Abstract
Aldosterone regulates electrolyte and fluid homeostasis through binding to the mineralocorticoid receptors (MR). Previous work provides evidence for a role of aldosterone in alcohol use disorders (AUD). We tested the hypothesis that high functional activity of the mineralocorticoid endocrine pathway contributes to vulnerability for AUD. In Study 1, we investigated the relationship between plasma aldosterone levels, ethanol self-administration, and the expression of CYP11B2 and mineralocorticoid receptor (NR3C2) genes in the prefrontal cortex area (PFC) and central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) in monkeys. Aldosterone significantly increased after 6 and 12-month ethanol self-administration. NR3C2 expression in the CeA was negatively correlated to average ethanol intake during the 12 months. In Study 2, we measured Nr3c2 mRNA levels in the PFC and CeA of dependent and nondependent rats and the correlates with ethanol drinking during acute withdrawal. Low Nr3c2 expression levels in the CeA were significantly associated with increased anxiety-like behavior and compulsive-like drinking in dependent rats. In Study 3, the relationship between plasma aldosterone levels, alcohol drinking and craving was investigated in alcohol-dependent patients. Non-abstinent patients had significantly higher aldosterone levels than abstinent patients. Aldosterone levels positively correlated with the number of drinks consumed, craving and anxiety scores. These findings support a relationship between ethanol drinking and the aldosterone/MR pathway in three different species.
Keywords: aldosterone, mineralocorticoid receptor, alcohol use disorders, monkeys, rats, alcoholic patients, alcohol craving, animal models, principal component analysis
Introduction
Several neuroendocrine pathways have been hypothesized to be involved in ethanol drinking and craving.[1] Among them, preliminary work suggests a role of aldosterone. Aldosterone, a steroid hormone of the mineralocorticoid family, is mainly produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. Aldosterone production is largely controlled by regulation of the CYP11B2 gene that encodes aldosterone synthase.[2, 3] Aldosterone, in turn, regulates electrolyte and fluid homeostasis through binding to mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs), which are encoded by the gene NR3C2. In the brain, aldosterone via MR signalling may play a role in anxiety and alcohol drinking. Particularly relevant, MRs are mainly expressed in limbic brain regions as the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex (PFC),[4–6] two key brain areas involved in the development and maintenance of excessive ethanol consumption.[7] Notably, the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) expresses MRs at greater levels compared to other amygdala nuclei.[8] The CeA plays an important role in anxiety, stress and stress-induced ethanol drinking;[9] alterations in its structure and function may result in disinhibition of downstream regions that regulate alcohol-related behaviors.[10–12] The PFC plays a critical role in addiction, including reinforcement learning, craving, and inhibitory control.[7] PFC neurons send projections to the CeA; changes in functional connectivity between PFC and CeA have been reported in individuals who are less able to cope with stressful events and alcohol-dependent individuals.[11, 13, 14].
Plasma aldosterone levels increase in alcoholic patients during early alcohol withdrawal and normalize during recovery[15]. This increase may contribute to clinically relevant hemodynamic changes during chronic alcohol use and withdrawal; indeed, there is a relationship between regulation of blood volume and ethanol drinking and craving.[15–17] For example, we previously reported a significant positive correlation between aldosterone levels and both anxiety and obsessive craving in a pilot study with alcohol-dependent patients.[18]
Here, we investigated the hypothesis that the aldosterone/MR pathway contributes to the vulnerability for alcohol use disorders (AUD) in studies of alcohol-related behaviors in macaques (Study 1), rats (Study 2) and humans (Study 3).
Subjects and methods
Study 1
Setting
This study was conducted at the Oregon National Primate Research Center (ONPRC). All procedures adhered to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the ONPRC IACUC.
Subjects
Subjects were male rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta, n=13), 4.5–5.5 year-old and from two cohorts (7a and 7b) of the ONPRC breeding colony (details in:www.MATRR.com). The monkeys were acclimated to the laboratory, established on an 11–13 light-dark cycle, and then extensively trained to comply with unanesthetized venipuncture. This procedure, taking samples from awake monkeys under calm conditions, was analogous to that used in the human protocol (Study 3). Monkeys were studied in a within-subject longitudinal design, and the animals were part of a larger study on adrenal response to ethanol self-administration.[19, 20]
Methods
Ethanol Self-Administration Monkey Model
Schedule-induced polydipsia, a form of adjunctive behavior where the scheduled delivery of small amounts of preferred food can induce large volumes of fluid intake, was used to establish rapid drinking without food deprivation (21). Monkeys were first induced to drink set doses of 4% (w/v) ethanol (0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 g/kg/day) in 30-day epochs followed by access to concurrent ethanol and water for 22 hours/day, 7 days/week for 14-months under a well-established protocol.[21, 22] The protocol consisted of: 1) 6 month of uninterrupted ethanol self-administration; followed by 2) 1 month of daily self-administration and four interspersed neuroimaging/pharmacological procedures (an imaging session and acute single doses of dexamethasone/ovine-corticotropin-releasing factor/saline). The 6 months and 1 month phases were then repeated to total 14 months. Self-administration was suspended only during the time it took for the procedures (~2 hours on a single day) and there were at least 3 self-administration sessions between procedures. The neuroimaging/pharmacological months were not included in the average self-administration data because of the abbreviated sessions and procedural effects. There was at least a 2-week period of uninterrupted ethanol self-administration prior to necropsy. Here, we present longitudinal data from pre-ethanol baseline, after both the first and the second self-administration 6-month blocks. Blood samples (20 μl) for blood ethanol concentration (BEC) were taken every 5–7 days, at 7 hours after session onset (see Figure 1A for experimental timeline).
Figure 1. Study 1 in monkeys: Experimental timeline.
