Abstract
Overproduction of H2O2 causes oxidative stress and is the hallmark of vascular diseases. Tracking native H2O2 in the endothelium is therefore indispensable to gain fundamental insights into this pathogenesis. Previous fluorescent probes for H2O2 imaging were generally arylboronates which were decomposed to emissive arylphenols in response to H2O2. Except the issue of specificity challenged by peroxynitrite, boric acid by-produced in this process is actually a waste with unknown biological effects. Therefore, improvements could be envisioned if a therapeutic agent is by-produced instead. Herein, we came up with a “click-to-release-two” strategy and demonstrate that dual functional probes could be devised by linking a fluorophore with a therapeutic agent via a H2O2-responsive bond. As a proof of concept, probe AP consisting of a 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl) benzothiazole fluorophore and an aspirin moiety has been prepared and confirmed for its theranostic effects. This probe features high specificity towards H2O2 than other reactive species including peroxynitrite. Its capability to image and ameliorate endothelial injury has been verified both in vitro and in vivo. Noteworthy, as a result of its endothelial-protective effect, AP also works well to reduce thrombosis formation in zebrafish model.
Keywords: theranostic probe, fluorescent imaging, hydrogen peroxide, endothelial injury, oxidative stress.
Introduction
Endothelial dysfunction is critically involved in the pathogenesis of cardio- and cerebro-vascular diseases 1. Although the underlying molecular mechanisms responsible for this pathological cascade remain elusive, it is affirmative that oxidative stress contributes to the etiology 2. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are therefore considered as crucial detrimental factors in the initiation and progression of neurovascular and cardiovascular disorders 3, 4. As a prime member of the ROS family, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) has been implicated in severe pathological conditions such as stroke 3, 4. Aberrant levels of H2O2 in endothelial cells can imbalance redox state, destroy endothelial function and result in cellular damage 5, 6. As a pro-oxidant molecule, H2O2 is mainly converted from superoxide spontaneously or following dismutation by superoxide dismutase 7. It is subsequently scavenged by enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase, thioredoxins, or peroxiredoxins (Prx) 8-10. H2O2 may also be converted to highly reactive hydroxyl radical either by exposure to ultraviolet light or via Fenton or Haber-Weiss reactions 11, 12. H2O2 can oxidize macromolecules such as lipids, proteins and DNA to cause cytotoxic damage 13-15. Nevertheless, on the contrary to its evil “Mr. Hyde” side, recent findings have lighted up its “Dr. Jekyll” role as a second messenger with pro-survival function in several physiological processes 16-18. As a Janus molecule, H2O2 has inspired great research interest on its role during redox signaling. It has been presumed that whether H2O2 is evil or good is determined largely by the context of production, local concentration, trafficking and consumption 19, which highlights the importance of detecting H2O2 dynamically in live organisms.
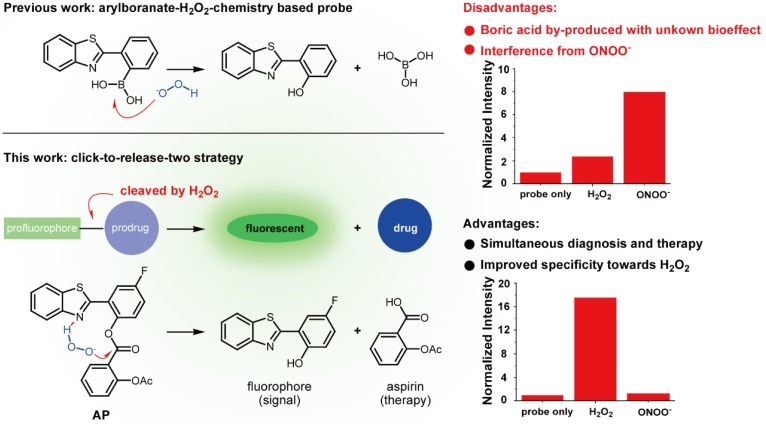
Numerous strategies have been developed to detect H2O2, including redox-sensitive fluorescent proteins 20-22, nanotubes 23, 24, hyperpolarization 25, ultrasound 26, mass spectrometry 27, PET 28, chemiluminescence 29,30, and H2O2-responsive small-molecule fluorescent probes 31-34, with the last one attracting particular interest due to its nondestructive nature and high sensitivity. To address the issue of lacking ROS specificity of commercially available probes such as dichlorodihydrofluorescein and dihydrorhodamine 35, Chang laboratory have pioneered with aryl boronate-based probes that are capable of undergoing biocompatible reactions with H2O2 to produce phenols 36-41. This innovation has benefited research on H2O2 biology and led to fruitful results 42. Importantly though, however, these aryl boronate-based probes are potentially threatened by their off-target reaction with peroxynitrite (ONOO-) which is far more reactive than H2O2, albeit exists of much lower abundance 43. Furthermore, boric acid by-produced in this process exists as a waste with unknown bioeffect (Figure 1). It is therefore envisioned that improvements could be made to devise new probes which release, instead of boric acid, but an agent helpful to ameliorate vascular damage accompanying the fluorescent signal. In our continuous research on the roles of redox-chemistry in the progression of vascular diseases 44, we report herein a theranostic probe that can not only sense H2O2 with high specificity, but is capable of neutralizing the oxidative damage incurred.
Figure 1.
Comparison of previous arylboranate-H2O2 chemistry-based probe, and probe AP in this work. For the same fluorophore, boric acid-based probe showed poor selectivity for H2O2, while aspirin-based probe AP was almost immune to ONOO-. Data were the normalized fluorescent intensity of the probes (10 μM) at 460 nm before or after the treatment of H2O2 (500 μM) or ONOO- (20 μM) for 30 min.
