Abstract
Root-knot nematodes (RKNs), particularly Meloidogyne incognita, are the most devastating soil-borne pathogens that significantly affect the production of Prunus spp. fruit. RKN infection is difficult to control and consequently causes massive yield losses each year. However, several germplasms of wild Prunus spp. have been shown to display resistance to M. incognita. Consequently, both the isolation of novel plant resistance (R) genes and the characterization of their resistance mechanisms are important strategies for future disease control. R proteins require the co-chaperone protein HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 to achieve correct folding, maturation, and stabilization. Here, we used homologous cloning to isolate the R gene PsoRPM2 from the RKN-resistant species Prunus sogdiana. PsoRPM2 was found to encode a TIR-NB-LRR-type protein and react with significantly elevated PsoRPM2 expression levels in response to RKN infection. Transient expression assays indicated PsoRPM2 to be located in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Four transgenic tobacco lines that heterologously expressed PsoRPM2 showed enhanced resistance to M. incognita. Yeast two-hybrid analysis and bimolecular fluorescence complementation analysis demonstrated that both PsoRAR1 and PsoRPM2 interacted with PsoHSP90-1 and PsoSGT1, but not with one another. These results indicate that the observed PsoRPM2-mediated RKN resistance requires both PsoHSP90-1 and PsoSGT1, further suggesting that PsoRAR1 plays a functionally redundant role in the HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 co-chaperone.
Keywords: Prunus sogdiana, PsoRPM2 gene, root-knot nematode, HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 co-chaperone, transgenics, Meloidogyne incognita
Introduction
Root-knot nematodes (RKNs) from the genus Meloidogyne are a class of sedentary, endozoic plant parasites with a wide host range (Mitkowski and Abawi, 2003). RKNs (particularly Meloidogyne incognita) cause significant economic damage in the range of hundreds of billions of dollars annually (Jones et al., 2013). M. incognita infected host plants may induce a series of disease resistance reactions that ultimately inhibit both invasion and life cycle completion of nematodes (Abad and Williamson, 2010). The plant immunity response typically consists of two stages: pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) and effector-triggered immunity (ETI) (Jones and Dangl, 2006). PTI requires pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) located in either the cytomembrane or cytoplasm (Boller and He, 2009; Dodds and Rathjen, 2010). Adaptive pathogens have been reported to interfere with host PTI via small secretory proteins known as effectors (Block et al., 2008; Göhre and Robatzek, 2008; Cunnac et al., 2009). Several plant species have evolved specific resistance genes (R genes) that are able to recognize particular effectors, thus facilitating ETI (Zipfel et al., 2006; Tsuda and Katagiri, 2010). Resistance associated with ETI has been shown to be stronger and more enduring than PTI associated resistance (Glazebrook, 2005; Torres et al., 2006; Underwood et al., 2007). R gene encoded R proteins play a pivotal role in detecting pathogens and in initiating immune responses (Jacob et al., 2013). Plant R proteins are typically composed of three major domains: a coiled-coil (CC) or a Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain, a nucleotide-binding (NB) domain, and a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain (Takken and Goverse, 2012). The R gene structure is highly conserved in both plants and mammals (Padmanabhan et al., 2009); however, plants possess considerably more R genes, suggesting that plant R genes are more pathogen-specific and potentially facilitate more diverse and complex immune responses than those of mammals.
R genes for RKNs have been isolated from various plants. The first isolated RKN R gene was Mi-1 (Vos et al., 1998), which originated from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and conferred race-specific resistance to RKN (Meloidogyne spp.) and potato aphids (Macrosiphum euphorbiae) (Milligan et al., 1998). Subsequently, RKN R genes have either been cloned or mapped from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum; GHNTR1) (Zhang et al., 2015), potato (Solanum tuberosum; Rmc) (van der Voort et al., 1999), pepper (Capsicum annuum; Me) (Celik et al., 2016), and myrobalan (Prunus cerasifera, Ma) (Claverie et al., 2011). These RKN R genes contain NBS-LRR domains and typically exhibit reduced expression levels in the absence of pathogens. However, RKN R gene expression significantly increases in response to RKN infection (Zhang et al., 2015). The plant hypersensitive response (HR) is a disease resistance mechanism that occurs in response to an incompatible plant–pathogen interaction and is typically accompanied by programmed cell death (Karrer et al., 1998). Mi-1 in tomato induces the HR 12 h after RKN infection, blocking the formation of feeding sites and therefore inhibiting RKN development (Melillo et al., 2006). However, the molecular mechanism underlying Mi-1-facilitated RKN resistance remains unclear. Furthermore, due to the species specificity of R genes, use of Mi-1 to engineer RKN resistance in heterologous plants did not result in stable RKN immunity. While transgenic Mi-1 expressing eggplant (Solanum melongena) varieties displayed RKN resistance, no aphid resistance could be found (Goggin et al., 2006). Furthermore, Mi-1 expressing Arabidopsis thaliana and tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana) exhibited no pathogen resistance (Williamson and Kumar, 2006). These results indicate that R gene induced resistance signaling pathways vary considerably between different plant species (Martin et al., 2003; Bonardi and Dangl, 2012). Plants with a longer lifespan than herbaceous plants (such as perennial fruit trees) have a higher risk of RKN infection, consequently warranting a more comprehensive, and thus more complex, mechanism of RKN resistance. The identification of novel RKN R genes from related plant species may assist in the engineering of stable and enduring RKN resistance.
Studies using model plant species revealed that R proteins require the co-chaperone protein complex HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 to achieve correct folding, maturation, and stabilization (Huang et al., 2014). The heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is a highly conserved protein in higher plants, is a suppressor of the G2 allele of skp1 (SGT1), and is required for mla12 resistance (RAR1) (Kadota and Shirasu, 2012). HSP90 is involved in the assembly, maturity, and stabilization of numerous critical signaling proteins in eukaryotic cells, and typically exists as a homodimer (Csermely et al., 1998; Hubert et al., 2003). SGT1 regulates important biochemical processes, such as ubiquitination and kinetochore assembly, and maintains the stability of the R protein structure in the absence of pathogens (Austin et al., 2002). RAR1 was first characterized in barley (Hordeum vulgare), and while rar1 mutant plants appear morphologically normal, they are less resistant to fungal pathogens, despite the presence of the R gene MLA12 (Bieri et al., 2004). Both HSP90 homodimer and SGT1 interact with a number of R proteins, and consequently, loss of function of HSP90, SGT1, or RAR1 will reduce the functionality of R proteins such as MLA1, MAL6, Rx, RPM1, RPS5, Mi-1, and I-2, thus compromising plant immunity (Lu et al., 2003; Bieri et al., 2004; Holt et al., 2005; Bhattarai et al., 2007; Botër et al., 2007; Van Ooijen et al., 2010). Recently, the relationship between the HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 co-chaperone protein complex and RKN resistance has been further characterized. While RKN resistance is not affected in Mi-1-engineered tomato in response to RNA interference induced reduction of SlRAR1 gene expression, reduced expression of SlHSP90 and SlSGT1 results in increased numbers of galls and egg mass in plants exposed to M. javanica RKNs (Bhattarai et al., 2007). This suggests that HSP90 and SGT1 also have a function in RKN resistance. Most studies that examine the relationship between R genes and the HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 co-chaperone protein have been based on herbaceous model plant species, and comparable research for woody plants is still missing.
The Xinjiang wild myrobalan (Prunus sogdiana) is distributed throughout native forests in the eastern region of the Tianshan Mountains (Esmenjaud et al., 1996; Wang et al., 2006; Kang et al., 2008). We collected P. sogdiana seeds from the Xinjiang Yili native forest in 2005 and used these seeds from 2007 onward to cultivate more than 150 individual P. sogdiana plants at the Shangzhuang experimental station of the China Agricultural University (CAU). Among the resulting plants, we found several individuals that displayed complete resistance to M. incognita and repeated this experiment six times, which lasted 6 years (Xiao et al., 2010; Li et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2015; Qiu et al., 2016). Via homologous cloning of genes from highly resistant P. sogdiana individuals based on reported RKN R gene sequences, we identified a series of NB domain fragments that respond to RKN invasion. Full-length R gene cDNA sequences were obtained via 3′- and 5′- RACE, revealing PsoRPM2 as the underlying R gene. To characterize the observed M. incognita resistance conferred by this gene, we created transgenic heterologously expressing PsoRPM2 lines of the RKN-susceptible tobacco variety W38 (Nicotiana tabacum cv. W38). Analyses of the interactions between PsoRPM2, PsoHSP90-1, and PsoSGT1 provided insight into the underlying mechanism of P. sogdiana RKN immunity.
Materials and Methods
Plant and Nematode Materials
Prunus sogdiana seedlings were planted at the Shangzhuang test station at the CAU. Following 5 years of evaluation, individual P. sogdiana plants were determined to be either highly resistant or susceptible to M. incognita and were used to source root tissue for hardwood cutting and RNA extraction.