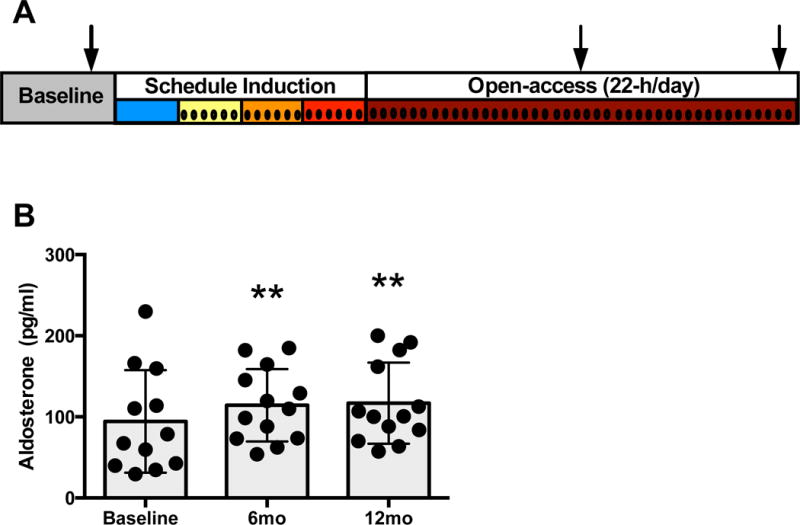
(A). All monkeys were trained during the baseline phase to participate in awake blood collection from the home cage and to operate an operant panel. Schedule-induced polydipsia began with a 1.5 g/kg volume equivalent of water, after which ethanol (4% w/v) was introduced and the daily dose increased each 30-days. Following ethanol induction, all animals had 22-h/day access to ethanol and water for approximately 14 months. Aldosterone was assayed from samples collected during baseline and after the first and second 6 months of self-administration as indicated by the arrows. Samples for blood ethanol concentration were collected throughout the experiment and are indicated by vertical lines. Plasma aldosterone levels before ethanol access (baseline), and following 6 and 12 months of voluntary ethanol self-administration (B). There was a significant effect of experimental phase (F2,23 = 6.19, **p = 0.0071). Tukey post hoc comparisons revealed that aldosterone was significantly higher at both 6 months (**p = 0.0075) and 12 months (**P = 0.0048) of self-administration, but no differences were found between 6 months and 12 months (p = 0.99). Results are expressed as m±s.d.
Necropsy
All monkeys were sent to necropsy at the end of the 14-month self-administration protocol, without experiencing abstinence employing a detailed procedure for brain perfusion in ice-cold artificial central spinal fluid, brain excision, dissection, and freezing in liquid nitrogen, maintaining the tissue at −80°C until RNA was extracted.[23]
Gene expression from RNA-Seq
Tissue samples were collected at necropsy from the PFC (area 32) and CeA for RNAseq analyses. These brain areas from the 13 monkeys described above were part of a larger group of samples used for full RNAseq gene expression analyses; the RNAseq methods and full results are detailed in Iancu et al. (in press, GEO accession ID: GSE84332).[24] Here we specifically assessed the correlation of normalized gene expression counts of two key enzymes (NR3C2 and CYP11B2) and a control gene (ACTB) with ethanol consumption in the same 13 monkeys (cohorts 7a and 7b) that underwent the ethanol self-administration protocol and were also assayed for plasma aldosterone levels.
Study 2
Setting
This study was conducted at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI). All procedures adhered to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the TSRI IACUC.
Subjects
Adult male Wistar rats (n=34; Charles River, Raleigh, NC, USA), weighing 225–275g at the beginning of the experiments, were housed in groups of 2–3 per cage in a temperature-controlled (22°C) vivarium on a 12–12 light-dark cycle (lights on at 20:00 hour). All behavioral tests were conducted during the dark phase of the cycle. Animals had ad libitum access to food and water.
Methods
The experimental timeline is shown in Figure 3. Rats were tested in the elevated plus maze prior to any exposure to ethanol to measure baseline anxiety-like behavior. The averages ± SEM for % time in the open arms (an index of anxiety-like behavior) were as follows: 28.2±5.5 and 22.0±4.1, for the dependent and nondependent groups, respectively. The rats were then trained in daily 30-min sessions to lever press for access to ethanol (10%, w/v, 0.1 ml per delivery) under a fixed-ratio 1 (FR1 schedule of reinforcement). The rats were assigned to two groups matched in terms of ethanol responding. The dependent (n=16) group was chronically exposed to daily cycles of ethanol intoxication (14 hours vapor ON; target BEC: 200 mg/dl) and withdrawal (10 hours vapor OFF), the nondependent (n=18) group was exposed to air without ethanol.
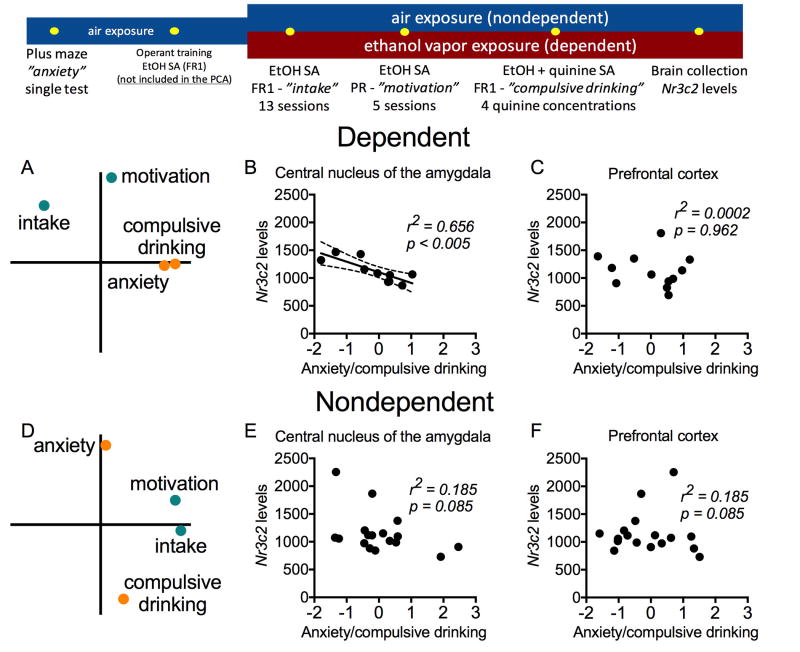
Figure 3. Study 2 in rats: experiment timeline (top panel) and behavioral findings in dependent and nondependent rats based on Nr3c2 expression levels in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) and prefrontal cortex (PFC).
Top panel: The rats were tested in the elevated plus maze prior to any exposure to ethanol to measure baseline anxiety-like behavior. The same rats were then trained in daily 30-min sessions to lever press for access to ethanol (10%, w/v, 0.1 ml per delivery) and assigned to two groups: dependent (n = 16; chronically exposed to ethanol vapor) and nondependent (n = 18; exposed to air without ethanol) rats. They were tested under a fixed-ratio 1 (FR1) schedule of reinforcement to measure “intake,” a progressive ratio (PR) schedule to measure “motivation” for ethanol, and tested for the persistence to drink ethanol adulterated with quinine (used herein as an index of “compulsive drinking”). At the end of the behavioral experiments, we measured Nr3c2 mRNA levels in the PFC and CeA.
