiting | 787.01 |
| Nausea alone | 787.02 |
| Vomiting alone | 787.03 |
| Acute bronchospasm | 519.11 |
| Acute interstitial pneumonitis | 516.33 |
| Idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonitis | 516.32 |
| Leukocytosis unspecified | 288.60 |
| Acute and sub-acute bacterial endocarditis | 421.0 |
| Endocarditis NEC | 424.99 |
| Secondary cardiomyopathy, unspecified | 425.9 |
| Angina pectoris NEC/NOS | 413.9 |
| Hypotension NEC | 458.8 |
| Hypotension NOS | 458.9 |
| Congestive heart failure NOS | 428.0 |
| Acute upper respiratory infection | 465.9 |
| Urinary tract infection NOS | 599.0 |
| Hypertension NOS (unspecified essential hypertension) | 401.9 |
| Pruritus ani | 698.0 |
| Alopecia NEC | 704.09 |
| Alopecia NOS | 704.00 |
| Non-specific skin eruption NEC (rash and other nonspecific skin eruption) | 782.1 |
| Diarrhea | 787.91 |
| Constipation NOS | 564.00 |
| Constipation NEC | 564.09 |
| Electrolyte and fluid disorders | 276.9 |
| Stomatitis/mucositis NOS | 528.00 |
| Other stomatitis/mucositis (ulcerative) | 528.09 |
| Dehydration | 276.51 |
| Proteinuria | 791.0 |
| Neuropathy due to drugs | 357.6 |
| Hemorrhage NOS | 459.0 |
| Acute pain NEC | 338.19 |
| Neoplasm related pain (acute) (chronic) | 338.3 |
| Myalgia and myositis NOS | 729.1 |
| Other anaphylactic reaction | 995.0 |
| Sepsis | 995.91 |
| Cough | 786.2 |
| Shortness of breath | 786.05 |
| Hyperosmolality (hyperosmolality and/or hypernatremia) | 276.0 |
| Hypocalcemia | 275.41 |
Abbreviations: ICD-9, International Classification of Disease, Ninth Revision; NEC, not elsewhere classified; NOS, not otherwise specified.
Table S2.
Charlson Comorbidity Index
| Comorbidity | ICD-9 | Points |
|---|---|---|
| Myocardial infarctiona | 410.x, 412.x | 1 |
| Congestive heart failurea | 428.x | 1 |
| Peripheral vascular diseasea | 440.x, 441.2, 441.4, 441.7, 441.9, 443.1 – 443.9, 447.1, 557.1, 557.9, V43.4 | 1 |
| Cerebrovascular diseasea | 430.x – 438.x | 1 |
| Dementiaa | 290.x | 1 |
| Chronic pulmonary diseasea | 490.x – 505.x, 506.4 | 1 |
| Rheumatologic diseasea | 710.0, 710.1, 710.4, 714.0 – 714.2, 714.81, 725.x | 1 |
| Peptic ulcer diseasea | 531.x – 534.x | 1 |
| Hemiplegia or paraplegiaa | 344.1, 342.x | 2 |
| Renal diseasea | 582.x, 583 – 583.7, 585.x, 586.x, 588.x | 2 |
| AIDS/HIVa | 042.x – 044.x | 6 |
| Age 40–49 years | 1 | |
| Age 50–59 years | 2 | |
| Age 60–69 years | 3 | |
| Age ≥70 years | 4 | |
| Diabetesb | ||
| With chronic complication | 250.4 – 250.6 | 2 |
| Without chronic complication | 250.0 – 250.3, 250.7 | 1 |
| Liver diseaseb | ||
| Moderate or severe | 456.0 – 456.21, 572.2 – 572.8 | 3 |
| Mild | 571.2, 571.4 – 571.6 | 1 |
| Cancersb | ||
| Metastatic solid tumor | 196.x – 199.1 or 140.x – 172.x, 174.x – 195.8c | 6 |
| Any malignancy, including leukemia and lymphoma | 140.x – 172.x, 174.x – 195.8, 200.x – 208.x | 2 |
Notes:
For these conditions, sum points for each row.
For these conditions, assign points for the first condition, if met, but not for the second. If the second condition is met but the first is not, assign the points for the second condition.
With Met 1 or higher for breast cancer, or second line or beyond for other solid cancers.
Abbreviations: HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ICD-9, International Classification of Disease, Ninth Revision.