Experimental section
Materials
Dry dichloromethane (DCM) was distilled from CaH2. Other reagents and chemicals for probe synthesis were obtained from commercial suppliers and used without further purification. Reactions were run under a nitrogen atmosphere and monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) carried out on Silica gel 60 F254 plates supplied by Qingdao Puke Separation Material Corporation, and UV light was used as the visualizing agent. Flash column chromatography was performed using 200-300 mesh silica gel supplied by Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China.
Reagents for biological experiments: Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) was purchased from Invitrogen, and fetal bovine serum (FBS) from Gibco (Carlsbad, CA). Unless otherwise stated, all other reagents and chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Hydrogen Peroxde Assay Kit was from Beyotime Biotechnology.
Instruments
1H NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker Fourier transform spectrometer (500 MHz) at 25 oC. 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Fourier transform spectrometer (125 MHz) spectrometer. All NMR spectra were calibrated using the residual solvent (CDCl3) as internal reference (1H NMR = 7.26, 13C NMR = 77.16). All chemical shifts were reported in parts per million (ppm) and coupling constants (J) in Hz. The following abbreviations were used to explain the multiplicities: d = doublet, t = triplet, m = multiplet. IR spectra were taken on a Bruker Vector 22 spectrophotometer as KBr pellets. High resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were measured on an Agilent 6224 TOF LC/MS spectrometer using ESI-TOF (electrospray ionization-time of flight). The reaction process between AP and H2O2 was monitored on a SHIMADZU LCMS-2020 spectrometer. UV-Vis spectra were taken on a HITACHI U-3010 Spectrophotometer. Fluorescence measurements were conducted on an Agilent Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer with slit widths to be 10 and 10 nm for excitation and emission respectively, and the photomultiplier (PMT) detector voltage was set at medium.
Probe synthesis and characterization
Procedures for the synthesis of probe AP1-AP4 were detailed in the supplementary information. For the synthesis of probe AP, aspirin (0.10 g, 0.56 mmol) was dissolved in dry dichloromethylene (25 mL) and the mixture was cooled to 0 oC with an ice bath. Dry DMF (0.10 mL, 1.3 mmol) and oxalyl chloride (95 μL, 1.1 mmol) were then subsequently added to the mixture dropwise under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction was stirred at ambient temperature for 8 h, after which the volatile parts were removed by rotary evaporation. The residue was dissolved in dry dichloromethylene (20 mL), cooled to 0 oC, and then treated subsequently with 2-(2'-hydroxy-4'-fluorophenyl) benzothiazole (0.10 g, 0.41 mmol) and Et3N (76 μL, 0.56 mmol). The mixture was stirred at ambient temperature for 8 h, after which H2O (2.0 mL) was added to quench the reaction. The mixture was diluted with dichloromethylene (30 mL) and then transferred to a separatory funnel. The organic phase was washed with H2O (2 × 20 mL) and brine (1 × 20 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product which was purified by flash column chromatography (SiO2, petroleum ether/EtOAc, 20:1) to yield probe AP as a white solid (35 mg, 21% yield).
Rf = 0.55 (20:1, petroleum ether:EtOAc). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, δ): 8.43 (dd, J = 7.9, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.15 (dd, J = 9.2, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (td, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (tt, J = 7.5, 1.0 Hz, 2H), 7.38 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.31 - 7.23 (m, 3H), 2.27 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3, δ): 169.74 (d, J = 10.2 Hz), 162.72, 160.97, 160.54 (d, J = 246.6 Hz), 152.84 (d, J = 5.7 Hz), 151.76, 144.23 (d, J = 3.5 Hz), 135.67, 135.15 (d, J = 9.0 Hz), 132.84 (d, J = 3.3 Hz), 128.13, 126.60 (d, J = 3.3 Hz), 126.42 (d, J = 6.5 Hz), 125.75 (d, J = 2.6 Hz), 125.56, 124.35 (d, J = 1.9 Hz), 123.69, 122.36 (d, J = 8.0 Hz), 121.65 (d, J = 3.3 Hz), 118.53 (d, J = 23.8 Hz), 116.68 (d, J = 25.7 Hz), 21.10 (d, J = 5.5 Hz). IR (KBr, cm-1): 3467, 3072, 2361, 1753, 1499, 1423, 1243, 1190, 1040, 754. ESI-HRMS (m/z): [M+H]+ calc'd. for C22H15FNO4S: 408.0706; found 408.0708.
Fluorometric analysis
Deionized water was used to prepare all aqueous solutions. All the photophysical characterization experiments were carried out at 37 oC. Phosphate buffer saline (PBS, 100 mM, pH 7.4) was purged with nitrogen for 5 min before use. AP was dissolved in DMSO to make a 10 mM stock solution. H2O2 and other reactive bio-relevant species were prepared as previously described 44. To test the fluorescent responses of AP towards H2O2 or other reactive species, aliquots of probe stock solution were diluted with PBS (with 1‰ cetrimonium bromide) and treated with analytes to make sure both probes and analytes were kept at desired final concentrations. After quick and vigorous shaking, the mixture was allowed standing in the dark at 37 oC for desired time and the fluorescent spectra were then recorded under excitation at 375 nm. The emission spectra were scanned from 400 to 600 nm. All fluorometric experiments were performed in triplicate, and data shown were the average.
Cell culture
EA.hy926 cell line was purchased from ATCC (ATCC CRL-2922). EA.hy926 cells were grown in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fresh bovine serum in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Cultured cells without treatment served as controls.