Bottom panel: The behavior and Nr3c2 mRNA levels data have been previously published[26]. Here, we present a new statistical analysis that has not been previously published. A PCA revealed the occurrence of two main factors for each dependent and nondependent group that were interpreted to reflect “intake/motivation” and “anxiety/compulsive drinking” (A and D; see Figure S1 for additional results). The Nr3c2 expression levels in the CeA were significantly correlated with “anxiety/compulsive drinking” in dependent (B), but not in nondependent rats (E). No significant correlations were found for the PFC data for either dependent (C) or nondependent (F) rats. Ethanol drinking tests and Nr3c2 level measurements were conducted during acute alcohol withdrawal in the dependent rats.
The dependent and nondependent rats were tested for ethanol intake in 30-min sessions where ethanol and water (0.1 ml) were concurrently available according to FR1 schedules. These sessions coincided with the peak of acute withdrawal in the dependent group (6–8 after alcohol vapor turned off), when BECs were negligible. Based on previous studies, the responding levels observed during FR1 operant sessions would be expected to yield BECs below 50 mg/dl in nondependent rats and above 100 mg/dl in dependent rats.[25] We also measured motivation for ethanol using a progressive ratio (PR) schedule, during which the number of lever presses required to obtain reinforcement increases progressively with each completed ratio. Finally, to measure the persistence to ethanol drinking despite punishment (used herein as an index of compulsive-like drinking), we adulterated the ethanol solution with increasing concentrations of quinine (5, 10, 25, and 50 mg/L; between-session design), which is bitter and aversive to rats. We observed that dependent rats displayed increased ethanol intake (FR1), motivation for ethanol (PR) and compulsive-like drinking compared with nondependent rats (for all behavioral data see Vendruscolo et al.[26]).
At the end of the behavioral experiments, we collected rats’ brains during acute withdrawal (24 hours post vapor) and measured Nr3c2 mRNA levels in the PFC and CeA using a nuclease protection array. We did not observe overall significant alterations in Nr3c2 mRNA levels between dependent and nondependent rats.[26] In the present study, we reanalyzed the behavioral data and Nr3c2 mRNA data from our previous work[26] using a novel statistical approach. The results of this analysis are new and have not been published previously.
Study 3
Setting
This study was conducted at the Alcoholism Treatment Unit, Institute of Internal Medicine, Catholic University, Rome (Italy). The study was approved by the local Ethics Committee and performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki. Participants signed an informed consent prior to participation.
Subjects
Participants were part of the Psychoneuroendocrinology Project, that aimed to explore secondary endocrine-related outcomes from patients who participated in the Baclofen Intervention Study (EudraCT: 2006-000713-37); details of the parent study have been reported elsewhere.[27] Briefly, out of 94 patients screened for inclusionary/exclusionary criteria (Table S1), 42 alcohol-dependent patients were enrolled and 37 completed the 12-weeks study. For demographics and baseline characteristics, see Table S2. During the study, all patients received: 1) study medication tablets (either baclofen or placebo in a double-blind randomized fashion); although no baclofen effect was found on the primary drinking outcomes,[27, 28] nor on blood aldosterone levels (data not shown), the medication condition was included as a covariate; and 2) psychological therapy provided by trained staff (BRENDA[29]) at each outpatient visit for nine sessions of ~30-minute each.[27] Participants were also encouraged to attend Alcoholics Anonymous.
Methods
Alcohol Drinking
At the screening visit (Week-00), patients were asked to abstain from alcohol at least 3 days prior to enrolment at the subsequent visit (Week-01). Patients were monitored daily between Week-00 and Week-01 visits. Patients with significant withdrawal symptoms were treated with benzodiazepines; patients who required >10 days of benzodiazepines treatment were excluded. Thus, all patients (N=42) started the study after at least 3 and no >10 days of alcohol abstinence. No benzodiazepines were administered at any other point in the study. The number of standard alcohol drinks consumed over the 28 days preceding the screening visit and between visits was recorded using the Timeline Follow-Back (TLFB) method[30] and further corroborated by BEC and liver enzymes (as blood biomarkers of alcohol use) at each visit.
Alcohol Craving
The obsessive–compulsive disorder scale (OCDS) scale was used to measure alcohol craving (OCDS total score), including the obsessive (ODS) and compulsive (CDS) subscales.[31, 32]
Anxiety
The State and Trait Inventory (STAI) test was used to assess state anxiety.[33]
Assays and Statistical Analysis in Studies 1–3: see Supplement.
Results
Study 1
Ethanol Self-Administration and Plasma Aldosterone in Monkeys
Similar to other studies using this ONPRC rhesus population and ethanol self-administration protocol, there was a wide range of average daily ethanol intakes.[22] As detailed above, the drinking data are divided experimentally with the first 6-months of uninterrupted 22 hour/day access treated as one block and the second 6-months of uninterrupted 22 hour/day access as a second block.[19]
Average (M±SEM) daily intakes for the first 6-month block was 2.04±0.2 g/kg/day and ranged from 1.2 g/kg/day to 3.3 g/kg/day. Average daily intakes for the first second month block was 2.7±0.2 g/kg/day and ranged from 1.4 g/kg/day to 3.7 g/kg/day. Overall, 12-month daily ethanol intake averaged 2.35±0.16 g/kg. Similarly, BECs collected at 7 hour after the daily session produced great individual variations. Average BEC (M±SEM) through the first 6-month block (35 samples/monkey) was 46±7 mg/dl and ranged from 9mg/dl to 87mg/dl. Average BEC through the second 6-month block (26 samples/monkey) was 78±9 mg/dl and range was 21–134 mg/dl.
Aldosterone (M±SD) increased from a baseline of 94±63 to 114±45 pg/ml after 6-month self-administration and 116±50 pg/ml after 12-month self-administration. This finding represented a significant effect of experimental phase (F2,23=6.19, p=0.0071). Tukey post-hoc comparisons revealed that aldosterone was significantly higher at both 6-months (p=0.0075) and 12-months (p=0.0048) of self-administration, but no differences were found between 6-months and 12-months (p=0.99) (Figure 1B). Aldosterone at 6-month or 12-month time point did not correlate with average ethanol intake (g/kg/day) or average BEC (mg/dl), but rather appeared to be an effect of chronically drinking at least an average of 1.2 g/kg/day (i.e., the average intake for the lowest drinking monkey).
