NEUROSCIENCE Correction for “Functional network inference of the suprachiasmatic nucleus,” by John H. Abel, Kirsten Meeker, Daniel Granados-Fuentes, Peter C. St. John, Thomas J. Wang, Benjamin B. Bales, Francis J. Doyle III, Erik D. Herzog, and Linda R. Petzold, which was first published April 4, 2016; 10.1073/pnas.1521178113 (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:4512–4517).
The authors note that Fig. 5 appeared incorrectly. The corrected figure and its legend appear below.
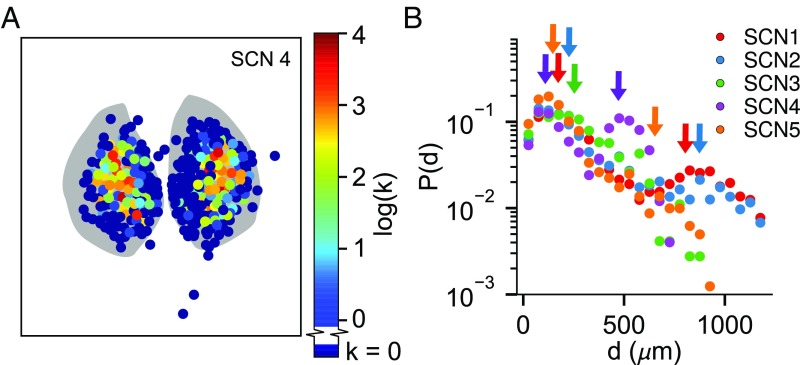
Fig. 5.
Hubs of the small-world network are located in the central SCN. (A) Heatmap of node degree [color ∝ log(k)] distribution for a representative SCN shows that hubs of the small-world network are preferentially located in SCN core regions. All SCNs are shown in Fig. S6. (B) Connection length (d μm) distributions for SCNs 1–5 plotted on a semilog scale. Two peaks (arrows) are identifiable for SCNs 1, 2, 4, and 5: a local peak corresponding to connections between physically nearby neurons, and a second peak corresponding to the distance for functional connections between central SCN regions. For SCN3, these peaks are indistinguishable due to lack of spatial separation between cores.