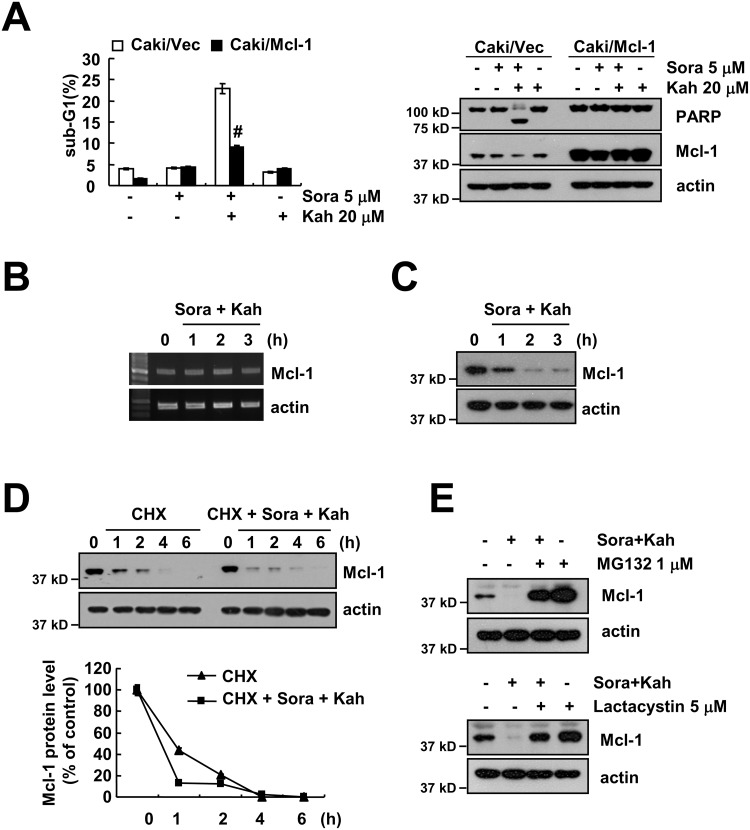
Figure 3. Down-regulation of Mcl-1 expression by sorafenib plus kahweol contributes to apoptosis.
(A) Vector cells (Caki/vector) and Mcl-1-overexpressed cells (Caki/Mcl-1) were treated with 20 μM kahweol (Kah) in the presence or absence of 5 μM sorafenib (sora) for 24 h. The sub-G1 fraction was measured by flow cytometry (left panel). The protein expression levels of PARP, Mcl-1 and actin were determined by Western blot (right panel). (B-C) Caki cells were treated with 20 μM kahweol and 5 μM sorafenib for the indicated time periods. The mRNA (B) and protein (C) expression levels of Mcl-1 and actin were determined by RT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively. (D) Caki cells were treated with or without 20 μM kahweol and 5 μM sorafenib in the presence of 20 μg/ml cyclohexamide (CHX) for the indicated time periods. The protein expression levels of Mcl-1 and actin were determined by Western blotting. The band intensity of the Mcl-1 protein was measured using ImageJ (public domain JAVA image-processing program ImageJ (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij). (E) Caki cells were pretreated with 1 μM MG132 and 5 μM lactacystin for 30 min and were then combined with 20 μM kahweol and 5 μM sorafenib for 24 h. The protein expression levels of Mcl-1 and actin were determined by Western blot. The level of actin was used as a loading control. The values in A represent the mean ± SD from three independent samples. # p < 0.01 compared to the combined treatment with sorafenib and kahweol-treated Caki/Vec.