Water and total (water+ethanol) fluid intake also showed a wide range of individual differences. As previously reported,[20] no relationship was found between ethanol or water intake. Over the first 6-months, the average water and total intakes were 945±104 and 1356±119 ml/day, respectively. Similar volumes were recorded during the second 6-months of self-administration, 913±115 and 1496±146 ml/day for water and total fluid, respectively. Total average daily fluid consumption across the entire self-administration ranged from 937±100 ml/day water and 1409±125 ml/day total intake. There was no correlation with aldosterone levels at either 6-months block or with average water consumption over the entire 12-months of ethanol self-administration (all r2 values<0.07, p values>0.41).
Post-mortem Gene Expression in Monkey Brain
Using a subset (n=13 monkeys analyzed in this manuscript) of an existing set of next generation sequencing project in this monkey model of alcohol self-administration (GEO accession ID: GSE84332), we found that NR3C2 was expressed in both PFC and CeA. Ethanol intake was negatively correlated with the expression of NR3C2 in the CeA, in both the second 6-months of drinking and over the entire 12-months of drinking (Figure 2A–B), but there was no significant correlation with the first 6-months of drinking (data not shown). Specifically, there was a stronger correlation to the intake over the second block of 6-months of drinking (n=13, r2=0.48; p=0.008; Figure 2A) than over the entire 12-months period (n=13, r2=0.33; p=0.042; Figure 2B). In contrast, the expression of NR3C2 in PFC was not correlated with ethanol intake at either the first block of 6-months, the second block of 6-months (time point closer to necropsy) or with ethanol intake over all 12-months (data not shown). The CYP11B2 gene was not expressed above detectible levels in either brain area. For reference, there was no correlation between ethanol intake and expression of ACTB (a common housekeeping or reference gene) at the second block of 6 months (r2 = 0.001; p = 0.92) nor at the overall 12 months (r2 = 0.038; p = 0.52) (data not shown).
Figure 2. Study 1: correlations between average ethanol intake (g/kg/day) and the mineralocorticoid nuclear receptor gene NR3C2 expression in the central nucleus of the amygdala (A, B) in rhesus macaques.
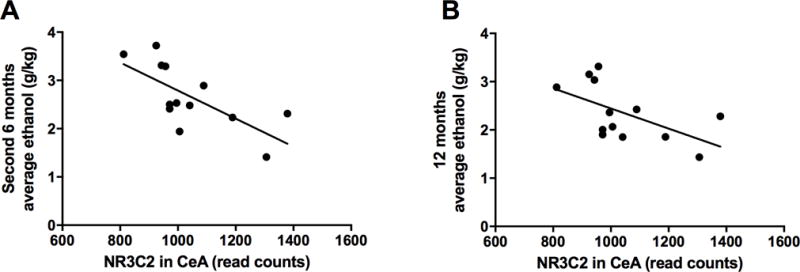
Ethanol intake is shown as an average during the second 6 months block (A) and over the entire 12 months period (B) of ethanol self-administration. There was a significant correlation between the expression of NR3C2 in the CeA and ethanol intake at both the second block of 6 months (A; r2 = 0.48; p = 0.008) and the overall 12 months (B; r2 = 0.33; p = 0.042).
Study 2
The PCA including measures of anxiety-like behavior (% time in the open arms of the elevated plus maze), ethanol intake (FR1), motivation for ethanol (PR) and compulsive-like ethanol intake (quinine adulteration) revealed the occurrence of two factors in each group that together accounted for 70–76% of the variance in behavior. The examination of factor loadings was interpreted to reflect two independent behavioral constructs: 1. “intake/motivation” and 2. “anxiety/compulsive drinking.” These factors independently accounted for comparable amounts of the behavioral variance, indicating that the “anxiety/compulsive drinking” factor (39.7% for dependent; 38.5% for nondependent) is nearly as important as the “intake/motivation” factor (32.1% for dependent; 38.3% for nondependent) in explaining the observed behavioral differences. Additional analyses indicated that ethanol intake and the motivation for ethanol consumption reflected the same underlying behavioral construct for both dependent and nondependent rats, i.e., rats that exhibited an increase in ethanol intake under FR1 were the same animals that were more motivated for ethanol under PR. Moreover, antecedent anxiety-like behavior (i.e., prior to any ethanol exposure) predicted compulsive-like ethanol drinking specifically in dependent rats (see Supplement and Figure S1).
The behaviors described above captured different aspects of ethanol dependence and provide a rationale for studying the relationship of Nr3c2 levels with “intake/motivation” and “anxiety/compulsive drinking.” Pearson’s test indicated a significant correlation between "anxiety/compulsive drinking” PCA scores and Nr3c2 expression levels in the CeA for dependent (r2=0.656; p<0.005; Figure 3B) but not nondependent (r2=0.185; p=0.085) rats (Figure 3E). No significant correlations were found between PCA scores and Nr3c2 expression levels in the prefrontal cortex for dependent (r2=0.0002; p=0.962; Figure 3C) or nondependent (r2=0.185; p=0.085; Figure 3C) rats.
Additional analyses indicated that the dependent rats that had increased levels of Nr3c2 mRNA in the CeA displayed a trend toward exhibiting lower levels of antecedent anxiety-like behavior and, more importantly, exhibited lower levels of compulsive-like ethanol drinking after the development of dependence (Figure S2).
Study 3
Effect of abstinent versus non-abstinent status on aldosterone levels
There was no significant difference in baseline (Week-00) average (M±SEM) aldosterone levels between the abstinent (233±58 pg/mL) and non-abstinent human subjects (175±22 pg/mL). However, at Week-12, patients who did not maintain abstinence had significantly higher aldosterone levels (232±57 pg/mL) compared to abstinent patients (134±13 pg/mL), (F1,213=4.53, p=0.047) (Figure 4). There was also a significant positive correlation between plasma aldosterone levels at Week-12 and the number of drinks consumed during the 12-week study period (r2=0.38, p=0.0007).
Figure 4. Study 3 in humans: Plasma aldosterone levels at Week 12 in abstinent versus non-abstinent alcohol-dependent patients.
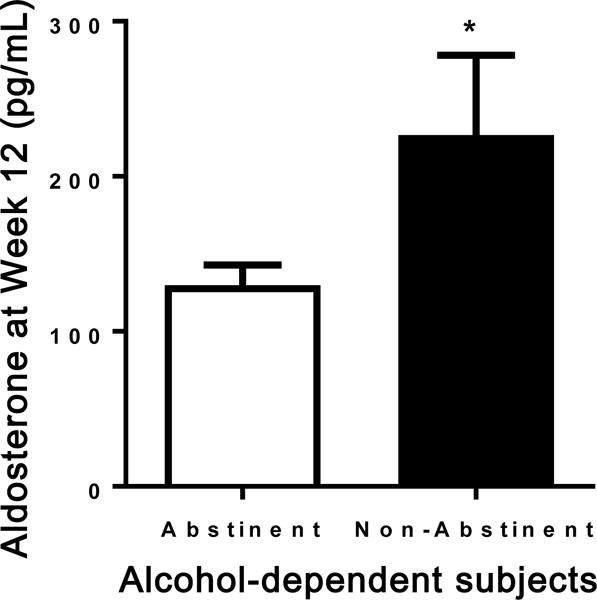
Patients who did not maintain abstinence had significantly higher aldosterone levels compared to abstinent patients (F1,213 = 4.53, *P = 0.047). Results are expressed as m±s.e.m.
