Abstract
This protocol describes the isolation of tonoplast vesicles from tomato fruit. The vesicles isolated using this procedure are of sufficiently high purity for downstream proteomic analysis whilst remaining transport competent for functional assays. The methodology was used to study the transport of amino acids during tomato fruit ripening (Snowden et al., 2015) and based on the procedure used by Betty and Smith (Bettey and Smith, 1993). Such vesicles may be useful in further studies into the dynamic transfer of metabolites across the tonoplast for storage and metabolism during tomato fruit development.
Materials and Reagents
Ultra centrifuge tubes, 32 ml capacity, thick wall, polycarbonate (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 355631)
3 ml pastettes
Solanum lycopersicum Lam. cv. M82 or cv. Micro-Tom
Bovine serum albumin (Fraction V) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7906)
D-Mannitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9647)
Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10256840)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E4884)
Polyvinylpyrrolidone average molecular weight 40,000 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: PVP40)
2-Amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1, 3-propanediol (Trizma® base) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503)
Butylated hydroxytoluene (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: W218405)
Potassium disulfite (K2S2O5) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P2522)
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluouride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626)
Ethanol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12468750)
(+)-Sodium L-ascorbate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7631)
DL-Dithiothreitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632)
Potassium hydroxide (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10366240)
Glycerol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10296200)
BIS-TRIS propane (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6755)
Tricine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0377)
Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0389)
Muslin cloth (100 % cotton)
2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3671)
Extraction buffer (see Recipes)
Resuspension buffer (see Recipes)
Sucrose steps (see Recipes)
Transport buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
Scalpel Handle Swan Morton No.4 (Philip Harris, catalog number: B8R00181)
Scalpel blades Swan Morton No. 24 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11712734)
Blender (For example a Waring 38BL41 with a 40 oz container)
Ultra centrifuge capable of 100,000 x g with swing out rotor (e.g. SW28 Ti)
Soft paint brush (Sable No.5 or equivalent)
1,000 µl micropipette
Procedure
The core procedure detailed here was designed to isolate high purity tonoplast vesicles for proteomic analysis. Modifications to the step gradient are included that allow higher yield preparations suitable for transport assays. As with all organelle isolation procedures the balance between yield and purity will depend on the downstream application. For example proteomic approaches are facilitated by a higher purity of membranes whilst transport assays require a higher yield of membrane. The scale of this protocol can be readily adapted for between 20 g to 80 g of starting material, maintaining the same proportion of plant biomass to buffer.
This procedure is carried out at 4 °C, in a cold room, using pre-chilled equipment and freshly prepared solutions incubated on ice for 4 h before starting.
-
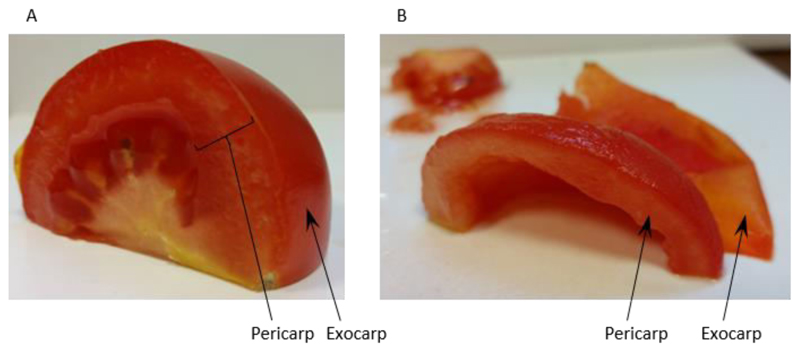
Homogenise 60 g of tomato fruit pericarp [exocarp (outer skin) removed] (see Figure 1) with 150 ml Extraction buffer (see Recipe 1) in a blender.
Note: To minimise heating the fruit are homogenised in 6 x 3 sec high speed pulses.
-
Filter the homogenate through 2 layers of muslin and distribute evenly between 6 ultra-centrifuge tubes. Approximately 180 ml of filtrate is usually collected giving approximately 30 ml of filtrate per centrifuge tube.
Note: The filtration should be done quickly and the transfer of foam should be avoided.
