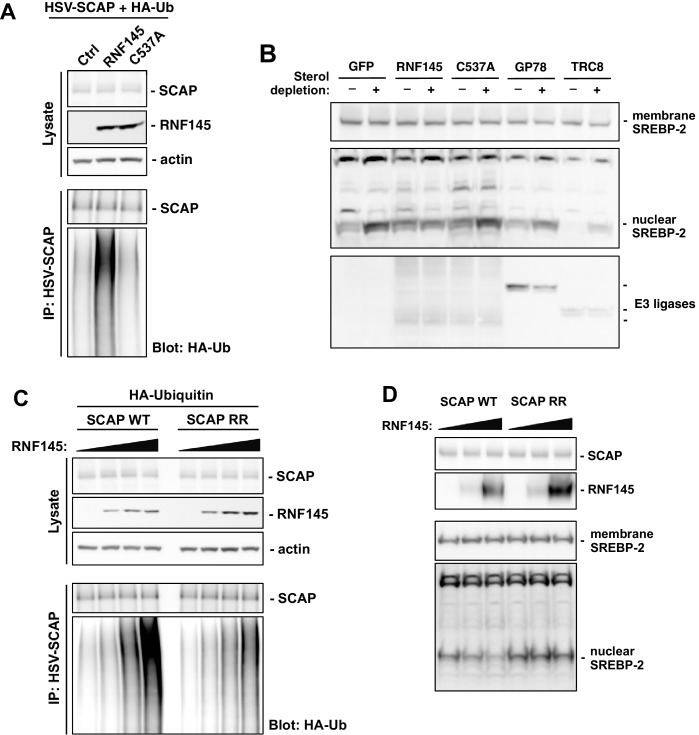
Figure 6. RNF145 ubiquitinates SCAP to inhibit SREBP processing.
(A) CHO cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HSV-tagged SCAP and HA-tagged ubiquitin, together with RNF145 or RING-mutant RNF145 (C537A). Cell lysates were blotted with the indicated antibodies. Cell lysates were also immunoprecipitated with HSV antibody, and the precipitated proteins were blotted with HA antibody. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HSV-tagged SREBP-2 under the control of a TK promoter, together with GFP control, RNF145 or RING-mutant RNF145, GP78, or TRC8. Cells were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS, or in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% lipoprotein-deficient serum and 25 μM simvastation overnight to deplete sterol, and then treated for 4 hr with MG132 (25 μM). Membrane and nuclear protein fractions of the cells were then isolated and blotted with the indicated antibodies. (C) CHO cells were transfected with plasmids encoding RNF145 and HA-tagged ubiquitin, together with HSV-tagged SCAP or mutant SCAP (K454R, K466R). Cell lysates were blotted with the indicated antibodies. Cell lysates were also immunoprecipitated with HSV antibody, and the precipitated proteins were blotted with HA antibody. (D) SCAP-knockout HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HSV-tagged SREBP-2 under the control of a TK promoter and RNF145, together with V5-tagged SCAP or ubiquitination-site mutant SCAP (K454R, K466R). Cells were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% lipoprotein-deficient serum and 25 μM simvastation overnight to deplete sterol, and then treated for 4 hr with MG132 (25 μM). Membrane and nuclear protein fractions were isolated and blotted with the indicated antibodies.