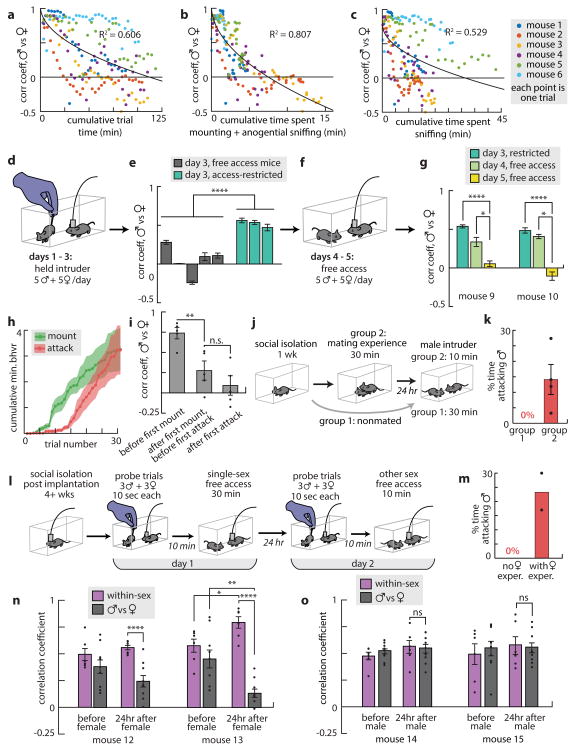
Figure 4. Social experience promotes ensemble separation.
a-c, PCC for the nth trial vs. cumulative social experience (a), cumulative mounting and anogenital sniffing (b) or cumulative body/face-directed sniffing (c). R2 values are for fit curve y = A√(x) + B (black). d, Illustration of “restricted-access” experiment. e, Ensemble separation for five mice with free access (gray) and three mice with restricted access (teal) were significantly different (one-way ANOVA). f,g, PCC decreased after two restricted-access mice received free access (day 4 and day 5; one-way ANOVA); day 3 bars duplicated from (e) to facilitate comparison. h, Cumulative time spent in behavior (n=5). i, Ensembles separate after mounting commences. j, Priming experiment. k, Males primed with females (group 2, n=4) attacked conspecific males; unprimed males (group 1, n=8) did not. l, Priming experiment adapted for imaging. m, Males primed with females fought. n, Mice primed with females (n=2) showed ensemble separation 24 hr later; Mice primed with males (n=2) did not (o).