The hardwood cutting experiment was performed from 2014 to 2015 using both resistant and susceptible plant individuals. Fifteen resistant and fifteen susceptible hardwood cuttings with heights between 20 and 30 cm and that displayed uniform growth were inoculated with 2000 M. incognita J2 nematodes per seedling. Five resistant and five susceptible seedlings were irrigated with identical amounts of water to serve as experimental controls. All of the root tips were collected at 0, 1, 3, and 5 days post-infection (dpi) for gene cloning and expression assays.
Seedlings of tobacco W38 (Nicotiana tabacum cv. W38) and Nicotiana benthamiana were cultured in a greenhouse. M. incognita nematodes were sourced from the laboratory of Jian Heng from the Institute of Plant Protection of the CAU. Nematode cultures were maintained according to published method (Priya et al., 2011) with slight modifications: eggs were collected from susceptible tobacco W38 roots, placed on nylon netting floating in water, and maintained in darkness at 30°C for 5 days, at which point juvenile nematodes (J2) were collected for analysis.
Gene Cloning and Expression Assays
RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
Total RNA was extracted via the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method from both resistant and susceptible myrobalans root tips at 0, 1, 3, and 5 dpi. cDNA was synthesized using a reverse transcription system (Promega, United States) and was used to either clone typical resistance gene analogs (RGAs) or for quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis (using the machine model ABIPRISM 7500).
PCR Amplification from cDNA to Clone RGAs
To obtain the typical RGAs for RKN-resistant P. sogdiana, cDNA was synthesized from the RNA of roots that have been collected at 1 dpi and from a single P. sogdiana-resistant plant. The RGA primer pair MP-F/MP-R (see Supplementary Table S1) was designed based on the consistently conserved P-loop sequence of NBS domains among known resistance R proteins; particularly Mi-1, Ma (resistant alleles), GHNTR1, and PkMi proteins, as previously described (Li et al., 2011). The utilized PCR program has previously been described (Bouktila et al., 2014). RGA fragments were connected with a TA-cloning Kit (Tiangen) and then sequenced. The amino acid sequences of all RGA fragments were predicted using BioXM 2.6 and sequences with continuous open reading frame (ORF) were chosen for querying databases via NCBI-BLAST1. Sequences with a predicted P-loop motif were selected as candidate R genes for further study. All primers were designed using the software package Primer 5.0.
Determining the Full-Length Sequence of PsoRPM2 via RACE and Expression Profiling
To obtain full-length sequences for candidate R genes from amplified RGA fragments, primers were designed for 5′- and 3′-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) PCR (see Supplementary Table S1). RACE was performed following previously described methods (Yeku and Frohman, 2011). The DNAMAN5.0 software was used to analyze the full-length cDNA sequence of the novel R gene and the predicted protein domains of this novel sequence were analyzed via NCBI-BLAST. The NB-ARC domain of the novel R protein was identified via the Phyre2 program2 (Kelley et al., 2015). The phylogenetic tree of the R protein was created in MEGA 5.1. All primers used for expression analysis are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The primer pair to target the coding sequence (CDS) of PsoRPM2 was designed to clone and compare alleles in both resistant and susceptible P. sogdiana plants (see Supplementary Table S1). qRT-PCR primers were designed to analyze the PsoRPM2 expression in resistant and susceptible plants following RKN infection (see Supplementary Table S1). qRT-PCR was performed via the SuperReal PreMix Plus (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., China) and an Applied Biosystems 7500 instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States), with 40 cycles of 95°C for 10 s followed by 60°C for 30 s. Relative expression levels were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method, the RPII gene was used as reference gene, and the primers referred to Tong et al. (2009).
Cloning of Co-chaperonin Genes
Homology-based cloning was used to clone genes that encoded members of the chaperonin complex (HSP90, SGT1, and RAR1) from a single resistant P. sogdiana plant. HSP90 typically has several homologues in plant genomes. Based on the genomic data of the related species Prunus mume3, three HSP90 candidate genes were identified after NCBI-BLAST database searches using the CDS of SlHSP90-1 (GeneID: 543902), HSP90-1 (GeneID: 103342005), HSP90-2 (Gene ID: 103319045), and HSP83 (GeneID: 103333719) as queries. In the genome of P. mume, PmSGT1 and PmRAR1 were selected as suitable candidates. This was done because they were both present in a single copy and displayed high-level conservation among higher plant genomes. The CDSs of PmSGT1 (GeneID: 103333704) and PmRAR1 (GeneID: 103333306) were identified after NCBI-BLAST database searches using SlSGT1 (GeneID: 101247681) and AtRAR1 (GenBank: AF192262.1) as queries, respectively. The primers that were designed for the cloning of these five genes are listed in Supplementary Table S1. All sequencing was performed and all primers were produced by the Taihe Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing).
Plasmid Construction
To isolate PsoRPM2, the BioXM 2.6 software package was used to analyze the restriction enzyme cutting sites within the PsoRPM2 CDS. Subsequently, the PsoRPM2 CDS was PCR amplified using primers designed via Primer 5.0 (see Supplementary Table S1). PsoRPM2 was then inserted between the NcoI and SpeI sites within the pCAMBIA 1305.1 plant expression vector, creating pCAMBIA 1305.1-35S-PsoRPM2-GFP. The T4 DNA ligase (TAKARA) was used to combine DNA fragments and sequencing was performed to verify vectors. pCAMBIA 1305.1-35S-GFP was selected as the negative control. All bacterial transformations during the cloning process were performed using the freeze-thaw method (Weigel and Glazebrook, 2006).
To create vectors for the protein interaction analysis, the internal restriction sites within PsoRPM2, PsoSGT1 (GeneBank: KY225327), PsoRAR1 (GeneBank: KY225328), PsoHSP90-1 (GeneBank: KY225329), PsoHSP90-2 (GeneBank: KY225330), and PsoHSP90-83 (GeneBank: KY225331) CDSs were determined via BioXM 2.6. Gene-specific primers that contained appropriate restriction sites (see Supplementary Table S1) were designed to both amplify and clone genes into expression vectors. The pGADT7 and pGBKT7 vectors described in the YeastmakerTM Yeast Transformation User Manual (Clontech) were used for a preliminary screen for candidate proteins that interacted with PsoHSP90 and were also used for in vitro protein interaction experiments. The vectors pCAMBIA1300-YFPn and pCAMBIA1300-YFPc were used to construct BiFC vectors that were used to confirm potential protein interactions in vivo. The primers and restriction enzymes used for this purpose are listed in Supplementary Table S1.
Protein Location Analysis of PsoRPM2
To further demonstrate the biological characteristics of the PsoRPM2 protein, the subcellular localization was analyzed. The transient transformation was performed following the procedure published by Sparkes et al. (2006). Agrobacterium tumefaciens liquid with reconstruction vectors was injected into 4-week-old N. benthamiana plants using a needleless syringe (1 ml). Three days after the injection, the infected leaf epidermis was analyzed using an Olympus BX61 fluorescence microscope (Olympus Fluo View FV1000).
Generation of Transgenic Tobacco Lines
The generated pCAMBIA 1305.1-35S-PsoRPM2-GFP vector was transformed into the A. tumefaciens strain EHA105. Cultures of the resulting transformed A. tumefaciens strain were infiltrated into leaves of N. benthamiana. Agroinfiltrated tobacco W38 leaves were placed on solid MS medium (1× MS, 2.0 μg/ml 6-BA, 0.5 μg/ml IAA, and 50 mg/ml Cef) and maintained in darkness. After 3 days, transformed leaves were subcultured in fresh antibiotic-containing MS (1× MS, 2.0 μg/ml 6-BA, 0.5 μg/ml IAA, and 50 mg/ml Cef) and maintained under a 16 h/8 h light/dark regime at 26°C. The PsoRPM2 tobacco transformants were selected via supplementing the antibiotic-containing MS with rifampicin (50 μg/ml). To detect the transgenic gene expression, gene-specific primers were designed for HYGROMYCIN PHOSPHOTRANSFERASE (HPT) (Suzuki et al., 2001) and PsoRPM2 (see Supplementary Table S1). RT-PCR amplicons corresponding to PsoRPM2 and HPT expression were observed in agarose gels and then purified and confirmed via sequencing. Several confirmed PsoRPM2 and GFP (negative control) transformants were then transplanted into culture bottles to create biological replicates.
RKN Inoculation and Resistance Assay
RKN infection assays were performed as previously described (Niu et al., 2015), with slight variation: To evaluate resistance conferred by M. incognita PsoRPM2 in tobacco, 2,000 nematode J2s (suspended in liquid) were infiltrated into the soil surrounding the roots of each tobacco plant. Thus, infected plants were cultivated in a greenhouse at 18–25°C. At 45 dpi, the roots were removed from the soil and cleaned; then, previously published methods (Vos et al., 1998) were utilized to quantify root weight, total number of roots, number of roots with galls, number of galls, and egg mass. To assay the expression level of PsoRPM2 in root of T1 tobaccos, qRT-PCR were used to test the root tips of T1 tobaccos 0, 1, 3, and 5 dpi with 2000 nematode J2s. Ntactin were used as reference gene and the qRT-PCR primers were consulted Duan et al. (2016). All statistical analyses and data summaries were obtained with the PASW Statistics 18 software.
