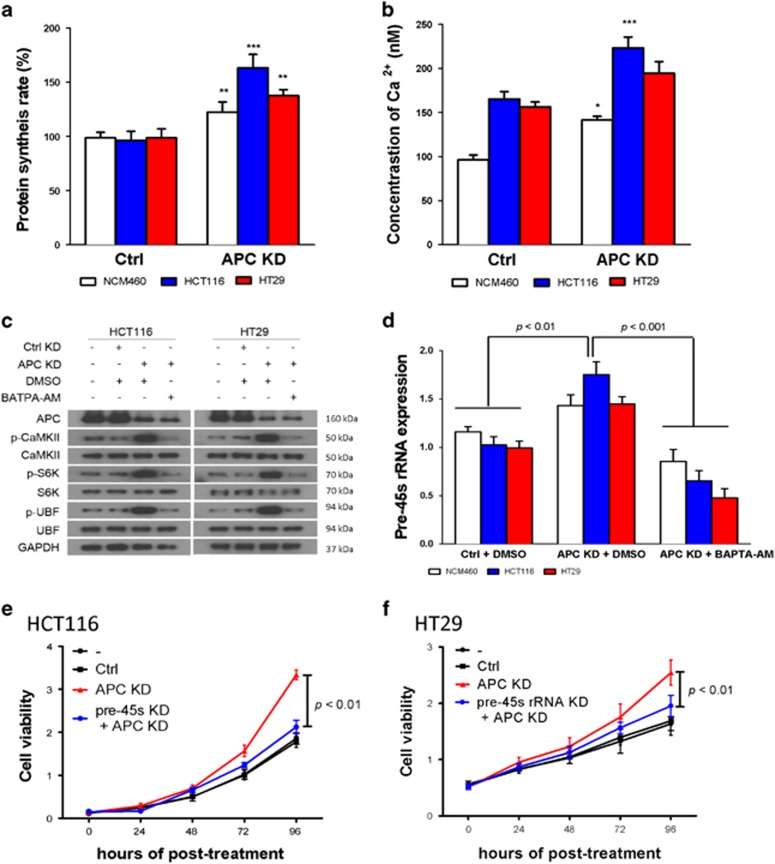
Figure 5.
Pre-45s rRNA was essential for supporting the cell growth in colon cancer cells with APC loss of function. (a) Knockdown of APC enhanced the rate of protein synthesis in colon cell lines. (b) Knockdown of APC led to elevation of free Ca2+ in the cytoplasm in colon cells. Real-time PCR was used to determine the expression level of pre-45s rRNA. (c) Activation of CaMKII-S6K-UBF signaling cascade in APC knocked down cells depended on free Ca2+. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Cells were treated with 5 μM of BATPA-AM. (d) Upregulation of pre-45s rRNA mediated by APC knockdown was abolished by BATPA-AM treatment in colon cancer cells. Expression of pre-45s rRNA was compared with untreated NCM460, HCT116 and HT29. Knockdown of pre-45s rRNA suppressed cell growth in colon cancer cells. (e) HCT116 and (f) HT29 with APC knocked down. Cell growth was evaluated by MTT assay. siRNA of 5 pmol against pre-45s rRNA was used to knockdown the rRNA in cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control in western blot. β-Atin was used as internal control for real-time PCR. All data points are represented as mean±s.d. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.