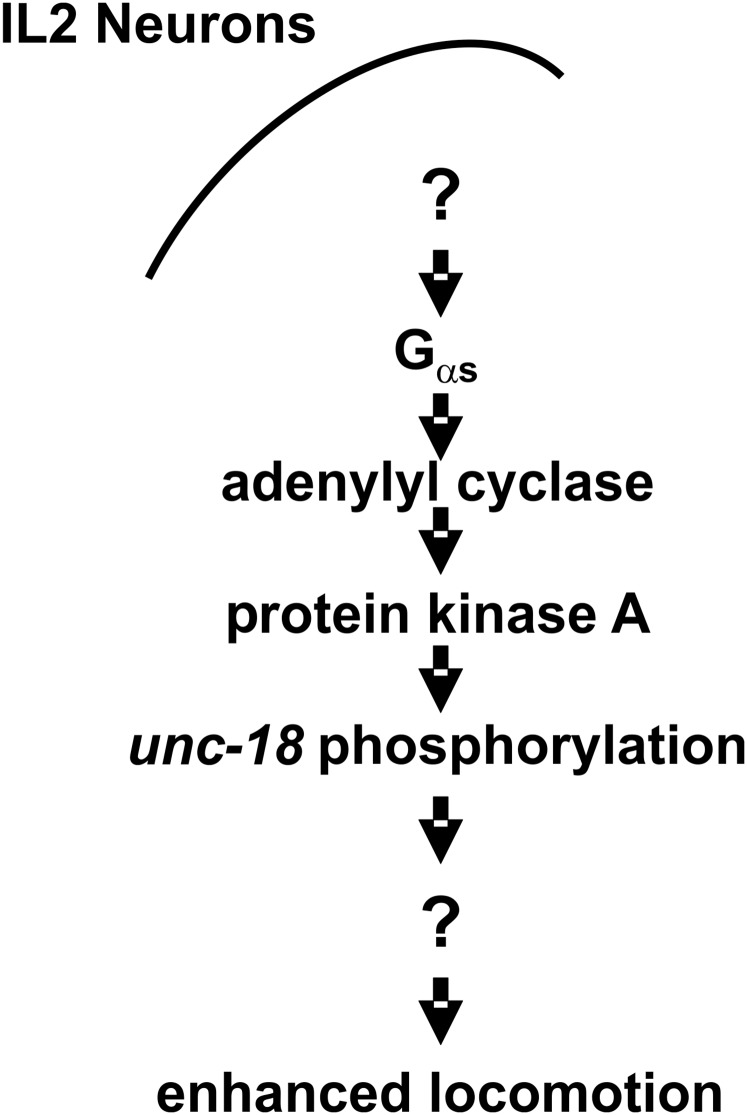
Figure 7.
A model for ethanol-dependent enhancement of locomotion in C. elegans. The addition of ethanol at a low external concentration (17 mM) activates a Gαs-dependent signaling pathway in the IL2 chemosensory neurons, likely through an as yet unidentified G-protein coupled receptor. Whether ethanol directly activates or modulates an existing signal remains to be determined. The Gαs-dependent signaling activates adenylyl cyclase and protein kinase A (PKA). PKA-dependent phosphorylation of the exocytotic protein UNC-18 at Ser322 in some way alters signaling from IL2 neurons, which feeds into the neurons controlling nematode locomotion.