FIGURE 1.
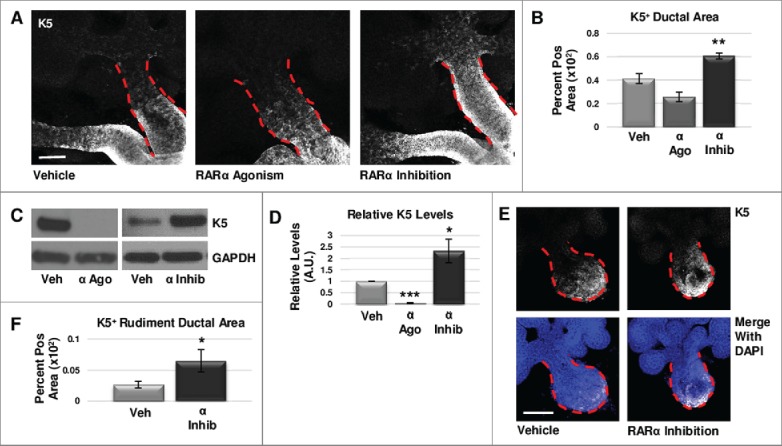
RARα negatively regulates K5+ salivary epithelial cells. (A) Whole explants cultured ex vivo for 72 hours with RARα (α ago) agonist show decreased expansion of K5+ cells in the main duct, while K5 extends beyond the primary duct relative to vehicle control (Veh) with RARα inhibition (α inhib) by ICC in single confocal sections. Ducts are outlined with red dotted line. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Quantification of K5+ area in the main duct normalized to the total main duct area indicates significantly increased K5+ with RARα inhibition. Veh n = 19, α ago n = 6, α inhib n = 15 explants. Statistical analysis completed using Student's two-tailed t-test. **p = 0.003, α ago p = 0.056. (C, D) E12.5 explants were cultured for 48 hours. Western blot and quantification of Western blot indicates significantly decreased levels of K5 with RARα agonism and significantly increased K5 levels with RARα inhibition as normalized to GAPDH levels. Mean represents three or more experiments with n ≥ 5 glands per condition. Statistical analysis completed using Student's two-tailed t-test. *p = 0.04, ***p<0.0001. (E, F) E12.5 epithelial rudiments were cultured for 48 hours. Quantification of the K5+ ductal area relative to total ductal area with RARα inhibition shows significantly increased K5+ area. Scale bar 100 μm. Veh n = 12, α inhib n = 11 explants. Statistical analysis completed using Student's two-tailed t-test. *p = 0.045.