Confocal fluorescence imaging methods
Cells were cultured on glass cover slips overnight and then pre-treated with AP for 15 min, followed by being exposed to H2O2 for indicated time. Cells were then fixed in 4% polyformaldehyde. Nuclei were stained with propidium iodide (PI, sigma) in PBS after fixation. Probe fluorescence in EA.hy926 cells were visualized by confocal microscopy (Nikon A1R) and data were analysed using Image J software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
CCK-8 assay for cytotoxicity
A Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (Dojindo; CK04) was used to measure cell viability. EA.hy926 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate at a density of 2.5 × 103 cells per well and incubated overnight. Cells were treated with different concentrations of probe AP or negative control for 24 h, then the medium was changed to fresh one (100 μl) and CCK-8 reagent (10 μl) was added. Following 1 h of incubation, cell viability was determined by measuring the optical absorbance at 450 nm with a multimode reader (Beckman Coulter; DTX880).
Oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) exposure
The oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) model was used to mimic the ischemia-like condition in live cells 45. Briefly, cell culture medium was replaced with glucose-free HBSS (Hank's balanced salt solution), and cells were then placed in an airtight experimental hypoxia chamber (Billups-Rothenberg) containing a gas mixture of 95% N2 and 5% CO2. Cells were exposed to OGD for 0.5, 1 and 2 h to induce injury. Cells without OGD treatment were served as controls.
Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model
The transient ischemia/reperfusion MCAO model was used to stimulate overproduction of H2O2 in mice. Model preparation was carried out as previously described 45. Animal procedures were approved by the Committee on Animal Experiments at the Zhejiang University. The mice were subjected to one hour of ischemia followed by reperfusion. The brain was then isolated and slices were prepared 24 h after ischemia. The slices were then treated with probe AP for 15 min, and visualized by confocal microscopy (Nikon A1R). Data were analysed using Image J software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Zebrafish care and maintenance
A wild-type AB strain of zebrafish (Batch Number 20150319) was used in the present study. The zebrafish were housed in a light and temperature controlled aquaculture facility with a standard 14-10 h light-dark conditions and fed with live brine shrimp twice daily and dry flake once a day. Four to five pairs of zebrafish were set up for natural mating every time, 200-300 embryos can thereby be generated. Embryos were maintained at 28 oC in fish water (0.2% Instant Ocean Salt in deionized water, pH 6.9-7.2, conductivity 480-510 µs/cm, and hardness 53.7-71.6 mg/L CaCO3). Embryos were washed and staged at 6 and 24 hpf (hours post fertilization).
Zebrafish thrombosis model
3-Dpf zebrafish were chosen to prepare thrombosis model using a platelet agonist (arachidonic acid, 80 μM) challenge method. Zebrafish treated with 0.1% DMSO was served as a vehicle control. Zebrafish from each group were randomly selected for visually qualitative assessment of the thrombus formation in the caudal vein at the lateral view with a dissecting stereomicroscope. The resting zebrafish were stained with O-dianisidine to quantify the heart red blood cells (RBCs) (hemoglobin level) which reversely correlated with the degree of thrombosis. The optimal concentration and incubation time of arachidonic acid treatment were selected according to the qualitative and quantitative results of thrombosis. Heart RBCs counts were performed using the NIS-Elements D3.10 image analysis software (Nikon). The effect of a test drug was calculated based on the formula below:
| Efficacy (%)= [[S(drug)-S(model)]/[S(vehicle)-S(model)]]x100% |
A positive percentage means that a tested drug could prevent and/or treat thrombus and a negative percentage suggests that the tested drug had no effect on thrombosis in the zebrafish model.
Results and Discussion
Initially, to fulfill the task of therapy, aspirin was judiciously selected as the prime building block attributing to its vascular-beneficial effects such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiplatelet 46. In particular, aspirin is not only efficient in reducing stroke incidence, but can also attenuate clinical deficits at stroke onset 47. To orchestrate the therapeutic effect of aspirin with a fluorescent diagnostic signal for H2O2, it should be combined with a fluorophore via a H2O2-sensitive linkage. Since H2O2 with pKa of 11.75 is slightly more acidic than H2O (pKa 13.99), we surmised that H2O2 in neutral aqueous solution might catalyze the hydrolysis of certain esters. Therefore, aspirin was combined with 2-(2'-hydroxy-4'-fluorophenyl) benzothiazole fluorophore with an ester bond to construct probe AP (Figure 1). We reasoned that the ester bond would block the excited state intramolecular proton transfer process (ESIPT) in the fluorophore which is essential for illumination 48, whereas the nitrogen atom on the fluorophore skeleton could bring HOO- within close proximity to the ester via a hydrogen bonding to accelerate the hydrolysis. AP was facilely prepared as detailed in the experimental section.
The optical response of AP towards H2O2 was tested in PBS (100 mM, pH 7.4). As shown in Figure 2A, AP showed the absorption maximized at 297 nm (c 30 μM, 15 463 M-1 cm-1). Treatment of H2O2 (1.0 mM) induced a time-dependent decrease of the original peak and the emergence of a new red-shifted band peaked at 336 nm, indicating the slow hydrolysis of the ester to yield the -OH group as a better auxochrome. Coinciding with the UV-Vis absorption response, H2O2 treatment also induced a time-dependent increase of AP fluorescence centred at 476 nm (Figure 2B, Figure S1-S4). When the response was observed over longer time, completion could be detected in 2 hours (Figure S5). Furthermore, AP (10 μM) responded to H2O2 with fluorescence enhancement in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 2C) with H2O2 concentrations higher than 1 mM bringing the response to its maximum (Fmax). Interestingly, the Napierian logarithm of Fmax minus F correlated linearly with H2O2 concentrations in the range of 0-500 μM (Figure S6, S7). Notably, the detection limit of the probe was found to be as low as 2.5 μM (Figure S8). These results suggest the great potential of probe AP to quantify H2O2 in PBS medium. The selectivity of AP towards various reactive species was also evaluated. Among the various biologically-relevant reactive species, only H2O2 was found capable of triggering on the fluorogenic response of AP with a 11-fold intensity increase, which is at least 8-fold more selective than ONOO-, a common interferent for boronate-based probes (Figure 2D and Figure S9). Furthermore, the effect of pH on the stability of probe AP was also studied. AP is quite stable below pH 7.0. Though slight hydrolysis of the ester group was observed at pH 7.5 as indicated by the 2.6 folds of fluorescence intensity increase, this increase is much smaller than that caused by H2O2 (Figure S10). Given the fact that cytosol generally has a pH of 7.2 and most organelles are below pH 7.2 49, probe AP should be stable enough to stand cellular pH gradients.