Relationship between aldosterone levels and craving scales
At Week-00, no significant correlations were found between aldosterone and craving scales. At Week-12, there was a significant positive correlation between aldosterone levels and the craving scales examined, OCDS (r2=0.21, p=0.02; Figure 5A), the obsessive ODS subscale (r2=0.19, p=0.02; Figure 5B) and the compulsive CDS subscale (r2=0.19, p=0.02; Figure 5C).
Figure 5. Study 3 in humans: Correlations between plasma aldosterone levels at Week 12 and alcohol craving scores in alcohol-dependent patients.
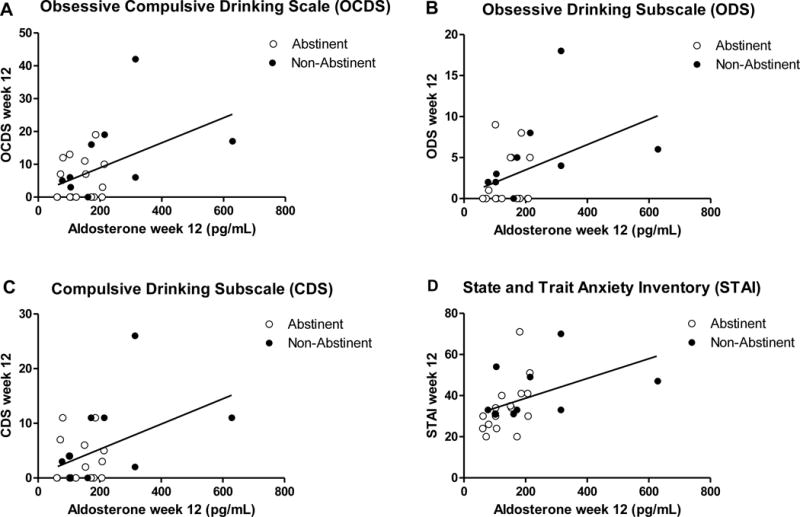
There were significant positive correlations between plasma aldosterone levels and the craving scales examined, i.e. Obsessive Compulsive Drinking Scale (OCDS) total score (r2 = 0.21, p = 0.02; A), the obsessive ODS subscale (r2 = 0.19, p = 0.02; B) and the compulsive CDS subscale (r2 = 0.19, p = 0.02; C). Correlation between plasma aldosterone levels at Week 12 and state anxiety measured by the State and Trait Inventory (STAI) Y1 scale in alcohol-dependent patients. There was a significant positive correlation between plasma aldosterone levels and state anxiety levels (r2 = 0.19, p = 0.03; D).
Relationship between aldosterone levels and anxiety scales
At Week-00, no significant correlations were found between aldosterone and the anxiety scales. At Week-12, a significant positive correlation was found between aldosterone levels and state anxiety (STAI-Y1) levels (r2=0.19, p=0.03; Figure 5D).
Discussion
The present set of findings support a link between the aldosterone/MR endocrine pathway and ethanol drinking. Notably, converging observations were obtained in three different species, i.e., a monkey model of ethanol self-administration, a rat model of alcohol dependence and compulsive-like drinking and humans with alcohol dependence.
In the monkey study, plasma aldosterone levels were significantly higher after 6-months and 12-months of ethanol self-administration compared to baseline. This within-subjects comparison suggests that aldosterone increased as a consequence of ethanol consumption. Indeed, while the identification of a specific threshold remains for future work (e.g. by using monkeys that drank less than 1.2 g/kg/day), the data suggest that chronic drinking of at least an average of 1.2 g/kg/day, roughly equivalent to 5 drinks/day in humans, is sufficient to raise circulating aldosterone. The increase in aldosterone seen in the monkeys at 6-months remained high after 12-months of continued drinking, and did not increase further. These data suggest that aldosterone levels become regulated at a new set-point under daily ethanol consumption, consistent with the hypothesis that chronic ethanol produces an allostatic shift of brain stress systems.[34] The monkey study also indicated a specific relationship with ethanol drinking, as no significant correlations were observed with water intake.
In the rat study, we found that Nr3c2 levels in the CeA, but not PFC, were correlated with anxiety-like behavior and compulsive-like alcohol drinking specifically in dependent rats. The dependent rats with high levels of Nr3c2 in the CeA exhibited a trend to be less anxious-like when tested in the elevated plus maze before alcohol exposure. These same dependent rats with high levels of Nr3c2 in the CeA exhibited less compulsive-like alcohol drinking compared with dependent rats with low levels of Nr3c2. This suggests that anxiety-like behavior prospectively predicted compulsive-like drinking in dependent rats, i.e.: the more anxious-like rats showed more compulsive-like ethanol drinking (drinking more despite the aversive bitter taste of quinine). Moreover, baseline anxiety-like behavior may be a marker of Nr3c2 plasticity in alcohol dependence. These findings suggest that high Nr3c2 levels in the CeA may be protective against compulsive ethanol drinking or, conversely, that low levels of Nr3c2 expression may convey vulnerability for anxiety-related compulsive ethanol drinking. However, our experimental design prohibits a conclusion regarding gene expression differences as a response to drinking or a predisposition to drinking patterns or a response to alcohol withdrawal. It is important to note that both behavioral testing and brain collection for gene expression analysis were conducted during acute ethanol withdrawal, when blood ethanol levels were negligible.
In the human study, a between-subjects comparison indicated that aldosterone levels were significantly higher in alcohol-dependent patients who were drinking during the 12-week period, compared to those who maintained abstinence during the same time frame. The human data were further corroborated by the observation that aldosterone levels correlated with the amount of ethanol consumed during the 12-week period, i.e. higher drinking levels were associated with higher plasma aldosterone levels.