Yeast Two-Hybrid Analysis
Yeast two-hybrid analysis was conducted as previously described (Gu et al., 2015) using the yeast strain AH109, synthetic dropout minimal medium, and β-galactosidase activity assay reagents according to the YeastmakerTM Yeast Transformation User Manual (Clontech). All restriction enzyme sites used to create the pGBKT7 or pGADT7 vectors are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Competent yeast cells were transformed with specific vector combinations using the freeze-thaw method. The AH109 yeast strain was grown on SD/-Leu-Trp medium for 4–5 days at 30°C, and 10 independent clones were picked and cultured on SD/-Ade-His-Leu-Trp medium at 30°C for 3–4 days. Then, they were analyzed for β-galactosidase activity via color development using α-X-Gal (4 mg/ml, 1–2 μl per colony). Primer used to construct victors were listed in Supplementary Table S1.
BiFC Analysis
Cultures of Agrobacterium strains that carried individual vectors (pCAMBIA 1300-35S-PsoHSP90-1-nYFP, pCAMBIA 1300-35S-PsoHSP90-1-cYFP, pCAMBIA 1300-35S-SGT1-cYFP, pCAMBIA 1300-35S-PsoRPM2-nYFP, pCAMBIA 1300-35S-PsoRAR1-nYFP and pCAMBIA 1300-35S-PsoRAR1-cYFP) were paired and co-infiltrated into healthy leaves of greenhouse-cultured N. benthamiana plants (Sparkes et al., 2006). The combination pCAMBIA 1300-35S-PsoRPM2-nYFP and pCAMBIA 1300-35S-PsoRAR1-cYFP was used as a negative control. Related primers see Supplementary Table S1. Five days after infiltration, the transformed leaf epidermis was analyzed via an Olympus BX61 fluorescence microscope (Olympus Fluo View FV1000).
Results
PsoRPM2 Gene Cloning and Protein Analysis
PCR amplification with primers that were designed to identify RGAs and root tissue from RKN-resistant P. sogdiana plants detected a single major amplicon with a size of approximately 520 bp. This fragment was cloned via TA-cloning and then sequenced. Protein BLAST analysis with the resulting sequence indicated it to be a partial NBS-ARC domain. To obtain the full-length nucleotide sequence of the amplified fragment, 3′- and 5′-RACE were utilized to amplify a 1000-bp sequence and a 2500-bp sequence, respectively. Following sequencing and splicing, the 3614-bp full-length target gene mRNA sequence was named P. sogdiana RESIST PATHOGEN M. incognita (PsoRPM2; GenBank: KU198632.1; Figure 1A). The CDS of PsoRPM2 had a length of 3297 bp and was flanked by a 92-bp 3′-UTR and a 225-bp 5′-UTR. Genomic DNA sequencing revealed no introns within PsoRPM2, and PsoRPM2 was found to contain a TIR domain (139 aa), a NB-ARC domain (267 aa), and a LRR domain (300 aa) (Figure 1B). The TIR domain contained three conserved motifs, the NBS-ARC domain contained a P-loop and kinases 1, 2, and 3 motifs, and the LRR domain contained 13 leucine-rich repeats (Figure 1C). The CDS regions of PsoRPM2 genes in resistance and susceptible P. sogdiana plants were identical. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that PsoRPM2 was closely related to homologous proteins of Prunus mume, Prunus persica, and Malus domestica (Figure 1D).
FIGURE 1.
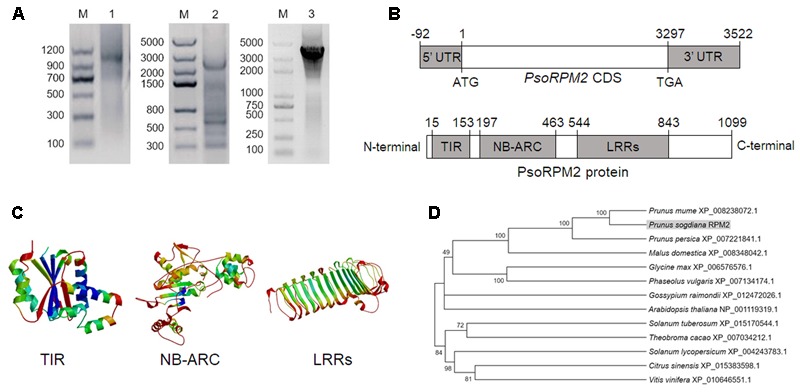
PsoRPM2 cloning and protein analysis. (A) The mRNA clone of PsoRPM2 generated by 3′-RACE (lane 1), 5′-RACE (lane 2), and full-length amplification (lane 3). M: DNA marker. (B) Schematic representations of PsoRPM2. (C) The predicted 3-dimensional structures of the TIR, NB-ARC, and LRR domains within PsoRPM2. (D) Phylogenetic tree containing PsoRPM2 (highlighted) and homologous proteins from other related plant species.
PsoRPM2 Expression and PsoRPM2 Subcellular Localization
Analysis of the tissue expression profile demonstrated that PsoRPM2 was expressed at comparable levels in root, stem, and leaf tissues both in resistant and susceptible plants of P. sogdiana (Figure 2A). However, the PsoRPM2 expression levels observed during M. incognita infection differed significantly between resistant and susceptible plants (Figure 2B). Prior to RKN inoculation (0 dpi), PsoRPM2 was expressed at a significantly higher level in susceptible plants than in resistant plants in comparison to the reference gene RPII (p < 0.05, Tukey’s test). At 1 dpi, PsoRPM2 expression in resistant plants rapidly increased to an approximately 500-fold higher level than that observed at 0 dpi, while the level of PsoRPM2 expression in susceptible plants remained unchanged. At 3 dpi, the PsoRPM2 expression level in resistant plants had still increased and the elevated expression persisted until 5 dpi, while the PsoRPM2 expression in susceptible plants decreased after 1 dpi reaching a level that was difficult to detect at 5 dpi (Figure 2B). An analysis of transiently expressing PsoRPM2-GFP N. benthamiana leaf epidermal cells indicated that PsoRPM2 was localized in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus (Figure 2C).
FIGURE 2.
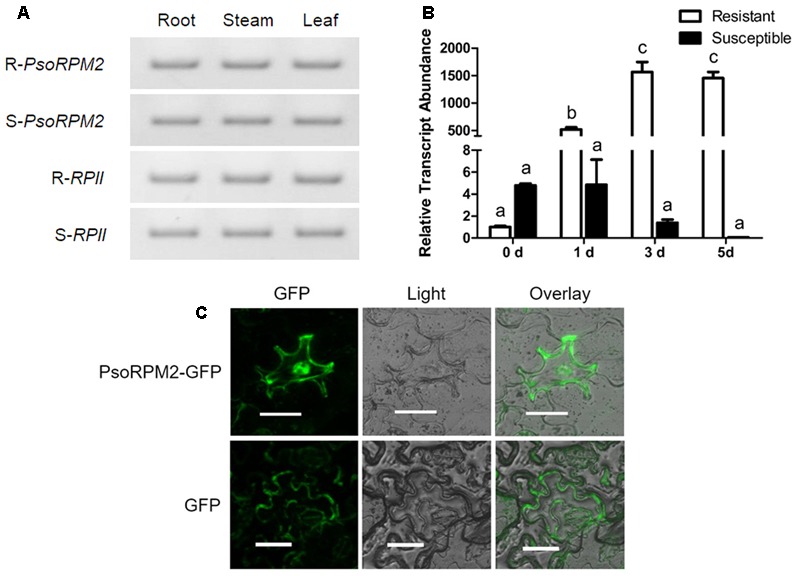
PsoRPM2 expression profile and subcellular localization of PsoRPM2 protein. (A) PsoRPM2 expression in various tissues of resistant (upper two panels) and susceptible (under two panels) P. sogdiana plants. RPII was used as a reference gene. (B) PsoRPM2 expression in root tips following M. incognita infection measured using qRT-PCR. The results show the means ± SD based on three biologic repetitions, each with three technical repetitions. Different letters denote a significant difference at p < 0.05 (Tukey’s test). (C) Protein localization analysis showing PsoRPM2-GFP in the cytoplasm and nucleus of N. benthamiana epidermal cells. Bar = 40 μm.
