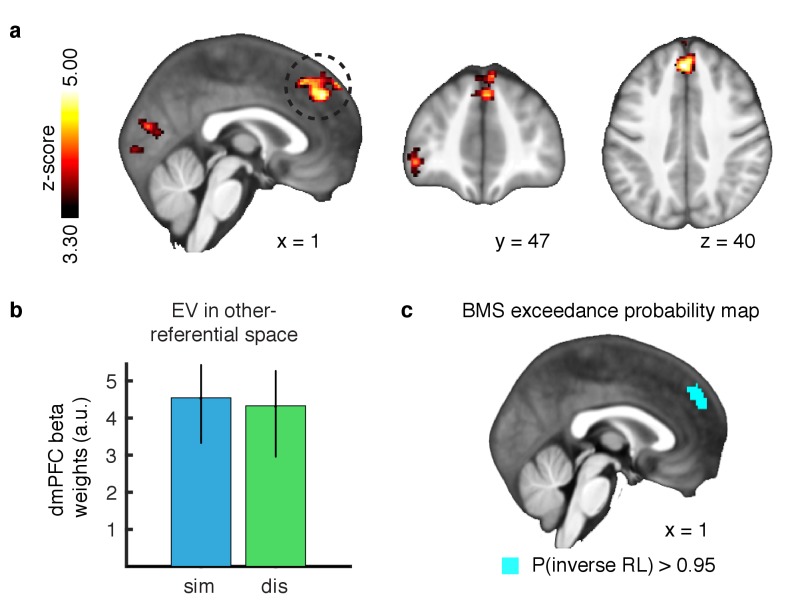
Figure 3. Outcome prediction signals in agent-referential preference space.
(A) Neural response to parametric changes in inverse RL outcome prediction in agent-referential space. Activity in dmPFC at the time of presumptive agent decision significantly correlated with outcome prediction inferred from the inverse RL model, independent of condition. All depicted clusters survive whole brain cluster correction FWE at p<0.05, with a height threshold of p<0.001. Z-score map threshold as indicated, for illustrative purposes. (B) Effect sizes of the outcome prediction correlation in dmPFC cluster separately for each condition (similar = blue, dissimilar = green, parameter estimates are extracted with a leave-one-out procedure, mean ±SEM across participants, p<0.05 for both conditions). (C) Group-level exceedance probability map of the Bayesian Model Selection, comparing predictions from the imitation RL against inverse RL voxelwise in an anatomically defined dmPFC region. The depicted map was thresholded to show voxels where the exceedance probability for the inverse RL model is greater than p=0.95, revealing that the anterior part of dmPFC is much more likely to encode inverse RL computations.