Together, the results suggest that inquiries into circulating aldosterone levels must look at both synthesis and receptor regulation. Post-mortem brain analysis from the monkeys, exploring the effects of aldosterone signaling on brain gene expression of aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) and the mineralocorticoid nuclear receptor (NR3C2) genes, sheds some light on brain adaptation to the elevated aldosterone levels associated with ethanol consumption. Albeit preliminary, these findings suggest that NR3C2 gene expression is sensitive to ethanol consumption in the CeA, but not in the PFC. The CeA is known to have key roles in modulating the effects of ethanol[10–12, 35] and the current data provide information suggestive of a potential selective role of aldosterone signaling in specific brain areas and pathways. Notably, the correlations with ethanol intake in the monkey are negative, with higher ethanol consumption predicting lower CeA NR3C2 gene expression. One possibility is that blood aldosterone may be a peripheral marker of central MR activity, i.e., increased peripheral aldosterone levels are a consequence of reduced MR-mediated negative feedback; alternatively, it may be that amygdalar MRs are downregulated as a compensatory effect of ethanol-induced increases in aldosterone. A third possibility is that peripheral aldosterone may be a proxy of central aldosterone synthesis; however, this latter hypothesis is unlikely. In fact, the CYP11B2 gene has been detected in the rat brain only at very low levels[36–38] and its function in the brain is unclear.[2] In our monkey study, the CYP11B2 gene was not expressed at detectible levels in either the CeA or the PFC, hence there is no evidence of aldosterone synthesis in these brain areas. Finally, changes in DNA methylation and/or microRNA may represent additional putative mechanisms how alcohol influences NR3C2 gene expression, as shown for the regulation of MRs[39] and volume-regulating hormones.[40] Because the CeA is an important area for anxiety, stress sensitization and stress-induced ethanol drinking,[9] it is possible that aldosterone might be relevant to negative reinforcement processes associated with the addiction cycle. In support of this hypothesis, our previous,[18] and the present human data, indicated a positive relationship between aldosterone levels and alcohol craving, as well as aldosterone levels and anxiety. The present rat study corroborates these clinical studies. Together, our findings across rats and humans support a role of the aldosterone/MR pathway in anxiety and ethanol drinking in AUD.
It is important to note that cortisol has a greater affinity for MRs than for glucocorticoid receptors. An added factor in the MR regulation is the interplay between aldosterone and cortisol. In general, aldosterone may modulate other stress-related neuropeptides (e.g., corticotropin-releasing factor, dynorphin-κ opioid systems, norepinephrine) in the extended amygdala that are known to drive a negative emotional state and excessive alcohol drinking.[9] Activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis characterizes initial alcohol use (binge/intoxication stage), but as dependence develops, HPA axis activity is blunted and activation of extra-hypothalamic brain stress systems characterize the withdrawal/negative-affect stage and protracted abstinence in the preoccupation/anticipation stage.[9] Among these changes accompanying the activation of these stress systems, one may include an amygdalar MR down-regulation, which in turn results in increased stress, anxiety and compulsive-like ethanol drinking. Future preclinical and human studies could test pharmacological approaches targeting the aldosterone/MR signaling towards developing novel medications for AUD.
The results presented here converge on the importance of aldosterone in alcohol-seeking behaviors via MR signaling. Previous work indicated lower plasma sodium levels in patients in early alcohol withdrawal[15] and increased concentration of fluid and salt preserving hormones, like aldosterone, during early alcohol withdrawal and subsequent decrease after abstinence.[41–46] However, our monkey and human studies were not conducted during acute withdrawal, only the rat study was. Both sodium and mean corpuscular volume (an indirect measure of osmolality) in Study 1 and Study 3 were in the normal range (data not shown), suggesting that peripheral aldosterone signaling at these time points was unlikely to contribute to alcohol-seeking behaviors. Obviously, peripheral actions of aldosterone may still be of relevance for engaging the MR system dysregulations (see above), and for other pathophysiological effects related to excessive alcohol use, such as alcohol-associated hypertension. Future work on this area could include hemodynamic studies and NR3C2 gene expression analysis of the adrenocortical cortex tissue.
Study strengths include: 1) the potential role of the aldosterone/MR pathway in alcohol-seeking behaviors has been understudied; 2) the investigation was carried out across monkeys, rats and humans, thus providing cross-species and translational validation; and 3) this investigation used a well-validated non-human primate model of alcohol use; a well-validated and reliable rat model of alcohol dependence[47, 48]; and a clinically-relevant sample of treatment seeking alcohol-dependent patients. Limitations include: 1) the small sample sizes, although the size of the monkey sample was consistent with previous work[49–51] and the human sample was relatively larger compared to our previous clinical study;[18] 2) the different designs, given that the three studies were not planned a priori to be conducted in parallel. This aspect, together with species differences, different methodologies and the small sample size of Study 1 may explain some cross-species differences like the lack of correlation between plasma aldosterone and alcohol drinking in monkeys, which was the case with human subjects; 3) the exploratory nature of some analyses in Study 3, where, consistent with previous recommendations,[52–54] statistical adjustment was not conducted; 4) the present data show correlations, but do not establish causality; therefore, future translational work is needed before drawing final conclusions; 5) unlike in monkeys and rats where the amount of alcohol consumption was observed, in humans alcohol intake was self-reported; we used BEC and liver enzymes to corroborate these self-reported data, however additional objective measurements (e.g.: carbohydrate-deficient transferrin, ethylglucuronide) were not included; and 6) we only assessed aldosterone in the morning; aldosterone secretion is highest in the morning and lowers during the afternoon and evening,[55] therefore future studies may consider serial aldosterone determinations to account for the circadian rhythm. In spite of these limitations, this set of data provides novel and important information and cross-species translation on the potential role of the aldosterone/MR pathway in AUD.
In conclusion, the present findings in monkeys, rats and humans provide support for a relationship between alcohol drinking and the aldosterone/MR pathway in the context of excessive alcohol use. This study provides compelling evidence that this endocrine pathway should be further investigated as a putative target for the development of new pharmacotherapies for AUD.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the following funding sources: European Foundation for Alcohol Research (ERAB) grant EA0619 (LL, GA) and ERAB exchange award EXA0802 (LL); National Institutes of Health (NIH) intramural funding ZIA-AA000218 (Section on Clinical Psychoneuroendocrinology and Neuropsychopharmacology; LL), jointly supported by the Division of Intramural Clinical and Biological Research of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA); National Institute of Mental Health grant MH101076 (research protected time for EGA under R25 mechanism); the Swedish Research Council (BE, MH); the Pearson Center for Alcoholism and Addiction Research (LFV, GFK); and NIAAA grants AA023867 (CLH-K), AA010760 (RH), AA08459 (LFV, GFK) and AA109431 (KAG).