Overexpression of PsoRPM2 in Tobacco Enhances RKN Resistance
We transferred PsoRPM2 into the RKN susceptible tobacco variety W38. Four resulting transgenic lines (L1, L2, L3, and L4) and control line (transmitted empty-vector) were selected by testing the HPT, PsoRPM2 and Ntactin in Figure 3A. The PsoRPM2 expression in L1-4 and control after RKN inoculation in 0, 1, 3, and 5 days were also examined by qRT-PCR. The expression profile of PsoRPM2 in transgenic L1-4 has no obvious difference between 0, 1, 3, and 5 dpi, L1 has the highest level compared with other three lines (p < 0.01) (Figure 3B).
FIGURE 3.
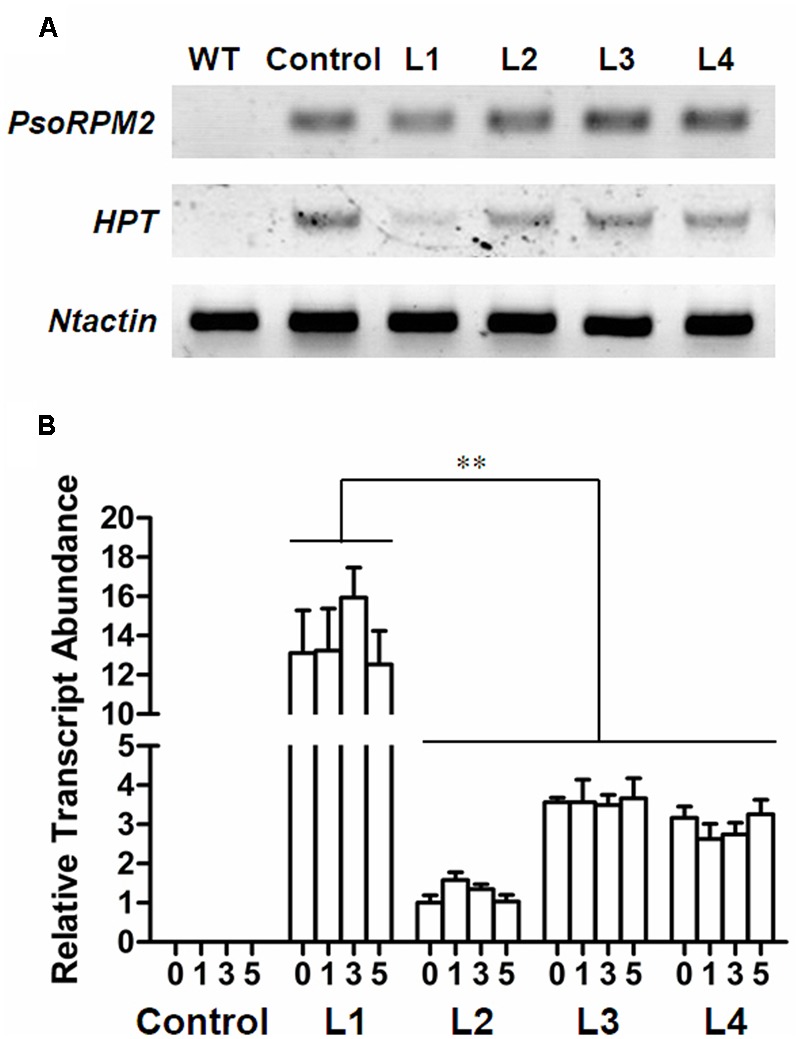
Expression of exogenous genes in transgenic tobacco lines. (A) Detection of PsoRPM2, HPT and Ntactin gene in transgenic W38 tobacco lines, the PsoRPM2 gene were positive in L1-4, HPT gene were positive in L1-4 and negative control, Ntactin was used as reference gene. To analyze each sample, 28 cycles were proceeded in RT-PCR. (B) Expression of PsoRPM2 gene in T1 plants inoculated. The abscissa 0, 1, 3, and 5 indicates the dpi with 2000 M. incognita J2 nematodes per seedling. The results represent the means ± SD based on three biologic repetitions, each with three technical repetitions. ∗∗Means extremely significantly different (each line, n = 3, p < 0.01, Tukey’s test).
A RKN resistance assay was performed using 2,000 M. incognita J2s per plant and the resulting tobacco roots were photographed at 45 dpi (Figures 4A–J). Control roots exhibited a dense distributed of many galls throughout the root mass, and multiple galls could be found on each root (Figure 4A). Most galls observed on control roots formed an egg mass, consisting of many RKN eggs (Figure 4B). The roots of the first transgenic PsoRPM2-expressing tobacco line (L1) displayed robust growth with a minimal number of galls and a complete lack of egg mass formation (Figures 4C,D). Roots of the second transgenic line (L2) displayed some galls, but fewer than in control roots (Figures 4E,F). Roots of the third (L3; Figures 4G,H) and fourth (L4; Figures 4I,J) transgenic lines displayed a higher gall density and egg mass production than L1, but a lower gall density and egg mass production than L2.
FIGURE 4.
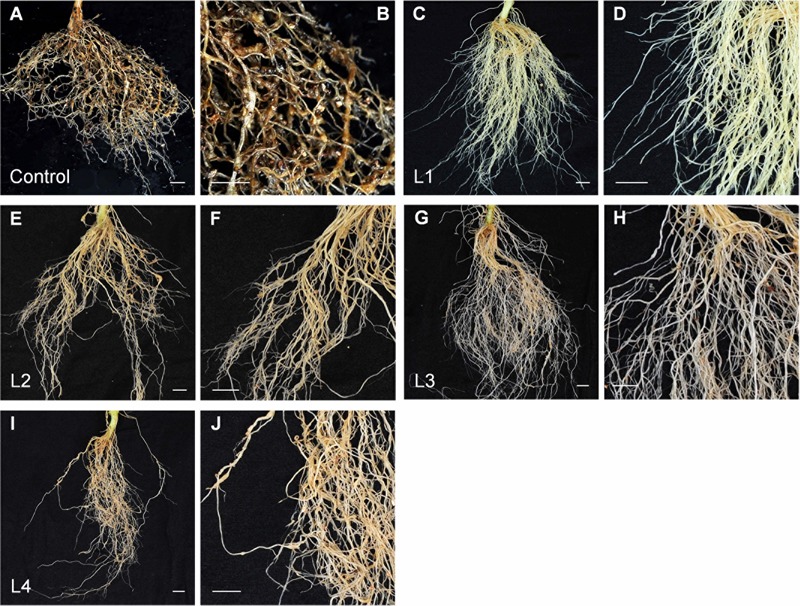
Total mass and magnified images of RKN-infected roots from wild-type and PsoRPM2-expressing transgenic tobacco lines. (A,B) Total mass (A) and magnified detail (B) of RKN-infected roots from transgenic W38 tobacco expressing GFP, included as a negative control. (C–J) Total mass (C,E,G,I) and magnified detail (D,F,H,J) of RKN-infected roots from PsoRPM2-expressing transgenic tobacco lines 1 (C,D), 2 (E,F), 3 (G,H), and 4 (I,J). Photographs were taken at 45 dpi.
To assess whether in planta PsoRPM2 expression conferred resistance to M. incognita, we inoculated L1, L2, L3, and L4 with 2,000 M. incognita J2s per plant. Compared to control plants, no apparent morphological differences were observed in the resulting transgenic plants. At 45 dpi, the average gall number was reduced both per total root number and per total root weight (Figures 5A,B), and the proportion of root mass that exhibited galls was significantly lower in transgenic lines than in the control (Figure 5C). In agreement with these findings, the average egg mass number was decreased both per total root number and per total root weight (Figures 5D,E), and the proportion of galls with egg mass was significantly lower in all transgenic lines than in the control (Figure 5F).
FIGURE 5.
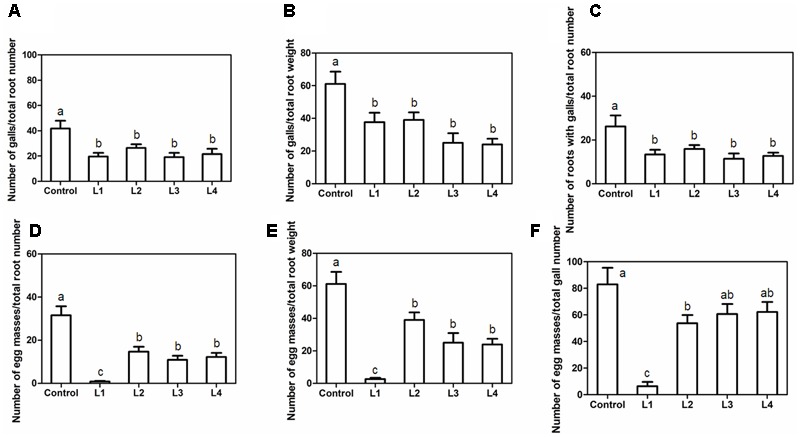
RKN resistance conferred by PsoRPM2 expression in T1 plants. (A) Number of galls/total root number. (B) Number of galls/total root weight. (C) Number of roots with galls/total root number. (D) Number of egg masses/total root number. (E) Number of egg masses/total root weight. (F) Number of egg masses/total gall number. The results show the means ± SD. (Control, n = 9; line 1, n = 11; line 2, n = 8; line 3, n = 9; line 4, n = 6). Different letters denote a significant difference at p < 0.05 (Tukey’s test).