Figure 2.
Photophysical responses of AP to H2O2. A) UV-Vis absorption response of AP (30 μM) towards H2O2 (1.0 mM) as time lapsed. B) Fluorescence response of AP (10 μM) towards H2O2 (200 μM) as time lapsed. C) Fluorescence response of AP (10 μM) towards various concentrations of H2O2 at a time point of 30 min. D) Fluorescent responses of AP (10 μM) toward various analytes (200 μM) after a reaction time of 30 min, where F represents the fluorescent intensity of AP at 476 nm after the treatment of various analytes, and F0 represents the intensity of blank AP solution at 476 nm. (1) probe blank, (2) H2O2, (3) 1O2, (4) O2-, (5) ClO-, (6) THBP, (7) ONOO-, (8) NO, (9) NO2-, (10) NO3-, (11) GSH, (12) Cys, (13) Hcy, (14) Gly, (15) Ala, (16) Mg2+, (17) Ca2+, (18) Fe3+, (19) Fe2+, (20) K+, (21) Cu2+, (22) Zn2+. All fluorescence data were collected in PBS (pH 7.4, 100 mM) at 37oC with λex 375 nm. UV data were obtained in PBS with 50% EtOH as co-solvent.
With the fluorogenic response of probe AP towards H2O2 systematically characterized, we next evaluated if aspirin would be released in this process as surmised in Figure 1. The reaction between AP and H2O2 in PBS was therefore tracked by LC-MS analysis to determine the structures of the products. Prior to this study, the LC-MS spectra of a mixture of AP, 2-(2'-hydroxy-4'-fluophenyl) benzothiazole fluorophore, aspirin and salicylic acid were recorded for reference. It turned out that treatment of AP with H2O2 induced a gradual decrease of the probe, accompanied by the simultaneous increase in the formation of the free fluorophore and aspirin in the form of salicylic acid (Figure S11-S15), indicating the efficient release of aspirin and the fluorophore triggered by H2O2. To make further confirmation, probe AP was treated with H2O2 in a flask, and 2-(2'-hydroxy-4'-fluophenyl) benzothiazole fluorophore was isolated and characterized by 1H NMR, further consolidating the mechanism shown in Figure 1 (Figure S16).
To find out if other fluorophores could also work in this design, probe AP1-AP4 were prepared by esterifying the phenol hydroxyl group in an acylnaphthalene, coumarin, naphthalimide, or hemicyanine (Figure S17). When their responses towards H2O2 were tested in comparison with probe AP, all the probes were found active with probe AP being the most sensitive one (Figure S18). This result demonstrates the generality of the acetosalicylic phenolic ester as a H2O2-responsive trigger.
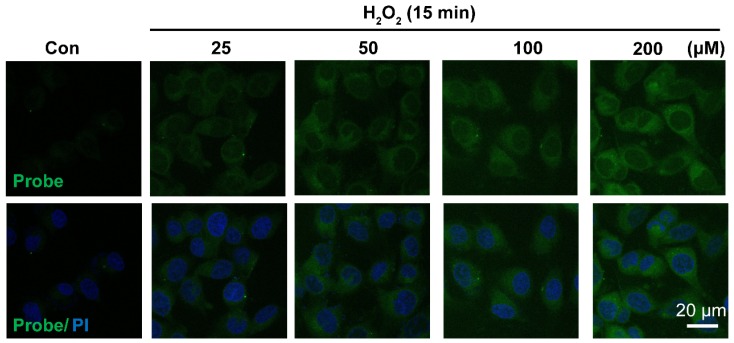
Having confirmed H2O2-triggered release of the free fluorophore and aspirin from probe AP in aqueous solution, we moved on to investigate the feasibility of AP to image H2O2 in EA.hy926 endothelial cells by confocal fluorescence microscopy. For this purpose, the cytotoxicity of probe AP was first evaluated by CCK8 assay. After treating EA.hy926 cells with various concentrations of AP, cell viability was monitored with a CCK8 kit and no significant AP toxicity was observed (Figure S19). Then, the response of EA.hy926 cells to probe AP was recorded. As shown in Figure 3, almost no detectable fluorescence signal was observed in control cells loaded with only probe AP. However, significant elevation of AP fluorescence was observed when the cells were exposed to exogenous H2O2, and the intracellular fluorescence increased in a H2O2 dose-dependent way. Time-dependent increase of AP fluorescence was also observed after the cells were exposed to H2O2 (50 μM) (Figure S20). Noteworthy, similar results were obtained in HUVEC cells, for which exogenous H2O2 exposure resulted in both H2O2 dose-dependent and time-dependent intensification of intracellular fluorescence (Figure S21, S22), indicating the potential of AP to track H2O2 levels in live cells.
Figure 3.
