Figure 4. Nup42 coordinates Gle1-Dbp5 interaction.
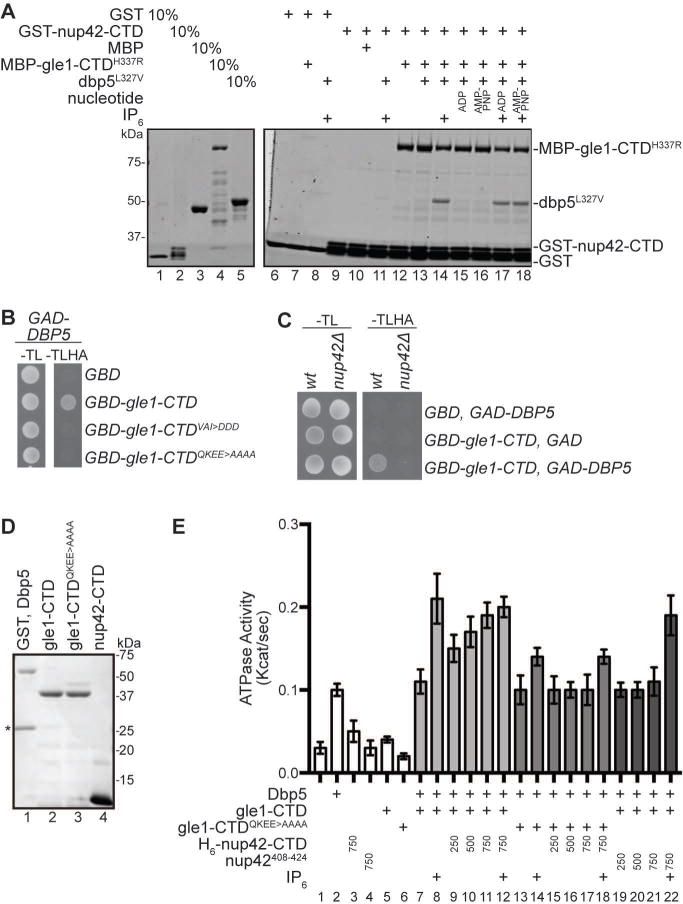
(A) Nup42, Gle1, and Dbp5 interact in a trimeric protein complex with IP6. Soluble binding assays were conducted with purified recombinant proteins immobilized on glutathione coupled Sepharose. Input and bound fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. Note: GST-nup42-CTD is proteolytically sensitive and resolves as several bands by SDS-PAGE (lane 2), as observed in23. (B) GBD-gle1-CTDQKEE>AAAA does not interact with GAD-Dbp5 via Y2H. Indicated plasmids were transformed into the Y2H reporter strain, grown to early log phase at 23°C, and plated on the synthetic media lacking indicated amino acids for growth at 23°C. (C) GBD-gle1-CTD does not interact with GAD-Dbp5 in nup42Δ mutants. Indicated plasmids were transformed into wild-type (wt) or nup42Δ Y2H reporter strains, grown to early log phase at 23°, and plated on the synthetic media lacking indicated amino acids for growth at 23°C. (D) Purified recombinant S. cerevisiae proteins used in ATPase assays. 1μg indicated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stained. Asterisk indicates GST cleaved (not removed) from Dbp5 sample. (E) nup42-CTD enhances Gle1 stimulation of Dbp5 ATPase activity in the absence of IP6. PK/LDH-coupled ATPase assays were performed with Dbp5 (500 nM) in the presence of 1 μM A30 RNA and 2 mM ATP gle1-CTD or gle1-CTDQKEE>AAAA (250 nM), IP6 (1 μM), and varying amounts of nup42-CTD or nup42408–424 peptide (250, 500, or 750 nM) were added as indicated. Reactions were incubated at 37°C for 40 min with the A340 monitored every 40 seconds to calculate Kcat. Mean shown for n=3, and standard error is indicated by error bars.