PsoRPM2 Interacts with PsoHSP90-1 and PsoSGT1 and Is Essential for RKN Resistance
Since the RKN-resistance of PsoRPM2 transgenic tobacco lines was enhanced and since the PsoRPM2 protein could be located in the cytoplasm, this suggests that PsoRPM2 might be synergistic with the HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 co-chaperone complex in P. sogdiana similar to herbaceous model plants. Thus, we designed a yeast two-hybrid test to analyze the interaction between the homologous genes PsoHSP90, PsoSGT1, and PsoRAR1, which are three members of the co-chaperone protein complex from P. sogdiana. Three HSP90 homologous genes were cloned from Xinjiang wild P. sogdiana via considering the genomic data of P. mume genome: PsoHSP90-1 (GeneBank: KY225329), PsoHSP90-2 (GeneBank: KY225330), and PsoHSP83 (GeneBank: KY225331); one SGT1 homologous gene, PsoSGT1 (GeneBank: KY225327); and one RAR1 homologous gene, PsoRAR1 (GeneBank: KY225328). The Yeast two-hybrid experiments showed that PsoHSP90-1, PsoHSP90-2, PsoHSP83, and PsoSGT1 proteins were able to grow on the 4-defect medium and could be blue-tinted via X-gal, indicating that they could from homodimers. PsoHSP90-1 did not interact with PsoHSP90-2 or PsoHSP83, and only PsoHSP90-1 interacted with PsoSGT1. No interaction was found between PsoHSP90-2 and PsoHSP83 with PsoSGT1 (Figure 6A). Considering that the same phenomenon had occurred in Arabidopsis (Takahashi et al., 2003), we suggest that PsoHSP90-1 may be involved in the formation of an immune-related co-chaperone protein complex in P. sogdiana. Thus, PsoHSP90-1 was selected for further analysis.
FIGURE 6.
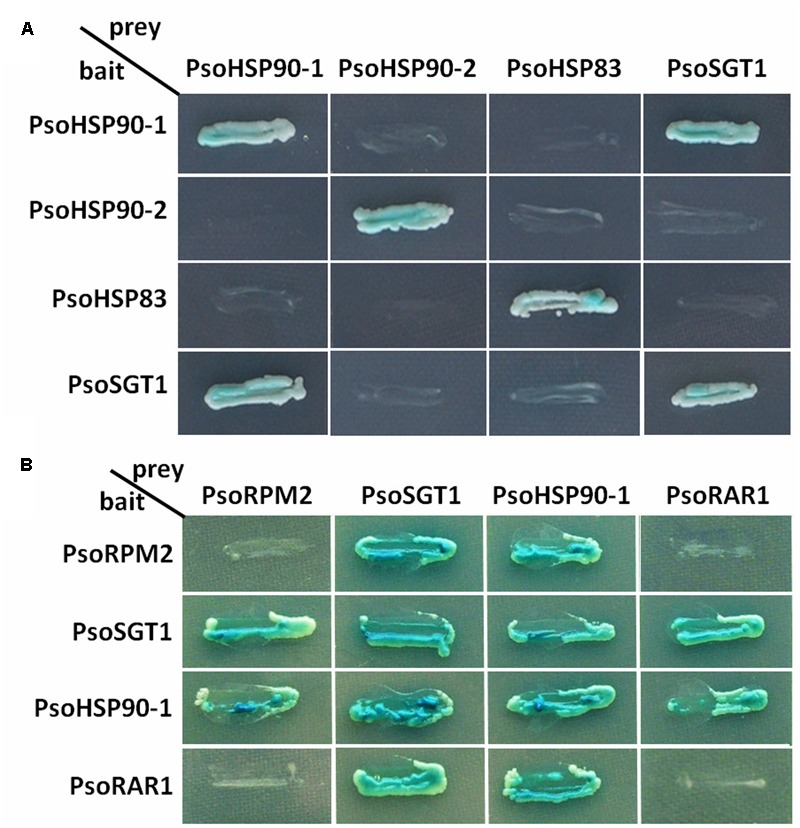
Analysis of interactions between PsoRPM2 and PsoHSP90-1, and PsoSGT1 and PsoRAR1 using the yeast two-hybrid system. β-Galactosidase activity was detected using X-α-Gal as a substrate. (A) Selection of candidate PsoSGT1-interacting PsoHSP90 proteins. (B) Interactions between PsoRPM2 and its chaperonin proteins.
In the subsequent interaction tests, yeast two-hybrid assays of PsoRPM2, PsoHSP90-1, PsoSGT1, and PsoRAR1 were used to test their relationship. In Figure 6B, the protein PsoRPM2 is shown to interact with PsoHSP90-1 and PsoSGT1, both as bait and target protein; however, no interactions of the PsoRPM2 protein itself or with the PsoRAR1 protein were found. The PsoSGT1 protein could interact with PsoRPM2, PsoHSP90-1, and PsoRAR1. The PsoHSP90-1 protein also interacted with all four proteins. However, the PsoRAR1 protein only interacted with PsoSGT1 and PsoHSP90-1, while PsoRAR1 itself or with the PsoRPM2 protein did not interact (Figure 6B).
To further verify the interactions between PsoRPM2 and its three chaperones in vivo, we constructed the bimolecular fluorescent vectors of PsoRPM2, PsoSGT1, PsoHSP90-1, and PsoRAR1 genes. The interaction fluorescence between the PsoRPM2 protein and the three co-chaperone proteins was observed in tobacco leaf epidermal cells via confocal microscopy, using a PsoRPM2-PsoRAR1 combination as negative control. The results showed that the interaction between the PsoRPM2 protein and different chaperone proteins was consistent with the results of the yeast two-hybrid assay. A combination of PsoRPM2-PsoSGT1, PsoRPM2-PsoHSP90-1, PsoSGT1-PsoHSP90-1, the PsoHSP90-1 homodimer, PsoRAR1-PsoHSP90-1, and PsoRAR1-PsoSGT1 was observed, whereas the combination PsoRPM2-PsoRAR1 still did not interact (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
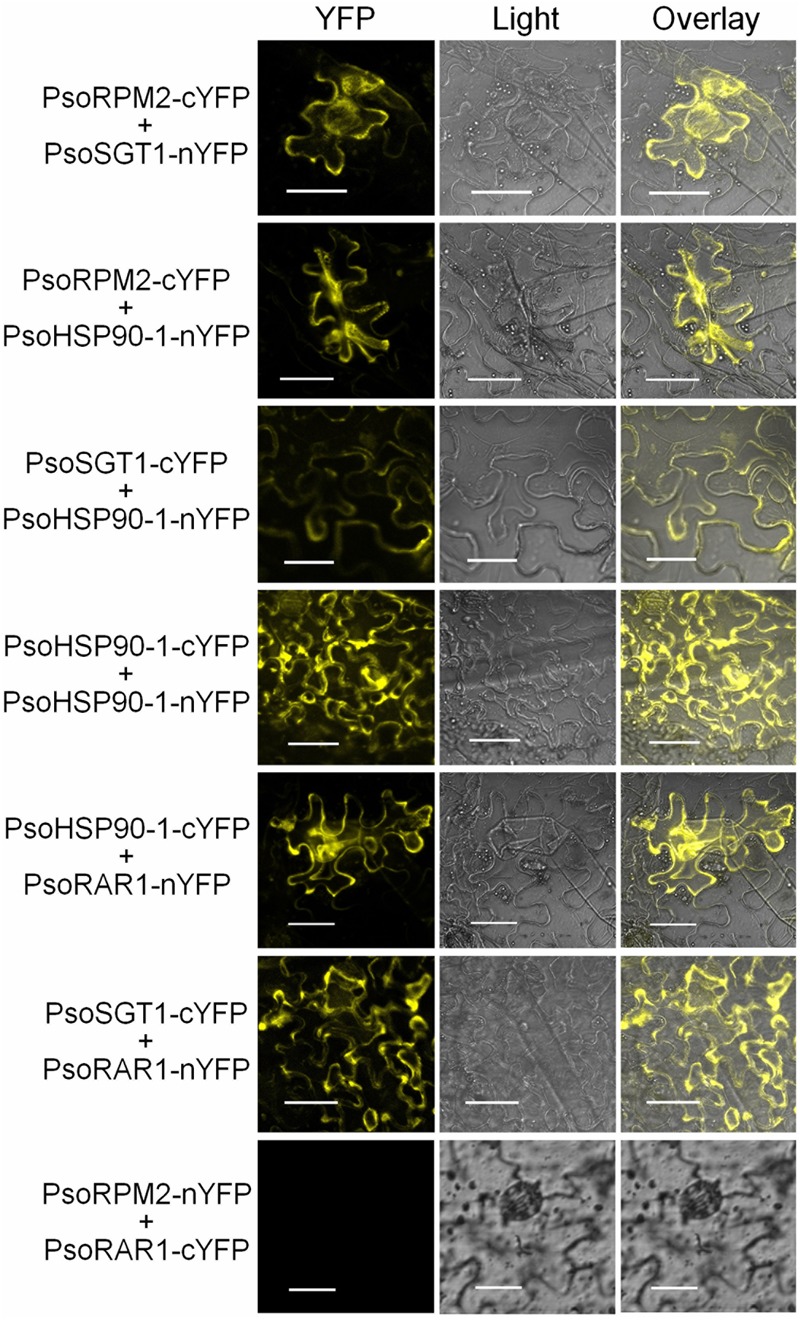
Interactions between PsoRPM2 and its three chaperonin proteins were determined by BiFC. YFP fluorescence in the upper epidermis cells of N. benthamiana leaves was detected by laser scanning confocal microscopy. Bar = 40 μm.