-
Centrifuge the homogenate at 20,000 x g for 20 min.
Note: This is an initial clarifying spin to remove cell debris and mitochondria.
-
Transfer the supernatant to clean ultra-centrifuge tubes and centrifuge at 100,000 x g for 60 min.
Note: This will pellet the membranes from the supernatant.
-
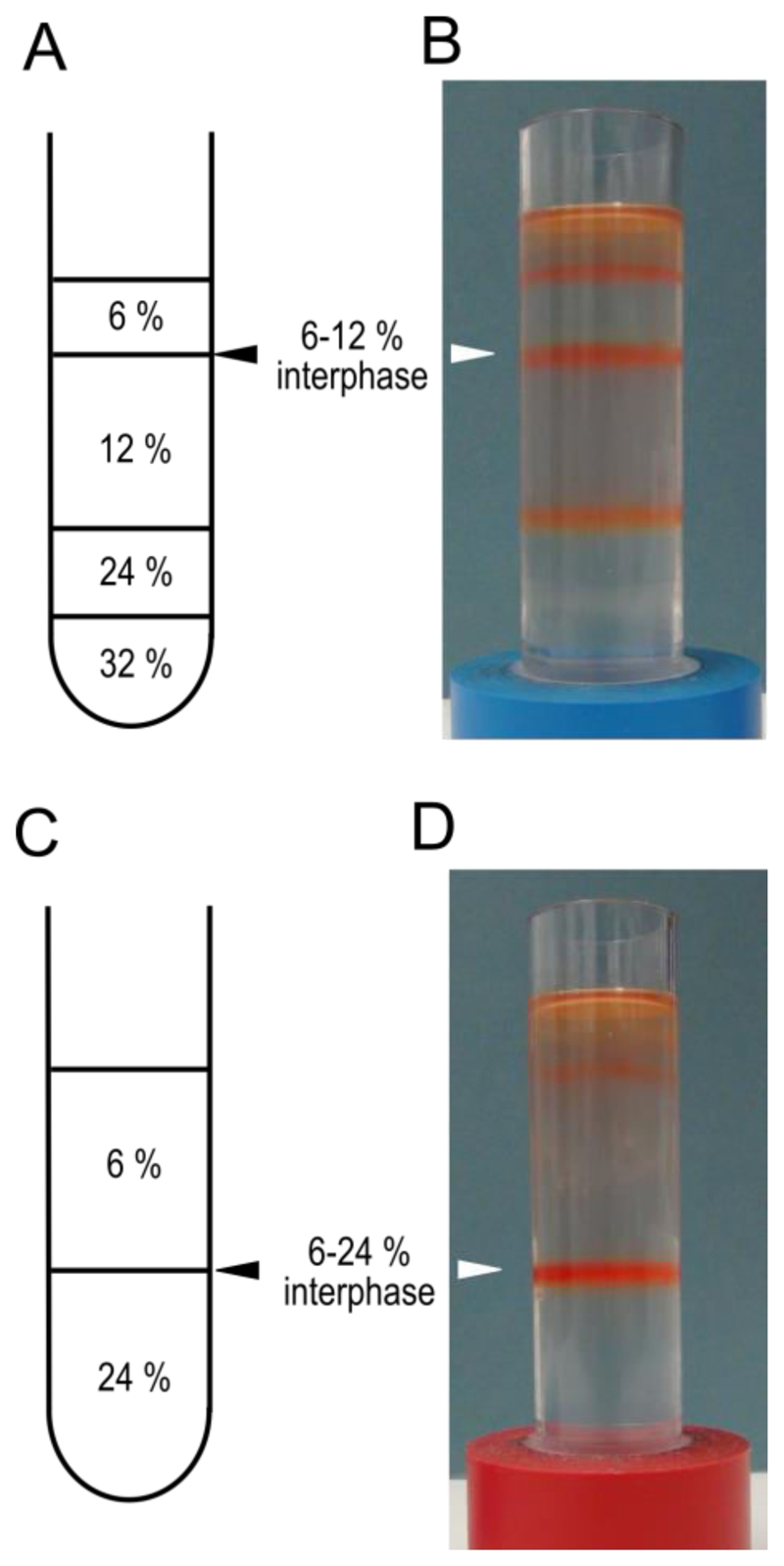
During the centrifugation prepare 2 step gradients. In clean, dry ultra-centrifuge tubes layer 5 ml of 32% sucrose, 5 ml of 24% sucrose, 10 ml of 12% sucrose and 5 ml of 6% sucrose (see Recipe 3 for sucrose solutions). Keep the gradients at 4 °C until needed.