Representative confocal images showed dose-dependent increase of AP fluorescence in endothelial cells. Cells were seeded on 24-well glass cover slips overnight and then pre-incubated with AP (5.0 μM) for 15 min, followed by challenging without or with H2O2 (25-200 μM) for 15 min. AP fluorescence (green, 460 nm) was excited at 405 nm. PI counterstaining indicated nuclear localization (blue, 620 nm). All images were captured using a Nikon A1R confocal microscope with the same settings. Overlay image of all captured fluorescence intensities are shown. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
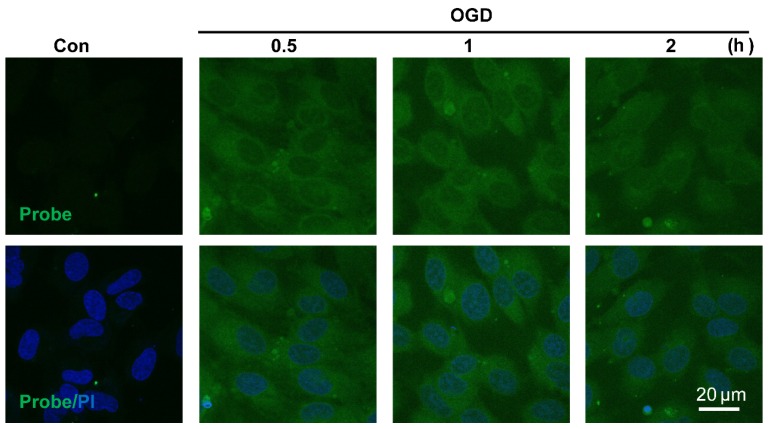
The sensitivity of probe AP to image endogenous H2O2 in live cells was also tested. Since aberrant accumulation of H2O2 has been reported in the progression of ischemic endothelial injury 50, we therefore evaluated if probe AP could track the dynamic change of endogenous H2O2 formation during endothelia injury. For this purpose, oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) stimulation model was employed to induce ischemic endothelial injury, and the fluorescent response of live cells after OGD stimulation was recorded. We first confirmed that probe AP was inert to OGD reagents (Figure S23). When EA.hy926 cells subjected to OGD treatment over 0.5-2 h were stained with AP, time-dependent accumulation of intracellular AP fluorescence was observed, which agreed well with the staining results obtained with a commercial Hydrogen Peroxde Assay Kit (Beyotime Biotechnology) (Figure S24), indicating the sensitivity of AP for endogenous H2O2 in live cells. This result also reveals the quick destroy of native redox homeostasis and the emergence of a more oxidative environment within endothelial cells upon injury, which is in agreement with previous reports 50.
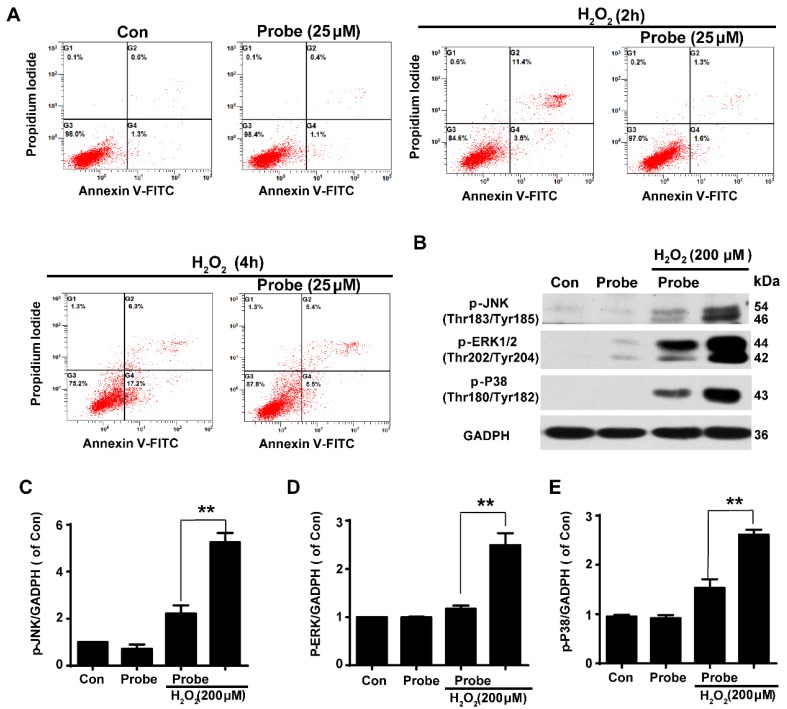
Having confirmed the ability of probe AP to image H2O2 accumulation during endothelial cell injury, we moved on to investigate if H2O2-triggered release of aspirin would display therapeutic effect against H2O2-induced endothelial apoptosis. Cell apoptosis was determined using flow cytometry with annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (PI). We first confirmed that probe AP (25 μM) by itself had no adverse effect on cell viability as AP treatment gave similar staining results as the control group. Furthermore, H2O2 (200 μM, 2 h) treatment was found to significantly induce elevation in the fraction of annexin V/PI positive cells (14.90%) compared to the control group (1.90%), suggesting its cytotoxicity. By contrast, AP incubation significantly reduced H2O2-induced cell apoptosis (2.90%; Figure 5A and Figure S25). Interestingly, this was particularly evident in HUVEC by flow cytometry assay (Figure S26). Furthermore, the protective effect of probe AP against H2O2-induced endothelial cell apoptosis was confirmed by reduced phosphorylation of JNK, ERK and p38 in H2O2-AP-treated cells in compare to H2O2-treated ones (Figure 5B-5E). Taken together, these data support the bifunctional roles of AP either for live cell imaging or to ameliorate endothelial injury during H2O2-induced oxidative stress.
Figure 5.