Discussion
Several methods for the prevention and control of RKN disease have been developed due to the severity of resulting damage to the agricultural industry; however, it remains a mainstream choice to seek naturally RKN-resistant R genes in plants. Previous studies have shown that the R gene initiates the identification of pathogen invasion and maintains a resting state if the pathogen is invaded (Jacob et al., 2013). This could reduce the cost of labor and pesticides compared to human intervention. However, the detection of novel R genes in plants often requires prior genomic data or prolonged hybridization to obtain resistance-related molecular markers. All this is more difficult to achieve in woody plants, especially in wild fruit tree germplasm resources. Fortunately, previous research has found that most of the R genes are highly conserved in their NB-ARC domains (Jacob et al., 2013). This conserved domain can be utilized as a molecular marker (Gupta and Rustgi, 2004), which makes it possible to clone novel R genes from plants without prior genomic data such as in the case of the Xinjiang wild myrobalan P. sogdiana. A number of resistant genes have been obtained via this RGAs homologous cloning method, such as MbR4 (Lee and Lee, 2005), Lr1 (Cloutier et al., 2007), and GHNTR1 (Zhang et al., 2015). This method is fast and causes low cost; however, it still has several shortcomings. For example, some R genes with considerable variability in the NB-ARC conserved region cannot be cloned via homologous (Liu et al., 2014). The PsoRPM2 gene can rapidly and significantly increase its expression in response to M. incognita invasion and thus enhance the RKN resistance of transgenic tobacco lines, suggesting that it is likely involved in disease resistance, which is similar to previous studies on the Mla gene (Halterman et al., 2003) and the GHNTR1 gene (Zhang et al., 2015) against powdery mildew and RKN, respectively.
The PsoRPM2 protein belongs to the TIR-NB-ARC-LRR subfamily, which is similar to Ma (Claverie et al., 2011), and the Mi-1 and the GHNTR1 proteins belong to the CC-NB-ARC-LRR subfamily (Milligan et al., 1998; Zhang et al., 2015). The difference between CC and TIR domains may affect the R gene function during plant immunity (Shirasu, 2009). The NB-ARC domain in the middle of R proteins has been suggested to act as an elicitor, which may maintain an intramolecular interaction with the LRR domain during the inactive protein state (Tameling et al., 2002; Steinbrenner et al., 2015). The NB-ARC domain structure of the PsoRPM2 protein was most similar to the ced-4 protein (Yan et al., 2004), which was obtained via three-dimensional structure analysis (confidence 100%, coverage 96%). The ced-4 protein mediated apoptosis (Yan et al., 2004), indicating that the NB-ARC domain may achieve the nematode resistance signal of PsoRPM2. This indicated that the NB-ARC domain of PsoRPM2 may induce RKN resistant signaling. The number of repeats of the LRR domain differs between different nematode proteins and its 3D structure was predicted to have a horseshoe structure (Takken and Goverse, 2012). This domain of PsoRPM2 may be associated with pathogen recognition and promotion of disease resistance as previously reported (Krasileva et al., 2010).
The gene function of wild-planted resources is relatively difficult to determine because the genetic transformation systems of these wild germplasms are largely immature or require several years of hybridization. Therefore, it forms a viable alternative approach to use a model plant material without nematode resistance to analyze candidate RKN-resistant genes. In our PsoRPM2 transgenic tobacco lines, L1–4 were associated with a remarkable reduction of M. incognita susceptibility (Figure 5). However, the level of RKN resistance varied between the four PsoRPM2-expressing transgenic lines. L1 displayed almost no nematode infection symptoms and has the highest expression of the four transgenic lines (Figure 3B), while the remaining three transgenic lines exhibited slight signs of nematode infection (Figures 5D,E). The expression changes of PsoRPM2 during nematode infection (0–5 dpi) in transgenic tobacco lines were not obvious (Figure 3B), suggest the 35S promoter may not infected by RKN infection. However, even the most RKN resistance L1 did not reach the resistance level of resistant P. sogdiana (Li et al., 2011). This demonstrated that xenogeneic transgene method has several shortcomings: several of the extreme examples of heterologous genes may be affected by the host plant immune system during gene expression or protein translation, or the foreign gene cannot properly match the local immunity signaling pathway. An extreme example is that the tomato Mi-1 gene is neither resistant to RKN nor to the potato aphid when it is expressed in the eggplant (Goggin et al., 2006). A further example is that host genetic background and dose-dependency may influence the Mi-1 RKN resistance in tomato varieties (Jacquet et al., 2005). In combination with the expression of the PsoRPM2 gene in resistance P. sogdiana and the resistance to RKN of transgenic tobaccos (i.e., L1, Figures 3B, 5), we found that the higher expression of the PsoRPM2 gene usually induced stronger RKN resistance, which is consistent with a previously reported observation for Mi-1.2 transgenic tomatoes (Milligan et al., 1998). In addition, we found that the PsoRPM2-expressing transgenic tobacco lines all exhibited early flowering, which implies that PsoRPM2 is also involved in plant reproductive development.
Previous studies have shown that the R protein is not only a single promote element in the immune systems of herbaceous model plants, but also requires assistance of the chaperone complex to promote disease resistance (Shirasu, 2009; Tran et al., 2017). With the help of genomic data of P. mume, we found that PsoRPM2 and its co-chaperones HSP90, SGT1, and RAR1 could also have interacted (Figures 6, 7), suggesting that the cooperative relationship of this R protein and its co-chaperone complex is also present in woody fruit tree. The sequence conservation of these chaperone proteins of different plants suggests that their function may be important for the immunity and physiological processes of plants (Kadota et al., 2010). A lack of HSP90, SGT1, or RAR1 proteins affects the resistance of many R genes including the RKN-resistant gene (Hubert et al., 2003; Bieri et al., 2004; Holt et al., 2005; Botër et al., 2007; Van Ooijen et al., 2010), while the SGT1 protein assists the HSP90 protein to maintain a safe R protein level, thus preventing an autoimmune response (Hahn, 2005; da Silva et al., 2007). Similar to Arabidopsis, multiple HSP90 homologues exist in P. mume and P. sogdiana; however, only the PsoHSP90-1 protein interacts with the PsoSGT1 protein (Figure 6). This unique manifestation is consistent with an effect observed in Arabidopsis (Takahashi et al., 2003). However, it is worth noting that HSP90.2 and HSP90.3 proteins are still involved in pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis (Krishna and Gloor, 2001), even though they do not interact with the SGT1-RAR1 protein, indicating redundancy in the function of the HSP90 protein. This suggests that HSP90-2 and HSP83 may also be involved in the disease resistance process of P. sogdiana. The PsoHSP90-1 and SGT1 genes are able to form dimers, which is consistent with the findings of previous reports (Nyarko et al., 2007; Röhl et al., 2013). Several R proteins can form homodimeric (Mestre and Baulcombe, 2006; Bai et al., 2012) or heterodimeric interactions (Williams et al., 2014) thus triggering immunity. However, in this study, no interaction was observed in the PsoRPM2 protein (Figure 6B), and this complex variation in the plant immune system may be associated with a different disease resistance pattern of the R gene. In the limited study of chaperone protein complexes in RKN-resistance publications, the normal function of Mi-1 requires the interaction of Hsp90-1 and Sgt1-1 proteins, whereas RAR1 had no effect on RKN resistance (Bhattarai et al., 2007). PsoRPM2-HSP90-1-SGT1-RAR1 may also possibly have formed a complex in P. sogdiana, and the resistant mechanism of the PsoRPM2 gene may be similar to other R genes that require assistance from the co-chaperone protein complex (Kadota et al., 2010).