Notes:
If the membranes are intended for transport assays a simplified gradient consisting of 12 ml of 24% and 12 ml of 6% sucrose can be used.
A schematic representation of the gradients is shown in Figure 2 A and C.
A short video of how to layer sucrose solutions is shown in Video 1.
-
Remove the supernatant after centrifugation in step 4, ideally this is carried out using a 200 μl micro-pipette tip connected to an aspirator.
Note: Keeping the end of the tip just below the surface of the supernatant will reduce the amount of liquid that sticks to the walls of the tube (you should hear a slurping noise when the tip is placed optimally). It is important to avoid touching the pellet with the tip as this will result in membrane loss.
-
Resuspend all 6 pellets in a total of 5 ml of Resuspension buffer (see Recipe 2) using a soft paint brush. Gently sweep the tip of the brush across the membrane pellet until resuspended.
Note: To maximise yields first resuspend the pellets in a total of 3 ml then rinse the tubes and brush with the remaining 2 ml and combine.
Layer 2.5 ml of resuspended membranes onto the top of each gradient and centrifuge at 100,000 x g for 60 min.
-
Harvest the membranes from the 6% to 12% interphase using a 1,000 μl pipette fitted with a tip cut at 45° (see Video 2) and transfer to a clean ultra-centrifuge tube.
Notes:
The membranes from the 2 gradients can be pooled at this point.
Preps for transport assays should be harvested from the 6%-24% interphase.
-
Add 20 ml of Resuspension buffer to the membranes and centrifuge at 100,000 x g for 60 min.
Note: This will wash the membranes.
-
Aspirate off the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 200 μl of Resuspension buffer.
Note: If the membranes are for use in transport assays resuspend in Transport buffer (see Recipe4).
For storage flash freeze membranes in liquid nitrogen and store at -80 °C.
Figure 1. Preparation of tomato fruit pericarp for homogenisation.
Panel A shows a quarter of a tomato fruit with the regions of pericarp tissue and the exocarp labelled. Panel B shows the same quarter prepared for homogenisation after removal of the exocarp and locule.
Figure 2. Sucrose step gradients for tonoplast vesicle isolation.
Schematic representations of the sucrose step gradients prepared in step 5 for high purity, A, and high yield C protocols. Panels B and D show examples of the gradients after centrifugation in step 8. The interphases to be harvested are indicated with triangles. These gradients have been used to isolate membranes from mature red fruit.
Representative data
Notes
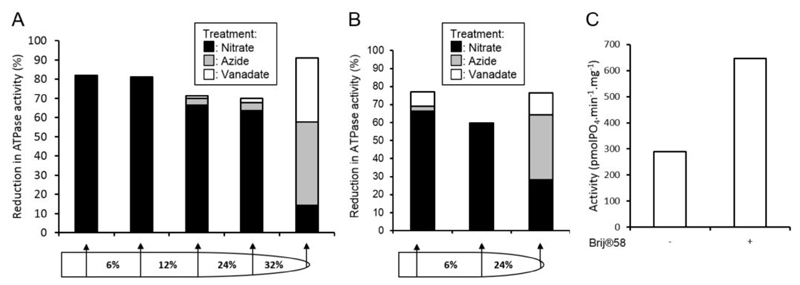
Membrane fraction purity can be assessed through ATPase assays (Oleski et al., 1987) using specific inhibitors of tonoplast, mitochondrial and plasma membrane ATPase (Smith et al., 1984). Membrane H+-ATPase complexes are highly indicative of specific membranes; V-type, tonoplast; F-type, mitochondrial; P-type, plasma membrane. By assaying the rate of ATP hydrolysis in a membrane fraction and measuring the reduction in activity in the presence of specific inhibitors the relative purity of a membrane fraction can be determined, see Figure 3 for example.