The protective role of AP against H2O2-induced endothelial apoptosis. A) The apoptosis of endothelial cells was labelled with annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (PI) and determined using flow cytometry. EA.hy926 cells were seeded on 12-well plates overnight and then pre-incubated with AP (25 μM) for 15 min, followed by stimulation with H2O2 (200 μM, 2 h or 4 h) in HBSS medium. B) The representative blots for phosphorylation of JNK, ERK and p38 in the presence of AP probe upon H2O2 (200 μM, 12 h) exposure in DMEM medium. Summary of phospho-JNK (C), phospho-ERK (D) and phospho-p38 (E) were indicated as densitometric values. **p < 0.01.
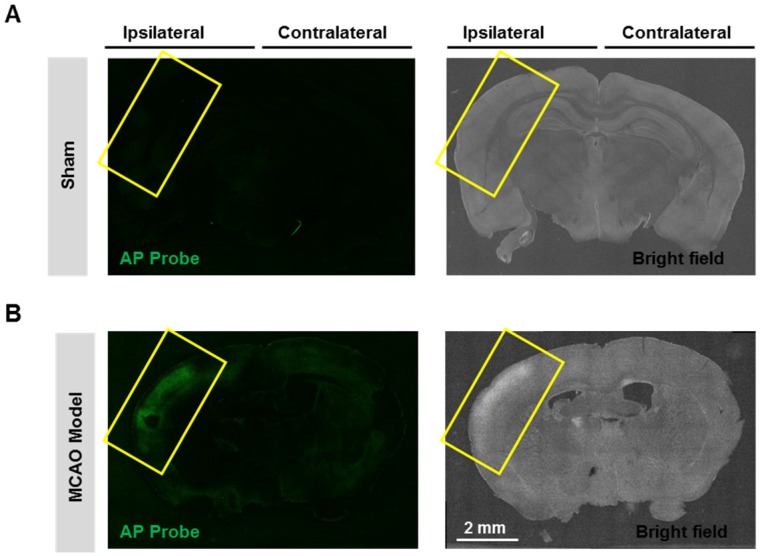
Having confirmed the good performance of probe AP in live cells, we next expand the scope to live tissues, and a middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was used to induce oxidative damage to the brain neurovascular system. Mice brain was isolated 24 h after ischemia and slices were prepared. When the slices were stained with probe AP, strong AP fluorescence was observed in the brain ischemic region of MCAO mice (Figure 6). However, no significant AP fluorescence was observed in the sham group. These results demonstrate the sensitivity and specificity of probe AP to image neurovascular cell injury.
Figure 6.
Visualizing endogenous H2O2 formation using AP in MCAO mouse. The representative confocal images showed changes of AP fluorescence (green) in brain ischemic region in MCAO mice. Insert frame: Brain ischemic region. Scale bar represents 2 mm.
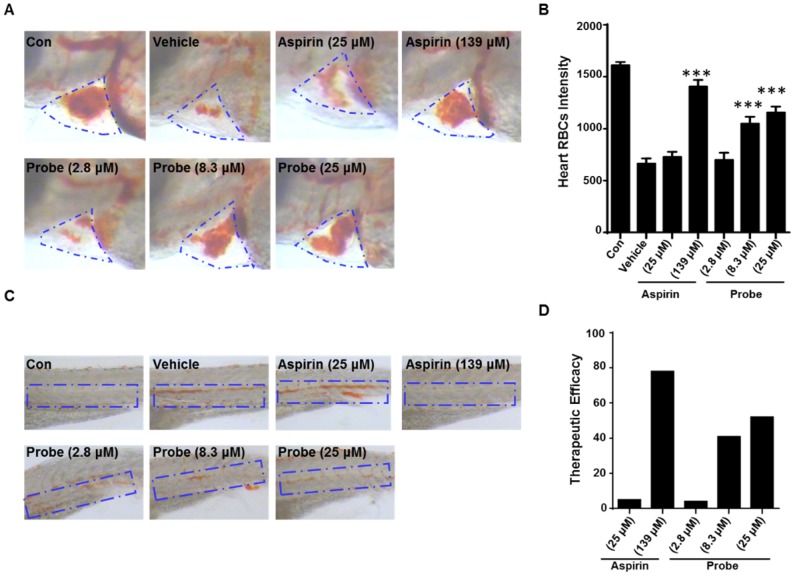
To further confirm the endothelial-protective effect of probe AP in zebrafish model, its anti-thrombotic effect was evaluated with aspirin as a positive control, because endothelial cell injury has been considered as the underlying pathogenesis of microvascular thrombosis and ischemia. Zebrafish thrombosis model was prepared as described and hemoglobin staining was used to indicate the degree of intravascular thrombosis 51. As shown in Figure 7, in contrast to the normal heart RBCs/hemoglobin staining in the control group, arachidonic acid (a platelet agonist) treatment resulted in only weak staining. However, probe AP (8.3 μM or 25 μM) treatment was observed to be able to significantly inhibit arachidonic acid-induced thrombosis formation in zebrafish compared to the vehicle group, and the potency was AP dose-dependent (Figure 7A-B). Furthermore, similar results were obtained in the caudal vein of Zebrafish with thrombosis (Figure 7C), for which the preventive efficacy on thrombosis formation was quantified to be 78% for aspirin (139 μM), 41% for probe AP (8.3 μM) and 52% for probe AP (25 μM), respectively (Figure 7D).
Figure 7.
The antithrombotic effect of probe AP. Zebrafish treated with arachidonic acid for 1.5 h were used as thrombosis model. A) Effects of probe AP on heart RBCs in thrombotic zebrafish. The heart red blood cells were stained with o-dianisidine staining. The heart RBCs intensity of zebrafish increased following AP probe treatment (1.5 h) in the presence of arachidonic acid (80 µM). B) Quantification data for Figure A. C) Effect of AP probe on thrombus formation in the caudal vein under a dissecting stereomicroscope. Images from aspirin or AP probe treatment are shown from a representative caudal vein of zebrafish from each group. Thrombus formation was markedly reduced in zebrafish treated with AP probe (1.5 h) in the presence of arachidonic acid. D) The therapeutic efficacy of AP probe on thrombosis formation.