In summary, our study showed that the PsoRPM2 gene enhanced the plant RKN-resistance and interacted with its chaperone protein complex. Future work should focus on the resistance mechanism of the PsoRPM2-HSP90-1-SGT1-RAR1 complex during RKN infection and should develop stable genetic transformation systems in P. sogdiana.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: XZ and JH. Performed the experiments: XZ, KX, and HC. Analyzed the data: XZ and KX. Wrote the manuscript: XZ, KX, and JH.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471842). We thank Prof. Heng Jian from China Agricultural University for providing the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita.
Footnotes
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02113/full#supplementary-material
References
- Abad P., Williamson V. M. (2010). Plant nematode interaction: a sophisticated dialogue. Adv. Bot. Res. 53 147–192. 10.1016/S0065-2296(10)53005-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Austin M. J., Muskett P., Kahn K., Feys B. J., Jones J. D., Parker J. E. (2002). Regulatory role of SGT1 in early R gene-mediated plant defenses. Science 295 2077–2080. 10.1126/science.1067747 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai S., Liu J., Chang C., Zhang L., Maekawa T., Wang Q., et al. (2012). Structure-function analysis of barley NLR immune receptor MLA10 reveals its cell compartment specific activity in cell death and disease resistance. PLOS Pathog. 8:e1002752. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002752 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai K. K., Li Q., Liu Y., Dinesh-Kumar S. P., Kaloshian I. (2007). The Mi-1-mediated pest resistance requires Hsp90 and Sgt1. Plant Physiol. 144 312–323. 10.1105/tpc.104.026682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieri S., Mauch S., Shen Q.-H., Peart J., Devoto A., Casais C., et al. (2004). RAR1 positively controls steady state levels of barley MLA resistance proteins and enables sufficient MLA6 accumulation for effective resistance. Plant Cell 16 3480–3495. 10.1105/tpc.104.026682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block A., Li G., Fu Z. Q., Alfano J. R. (2008). Phytopathogen type III effector weaponry and their plant targets. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 11 396–403. 10.1016/j.pbi.2008.06.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller T., He S. Y. (2009). Innate immunity in plants: an arms race between pattern recognition receptors in plants and effectors in microbial pathogens. Science 324 742–744. 10.1126/science.1171647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonardi V., Dangl J. L. (2012). How complex are intracellular immune receptor signaling complexes? Front. Plant Sci. 3:237. 10.3389/fpls.2012.00237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botër M., Amigues B., Peart J., Breuer C., Kadota Y., Casais C., et al. (2007). Structural and functional analysis of SGT1 reveals that its interaction with HSP90 is required for the accumulation of Rx, an R protein involved in plant immunity. Plant Cell 19 3791–3804. 10.1105/tpc.107.050427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouktila D., Habachi-Houimli Y., Khalfallah Y., Mezghani-Khemakhem M., Makni M., Makni H. (2014). Characterization of novel wheat NBS domain-containing sequences and their utilization, in silico, for genome-scale R -gene mining. Mol. Genet. Genomics 289 1–15. 10.1007/s00438-014-0834-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celik I., Sogut M. A., Ozkaynak E., Doganlar S., Frary A. (2016). Physical mapping of NBS-coding resistance genes to the Me-gene cluster on chromosome P9 reveals markers tightly linked to the N gene for root-knot nematode resistance in pepper. Mol. Breed. 36:137 10.1007/s11032-016-0560-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. F., Xiao K., Zhu X., Chen W. Y., Yang Y., Hu J. F. (2015). Development of giant cells and roles of CCS52B gene work in Meloidogyne incognita resistant Prunus sogdiana. Acta Hortic. Sin. 42 843–852. 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0062 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie M., Dirlewanger E., Bosselut N., Van Ghelder C., Voisin R., Kleinhentz M., et al. (2011). The Ma gene for complete-spectrum resistance to Meloidogyne species in Prunus is a TNL with a huge repeated C-terminal post-LRR region. Plant Physiol. 156 779–792. 10.1104/pp.111.176230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloutier S., McCallum B. D., Loutre C., Banks T. W., Wicker T., Feuillet C., et al. (2007). Leaf rust resistance gene Lr1, isolated from bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a member of the large psr567 gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 65 93–106. 10.1007/s11103-007-9201-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csermely P., Schnaider T., Soti C., Prohászka Z., Nardai G. (1998). The 90-kDa molecular chaperone family: structure, function, and clinical applications. A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 79 129–168. 10.1016/S0163-7258(98)00013-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunnac S., Lindeberg M., Collmer A. (2009). Pseudomonas syringae type III secretion system effectors: repertoires in search of functions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 12 53–60. 10.1016/j.mib.2008.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, Correia J., Miranda Y., Leonard N., Ulevitch R. (2007). SGT1 is essential for Nod1 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 6764–6769. 10.1073/pnas.0610926104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds P. N., Rathjen J. P. (2010). Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant–pathogen interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11 539–548. 10.1038/nrg2812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan X., Zhang W., Huang J., Hao L., Wang S., Wang A., et al. (2016). PbWoxT1 mRNA from pear (Pyrus betulaefolia) undergoes long-distance transport assisted by a polypyrimidine tract binding protein. New Phytol. 210 511–524. 10.1111/nph.13793 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmenjaud D., Minot J., Voisin R., Bonnet A., Salesses G. (1996). Inheritance of resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne arenaria in Myrobalan plum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 92 873–879. 10.1007/BF00221900 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazebrook J. (2005). Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 43 205–227. 10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.040204.135923 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goggin F. L., Jia L., Shah G., Hebert S., Williamson V. M., Ullman D. E. (2006). Heterologous expression of the Mi-1.2 gene from tomato confers resistance against nematodes but not aphids in eggplant. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 19 383–388. 10.1094/MPMI-19-0383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göhre V., Robatzek S. (2008). Breaking the barriers: microbial effector molecules subvert plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 46 189–215. 10.1146/annurev.phyto.46.120407.110050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Meng D., Yang Q., Yuan H., Wang A., Li W., et al. (2015). A CBL gene, MdCBL5, controls the calcium signal and influences pollen tube growth in apple. Tree Genet. Genomes 11 1–11. 10.1007/s11295-015-0853-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Rustgi S. (2004). Molecular markers from the transcribed/expressed region of the genome in higher plants. Funct. Integr. Genomics 4 139–162. 10.1007/s10142-004-0107-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J.-S. (2005). Regulation of Nod1 by Hsp90 chaperone complex. FEBS Lett. 579 4513–4519. 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.07.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halterman D. A., Wei F., Wise R. P. (2003). Powdery mildew-induced Mla mRNAs are alternatively spliced and contain multiple upstream open reading frames. Plant Physiol. 131 558–567. 10.1104/pp.014407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt B. F., Belkhadir Y., Dangl J. L. (2005). Antagonistic control of disease resistance protein stability in the plant immune system. Science 309 929–932. 10.1126/science.1109977 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Monaghan J., Zhong X., Lin L., Sun T., Dong O. X., et al. (2014). HSP90s are required for NLR immune receptor accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 79 427–439. 10.1111/tpj.12573 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert D. A., Tornero P., Belkhadir Y., Krishna P., Takahashi A., Shirasu K., et al. (2003). Cytosolic HSP90 associates with and modulates the Arabidopsis RPM1 disease resistance protein. EMBO J. 22 5679–5689. 10.1093/emboj/cdg547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob F., Vernaldi S., Maekawa T. (2013). Evolution and conservation of plant NLR functions. Front. Immunol. 4:297. 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet M., Bongiovanni M., Martinez M., Verschave P., Wajnberg E., Castagnone-Sereno P. (2005). Variation in resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita in tomato genotypes bearing the Mi gene. Plant Pathol. 54 93–99. 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2005.01143.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. D., Dangl J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444 323–329. 10.1038/nature05286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. T., Haegeman A., Danchin E. G., Gaur H. S., Helder J., Jones M. G., et al. (2013). Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 14 946–961. 10.1111/mpp.12057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadota Y., Shirasu K. (2012). The HSP90 complex of plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1823 689–697. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.09.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadota Y., Shirasu K., Guerois R. (2010). NLR sensors meet at the SGT1–HSP90 crossroad. Trends Biochem. Sci. 35 199–207. 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.12.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang L., Huifang L., Wenjuan G., Ting L. (2008). Primary research on cutting propagation of wild cherry plum. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 3:019. [Google Scholar]