The intactness of membrane vesicles can be assessed through ATPase assays in the presence and absence of the non-ionic surfactant Brij® 58 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5884).
To remove peripheral and soluble proteins a carbonate wash of the membranes can be performed. This should not be done on vesicles required for transport assays as you will no longer have sealed vesicles.
Membrane yield can be assessed through protein content using common protein concentration assays e.g. Bradford method.
Figure 3. Assessment of vesicle purity and integrity.
Membrane fraction purities from full A and simplified B gradients were assessed by the inhibition of ATPase activities by 500 μM sodium orthovanadate (inhibits plasma membrane ATPase), 500 μM sodium azide (inhibits mitochondrial ATPase), or 50 mM KNO3 (inhibits tonoplast ATPase). C. Tonoplast vesicle integrity from the 6-24% membrane fraction of the gradient in panel B was assessed by the increase in ATPase activity in the presence of the detergent Brij® 58 (final concentration 0.015 mg ml-1).
Recipes
-
Extraction buffer
450 mM mannitol
3 mM MgSO4˙7H2O
5 mM Na2-EDTA
0.5% (w/v) PVP-40
50 mM TRIS
500 μM butylated hydroxyltoluene
26 mM potassium disulfite
200 mM sodium ascorbate
0.5% (w/v) BSA
1 mM PMSF
10 mM DTT
pH 8.0 (KOH)
-
Resuspension buffer
1.1 M Glycerol
1 mM Na2-EDTA
10 mM BTP
2 mM DTT
pH 8.0 (Tricine)
-
Sucrose steps
6, 12, 24 and 32% sucrose (w/v) in resuspension buffer
-
Transport buffer
50 mM 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES)/BTP (pH 7.0)
5 mM KCl
5 mM MgSO4˙7H2O
1 mM DTT
Supplementary Material
The video shows the layering of 24% sucrose solution onto a layer of 32% sucrose. Note the starting position of the pastette just above the meniscus of the 32% sucrose layer. The pastette is raised slowly maintaining contact with the growing 24% layer.
The video shows how to harvest an interphase from a sucrose step gradient. The initial removal of the upper phases above the desired interphase is carried out with a 3 ml pastette, this step reduces contamination from carry through as a pipette tip passes through a membrane layer. Care is taken not to disturb the target interphase leaving approximately 0.5 cm of solution above this layer. The membrane is harvested using a 1,000 μl pipette tip cut to 45°.
Acknowledgements
The research leading to the development of this protocol was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, UK (grant BB/H00338X/1) and Syngenta.
References
- 1.Bettey M, Smith JA. Dicarboxylate transport at the vacuolar membrane of the CAM plant Kalanchoe daigremontiana: sensitivity to protein-modifying and sulphydryl reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1152(2):270–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Oleski N, Mahdavi P, Peiser G, Bennett AB. Transport properties of the tomato fruit tonoplast: I. Identification and characterization of an anion-sensitive H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1987;84(4):993–996. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Smith JA, Uribe EG, Ball E, Heuer S, Luttge U. Characterization of the vacuolar ATPase activity of the crassulacean-acid-metabolism plant Kalanchoe daigremontiana. Receptor modulating. Eur J Biochem. 1984;141(2):415–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Snowden CJ, Thomas B, Baxter CJ, Smith JA, Sweetlove LJ. A tonoplast Glu/Asp/GABA exchanger that affects tomato fruit amino acid composition. Plant J. 2015;81(5):651–660. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The video shows the layering of 24% sucrose solution onto a layer of 32% sucrose. Note the starting position of the pastette just above the meniscus of the 32% sucrose layer. The pastette is raised slowly maintaining contact with the growing 24% layer.
The video shows how to harvest an interphase from a sucrose step gradient. The initial removal of the upper phases above the desired interphase is carried out with a 3 ml pastette, this step reduces contamination from carry through as a pipette tip passes through a membrane layer. Care is taken not to disturb the target interphase leaving approximately 0.5 cm of solution above this layer. The membrane is harvested using a 1,000 μl pipette tip cut to 45°.