The authors would also like to thank Ms. Karen Smith (NIH Library) for bibliographic assistance, Lisa Farinelli (Section on Clinical Psychoneuroendocrinology and Neuropsychopharmacology, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and National Institute on Drug Abuse) for providing support with the preparation of the manuscript, and Dr. Christa Helms for initial data organization.
Footnotes
Contributors
LL and GA designed the human study; KAG designed the non-human primate study; RH designed the next generation RNA sequencing study; LFV, EB, MH and GFK designed the rat study. LL, GA, MH, RH, GFK and KAG provided funding used to conduct the studies. LL, AF and GA conducted the human study, including collection of the clinical research data and patient care. EGA conducted all the analyses of the human study. VAJ conducted the analysis of the non-human primate study. PD generated and NARW analyzed the gene expression data of the non-human primate study. LFV and EB conducted the experiments of the rat study; LFV, EB, MH and GFK analyzed the data of the rat study. EGA, VAJ, LFV, NARW, EB, CLH-K, MRL, GA, MH, GFK, KAG and LL participated in the interpretation of data for important intellectual contents. EGA and LL wrote the first draft of the manuscript. VAJ, LFV, NARW, EB, CLH-K, MRL, GA, MH, GFK and KAG contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
References
- 1.Kenna GA, Swift RM, Hillemacher T, Leggio L. The relationship of appetitive, reproductive and posterior pituitary hormones to alcoholism and craving in humans. Neuropsychol Rev. 2012;22:211–228. doi: 10.1007/s11065-012-9209-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bureik M, Lisurek M, Bernhardt R. The human steroid hydroxylases CYP1B1 and CYP11B2. Biol Chem. 2002;383:1537–1551. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hargovan M, Ferro A. Aldosterone synthase inhibitors in hypertension: current status and future possibilities. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;3 doi: 10.1177/2048004014522440. eCollection 2048004014522014 Jan. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mitra R, Ferguson D, Sapolsky RM. Mineralocorticoid receptor overexpression in basolateral amygdala reduces corticosterone secretion and anxiety. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;66:686–690. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kruk MR, Haller J, Meelis W, de Kloet ER. Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade during a rat’s first violent encounter inhibits its subsequent propensity for violence. Behav Neurosci. 2013;127:505–514. doi: 10.1037/a0033553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wingenfeld K, Kuehl LK, Dziobek I, Roepke S, Otte C, Hinkelmann K. Effects of mineralocorticoid receptor blockade on empathy in patients with major depressive disorder. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2016;16:902–910. doi: 10.3758/s13415-016-0441-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Edwards S, Koob GF. Neurobiology of dysregulated motivational systems in drug addiction. Future Neurol. 2010;5:393–401. doi: 10.2217/fnl.10.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reul JM, de Kloet ER. Two receptor systems for corticosterone in rat brain: microdistribution and differential occupation. Endocrinology. 1985;117:2505–2511. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Koob GF. The dark side of emotion: The addiction perspective. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;753:73–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.11.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dhaher R, Finn D, Snelling C, Hitzemann R. Lesions of the Extended Amygdala in C57BL/6J Mice Do Not Block the Intermittent Ethanol Vapor-Induced Increase in Ethanol Consumption. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008;32:197–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gilpin NW, Herman MA, Roberto M. The Central Amygdala as an Integrative Hub for Anxiety and Alcohol Use Disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:859–869. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roberto M, Gilpin NW, Siggins GR. The Central Amygdala and Alcohol: Role of -Aminobutyric Acid, Glutamate, and Neuropeptides. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2:a012195–a012195. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Koob GF, Volkow ND. Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3:760–773. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(16)00104-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sinha R, Lacadie CM, Constable RT, Seo D. Dynamic neural activity during stress signals resilient coping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:8837–8842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600965113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kovács GL. The role of atrial natriuretic peptide in alcohol withdrawal: a peripheral indicator and central modulator? Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;405:103–112. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Doring WKH, Herzenstiel M-Nl, Krampe H, Jahn H, Pralle L, Sieg S, et al. Persistent Alterations of Vasopressin and N-Terminal Proatrial Natriuretic Peptide Plasma Levels in Long-Term Abstinent Alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:849–861. doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000065433.17403.DE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hillemacher T. Volume intake and craving in alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006;41:61–65. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agh235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Leggio L, Ferrulli A, Cardone S, Miceli A, Kenna GA, Gasbarrini G, et al. Renin and aldosterone but not the natriuretic peptide correlate with obsessive craving in medium-term abstinent alcohol-dependent patients: a longitudinal study. Alcohol. 2008;42:375–381. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.03.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Helms CM, Park B, Grant KA. Adrenal steroid hormones and ethanol self-administration in male rhesus macaques. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2014;231:3425–3436. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3590-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Helms CM, Rau A, Shaw J, Stull C, Gonzales SW, Grant KA. The effects of age at the onset of drinking to intoxication and chronic ethanol self-administration in male rhesus macaques. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2014;231:1853–1861. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3417-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grant KA, Leng X, Green HL, Szeliga KT, Rogers LSM, Gonzales SW. Drinking Typography Established by Scheduled Induction Predicts Chronic Heavy Drinking in a Monkey Model of Ethanol Self-Administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008;32:1824–1838. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baker EJ, Farro J, Gonzales S, Helms C, Grant KA. Chronic Alcohol Self-Administration in Monkeys Shows Long-Term Quantity/Frequency Categorical Stability. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014;38:2835–2843. doi: 10.1111/acer.12547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Daunais JB, Davenport AT, Helms CM, Gonzales SW, Hemby SE, Friedman DP, et al. Monkey Alcohol Tissue Research Resource: Banking Tissues for Alcohol Research. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014;38:1973–1981. doi: 10.1111/acer.12467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Iancu OD, CA, Walter NAR, Darakjian P, Oberbeck DL, Daunais JB, et al. On the Relationships in Rhesus Macaques between Chronic Ethanol Consumption and the Brain Transcriptome. Addict Biol. doi: 10.1111/adb.12501. [under review] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Richardson HN, Lee SY, O’Dell LE, Koob GF, Rivier CL. Alcohol self-administration acutely stimulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, but alcohol dependence leads to a dampened neuroendocrine state. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;28:1641–1653. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vendruscolo LF, Barbier E, Schlosburg JE, Misra KK, Whitfield TW, Jr, Logrip ML, et al. Corticosteroid-dependent plasticity mediates compulsive alcohol drinking in rats. J Neurosci. 