- Karrer E. E., Beachy R. N., Holt C. A. (1998). Cloning of tobacco genes that elicit the hypersensitive response. Plant Mol. Biol. 36 681–690. 10.1023/A:1005949304445 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley L. A., Mezulis S., Yates C. M., Wass M. N., Sternberg M. J. (2015). The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 10 845–858. 10.1038/nprot.2015.053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasileva K. V., Dahlbeck D., Staskawicz B. J. (2010). Activation of an Arabidopsis resistance protein is specified by the in planta association of its leucine-rich repeat domain with the cognate oomycete effector. Plant Cell 22 2444–2458. 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2004.01339.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna P., Gloor G. (2001). The Hsp90 family of proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell Stress Chaperones 6 238–246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S.-Y., Lee D.-H. (2005). Expression of MbR4, a TIR-NBS type of apple R gene, confers resistance to bacterial spot disease in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Biol. 48 220–228. 10.1007/BF03030411 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li F., Zhou L., Xiao F., Liao K., Hu J. (2011). Characterization of the psoRPM1 gene for resistance to root-knot nematodes in wild myrobalan plum (Prunus sogdiana). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10 12859–12867. 10.5897/AJB11.1282 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J.-J., Sniezko R. A., Sturrock R. N., Chen H. (2014). Western white pine SNP discovery and high-throughput genotyping for breeding and conservation applications. BMC Plant Biol. 14:380. 10.1186/s12870-014-0380-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q., Qiao F., Zhu X., Lu C. L., Li T. Z., Hu J. F. (2013). Morphology and development of root knot in Xinjiang wild Myrobalan plum infected by Meloidogyne incognita. J. China Agric. Univ. 18 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lu R., Malcuit I., Moffett P., Ruiz M. T., Peart J., Wu A. J., et al. (2003). High throughput virus-induced gene silencing implicates heat shock protein 90 in plant disease resistance. EMBO J. 22 5690–5699. 10.1093/emboj/cdg546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. B., Bogdanove A. J., Sessa G. (2003). Understanding the functions of plant disease resistance proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 54 23–61. 10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.135035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melillo M. T., Leonetti P., Bongiovanni M., Castagnone-Sereno P., Bleve-Zacheo T. (2006). Modulation of reactive oxygen species activities and H2O2 accumulation during compatible and incompatible tomato–root-knot nematode interactions. New Phytol. 170 501–512. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01724.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestre P., Baulcombe D. C. (2006). Elicitor-mediated oligomerization of the tobacco N disease resistance protein. Plant Cell 18 491–501. 10.1105/tpc.105.037234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan S. B., Bodeau J., Yaghoobi J., Kaloshian I., Zabel P., Williamson V. M. (1998). The root knot nematode resistance gene Mi from tomato is a member of the leucine zipper, nucleotide binding, leucine-rich repeat family of plant genes. Plant Cell 10 1307–1319. 10.1105/tpc.10.8.1307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitkowski N., Abawi G. (2003). Root-knot nematodes. Plant Health Instructor 10 194 10.1094/PHI-I-2003-0917-01 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Niu J., Liu P., Liu Q., Chen C., Guo Q., Yin J., et al. (2015). Msp40 effector of root-knot nematode manipulates plant immunity to facilitate parasitism. Sci. Rep. 6:19443. 10.1038/srep19443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyarko A., Mosbahi K., Rowe A. J., Leech A., Boter M., Shirasu K., et al. (2007). TPR-Mediated self-association of plant SGT1. Biochemistry 46 11331–11341. 10.1021/bi700735t [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan M., Cournoyer P., Dinesh-Kumar S. (2009). The leucine-rich repeat domain in plant innate immunity: a wealth of possibilities. Cell. Microbiol. 11 191–198. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01260.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priya D. B., Somasekhar N., Prasad J. S., Kirti P. (2011). Transgenic tobacco plants constitutively expressing Arabidopsis NPR1 show enhanced resistance to root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. BMC Res. Notes 4:231. 10.1186/1756-0500-4-231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Z. N., Yang H. T., Chen W. Y., Yang Y., Xiao K., Zhu X., et al. (2016). Hypersensitive response and evaluation on resistance to Meloidogyne incognita in Xinjiang wild myrobalan plum (Prunus sogdiana). J. China Agric. Univ. 21 46–52. 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.03.07 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Röhl A., Rohrberg J., Buchner J. (2013). The chaperone Hsp90: changing partners for demanding clients. Trends Biochem. Sci. 38 253–262. 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasu K. (2009). The HSP90-SGT1 chaperone complex for NLR immune sensors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 60 139–164. 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes I. A., Runions J., Kearns A., Hawes C. (2006). Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat. Protoc. 1 2019–2025. 10.1038/nprot.2006.286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrenner A. D., Goritschnig S., Staskawicz B. J. (2015). Recognition and activation domains contribute to allele-specific responses of an Arabidopsis NLR receptor to an oomycete effector protein. PLOS Pathog. 11:e1004665. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Supaibulwatana K., Mii M., Nakano M. (2001). Production of transgenic plants of the Liliaceous ornamental plant Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis (Leighton) Leighton via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic calli. Plant Sci. 161 89–97. 10.1007/s00299-003-0700-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi A., Casais C., Ichimura K., Shirasu K. (2003). HSP90 interacts with RAR1 and SGT1 and is essential for RPS2-mediated disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 11777–11782. 10.1073/pnas.2033934100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takken F. L., Goverse A. (2012). How to build a pathogen detector: structural basis of NB-LRR function. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15 375–384. 10.1016/j.pbi.2012.05.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tameling W. I. L., Elzinga S. D. J., Darmin P. S., Vossen J. H., Takken F. L. W., Haring M. A., et al. (2002). The tomato R gene products I-2 and MI-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity. Plant Cell 14 2929–2939. 10.1105/tpc.005793 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong Z., Gao Z., Wang F., Zhou J., Zhang Z. (2009). Selection of reliable reference genes for gene expression studies in peach using real-time PCR. BMC Mol. Biol. 10:71. 10.1186/1471-2199-10-71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M. A., Jones J. D., Dangl J. L. (2006). Reactive oxygen species signaling in response to pathogens. Plant Physiol. 141 373–378. 10.1104/pp.106.079467 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran D. T., Chung E.-H., Habring-Müller A., Demar M., Schwab R., Dangl J. L., et al. (2017). Activation of a plant NLR complex through heteromeric association with an autoimmune risk variant of another NLR. Curr. Biol. 27 1148–1160. 10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda K., Katagiri F. (2010). Comparing signaling mechanisms engaged in pattern-triggered and effector-triggered immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 13 459–465. 10.1016/j.pbi.2010.04.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood W., Zhang S., He S. Y. (2007). The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector tyrosine phosphatase HopAO1 suppresses innate immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 52 658–672. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03262.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Voort J. N. R., Janssen G. J., Overmars H., van Zandvoort P. M., van Norel A., Scholten O. E., et al. (1999). Development of a PCR-based selection assay for root-knot nematode resistance (Rmc1) by a comparative analysis of the Solanum bulbocastanum and S. tuberosum genome. Euphytica 106 187–195. 10.1023/A:1003587807399 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ooijen G., Lukasik E., Van Den Burg H. A., Vossen J. H., Cornelissen B. J., Takken F. L. (2010). The small heat shock protein 20 RSI2 interacts with and is required for stability and function of tomato resistance protein I-2. Plant J. 63 563–572. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04260.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., Simons G., Jesse T., Wijbrandi J., Heinen L., Hogers R., et al. (1998). The tomato Mi-1 gene confers resistance to both root-knot nematodes and potato aphids. Nat. Biotechnol. 16 1365–1369. 10.1038/4350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Xu Z., Liao K., Zhao Y. S., Zhou L. (2006). Study on ecology-biology of wild cherry plum (Prunus divaricata) in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 43 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Glazebrook J. (2006). Transformation of agrobacterium using the freeze-thaw method. CSH Protoc. 2006:pdb.rot4666. 10.1101/pdb.prot4666 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. J., Sohn K. H., Wan L., Bernoux M., Sarris P. F., Segonzac C., et al. (2014). Structural basis for assembly and function of a heterodimeric plant immune receptor. Science 344 299–303. 10.1126/science.1247357 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Kumar A. (2006). Nematode resistance in plants: the battle underground. Trends Genet. 22 396–403. 10.1016/j.tig.2006.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao F. Q., Hu J. F., Xu Z., Liao K., Li T. Z. (2010). Cloning and expression analysis of fragments related to root-knot nematode resistance from wild Myrobalan plum (Prunus sogdiana). J. China Agric. Univ. 15 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Yan N., Gu L., Kokel D., Chai J., Li W., Han A., et al. (2004). Structural, biochemical, and functional analyses of CED-9 recognition by the proapoptotic proteins EGL-1 and CED-4. Mol. Cell 15 999–1006. 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeku O., Frohman M. A. (2011). Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE). Methods Protoc. 703 107–122. 10.1007/978-1-59745-248-9_8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Yang Y., Wang J., Ling X., Hu Z., Liu T., et al. (2015). A CC-NBS-LRR type gene GHNTR1 confers resistance to southern root-knot nematode in Nicotiana benthamiana and Nicotiana tabacum. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 142 715–729. 10.1007/s10658-015-0646-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zipfel C., Kunze G., Chinchilla D., Caniard A., Jones J. D., Boller T., et al. (2006). Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 125 749–760. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