Conclusions
In summary, targeting the oxidative microenvironment of vascular diseases represented by the overproduction of H2O2, we have developed the first theranostic probe for its simultaneous imaging and neutralization by combining a fluorophore with an endothelial-protective agent via a H2O2-sensitive bond. The probe has been proven suitable for imaging native H2O2 generation in live cells, and is capable of eliciting protective effects against both H2O2-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and vascular pathology in Zebrafish thrombosis mode. The probe should hold promise to serve as a dual functional imaging tool to explore H2O2 signalling under a variety of pathological contexts. The design strategy illustrated in this work should be inspiring for future probe design.
Figure 4.
Visualizing endogenous H2O2 formation using AP in endothelial cells following oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). The representative confocal images showed temporal changes of AP fluorescence (green, 460 nm) in EA.hy926 endothelial cells over 0.5 to 2 h following OGD. PI counterstaining indicated nuclear localization (blue, 620 nm). Overlay image of AP fluorescence and PI are shown. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFE0125400), National Natural Science Foundations of China (81473202, 81573411, 21642007), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Z16H310003, LY15H300003), Zhejiang Provincial Science and Technology Planning Project (2017C33053), Zhejiang Province Program for Cultivation of High-level Health talents.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1-S26, synthesis and characterization of AP1-AP4, NMR traces of probe AP.
References
- 1.Vanhoutte PM, Shimokawa H, Tang EH, Feletou M. Endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2009;196:193–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.01964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kasote DM, Hegde MV, Katyare SS. Mitochondrial dysfunction in psychiatric and neurological diseases: cause(s), consequence(s), and implications of antioxidant therapy. Biofactors. 2013;39:392–406. doi: 10.1002/biof.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McCann SK, Roulston CL. NADPH Oxidase as a Therapeutic Target for Neuroprotection against Ischaemic Stroke: Future Perspectives. Brain Sci. 2013;3:561–98. doi: 10.3390/brainsci3020561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schriewer JM, Peek CB, Bass J, Schumacker PT. ROS-mediated PARP activity undermines mitochondrial function after permeability transition pore opening during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e159. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hao XL, Kang Y, Li JK, Li QS, Liu EL, Liu XX. Protective effects of hyperoside against H2O2-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14:399–405. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhai L, Zhang P, Sun RY, Liu XY, Liu WG, Guo XL. Cytoprotective effects of CSTMP, a novel stilbene derivative, against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human endothelial cells. Pharmacol Rep. 2011;63:1469–80. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70711-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.He C, Murthy S, McCormick ML, Spitz DR, Ryan AJ, Carter AB. Mitochondrial Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase mediates pulmonary fibrosis by augmenting H2O2 generation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:15597–607. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bagulho A, Vilas-Boas F, Pena A. et al. The extracellular matrix modulates H2O2 degradation and redox signaling in endothelial cells. Redox Biol. 2015;6:454–60. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rocha S, Gomes D, Lima M, Bronze-da-Rocha E, Santos-Silva A. Peroxiredoxin 2, glutathione peroxidase, and catalase in the cytosol and membrane of erythrocytes under H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 2015;49:990–1003. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1028402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Miguel F, Augusto AC, Gurgueira SA. Effect of acute vs chronic H2O2-induced oxidative stress on antioxidant enzyme activities. Free Radic Res. 2009;43:340–7. doi: 10.1080/10715760902751894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guntur AR, Gu P, Takle K, Chen J, Xiang Y, Yang CH. Drosophila TRPA1 isoforms detect UV light via photochemical production of H2O2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:E5753–61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1514862112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yalfani MS, Contreras S, Medina F, Sueiras JE. Hydrogen substitutes for the in situ generation of H2O2: an application in the Fenton reaction. J Hazard Mater. 2011;192:340–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Choi DJ, Kim SL, Choi JW, Park YI. Neuroprotective effects of corn silk maysin via inhibition of H2O2-induced apoptotic cell death in SK-N-MC cells. Life Sci. 2014;109:57–64. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kubota Y, Shimizu S, Yasuhira S, Horiuchi S. SNF2H interacts with XRCC1 and is involved in repair of H2O2-induced DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst) 2016;43:69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martins D, Titorenko VI, English AM. Cells with impaired mitochondrial H2O2 sensing generate less •OH radicals and live longer. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21:1490–503. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stone JR, Yang S. Hydrogen peroxide: a signaling messenger. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:243–70. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sies H. Role of metabolic H2O2 generation: redox signaling and oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:8735–41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R113.544635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rice ME. H2O2: a dynamic neuromodulator. Neuroscientist. 2011;17:389–406. doi: 10.1177/1073858411404531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang ZH, Liu JL, Wu L, Yu Z, Yang HT. Concentration-dependent wrestling between detrimental and protective effects of H2O2 during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1297. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schwarzländer M, Dick TP, Meyer AJ, Morgan B. Dissecting Redox Biology Using Fluorescent Protein Sensors. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016;24:680–712. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bilan DS, Pase L, Joosen L. et al. HyPer-3: a genetically encoded H2O2 probe with improved performance for ratiometric and fluorescence lifetime imaging. ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8:535–42. doi: 10.1021/cb300625g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lukyanov KA, Belousov VV. Genetically encoded fluorescent redox sensors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840:745–56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.05.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sun Y, He K, Zhang Z, Zhou A, Duan H. Real-time electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide secretion in live cells by Pt nanoparticles decorated graphene-carbon nanotube hybrid paper electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;68:358–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mu B, Zhang J, McNicholas TP, Reuel NF, Kruss S, Strano MS. Recent advances in molecular recognition based on nanoengineered platforms. Acc Chem Res. 2014;47:979–88. doi: 10.1021/ar400162w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lippert AR, Keshari KR, Kurhanewicz J, Chang CJ. A hydrogen peroxide-responsive hyperpolarized 13C MRI contrast agent. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:3776–9. doi: 10.1021/ja111589a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Olson ES, Orozco J, Wu Z. et al. Toward in vivo detection of hydrogen peroxide with ultrasound molecular imaging. Biomaterials. 2013;34:8918–24. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.06.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cochemé HM, Quin C, McQuaker SJ. et al. Measurement of H2O2 within living Drosophila during aging using a ratiometric mass spectrometry probe targeted to the mitochondrial matrix. Cell Metab. 2011;13:340–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Carroll V, Michel BW, Blecha J. et al. A boronate-caged [18F]FLT probe for hydrogen peroxide detection using positron emission tomography. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:14742–5. doi: 10.1021/ja509198w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Van de Bittner GC, Dubikovskaya EA, Bertozzi CR, Chang CJ. In vivo imaging of hydrogen peroxide production in a murine tumor model with a chemoselective bioluminescent reporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:21316–21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012864107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Van de Bittner GC, Bertozzi CR, Chang CJ. Strategy for dual-analyte luciferin imaging: in vivo bioluminescence detection of hydrogen peroxide and caspase activity in a murine model of acute inflammation. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:1783–95. doi: 10.1021/ja309078t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kolanowski JL, Kaur A, New EJ. Selective and Reversible Approaches Toward Imaging Redox Signaling Using Small-Molecule Probes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016;24:713–30. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lin VS, Dickinson BC, Chang CJ. Boronate-based fluorescent probes: imaging hydrogen peroxide in living systems. Methods Enzymol. 2013;526:19–43. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405883-5.00002-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dickinson BC, Srikun D, Chang CJ. Mitochondrial-targeted fluorescent probes for reactive oxygen species. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14:50–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Miller EW, Chang CJ. Fluorescent probes for nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide in cell signaling. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007;11:620–5. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.09.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wardman P. Fluorescent and luminescent probes for measurement of oxidative and nitrosative species in cells and tissues: progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43:995–1022. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.06.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Miller EW, Albers AE, Pralle A, Isacoff EY, Chang CJ. Boronate-based fluorescent probes for imaging cellular hydrogen peroxide. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:16652–9. doi: 10.1021/ja054474f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Srikun D, Miller EW, Domaille DW, Chang CJ. An ICT-based approach to ratiometric fluorescence imaging of hydrogen peroxide produced in living cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:4596–7. doi: 10.1021/ja711480f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Dickinson BC, Chang CJ. A targetable fluorescent probe for imaging hydrogen peroxide in the mitochondria of living cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:9638–9. doi: 10.1021/ja802355u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Srikun D, Albers AE, Nam CI, Iavarone AT, Chang CJ. Organelle-targetable fluorescent probes for imaging hydrogen peroxide in living cells via SNAP-Tag protein labeling. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:4455–65. doi: 10.1021/ja100117u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dickinson BC, Huynh C, Chang CJ. A palette of fluorescent probes with varying emission colors for imaging hydrogen peroxide signaling in living cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:5906–15. doi: 10.1021/ja1014103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lippert AR, Van de Bittner GC, Chang CJ. Boronate oxidation as a bioorthogonal reaction approach for studying the chemistry of hydrogen peroxide in living systems. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44:793–804. doi: 10.1021/ar200126t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fu X, Tang Y, Dickinson BC, Chang CJ, Chang Z. An oxidative fluctuation hypothesis of aging generated by imaging H2O2 levels in live Caenorhabditis elegans with altered lifespans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;458:896–900. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brewer TF, Garcia FJ, Onak CS, Carroll KS, Chang CJ. Chemical approaches to discovery and study of sources and targets of hydrogen peroxide redox signaling through NADPH oxidase proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 2015;84:765–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-034018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li X, Tao RR, Hong LJ. et al. Visualizing peroxynitrite fluxes in endothelial cells reveals the dynamic progression of brain vascular injury. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:12296–303. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b06865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tao RR, Wang H, Hong LJ. et al. Nitrosative stress induces peroxiredoxin 1 ubiquitination during ischemic insult via E6AP activation in endothelial cells both in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21:1–16. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kong DF. Aspirin in cardiovascular disorders. What is the optimum dose? Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2004;4:151–8. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200404030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wilterdink JL, Bendixen B, Adams HJ, Woolson RF, Clarke WR, Hansen MD. Effect of prior aspirin use on stroke severity in the trial of Org 10172 in acute stroke treatment (TOAST) Stroke. 2001;32:2836–40. doi: 10.1161/hs1201.099384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Woolfe GJ, Melzig M, Schneider S, Dörr F. The Role of Tautomeric and Rotameric Species in the Photophysics of 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazole. Chem Physics. 1983;77:213–21. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Casey JR, Grinstein S, Orlowski J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:50–61. doi: 10.1038/nrm2820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cai H. Hydrogen peroxide regulation of endothelial function: origins, mechanisms, and consequences. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;68:26–36. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhu XY, Liu HC, Guo SY. et al. A Zebrafish Thrombosis Model for Assessing Antithrombotic Drugs. Zebtafish. 2016;13:335–44. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2016.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1-S26, synthesis and characterization of AP1-AP4, NMR traces of probe AP.