2012;32:7563–7571. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0069-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Addolorato G, Leggio L, Ferrulli A, Cardone S, Bedogni G, Caputo F, et al. Dose-Response Effect of Baclofen in Reducing Daily Alcohol Intake in Alcohol Dependence: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Alcohol Alcohol. 2011;46:312–317. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agr017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Addolorato G, Leggio L. Safety and efficacy of baclofen in the treatment of alcohol-dependent patients. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16:2113–2117. doi: 10.2174/138161210791516440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Starosta AN, Leeman RF, Volpicelli JR. The BRENDA model: integrating psychosocial treatment and pharmacotherapy for the treatment of alcohol use disorders. J Psychiatr Pract. 2006;12:80–89. doi: 10.1097/00131746-200603000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sobell LC, Sobell MB, Leo GI, Cancilla A. Reliability of a Timeline Method: assessing normal drinkers’ reports of recent drinking and a comparative evaluation across several populations. Addiction. 1988;83:393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1988.tb00485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Anton RF, Moak DH, Latham P. The Obsessive Compulsive Drinking Scale: A Self-Rated Instrument for the Quantification of Thoughts about Alcohol and Drinking Behavior. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1995;19:92–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1995.tb01475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Janiri L, Calvosa F, Dario T, Pozzi G, Ruggeri A, Addolorato G, et al. The Italian version of the Obsessive–Compulsive Drinking Scale: validation, comparison with the other versions, and difference between type 1- and type 2-like alcoholics. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2004;74:187–195. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2004.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Spielberger CD, Edwards CD, Montouri J, Lushene R. Manual for the State and Trait Anxiety Inventory. Consulting Psychologist Press; Palo Alto, CA: 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 34.George O, Le Moal M, Koob GF. Allostasis and addiction: Role of the dopamine and corticotropin-releasing factor systems. Physiol Behav. 2012;106:58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vendruscolo LF, Estey D, Goodell V, Macshane LG, Logrip ML, Schlosburg JE, et al. Glucocorticoid receptor antagonism decreases alcohol seeking in alcohol-dependent individuals. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:3193–3197. doi: 10.1172/JCI79828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stromstedt M, Waterman MR. Messenger RNAs encoding steroidogenic enzymes are expressed in rodent brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995;34:75–88. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00140-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gomez-Sanchez CE, Zhou MY, Cozza EN, Morita H, Foecking MF, Gomez-Sanchez EP. Aldosterone biosynthesis in the rat brain. Endocrinology. 1997;138:3369–3373. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.8.5326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gomez-Sanchez EP, Gomez-Sanchez CM, Plonczynski M, Gomez-Sanchez CE. Aldosterone synthesis in the brain contributes to Dahl salt-sensitive rat hypertension. Exp Physiol. 2010;95:120–130. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2009.048900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Petropoulos S, Matthews SG, Szyf M. Adult glucocorticoid exposure leads to transcriptional and DNA methylation changes in nuclear steroid receptors in the hippocampus and kidney of mouse male offspring. Biol Reprod. 2014;90:43. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.115899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Glahn A, Riera Knorrenschild R, Rhein M, Haschemi Nassab M, Groschl M, Heberlein A, et al. Alcohol-induced changes in methylation status of individual CpG sites, and serum levels of vasopressin and atrial natriuretic peptide in alcohol-dependent patients during detoxification treatment. Eur Addict Res. 2014;20:143–150. doi: 10.1159/000357473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bannan LT, Potter JF, Beevers DG, Saunders JB, Walters JRF, Ingram MC. Effect of alcohol withdrawal on blood pressure, plasma renin activity, aldosterone, cortisol and dopamine β-hydroxylase. Clin Sci. 1984;66:659–663. doi: 10.1042/cs0660659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bezzegh A, Nyuli L, Kovács GL. α-Atrial natriuretic peptide, aldosterone secretion and plasma renin activity during ethanol withdrawal: a correlation with the onset of delirium tremens? Alcohol. 1991;8:333–336. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(91)90513-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.De Marchi S, Cecchin E, Basile A, Bertotti A, Nardini R, Bartoli E. Renal Tubular Dysfunction in Chronic Alcohol Abuse – Effects of Abstinence. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1927–1934. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312233292605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Regan TJ, Pathan A, Weisse AB, Eaddy C, Torres R. The Contribution of Arterial Pressure to the Cardiac Dysfunction of Chronic Alcoholism. Acta Med Scand. 2009;218:273–280. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1985.tb08923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mander AJ, Weppner GJ, Chick JD, Morton JJ, Best JJ. An NMR study of cerebral oedema and its biological correlates during withdrawal from alcohol. Alcohol Alcohol. 1988;23:97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mander AJ, Young A, MacDonald TM, Williams BC, Waugh CJ, Edwards CR. Blood pressure, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis and cortisol changes during withdrawal from alcohol. Alcohol Alcohol. 1989;24:409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vendruscolo LF, Roberts AJ. Operant alcohol self-administration in dependent rats: focus on the vapor model. Alcohol. 2014;48:277–286. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2013.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Meinhardt MW, Sommer WH. Postdependent state in rats as a model for medication development in alcoholism. Addict Biol. 2015;20:1–21. doi: 10.1111/adb.12187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Beattie MC, Maldonado-Devincci AM, Porcu P, O’Buckley TK, Daunais JB, Grant KA, et al. Voluntary ethanol consumption reduces GABAergic neuroactive steroid (3alpha,5alpha)3-hydroxypregnan-20-one (3alpha,5alpha-THP) in the amygdala of the cynomolgus monkey. Addict Biol. 2015 doi: 10.1111/adb.12326. epub ahead of print 2 Dec 2015. doi: 2010.1111/adb.12326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Jimenez VA, Helms CM, Cornea A, Meshul CK, Grant KA. An ultrastructural analysis of the effects of ethanol self-administration on the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in rhesus macaques. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9 doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pleil KE, Helms CM, Sobus JR, Daunais JB, Grant KA, Kash TL. Effects of chronic alcohol consumption on neuronal function in the non-human primate BNST. Addict Biol. 2015 doi: 10.1111/adb.12289. n/a–n/a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bender R, Lange S. Adjusting for multiple testing—when and how? J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54:343–349. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(00)00314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rothman KJ. No Adjustments Are Needed for Multiple Comparisons. Epidemiology. 1990;1:43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Perneger TV. What’s wrong with Bonferroni adjustments. BMJ. 1998;316:1236–1238. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7139.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Charloux A, Gronfier C, Lonsdorfer-Wolf E, Piquard F, Brandenberger G. Aldosterone release during the sleep-wake cycle in humans. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:E43–49. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1999.276.1.E43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.